2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE seats
[x] Cancel search: seatsPage 1304 of 2199

ENGINE - 4.7L
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE - 4.7L
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.7L ENGINE.............63
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION...........64
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE...........65
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL.............66
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - LUBRICATION.............67
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE.............68
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE......69
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS.........70
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-
PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS.........70
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE
GASKET SURFACE PREPARATION........70
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE
AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS..............71
REMOVAL.............................71
INSTALLATION.........................73
SPECIFICATIONS
4.7L ENGINE.........................74
SPECIFICATIONS - 4.7L H.O. ENGINE.....77
TORQUE............................79
SPECIAL TOOLS
4.7L ENGINE.........................80
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 4.7L........................83
INSTALLATION - 4.7L....................83
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL - 4.7L........................84
INSTALLATION - 4.7L....................84
CYLINDER HEAD - LEFT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - CYLINDER HEAD........84
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES..........84
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
LASH ADJUSTER.....................84
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER
HEAD GASKET.......................85
REMOVAL.............................85
CLEANING............................86
INSPECTION..........................87INSTALLATION.........................87
CAMSHAFT(S) - LEFT
DESCRIPTION.........................88
REMOVAL.............................89
INSTALLATION.........................90
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - LEFT
DESCRIPTION.........................93
REMOVAL - LEFT SIDE..................93
CLEANING............................93
INSTALLATIONÐLEFT SIDE...............93
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS
DESCRIPTION.........................94
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐREFACING......94
REMOVAL.............................94
