2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE high output
[x] Cancel search: high outputPage 1163 of 2199
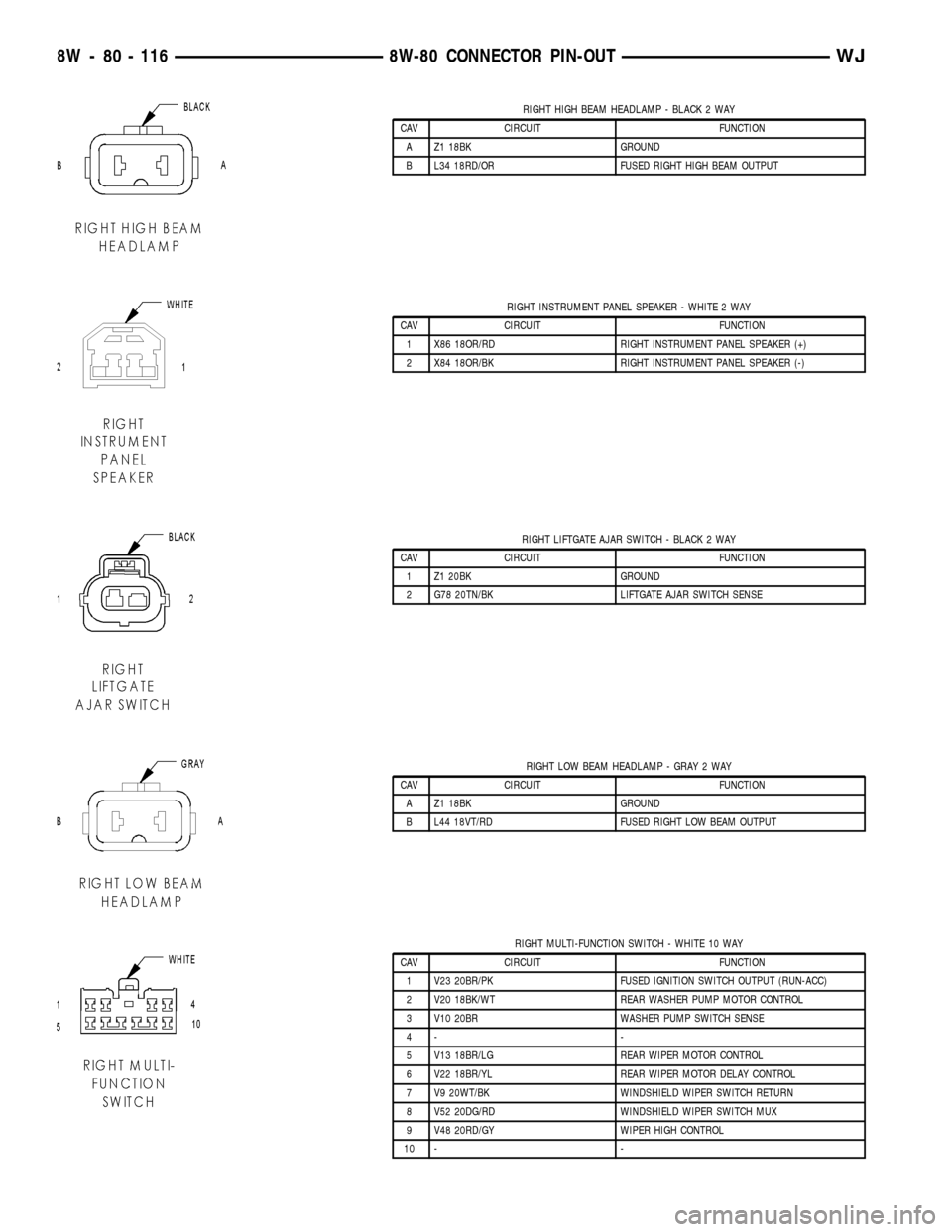
RIGHT HIGH BEAM HEADLAMP - BLACK 2 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
A Z1 18BK GROUND
B L34 18RD/OR FUSED RIGHT HIGH BEAM OUTPUT
RIGHT INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKER - WHITE 2 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 X86 18OR/RD RIGHT INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKER (+)
2 X84 18OR/BK RIGHT INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKER (-)
RIGHT LIFTGATE AJAR SWITCH - BLACK 2 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 Z1 20BK GROUND
2 G78 20TN/BK LIFTGATE AJAR SWITCH SENSE
