2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE fuel ram
[x] Cancel search: fuel ramPage 1470 of 2199

In Closed Loop operation, the PCM monitors cer-
tain O2 sensor input(s) along with other inputs, and
adjusts the injector pulse width accordingly. During
Open Loop operation, the PCM ignores the O2 sensor
input. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width based
on preprogrammed (fixed) values and inputs from
other sensors.
Upstream Sensor (Non-California Emissions):
The upstream sensor (1/1) provides an input voltage
to the PCM. The input tells the PCM the oxygen con-
tent of the exhaust gas. The PCM uses this informa-
tion to fine tune fuel delivery to maintain the correct
oxygen content at the downstream oxygen sensor.
The PCM will change the air/fuel ratio until the
upstream sensor inputs a voltage that the PCM has
determined will make the downstream sensor output
(oxygen content) correct.
The upstream oxygen sensor also provides an input
to determine catalytic convertor efficiency.
Downstream Sensor (Non-California Emis-
sions):The downstream oxygen sensor (1/2) is also
used to determine the correct air-fuel ratio. As the
oxygen content changes at the downstream sensor,
the PCM calculates how much air-fuel ratio change is
required. The PCM then looks at the upstream oxy-
gen sensor voltage and changes fuel delivery until
the upstream sensor voltage changes enough to cor-
rect the downstream sensor voltage (oxygen content).
The downstream oxygen sensor also provides an
input to determine catalytic convertor efficiency.
Upstream Sensors (California Engines):Tw o
upstream sensors are used (1/1 and 2/1). The 1/1 sen-
sor is the first sensor to receive exhaust gases from
the #1 cylinder. They provide an input voltage to the
PCM. The input tells the PCM the oxygen content of
the exhaust gas. The PCM uses this information to
fine tune fuel delivery to maintain the correct oxygen
content at the downstream oxygen sensors. The PCM
will change the air/fuel ratio until the upstream sen-
sors input a voltage that the PCM has determined
will make the downstream sensors output (oxygen
content) correct.
The upstream oxygen sensors also provide an input
to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main catalytic
convertor efficiency is not calculated with this pack-
age.
Downstream Sensors (California Engines):
Two downstream sensors are used (1/2 and 2/2). The
downstream sensors are used to determine the cor-
rect air-fuel ratio. As the oxygen content changes at
the downstream sensor, the PCM calculates how
much air-fuel ratio change is required. The PCM
then looks at the upstream oxygen sensor voltage,
and changes fuel delivery until the upstream sensor
voltage changes enough to correct the downstream
sensor voltage (oxygen content).The downstream oxygen sensors also provide an
input to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main cat-
alytic convertor efficiency is not calculated with this
package.
Engines equipped with either a downstream sen-
sor(s), or a post-catalytic sensor, will monitor cata-
lytic convertor efficiency. If efficiency is below
emission standards, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated and a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will be set. Refer to Monitored Systems
in Emission Control Systems for additional informa-
tion.
REMOVAL
Never apply any type of grease to the oxygen
sensor electrical connector, or attempt any sol-
dering of the sensor wiring harness.
Oxygen sensor (O2S) locations are shown in (Fig.
33) and (Fig. 34).
WARNING: THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD, EXHAUST
PIPES AND CATALYTIC CONVERTER(S) BECOME
VERY HOT DURING ENGINE OPERATION. ALLOW
ENGINE TO COOL BEFORE REMOVING OXYGEN
SENSOR.
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Disconnect O2S pigtail harness from main wir-
ing harness.
(3) If equipped, disconnect sensor wire harness
mounting clips from engine or body.
CAUTION: When disconnecting sensor electrical
connector, do not pull directly on wire going into
sensor.
(4) Remove O2S sensor with an oxygen sensor
removal and installation tool.
INSTALLATION
Threads of new oxygen sensors are factory coated
with anti-seize compound to aid in removal.DO
NOT add any additional anti-seize compound to
threads of a new oxygen sensor.
(1) Install O2S sensor. Tighten to 30 N´m (22 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect O2S sensor wire connector to main
wiring harness.
(3) If equipped, connect sensor wire harness
mounting clips to engine or body.When Equipped:
The O2S pigtail harness must be clipped and/or
bolted back to their original positions on
engine or body to prevent mechanical damage
to wiring..
(4) Lower vehicle.
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 51
O2S SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1561 of 2199

(11) Move transmission forward. Then raise, lower
or tilt transmission to align converter housing with
engine block dowels.