INSTALLATION.........................95
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION.........................96
REMOVAL.............................96
INSTALLATION.........................96
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION.........................97
VALVE STEM SEALS
DESCRIPTION.........................97
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - CYLINDER HEAD........97
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES..........97
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER
HEAD GASKET.......................97
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
LASH ADJUSTER.....................98
REMOVAL.............................98
CLEANING............................99
INSPECTION..........................99
INSTALLATION.........................99
CAMSHAFT(S) - RIGHT
DESCRIPTION........................100
REMOVAL............................100
INSTALLATION........................102
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - RIGHT
DESCRIPTION........................104
REMOVAL - RIGHT SIDE................104
CLEANING...........................104
INSTALLATION - RIGHT SIDE.............104
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS
DESCRIPTION........................104
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐREFACING.....105
REMOVAL............................105
INSTALLATION........................106
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 61
Page 1309 of 2199
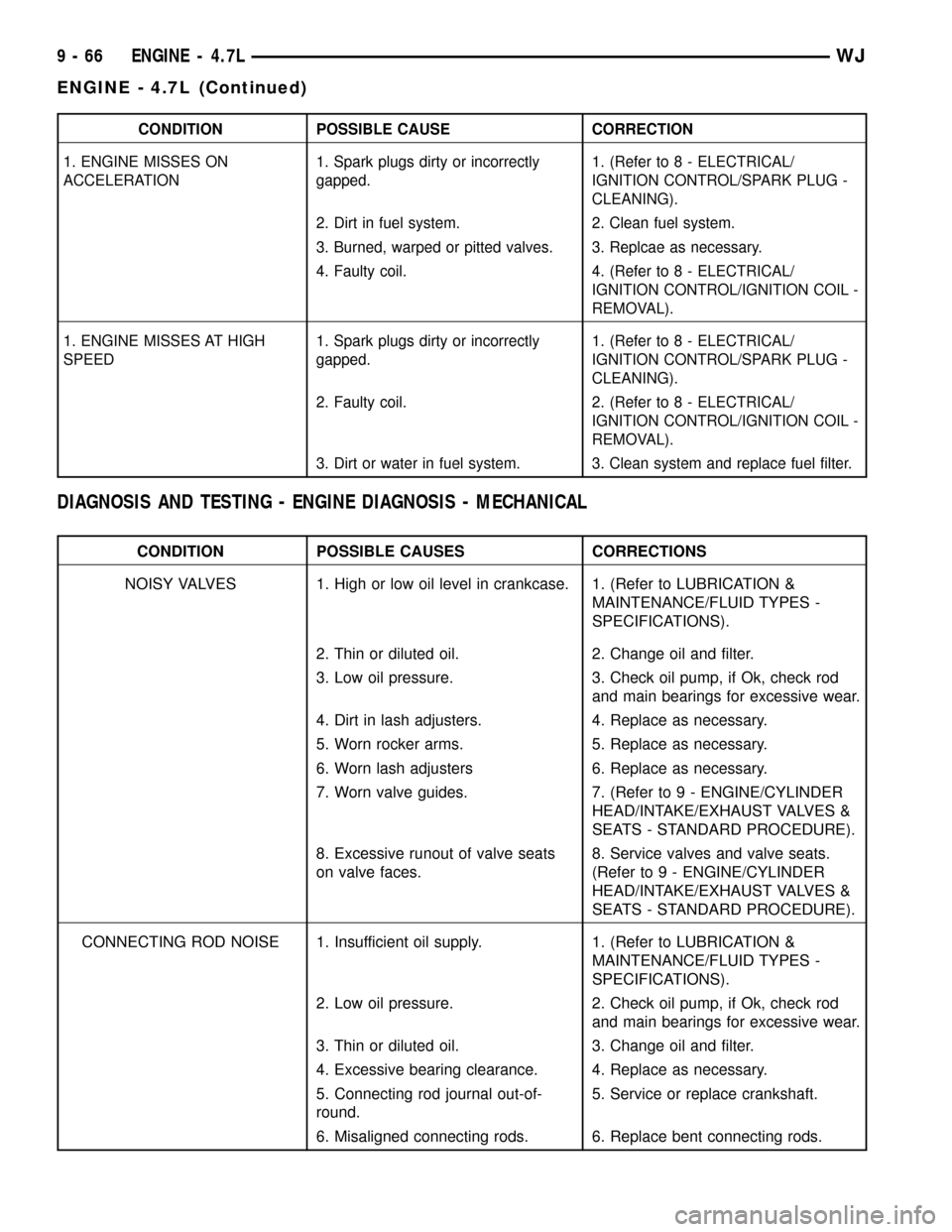
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
1. ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
2. Dirt in fuel system. 2. Clean fuel system.
3. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 3. Replcae as necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
REMOVAL).
1. ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH
SPEED1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
2. Faulty coil. 2. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
REMOVAL).
3. Dirt or water in fuel system. 3. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in crankcase. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Worn lash adjusters 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. Service valves and valve seats.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal out-of-
round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
9 - 66 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1311 of 2199
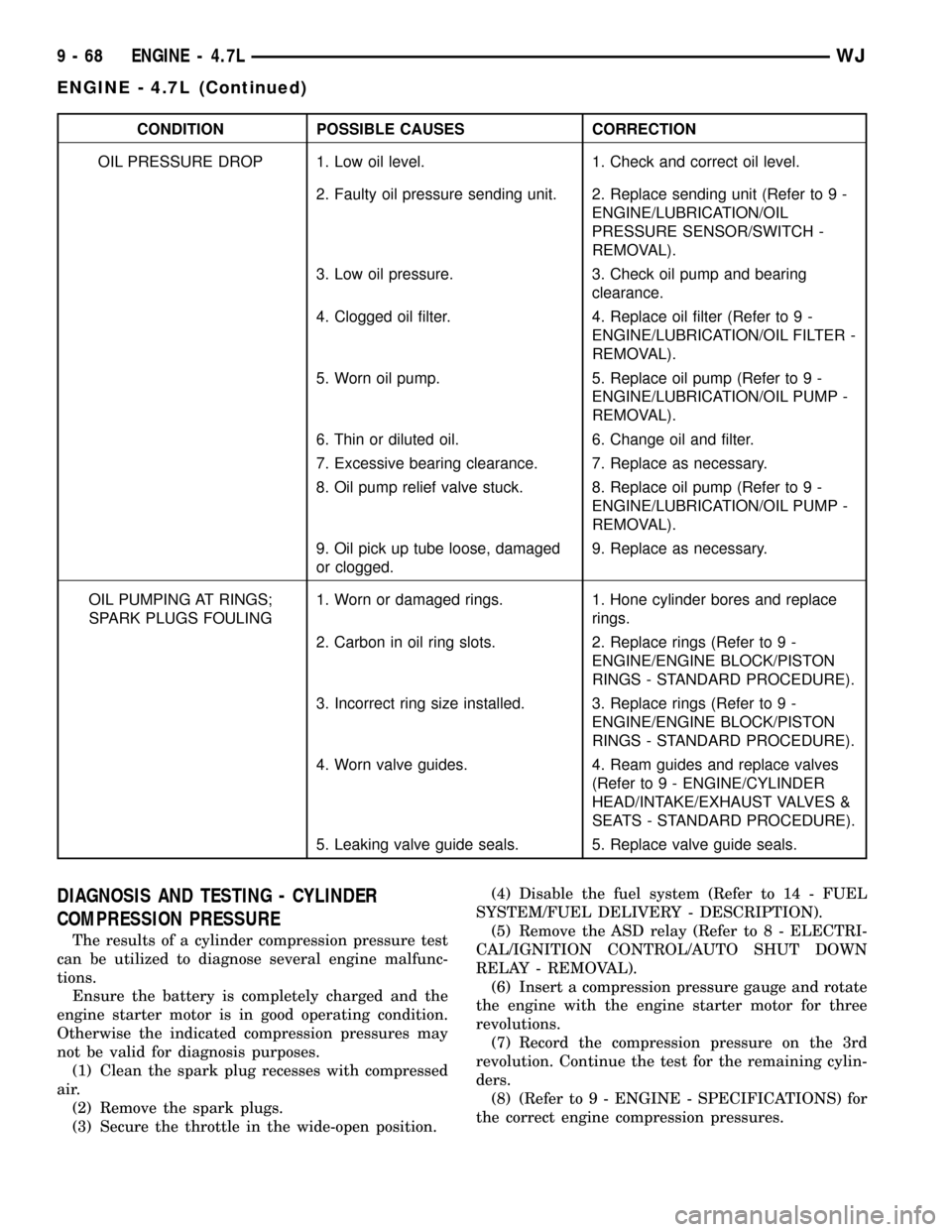
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check and correct oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Replace sending unit (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH -
REMOVAL).
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump and bearing
clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Replace oil filter (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER -
REMOVAL).
5. Worn oil pump. 5. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP -
REMOVAL).
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil and filter.
7. Excessive bearing clearance. 7. Replace as necessary.
8. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 8. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP -
REMOVAL).
9. Oil pick up tube loose, damaged
or clogged.9. Replace as necessary.
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS;
SPARK PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
5. Leaking valve guide seals. 5. Replace valve guide seals.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs.
(3) Secure the throttle in the wide-open position.(4) Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
(5) Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUT DOWN
RELAY - REMOVAL).
(6) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(7) Record the compression pressure on the 3rd
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(8) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for
the correct engine compression pressures.
9 - 68 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1330 of 2199

INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the cylinder head for out-of-flatness,
using a straightedge and a feeler gauge. If tolerances
exceed 0.0508 mm (0.002 in.) replace the cylinder
head.
(2) Inspect the valve seats for damage. Service the
valve seats as necessary.(3) Inspect the valve guides for wear, cracks or
looseness. If either condition exist, replace the cylin-
der head.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The cylinder head bolts are tightened using
a torque plus angle procedure. The bolts must be
examined BEFORE reuse. If the threads are necked
down the bolts should be replaced.
Necking can be checked by holding a straight edge
against the threads. If all the threads do not contact
the scale, the bolt should be replaced (Fig. 13).
CAUTION: When cleaning cylinder head and cylin-
der block surfaces, DO NOT use a metal scraper
because the surfaces could be cut or ground. Use
only a wooden or plastic scraper.
(1) Clean the cylinder head and cylinder block
mating surfaces (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(2) Position the new cylinder head gasket on the
locating dowels.
CAUTION: When installing cylinder head, use care
not damage the tensioner arm or the guide arm.