RIGHT LOW BEAM HEADLAMP - GRAY 2 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
A Z1 18BK GROUND
B L44 18VT/RD FUSED RIGHT LOW BEAM OUTPUT
RIGHT MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH - WHITE 10 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 V23 20BR/PK FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-ACC)
2 V20 18BK/WT REAR WASHER PUMP MOTOR CONTROL
3 V10 20BR WASHER PUMP SWITCH SENSE
4- -
5 V13 18BR/LG REAR WIPER MOTOR CONTROL
6 V22 18BR/YL REAR WIPER MOTOR DELAY CONTROL
7 V9 20WT/BK WINDSHIELD WIPER SWITCH RETURN
8 V52 20DG/RD WINDSHIELD WIPER SWITCH MUX
9 V48 20RD/GY WIPER HIGH CONTROL
10 - -
8W - 80 - 116 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTWJ
Page 1181 of 2199
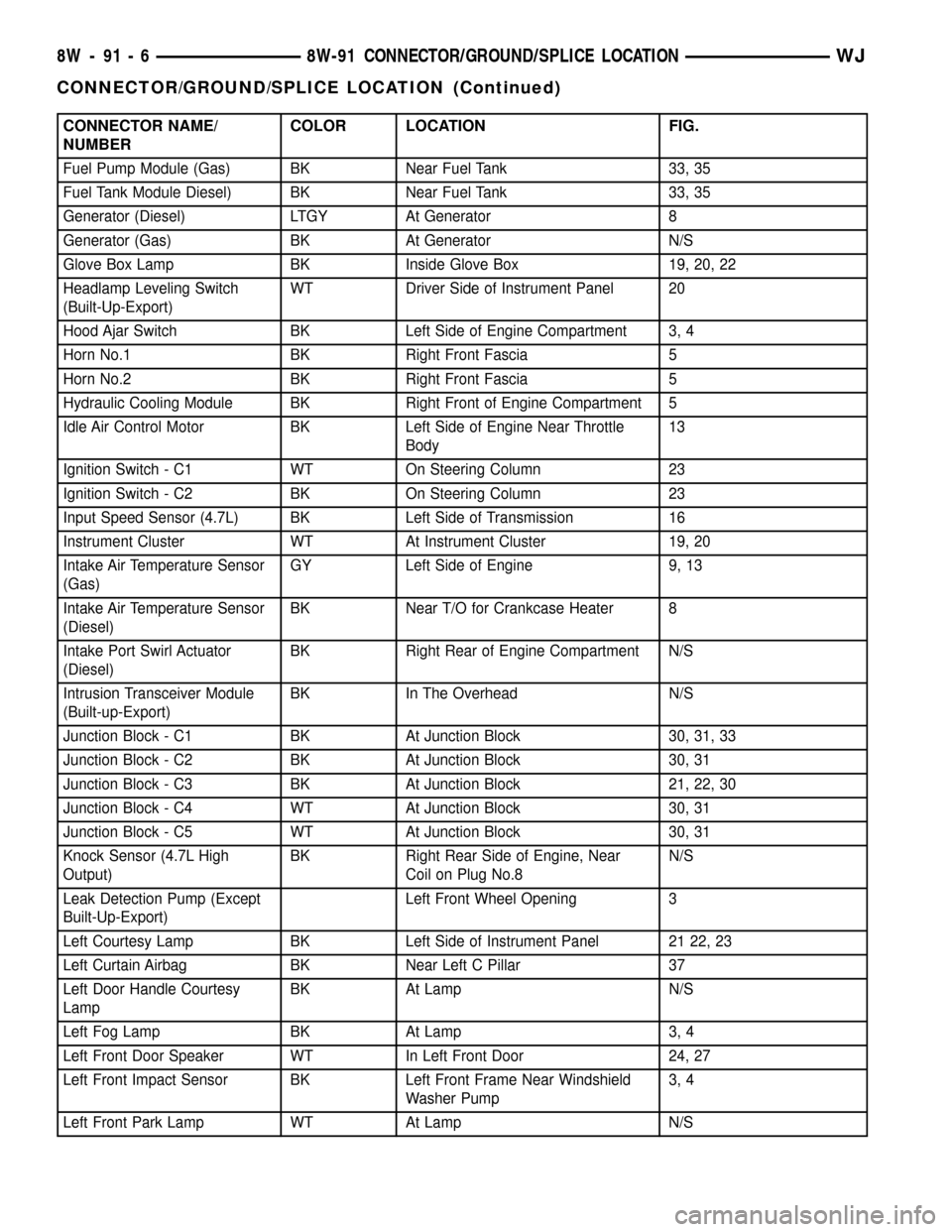
CONNECTOR NAME/
NUMBERCOLOR LOCATION FIG.