(12) Carefully work transmission forward and over
engine block dowels until converter hub is seated in
crankshaft.
(13) Install two bolts to attach converter housing
to engine.
(14) Install the upper transmission bending braces
to the torque converter housing and the overdrive
unit. Tighten the bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft.lbs.).
(15) Install remaining torque converter housing to
engine bolts. Tighten to 68 N´m (50 ft.lbs.).
(16) Install rear transmission crossmember.
Tighten crossmember to frame bolts to 68 N´m (50
ft.lbs.).
(17) Install rear support to transmission. Tighten
bolts to 47 N´m (35 ft.lbs.).
(18) Lower transmission onto crossmember and
install bolts attaching transmission mount to cross-
member. Tighten clevis bracket to crossmember bolts
to 47 N´m (35 ft.lbs.). Tighten the clevis bracket to
rear support bolt to 68 N´m (50 ft.lbs.).
(19) Remove engine support fixture.
(20) Install crankshaft position sensor. (Refer to 14
- FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/CRANKSHAFT
POSITION SENSOR - INSTALLATION)
(21) Install new plastic retainer grommet on any
shift cable that was disconnected. Grommets should
not be reused. Use pry tool to remove rod from grom-
met and cut away old grommet. Use pliers to snap
new grommet into cable and to snap grommet onto
lever.
(22) Connect gearshift and throttle valve cable to
transmission.
(23) Connect wires to park/neutral position switch
and transmission solenoid connector. Be sure trans-
mission harnesses are properly routed.CAUTION: It is essential that correct length bolts be
used to attach the converter to the driveplate. Bolts
that are too long will damage the clutch surface
inside the converter.
(24) Install all torque converter-to-driveplate bolts
by hand.
(25) Verify that the torque converter is pulled
flush to the driveplate. Tighten bolts to 31 N´m (270
in. lbs.).
(26) Install converter housing access cover. Tighten
bolt to 23 N´m (200 in.lbs.).
(27) Install the bell housing brace to the torque
converter cover and the engine to transmission bend-
ing brace. Tighten the bolts and nut to 41 N´m (30
ft.lbs.).
(28) Install starter motor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLA-
TION) and cooler line bracket.
(29) Connect cooler lines to transmission.
(30) Install transmission fill tube. Install new seal
on tube before installation.
(31) Install exhaust components.
(32) Install transfer case. Tighten transfer case
nuts to 35 N´m (26 ft.lbs.).
(33) Install the transfer case shift cable to the
cable support bracket and the transfer case shift
lever.
(34) Align and connect propeller shaft(s).
(35) Adjust gearshift linkage and throttle valve
cable if necessary.
(36) Lower vehicle.
(37) Fill transmission with MopartATF +4, type
9602, fluid.
21 - 42 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1902 of 2199

(8) Loosen screw under hood hinge, attaching
fender to engine compartment rail.
(9) Remove screws attaching fender to engine com-
partment rail (Fig. 7).
(10) Right fender only:
(a) If equipped, remove radio antenna.
(11) Separate fender from body.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fender on body.
(2) Right fender only:
(a) If equipped, install radio antenna.
(3) Install all screws finger-tight.
(4) Align fender with adjacent body panels and
wax crayon reference marks.
(5) Tighten all screws.
(6) Install inner fender liner.
FUEL FILL DOOR
REMOVAL
(1) Open the fuel filler door.
(2) Remove the screws attaching the door to the
quarter panel (Fig. 8).
(3) Remove the door from the panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the fuel filler door on the quarter
panel with the screw holes aligned.(2) Install the screws attaching the fuel filler door
to the quarter panel.
GRILLE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fascia, refer to (Refer to 13 - FRAMES
& BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT FASCIA - REMOV-
AL).
(2) Disengage retainers attaching grille insert to
grille/fascia.
(3) Separate grille insert from grille/fascia (Fig. 9).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position grille insert in grille/fascia (Fig. 9).
(2) Engage retainers attaching grille insert to
grille/fascia.