Fig. 11 Camshaft Sprocket V8 Marks
1 - LEFT CYLINDER HEAD
2 - RIGHT CYLINDER HEAD
Fig. 12 Cylinder Head Access Plugs
1 - RIGHT CYLINDER HEAD ACCESS PLUG
2 - LEFT CYLINDER HEAD ACCESS PLUG
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 87
CYLINDER HEAD - LEFT (Continued)
Page 1331 of 2199

(3) Position the cylinder head onto the cylinder
block. Make sure the cylinder head seats fully over
the locating dowels.
NOTE: The four smaller cylinder head mounting
bolts require sealant to be added to them before
installing. Failure to do so may cause leaks.
(4) Lubricate the cylinder head bolt threads with
clean engine oil and install the ten M11 bolts.
(5) Coat the four M8 cylinder head bolts with
MopartLock and Seal Adhesivethen install the
bolts.
NOTE: The cylinder head bolts are tightened using
an angle torque procedure, however, the bolts are
not a torque-to-yield design.
(6) Tighten the bolts in sequence (Fig. 14) using
the following steps and torque values:
²Step 1: Tighten bolts 1±10, 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
²Step 2: Verify that bolts 1±10, all reached 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.), by repeating step-1 without loosen-
ing the bolts. Tighten bolts 11 thru 14 to 14 N´m (10
ft. lbs.).
²Step 3: Tighten bolts 1±10, 90 degrees.
²Step 4: Tighten bolts 1±10, 90 degrees, again.
Tighten bolts 11±14, 26 N´m (19 ft. lbs.)
(7) Install the secondary chain and secondary
chain guide (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the cylinder head access plug.
(9) Re-set and Install the left side secondary chain
tensioner (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Remove Special Tool 8515.(11) Install the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(12) Install the crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
INSTALLATION).
(13) Install the power steering pump.
(14) Install the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(15) Install the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).
(16) Refill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(17) Raise the vehicle.
(18) Install the exhaust pipe onto the left exhaust
manifold.
(19) Lower the vehicle.
(20) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(21) Start the engine and check for leaks.
CAMSHAFT(S) - LEFT
DESCRIPTION
The camshafts consist of powdered metal steel
lobes which are sinter-bonded to a steel tube. A steel
post or nose piece is friction-welded to the steel cam-
shaft tube. Five bearing journals are machined into
the camshaft, four on the steel tube and one on the
steel nose piece. Camshaft end play is controlled by
two thrust walls that border the nose piece journal.
Engine oil enters the hollow camshafts at the third
journal and lubricates every intake lobe rocker
through a drilled passage in the intake lobe.
Fig. 13 Checking Cylinder Head Bolts for Stretching
(Necking)
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLTFig. 14 Cylinder Head Tightening Sequence
9 - 88 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
CYLINDER HEAD - LEFT (Continued)
Page 1337 of 2199

INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel and
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Each
valve is actuated by a roller rocker arm which pivots
on a stationary lash adjuster. All valves use three
bead lock keepers to retain the springs and promote
valve rotation.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐREFACING
NOTE: Valve seats that are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat
width are maintained. Otherwise the cylinder head
must be replaced.
NOTE: When refacing valves and valve seats, it is
important that the correct size valve guide pilot be
used for reseating stones. A true and complete sur-
face must be obtained.
(1) Using a suitable dial indicator measure the
center of the valve seat Total run out must not
exceed 0.051 mm (0.002 in).
(2) Apply a small amount of Prussian blue to the
valve seat, insert the valve into the cylinder head,
while applying light pressure on the valve rotate the
valve. Remove the valve and examine the valve face.
If the blue is transferred below the top edge of the
valve face, lower the valve seat using a 15 degree
stone. If the blue is transferred to the bottom edge of
the valve face, raise the valve seat using a 65 degree
stone.
(3) When the seat is properly positioned the width
of the intake seat must be 1.75 ± 2.36 mm (0.0689 ±
0.0928 in.) and the exhaust seat must be 1.71 ± 2.32
mm (0.0673 ± 0.0911 in.).
(4) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat. The installed height for
both intake and exhaust valve springs must not
exceed 41.44 mm (1.6315 in.).