Fuel Pump Module (Gas) BK Near Fuel Tank 33, 35
Fuel Tank Module Diesel) BK Near Fuel Tank 33, 35
Generator (Diesel) LTGY At Generator 8
Generator (Gas) BK At Generator N/S
Glove Box Lamp BK Inside Glove Box 19, 20, 22
Headlamp Leveling Switch
(Built-Up-Export)WT Driver Side of Instrument Panel 20
Hood Ajar Switch BK Left Side of Engine Compartment 3, 4
Horn No.1 BK Right Front Fascia 5
Horn No.2 BK Right Front Fascia 5
Hydraulic Cooling Module BK Right Front of Engine Compartment 5
Idle Air Control Motor BK Left Side of Engine Near Throttle
Body13
Ignition Switch - C1 WT On Steering Column 23
Ignition Switch - C2 BK On Steering Column 23
Input Speed Sensor (4.7L) BK Left Side of Transmission 16
Instrument Cluster WT At Instrument Cluster 19, 20
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
(Gas)GY Left Side of Engine 9, 13
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
(Diesel)BK Near T/O for Crankcase Heater 8
Intake Port Swirl Actuator
(Diesel)BK Right Rear of Engine Compartment N/S
Intrusion Transceiver Module
(Built-up-Export)BK In The Overhead N/S
Junction Block - C1 BK At Junction Block 30, 31, 33
Junction Block - C2 BK At Junction Block 30, 31
Junction Block - C3 BK At Junction Block 21, 22, 30
Junction Block - C4 WT At Junction Block 30, 31
Junction Block - C5 WT At Junction Block 30, 31
Knock Sensor (4.7L High
Output)BK Right Rear Side of Engine, Near
Coil on Plug No.8N/S
Leak Detection Pump (Except
Built-Up-Export)Left Front Wheel Opening 3
Left Courtesy Lamp BK Left Side of Instrument Panel 21 22, 23
Left Curtain Airbag BK Near Left C Pillar 37
Left Door Handle Courtesy
LampBK At Lamp N/S
Left Fog Lamp BK At Lamp 3, 4
Left Front Door Speaker WT In Left Front Door 24, 27
Left Front Impact Sensor BK Left Front Frame Near Windshield
Washer Pump3, 4
Left Front Park Lamp WT At Lamp N/S
8W - 91 - 6 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONWJ
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1189 of 2199
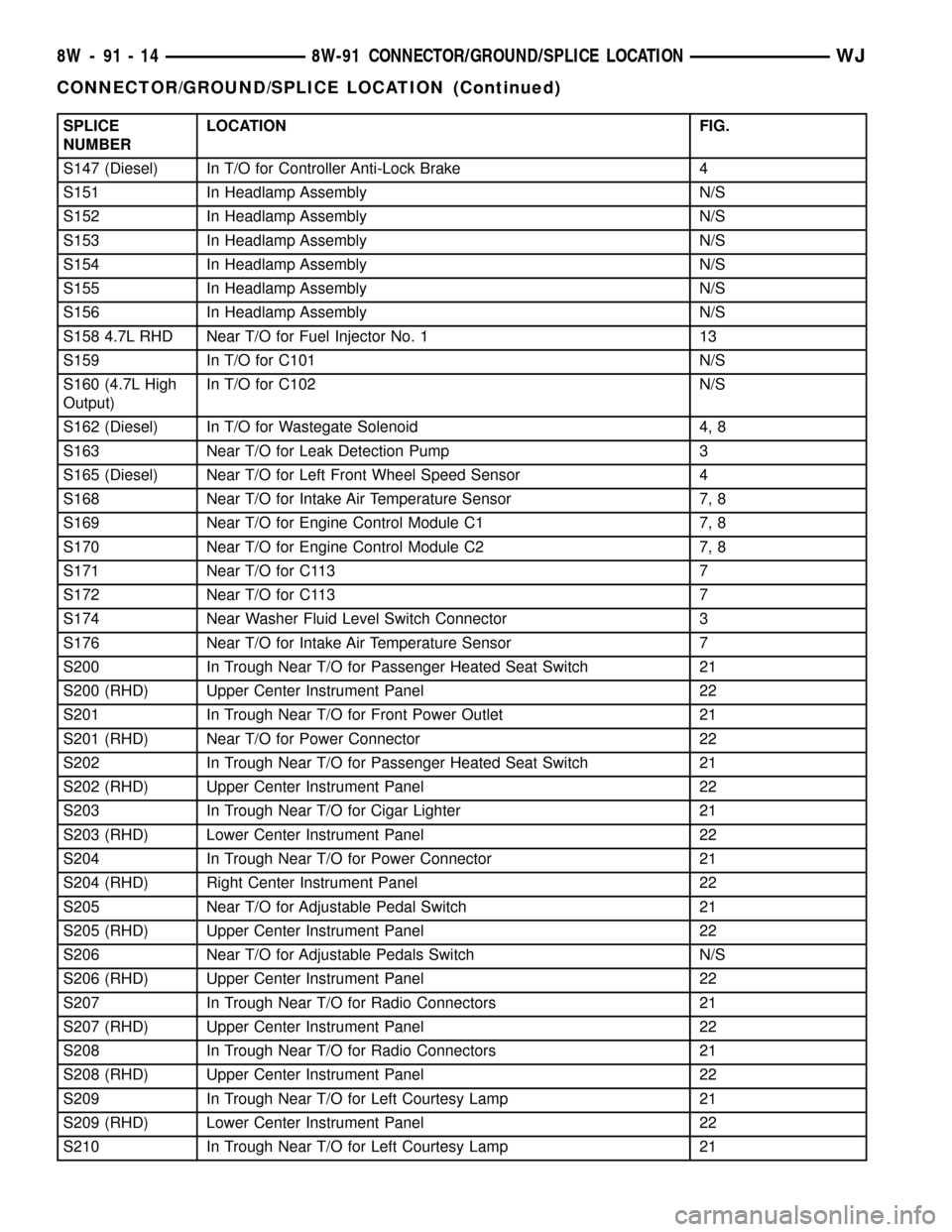
SPLICE
NUMBERLOCATION FIG.