Fig. 7 Upper Fender Mounting
1 - FENDER
2 - BODY
Fig. 8 Fuel Filler Door
1 - FUEL FILL DOOR
Fig. 9 Grille Insert
1 - GRILLE/FASCIA
2 - INSERT
WJEXTERIOR 23 - 29
FRONT FENDER (Continued)
Page 2157 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connect
the DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0031 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0032 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0037 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0038 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0043 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0044 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0051 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0052 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2164 of 2199
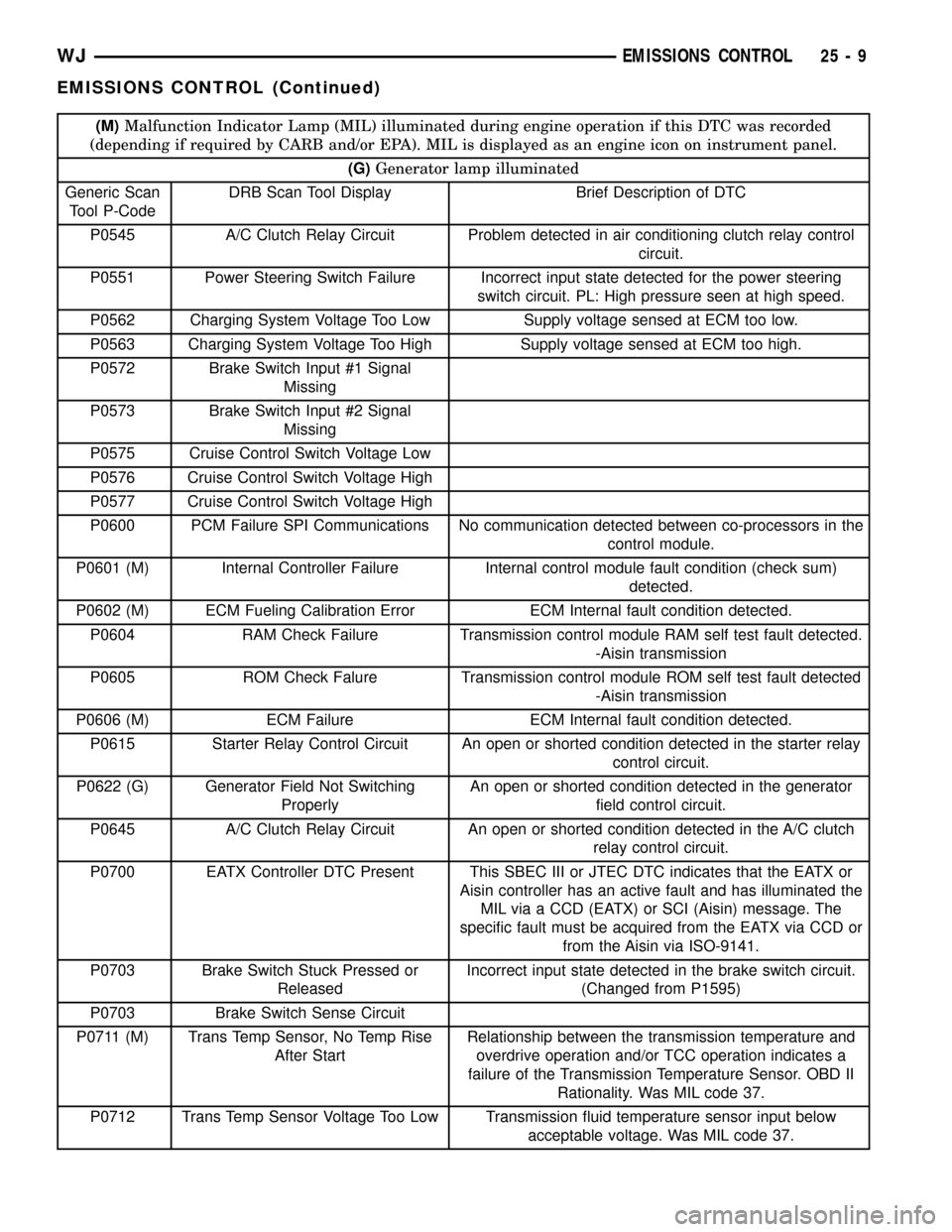
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0545 A/C Clutch Relay Circuit Problem detected in air conditioning clutch relay control
circuit.
P0551 Power Steering Switch Failure Incorrect input state detected for the power steering
switch circuit. PL: High pressure seen at high speed.
P0562 Charging System Voltage Too Low Supply voltage sensed at ECM too low.
P0563 Charging System Voltage Too High Supply voltage sensed at ECM too high.
P0572 Brake Switch Input #1 Signal
Missing
P0573 Brake Switch Input #2 Signal
Missing
P0575 Cruise Control Switch Voltage Low
P0576 Cruise Control Switch Voltage High
P0577 Cruise Control Switch Voltage High
P0600 PCM Failure SPI Communications No communication detected between co-processors in the
control module.
P0601 (M) Internal Controller Failure Internal control module fault condition (check sum)
detected.