(5) The valve seat and valve face must maintain a
face angle of 44.5 ± 45 degrees angle (Fig. 23).
REMOVAL
NOTE: The cylinder heads must be removed in
order to preform this procedure.
(1) Remove rocker arms and lash adjusters. Refer
to procedures in this section (Fig. 24).
(2) Remove the camshaft bearing caps and the
camshaft.
Fig. 23 Valve Assembly Configuration
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
Fig. 24 Rocker Arm Removal
1 - CAMSHAFT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8516
9 - 94 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
Page 1338 of 2199

NOTE: All eight valve springs and valves are
removed in the same manner; this procedure only
covers one valve and valve spring.
(3) Using Special Tool C-3422±B or C-3422±C
Valve Spring Compressor and Special tool 8519
Adapter, compress the valve spring.
NOTE: It may be necessary to tap the top of the
valve spring to loosen the spring retainers locks
enough to be removed.
(4) Remove the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(5) Remove the valve spring compressor.
(6) Remove the spring retainer, and the spring.
NOTE: Check for sharp edges on the keeper
grooves. Remove any burrs from the valve stem
before removing the valve from the cylinder head.
(7) Remove the valve from the cylinder head.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
(8) Remove the valve stem seal. Mark the valve for
proper installation.
TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
NOTE: Whenever the valves are removed from the
cylinder head it is recommended that the valve
springs be inspected and tested for reuse.
Inspect the valve springs for physical signs of wear
or damage. Turn table of tool C-647 until surface is
in line with the 40.69 mm (1.602 in.) mark on the
threaded stud and the zero mark on the front. Place
spring over the stud on the table and lift compress-
ing lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench
until Ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench
at this instant. Multiply this reading by two. This
will give the spring load at test length. Fractional
measurements are indicated on the table for finer
adjustments. Refer to Specifications Section to obtain
specified height and allowable tensions. Replace any
springs that do not meet specifications. (Fig. 25)
INSTALLATION
(1) coat the valve stem with clean engine oil and
insert it into the cylinder head.
(2) Install the valve stem seal. make sure the seal
is fully seated and that the garter spring at the top
of the seal is intact.
(3) Install the spring and the spring retainer (Fig.
26).
(4) Using the valve spring compressor, compress
the spring and install the two valve spring retainer
halves.
(5) Release the valve spring compressor and make
sure the two spring retainer halves and the spring
retainer are fully seated.
(6) lubricate the camshaft journal with clean
engine oil then Position the camshaft (with the
sprocket dowel on the left camshaft at 11 o'clock and
the right camshaft at 12 o'clock), then position the
camshaft bearing caps.
(7) Install the camshaft bearing cap retaining
bolts. Tighten the bolts 9±13 N´m (100 in. lbs.) in
1¤2
turn increments in the sequence shown (Fig. 27).
(8) Position the hydraulic lash adjusters and
rocker arms (Fig. 24).
Fig. 25 Testing Valve Springs
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-647
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 95
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1339 of 2199

ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The rocker arms are steel stampings with an inte-
gral roller bearing. The rocker arms incorporate a 2.8
mm (0.11 inch) oil hole in the lash adjuster socket for
roller and camshaft lubrication.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Disconnect the battery negative cable to pre-
vent accidental starter engagement.
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 3 and 5
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
exhaust stroke.
(3) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 2 and 8
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(4) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 4 and 6
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #3 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(5) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 1 and 7
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #2 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(6) Using special tool 8516 Rocker Arm Remover,
press downward on the valve spring, remove rocker
arm (Fig. 28).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Make sure the rocker arms are installed
with the concave pocket over the lash adjusters.
Failure to do so may cause severe damage to the
rocker arms and/or lash adjusters.
NOTE: Coat the rocker arms with clean engine oil
prior to installation.
(1) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 3 and
5 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
exhaust stroke.
(2) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 2 and
8 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(3) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 4 and
6 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #3 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(4) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 1 and
7 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #2 is at TDC
compression stroke.
Fig. 26 Valve Assembly Configuration
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
Fig. 27 Camshaft Bearing Caps Tightening
Sequence
9 - 96 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)