S147 (Diesel) In T/O for Controller Anti-Lock Brake 4
S151 In Headlamp Assembly N/S
S152 In Headlamp Assembly N/S
S153 In Headlamp Assembly N/S
S154 In Headlamp Assembly N/S
S155 In Headlamp Assembly N/S
S156 In Headlamp Assembly N/S
S158 4.7L RHD Near T/O for Fuel Injector No. 1 13
S159 In T/O for C101 N/S
S160 (4.7L High
Output)In T/O for C102 N/S
S162 (Diesel) In T/O for Wastegate Solenoid 4, 8
S163 Near T/O for Leak Detection Pump 3
S165 (Diesel) Near T/O for Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor 4
S168 Near T/O for Intake Air Temperature Sensor 7, 8
S169 Near T/O for Engine Control Module C1 7, 8
S170 Near T/O for Engine Control Module C2 7, 8
S171 Near T/O for C113 7
S172 Near T/O for C113 7
S174 Near Washer Fluid Level Switch Connector 3
S176 Near T/O for Intake Air Temperature Sensor 7
S200 In Trough Near T/O for Passenger Heated Seat Switch 21
S200 (RHD) Upper Center Instrument Panel 22
S201 In Trough Near T/O for Front Power Outlet 21
S201 (RHD) Near T/O for Power Connector 22
S202 In Trough Near T/O for Passenger Heated Seat Switch 21
S202 (RHD) Upper Center Instrument Panel 22
S203 In Trough Near T/O for Cigar Lighter 21
S203 (RHD) Lower Center Instrument Panel 22
S204 In Trough Near T/O for Power Connector 21
S204 (RHD) Right Center Instrument Panel 22
S205 Near T/O for Adjustable Pedal Switch 21
S205 (RHD) Upper Center Instrument Panel 22
S206 Near T/O for Adjustable Pedals Switch N/S
S206 (RHD) Upper Center Instrument Panel 22
S207 In Trough Near T/O for Radio Connectors 21
S207 (RHD) Upper Center Instrument Panel 22
S208 In Trough Near T/O for Radio Connectors 21
S208 (RHD) Upper Center Instrument Panel 22
S209 In Trough Near T/O for Left Courtesy Lamp 21
S209 (RHD) Lower Center Instrument Panel 22
S210 In Trough Near T/O for Left Courtesy Lamp 21
8W - 91 - 14 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONWJ
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1462 of 2199

(5) Push sensor against flywheel/drive plate. With
sensor pushed against flywheel/drive plate, tighten
mounting bolt to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Route sensor wiring harness into wire shield.
(7) Connect sensor pigtail harness electrical con-
nector to main wiring harness.
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
(1) Clean out machined hole in engine block.
(2) Apply a small amount of engine oil to sensor
o-ring.
(3) Install sensor into engine block with a slight
rocking action. Do not twist sensor into position as
damage to o-ring may result.
CAUTION: Before tightening sensor mounting bolt,
be sure sensor is completely flush to cylinder
block. If sensor is not flush, damage to sensor
mounting tang may result.
(4) Install mounting bolt and tighten to 28 N´m
(21 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(6) Install starter motor. Refer to Starter Removal/
Installation.
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION
A separate fuel injector (Fig. 24) is used for each
individual cylinder.