P0602 (M) ECM Fueling Calibration Error ECM Internal fault condition detected.
P0604 RAM Check Failure Transmission control module RAM self test fault detected.
-Aisin transmission
P0605 ROM Check Falure Transmission control module ROM self test fault detected
-Aisin transmission
P0606 (M) ECM Failure ECM Internal fault condition detected.
P0615 Starter Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the starter relay
control circuit.
P0622 (G) Generator Field Not Switching
ProperlyAn open or shorted condition detected in the generator
field control circuit.
P0645 A/C Clutch Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the A/C clutch
relay control circuit.
P0700 EATX Controller DTC Present This SBEC III or JTEC DTC indicates that the EATX or
Aisin controller has an active fault and has illuminated the
MIL via a CCD (EATX) or SCI (Aisin) message. The
specific fault must be acquired from the EATX via CCD or
from the Aisin via ISO-9141.
P0703 Brake Switch Stuck Pressed or
ReleasedIncorrect input state detected in the brake switch circuit.
(Changed from P1595)
P0703 Brake Switch Sense Circuit
P0711 (M) Trans Temp Sensor, No Temp Rise
After StartRelationship between the transmission temperature and
overdrive operation and/or TCC operation indicates a
failure of the Transmission Temperature Sensor. OBD II
Rationality. Was MIL code 37.
P0712 Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too Low Transmission fluid temperature sensor input below
acceptable voltage. Was MIL code 37.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 9
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2173 of 2199

tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode:The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º
water. The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid
as the system begins to pump up to this pressure. As
the pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop
off. If there is no leak in the system, the pump would
eventually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .040º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
FUEL SYSTEM MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the Air Fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S sensor output. The programmed
memory acts as a self calibration tool that the engine
controller uses to compensate for variations in engine
specifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue
over the life span of the engine. By monitoring the
actual fuel-air ratio with the O2S sensor (short term)
and multiplying that with the program long-term
(adaptive) memory and comparing that to the limit,
it can be determined whether it will pass an emis-
sions test. If a malfunction occurs such that the PCM
cannot maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the
MIL will be illuminated.
CATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.
Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. This can increase vehicle emissions
25 - 18 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2176 of 2199

OPERATION - TASK MANAGER
The Task Manager determines which tests happen
when and which functions occur when. Many of the
diagnostic steps required by OBD II must be per-
formed under specific operating conditions. The Task
Manager software organizes and prioritizes the diag-
nostic procedures. The job of the Task Manager is to
determine if conditions are appropriate for tests to be
run, monitor the parameters for a trip for each test,
and record the results of the test. Following are the
responsibilities of the Task Manager software:
²Test Sequence
²MIL Illumination
²Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
²Trip Indicator
²Freeze Frame Data Storage
²Similar Conditions Window
Test Sequence
In many instances, emissions systems must fail
diagnostic tests more than once before the PCM illu-
minates the MIL. These tests are know as 'two trip
monitors.' Other tests that turn the MIL lamp on
after a single failure are known as 'one trip moni-
tors.' A trip is defined as 'start the vehicle and oper-
ate it to meet the criteria necessary to run the given
monitor.'
Many of the diagnostic tests must be performed
under certain operating conditions. However, there
are times when tests cannot be run because another
test is in progress (conflict), another test has failed
(pending) or the Task Manager has set a fault that
may cause a failure of the test (suspend).
²Pending
Under some situations the Task Manager will not
run a monitor if the MIL is illuminated and a fault is
stored from another monitor. In these situations, the
Task Manager postpones monitorspendingresolu-
tion of the original fault. The Task Manager does not
run the test until the problem is remedied.
For example, when the MIL is illuminated for an
Oxygen Sensor fault, the Task Manager does not run
the Catalyst Monitor until the Oxygen Sensor fault is
remedied. Since the Catalyst Monitor is based on sig-
nals from the Oxygen Sensor, running the test would
produce inaccurate results.
²Conflict
There are situations when the Task Manager does
not run a test if another monitor is in progress. In
these situations, the effects of another monitor run-
ning could result in an erroneous failure. If thiscon-
flictis present, the monitor is not run until the
conflicting condition passes. Most likely the monitor
will run later after the conflicting monitor has
passed.
For example, if the Fuel System Monitor is inprogress, the Task Manager does not run the EGR
Monitor. Since both tests monitor changes in air/fuel
ratio and adaptive fuel compensation, the monitors
will conflict with each other.