OPERATION
OPERATION
The fuel injectors are electrical solenoids. The
injector contains a pintle that closes off an orifice at
the nozzle end. When electric current is supplied to
the injector, the armature and needle move a short
distance against a spring, allowing fuel to flow out
the orifice. Because the fuel is under high pressure, a
fine spray is developed in the shape of a pencil
stream. The spraying action atomizes the fuel, add-
ing it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
The top (fuel entry) end of the injector (Fig. 24) is
attached into an opening on the fuel rail.
The nozzle (outlet) ends of the injectors are posi-
tioned into openings in the intake manifold just
above the intake valve ports of the cylinder head.
The engine wiring harness connector for each fuel
injector is equipped with an attached numerical tag
(INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.). This is used to identify each fuel
injector.
The injectors are electrically energized, individu-
ally and in a sequential order by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The PCM will adjust injector
pulse width by switching the ground path to each
individual injector on and off. Injector pulse width is
the period of time that the injector is energized. The
PCM will adjust injector pulse width based on vari-
ous inputs it receives.
Battery voltage is supplied to the injectors through
the ASD relay.
The PCM determines injector pulse width based on
various inputs.
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The nozzle ends of the injectors are positioned into
openings in the intake manifold just above the intake
valve ports of the cylinder head. The engine wiring
harness connector for each fuel injector is equipped
with an attached numerical tag (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.).
This is used to identify each fuel injector with its
respective cylinder number.
The injectors are energized individually in a
sequential order by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM will adjust injector pulse width by
switching the ground path to each individual injector
on and off. Injector pulse width is the period of time
that the injector is energized. The PCM will adjust
injector pulse width based on various inputs it
receives.
Battery voltage (12 volts +) is supplied to the injec-
tors through the ASD relay. The ASD relay will shut-
down the 12 volt power source to the fuel injectors if
the PCM senses the ignition is on, but the engine is
not running. This occurs after the engine has not
been running for approximately 1.8 seconds.
Fig. 24 Fuel InjectorÐ4.0L/4.7L Engines
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - NOZZLE
3 - TOP (FUEL ENTRY)
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 43
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1467 of 2199

MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
On the 4.0L six-cylinder engine the MAP sensor is
mounted to the engine throttle body. On the 4.7L V-8
engine the MAP sensor is mounted to front of the
intake manifold.
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
intake manifold. An o-ring seals the sensor to the
intake manifold.
OPERATION
The MAP sensor is used as an input to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). It contains a silicon
based sensing unit to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When manifold absolute pressure (MAP) equals
Barometric pressure, the pulse width will be at max-
imum.
A 5 volt reference is supplied from the PCM and
returns a voltage signal to the PCM that reflects
manifold pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V
and full scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of 0±15
psi, the voltage changes 4.0V. To operate the sensor,
it is supplied a regulated 4.8 to 5.1 volts. Ground is
provided through the low-noise, sensor return circuit
at the PCM.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to fuel injector pulse width. The most important
function of the MAP sensor is to determine baromet-
ric pressure. The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is
at sea level or at a higher altitude, because the air
density changes with altitude. It will also help to cor-
rect for varying barometric pressure. Barometric
pressure and altitude have a direct inverse correla-
tion; as altitude goes up, barometric goes down. At
key-on, the PCM powers up and looks at MAP volt-
age, and based upon the voltage it sees, it knows the
current barometric pressure (relative to altitude).
Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at the voltage
again, continuously every 12 milliseconds, and com-
pares the current voltage to what it was at key-on.
The difference between current voltage and what it
was at key-on, is manifold vacuum.
During key-on (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring a known good sensor.
As the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to avery different altitude than where it was at key-on,
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open Throttle (WOT), based
upon Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) angle and RPM,
it will update barometric pressure in the MAP mem-
ory cell. With periodic updates, the PCM can make
its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor input to aid in cal-
culating the following:
²Manifold pressure
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (certain automatic trans-
missions only)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The MAP sensor signal is provided from a single
piezoresistive element located in the center of a dia-
phragm. The element and diaphragm are both made
of silicone. As manifold pressure changes, the dia-
phragm moves causing the element to deflect, which
stresses the silicone. When silicone is exposed to
stress, its resistance changes. As manifold vacuum
increases, the MAP sensor input voltage decreases
proportionally. The sensor also contains electronics
that condition the signal and provide temperature
compensation.
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; meaning as
pressure changes, voltage changes proportionately.
The range of voltage output from the sensor is usu-
ally between 4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3
volts at 26 in. of Hg. Barometric pressure is the pres-
sure exerted by the atmosphere upon an object. At
sea level on a standard day, no storm, barometric
pressure is approximately 29.92 in Hg. For every 100
feet of altitude, barometric pressure drops .10 in. Hg.
If a storm goes through it can change barometric
pressure from what should be present for that alti-
tude. You should know what the average pressure
and corresponding barometric pressure is for your
area.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted to the side of the
throttle body (Fig. 40). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
31).
(1) Remove air cleaner duct and air resonator box
at throttle body.
14 - 48 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
Page 1469 of 2199

The other two heater elements (downstream sen-
sors 1/2 and 2/2) are controlled by the downstream
heater relay through output signals from the PCM.
To avoid a large simultaneous current surge, power
is delayed to the 2 downstream heater elements by
the PCM for approximately 2 seconds.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
O2S SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Oxygen Sensors (O2S) are attached to, and
protrude into the vehicle exhaust system. Depending
on the emission package, the vehicle may use a total
of either 2 or 4 sensors.
Federal Emissions Package:Two sensors are
used: upstream (referred to as 1/1) and downstream
(referred to as 1/2). With this emission package, the
upstream sensor (1/1) is located just before the main
catalytic convertor. The downstream sensor (1/2) is
located just after the main catalytic convertor.
4.7L V-8 With California Emissions Package:
On this emissions package, 4 sensors are used: 2
upstream (referred to as 1/1 and 2/1) and 2 down-
stream (referred to as 1/2 and 2/2). With this emis-
sion package, the right upstream sensor (2/1) is
located in the right exhaust downpipe just before the
mini-catalytic convertor. The left upstream sensor
(1/1) is located in the left exhaust downpipe just
before the mini-catalytic convertor. The right down-
stream sensor (2/2) is located in the right exhaust
downpipe just after the mini-catalytic convertor, and
before the main catalytic convertor. The left down-
stream sensor (1/2) is located in the left exhaust
downpipe just after the mini-catalytic convertor, and
before the main catalytic convertor.
4.0L 6±Cylinder With California Emissions
Package:On this emissions package, 4 sensors are
used: 2 upstream (referred to as 1/1 and 2/1) and 2
downstream (referred to as 1/2 and 2/2). With this
emission package, the rear/upper upstream sensor
(2/1) is located in the exhaust downpipe just beforethe rear mini-catalytic convertor. The front/upper
upstream sensor (1/1) is located in the exhaust down-
pipe just before the front mini-catalytic convertor.
The rear/lower downstream sensor (2/2) is located in
the exhaust downpipe just after the rear mini-cata-
lytic convertor, and before the main catalytic conver-
tor. The front/lower downstream sensor (1/2) is
located in the exhaust downpipe just after the front
mini-catalytic convertor, and before the main cata-
lytic convertor.
OPERATION
An O2 sensor is a galvanic battery that provides
the PCM with a voltage signal (0-1 volt) inversely
proportional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
In other words, if the oxygen content is low, the volt-
age output is high; if the oxygen content is high the
output voltage is low. The PCM uses this information
to adjust injector pulse-width to achieve the
14.7±to±1 air/fuel ratio necessary for proper engine
operation and to control emissions.
The O2 sensor must have a source of oxygen from
outside of the exhaust stream for comparison. Cur-
rent O2 sensors receive their fresh oxygen (outside
air) supply through the O2 sensor case housing.
Four wires (circuits) are used on each O2 sensor: a
12±volt feed circuit for the sensor heating element; a
ground circuit for the heater element; a low-noise
sensor return circuit to the PCM, and an input cir-
cuit from the sensor back to the PCM to detect sen-
sor operation.
Oxygen Sensor Heaters/Heater Relays:
Depending on the emissions package, the heating ele-
ments within the sensors will be supplied voltage
from either the ASD relay, or 2 separate oxygen sen-
sor relays. Refer to Wiring Diagrams to determine
which relays are used.
The O2 sensor uses a Positive Thermal Co-efficient
(PTC) heater element. As temperature increases,
resistance increases. At ambient temperatures
around 70ÉF, the resistance of the heating element is
approximately 4.5 ohms on 4.0L engines. It is
approximately 13.5 ohms on the 4.7L engine. As the
sensor's temperature increases, resistance in the
heater element increases. This allows the heater to
maintain the optimum operating temperature of
approximately 930É-1100ÉF (500É-600É C). Although
the sensors operate the same, there are physical dif-
ferences, due to the environment that they operate
in, that keep them from being interchangeable.
Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all
times allows the system to enter into closed loop
operation sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain
in closed loop operation during periods of extended
idle.