²Suspend
Occasionally the Task Manager may not allow a two
trip fault to mature. The Task Manager willsus-
pendthe maturing of a fault if a condition exists
that may induce an erroneous failure. This prevents
illuminating the MIL for the wrong fault and allows
more precis diagnosis.
For example, if the PCM is storing a one trip fault
for the Oxygen Sensor and the EGR monitor, the
Task Manager may still run the EGR Monitor but
will suspend the results until the Oxygen Sensor
Monitor either passes or fails. At that point the Task
Manager can determine if the EGR system is actu-
ally failing or if an Oxygen Sensor is failing.MIL Illumination
The PCM Task Manager carries out the illumina-
tion of the MIL. The Task Manager triggers MIL illu-
mination upon test failure, depending on monitor
failure criteria.
The Task Manager Screen shows both a Requested
MIL state and an Actual MIL state. When the MIL is
illuminated upon completion of a test for a third trip,
the Requested MIL state changes to OFF. However,
the MIL remains illuminated until the next key
cycle. (On some vehicles, the MIL will actually turn
OFF during the third key cycle) During the key cycle
for the third good trip, the Requested MIL state is
OFF, while the Actual MIL state is ON. After the
next key cycle, the MIL is not illuminated and both
MIL states read OFF.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
With OBD II, different DTC faults have different
priorities according to regulations. As a result, the
priorities determine MIL illumination and DTC era-
sure. DTCs are entered according to individual prior-
ity. DTCs with a higher priority overwrite lower
priority DTCs.
Priorities
²Priority 0 ÐNon-emissions related trouble codes
²Priority 1 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for non-fuel system and non-misfire.
²Priority 2 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) or misfire.
²Priority3ÐTwotrip failure for a non-fuel sys-
tem and non-misfire or matured one trip comprehen-
sive component fault.
²Priority4ÐTwotrip failure or matured fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) and misfire or one trip cat-
alyst damaging misfire.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 21
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2177 of 2199

Non-emissions related failures have no priority.
One trip failures of two trip faults have low priority.
Two trip failures or matured faults have higher pri-
ority. One and two trip failures of fuel system and
misfire monitor take precedence over non-fuel system
and non-misfire failures.
DTC Self Erasure
With one trip components or systems, the MIL is
illuminated upon test failure and DTCs are stored.
Two trip monitors are components requiring failure
in two consecutive trips for MIL illumination. Upon
failure of the first test, the Task Manager enters a
maturing code. If the component fails the test for a
second time the code matures and a DTC is set.
After three good trips the MIL is extinguished and
the Task Manager automatically switches the trip
counter to a warm-up cycle counter. DTCs are auto-
matically erased following 40 warm-up cycles if the
component does not fail again.
For misfire and fuel system monitors, the compo-
nent must pass the test under a Similar Conditions
Window in order to record a good trip. A Similar Con-
ditions Window is when engine RPM is within 375
RPM and load is within 10% of when the fault
occurred.
NOTE: It is important to understand that a compo-
nent does not have to fail under a similar window of
operation to mature. It must pass the test under a
Similar Conditions Window when it failed to record
a Good Trip for DTC erasure for misfire and fuel
system monitors.
DTCs can be erased anytime with a DRB III. Eras-
ing the DTC with the DRB III erases all OBD II
information. The DRB III automatically displays a
warning that erasing the DTC will also erase all
OBD II monitor data. This includes all counter infor-
mation for warm-up cycles, trips and Freeze Frame.
Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
²Specific Good Trip
²Fuel System Good Trip
²Misfire Good Trip
²Alternate Good Trip (appears as a Global Good
Trip on DRB III)
²Comprehensive Components
²Major Monitor
²Warm-Up CyclesSpecific Good Trip
The term Good Trip has different meanings
depending on the circumstances:
²If the MIL is OFF, a trip is defined as when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst Monitor
have been completed in the same drive cycle.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by the Fuel
Monitor or Misfire Monitor (both continuous moni-
tors), the vehicle must be operated in the Similar
Condition Window for a specified amount of time.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by a Task
Manager commanded once-per-trip monitor (such as
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst Monitor, Purge
Flow Monitor, Leak Detection Pump Monitor, EGR
Monitor or Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor), a good
trip is when the monitor is passed on the next start-
up.
²If the MIL is ON and any other emissions DTC
was set (not an OBD II monitor), a good trip occurs
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Mon-
itor have been completed, or two minutes of engine
run time if the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst
Monitor have been stopped from running.
Fuel System Good Trip
To count a good trip (three required) and turn off
the MIL, the following conditions must occur:
²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfire
Warm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
25 - 22 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)