14 - 50 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
O2S HEATER RELAY (Continued)
Page 1480 of 2199
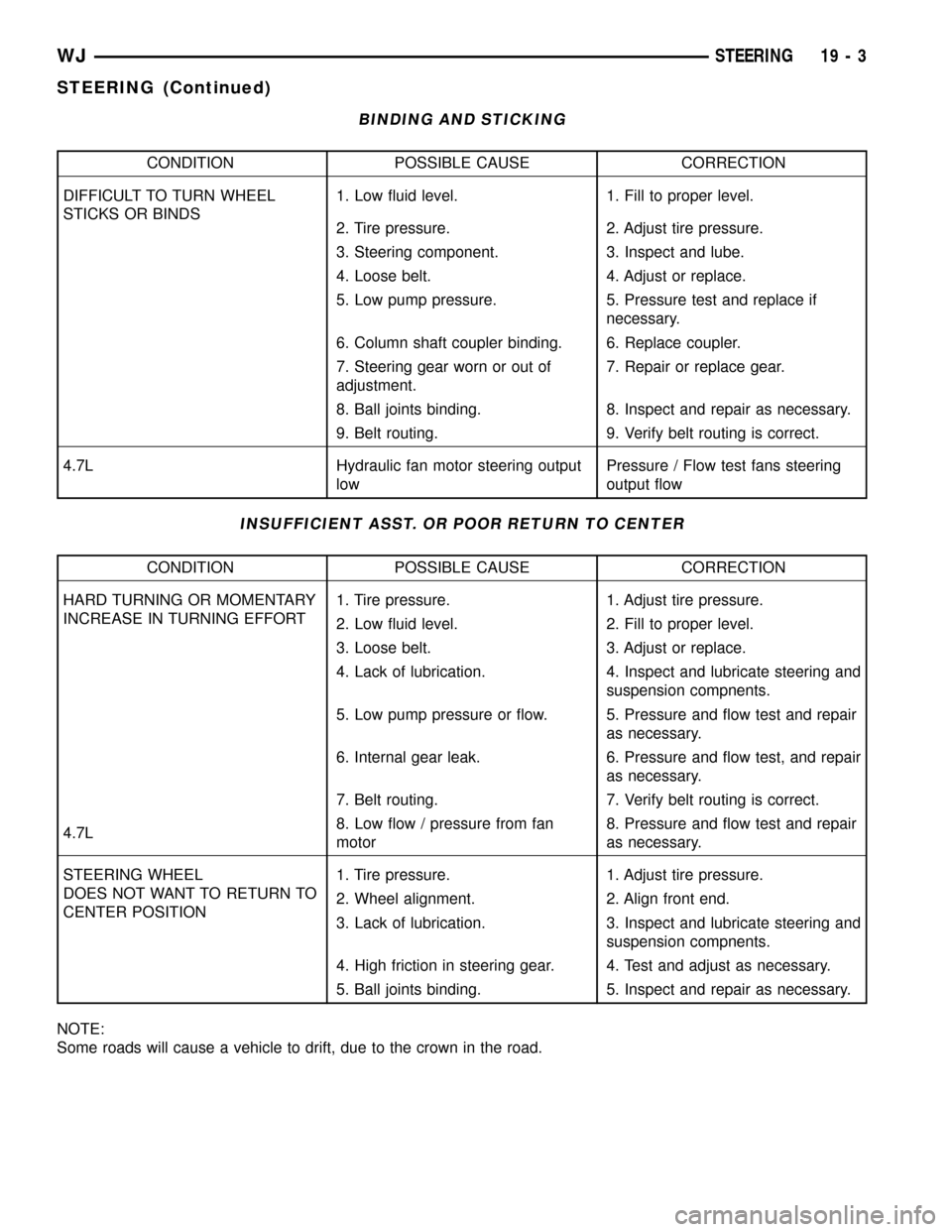
BINDING AND STICKING
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
DIFFICULT TO TURN WHEEL
STICKS OR BINDS1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Tire pressure. 2. Adjust tire pressure.
3. Steering component. 3. Inspect and lube.
4. Loose belt. 4. Adjust or replace.
5. Low pump pressure. 5. Pressure test and replace if
necessary.
6. Column shaft coupler binding. 6. Replace coupler.
7. Steering gear worn or out of
adjustment.7. Repair or replace gear.
8. Ball joints binding. 8. Inspect and repair as necessary.
9. Belt routing. 9. Verify belt routing is correct.
4.7L Hydraulic fan motor steering output
lowPressure / Flow test fans steering
output flow
INSUFFICIENT ASST. OR POOR RETURN TO CENTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
HARD TURNING OR MOMENTARY
INCREASE IN TURNING EFFORT1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Low fluid level. 2. Fill to proper level.
3. Loose belt. 3. Adjust or replace.
4. Lack of lubrication. 4. Inspect and lubricate steering and
suspension compnents.
5. Low pump pressure or flow. 5. Pressure and flow test and repair
as necessary.
6. Internal gear leak. 6. Pressure and flow test, and repair
as necessary.
7. Belt routing. 7. Verify belt routing is correct.
4.7L8. Low flow / pressure from fan
motor8. Pressure and flow test and repair
as necessary.
STEERING WHEEL
DOES NOT WANT TO RETURN TO
CENTER POSITION1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Wheel alignment. 2. Align front end.
3. Lack of lubrication. 3. Inspect and lubricate steering and
suspension compnents.
4. High friction in steering gear. 4. Test and adjust as necessary.
5. Ball joints binding. 5. Inspect and repair as necessary.
NOTE:
Some roads will cause a vehicle to drift, due to the crown in the road.
WJSTEERING 19 - 3
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1482 of 2199

(8) Start engine and let idle long enough to circu-
late power steering fluid through flow/pressure test
gauge.
(9) Shut off the engine and check the fluid level,
add fluid as necessary. Start engine again and let
idle.
(10) The initial pressure reading should be
345-552 kPa (50-80 psi). If pressure is higher inspect
the hoses for restrictions and repair as necessary.
(11) Increase the engine speed to 1500 RPM and
read the flow meter. The reading should be 2.4 - 2.8
GPM, if the reading is below this specification the
pump should be replaced.
CAUTION: This next step involves testing maximum
pump pressure output and flow control valve oper-
ation. Do not leave valve closed for more than three
seconds as the pump could be damaged.
(12) Close valve fully three times for three seconds
and record highest pressure indicated each time.All
three readings must be at pump relief pressure
specifications and within 345 kPa (50 psi) of
each other.
²Pressures above specifications but not within
345 kPa (50 psi) of each other, replace pump.
²Pressures within 345 kPa (50 psi) of each other
but below specifications, replace pump.
CAUTION: Do not force the pump to operate against
the stops for more than 2 to 4 seconds at a time
because, pump damage will result.
(13) Open the test valve and turn the steering
wheel to the extreme left and right positions against
the stops. Record the highest pressure reading at
each position. Compare readings to the pump specifi-
cations chart. If pressures readings are not within 50
psi. of each other, the gear is leaking internally and
must be repaired.
GEAR INLET SPECIFICATIONS 4.0L & 4.7L
ENGINERELIEF
PRESSURE 50FLOW RATE
(GPM)
4.0L 9653 kPa (1400 psi)
1500 RPM 2.4 - 2.8
GPM
4.7L 9653 kPa (1450 psi)
PUMP MOTOR SPECIFICATIONS 4.7L
ENGINERELIEF
PRESSURE 50FLOW RATE
(GPM)
4.7L 9653 kPa (1900 psi)1100 RPM 2.4-2.8
GPM Minium
@ 200 psi
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4.7L -
HYDRAULIC
The following procedures are used to test the oper-
ation of the power steering and hydraulic fan sys-
tems on the vehicle. This test will provide the gallons
per minute (GPM) or flow rate of the power steering
pump along with any maximum relief pressure. Per-
form test anytime a power steering system problem
is present. This test will determine if the power
steering pump, hydraulic fan, and power steering
gear are not functioning properly. It will also deter-
mine if the flow coming out of the hydraulic fan
motor is sufficient for the power steering gear. The
following pressure and flow test is performed using
the Power Steering Analyzer Tool kit 6815 (Fig. 2)
and Adapter kit 8630 (Fig. 3).
FLOW TEST - FLOW FROM POWER STEERING
PUMP
(1) Check the power steering belt to ensure it is in
good condition and adjusted properly.
(2) Connect the pressure gauge hose from the
Power Steering Analyzer to Tube 8630-2.
(3) Connect Adapter 8630-3 to Power Steering
Analyzer test valve end.
(4) Disconnect the high pressure hose from the
power steering pump.
(5) Connect Tube 8630-2 to the pump hose fitting.
(6) Connect the power steering hose from the fan
motor to Adapter 8630-3.
(7) Open the test valve completely.
(8) Start engine and let idle long enough to circu-
late power steering fluid through the flow/pressure
test gauge.
(9) Shut off the engine and check the fluid level,
add fluid ass necessary. Start engine again and let
idle.
(10) The initial pressure reading should be 483 -
690 kPa (70 - 100 psi). If pressure is higher inspect
the hoses for restrictions and repair as necessary.
Fig. 3 4.7L HYDRAULIC POWER STEERING TEST
ADAPTERS
WJSTEERING 19 - 5
STEERING (Continued)