2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 4.7l intake manifold
[x] Cancel search: 4.7l intake manifoldPage 1465 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
The IAC motor is located on the throttle body.
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.
(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
(4) Install air cleaner duct/air box to throttle body.
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.
(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
(4) Install air duct/air box to throttle body.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The 2±wire Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT)
sensor is installed in the intake manifold with the
sensor element extending into the air stream.
The IAT sensor is a two-wire Negative Thermal
Coefficient (NTC) sensor. Meaning, as intake mani-
fold temperature increases, resistance (voltage) in the
sensor decreases. As temperature decreases, resis-
tance (voltage) in the sensor increases.
OPERATION
The IAT sensor provides an input voltage to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) indicating the
density of the air entering the intake manifold based
upon intake manifold temperature. At key-on, a
5±volt power circuit is supplied to the sensor from
the PCM. The sensor is grounded at the PCM
through a low-noise, sensor-return circuit.
The PCM uses this input to calculate the following:
²Injector pulse-width
²Adjustment of spark timing (to help prevent
spark knock with high intake manifold air-charge
temperatures)
The resistance values of the IAT sensor is the same
as for the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) sensor
is installed into the intake manifold plenum near the
front of the throttle body (Fig. 27).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
(2) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
REMOVAL - 4.7L
The Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) sensor
is located on the left side of the intake manifold.
Threaded Type Sensor
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
(2) Remove sensor from intake manifold (Fig. 28).
Snap-In Type Sensor
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from IAT sen-
sor.
(2) Clean dirt from intake manifold at sensor base.
(3) Gently lift on small plastic release tab (Fig. 30)
or (Fig. 29) and rotate sensor about 1/4 turn counter-
clockwise for removal.
(4) Check condition of sensor o-ring.
Fig. 27 Intake Manifold Air Sensor LocationÐ4.0L
Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - THROTTLE BODY
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
5 - TPS
6 - MAP SENSOR
7 - ELEC. CONN.
8 - IAT SENSOR
9 - ELEC. CONN.
14 - 46 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1466 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
The Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) sensor
is installed into the intake manifold plenum near the
front of the throttle body (Fig. 27).
(1) Install sensor into intake manifold. Tighten
sensor to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
Threaded Type Sensor
(1) Install sensor (Fig. 28) into intake manifold.
Tighten sensor to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
Snap-In Type Sensor
(1) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 30).
(2) Clean sensor mounting hole in intake manifold.(3) Position sensor (Fig. 29) into intake manifold
and rotate clockwise until past release tab.
(4) Install electrical connector.
Fig. 28 IAT - 4.7L (THREADED TYPE)
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - TPS
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - IAT SENSOR (THREADED TYPE)
5 - MOUNTING SCREWS
Fig. 29 IAT SENSOR - 4.7L (SNAP-IN TYPE)
1 - LEFT SIDE OF THROTTLE BODY
2 - ELEC. CONNECT.
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - RELEASE TAB
Fig. 30 IAT SENSOR TAB / O-RING - 4.7L (SNAP-IN
TYPE)
1 - IAT SENSOR
2 - SENSOR O-RING
3 - RELEASE TAB
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 47
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1467 of 2199

MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
On the 4.0L six-cylinder engine the MAP sensor is
mounted to the engine throttle body. On the 4.7L V-8
engine the MAP sensor is mounted to front of the
intake manifold.
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
intake manifold. An o-ring seals the sensor to the
intake manifold.
OPERATION
The MAP sensor is used as an input to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). It contains a silicon
based sensing unit to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When manifold absolute pressure (MAP) equals
Barometric pressure, the pulse width will be at max-
imum.
A 5 volt reference is supplied from the PCM and
returns a voltage signal to the PCM that reflects
manifold pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V
and full scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of 0±15
psi, the voltage changes 4.0V. To operate the sensor,
it is supplied a regulated 4.8 to 5.1 volts. Ground is
provided through the low-noise, sensor return circuit
at the PCM.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to fuel injector pulse width. The most important
function of the MAP sensor is to determine baromet-
ric pressure. The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is
at sea level or at a higher altitude, because the air
density changes with altitude. It will also help to cor-
rect for varying barometric pressure. Barometric
pressure and altitude have a direct inverse correla-
tion; as altitude goes up, barometric goes down. At
key-on, the PCM powers up and looks at MAP volt-
age, and based upon the voltage it sees, it knows the
current barometric pressure (relative to altitude).
Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at the voltage
again, continuously every 12 milliseconds, and com-
pares the current voltage to what it was at key-on.
The difference between current voltage and what it
was at key-on, is manifold vacuum.
During key-on (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring a known good sensor.
As the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to avery different altitude than where it was at key-on,
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open Throttle (WOT), based
upon Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) angle and RPM,
it will update barometric pressure in the MAP mem-
ory cell. With periodic updates, the PCM can make
its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor input to aid in cal-
culating the following:
²Manifold pressure
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (certain automatic trans-
missions only)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The MAP sensor signal is provided from a single
piezoresistive element located in the center of a dia-
phragm. The element and diaphragm are both made
of silicone. As manifold pressure changes, the dia-
phragm moves causing the element to deflect, which
stresses the silicone. When silicone is exposed to
stress, its resistance changes. As manifold vacuum
increases, the MAP sensor input voltage decreases
proportionally. The sensor also contains electronics
that condition the signal and provide temperature
compensation.
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; meaning as
pressure changes, voltage changes proportionately.
The range of voltage output from the sensor is usu-
ally between 4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3
volts at 26 in. of Hg. Barometric pressure is the pres-
sure exerted by the atmosphere upon an object. At
sea level on a standard day, no storm, barometric
pressure is approximately 29.92 in Hg. For every 100
feet of altitude, barometric pressure drops .10 in. Hg.
If a storm goes through it can change barometric
pressure from what should be present for that alti-
tude. You should know what the average pressure
and corresponding barometric pressure is for your
area.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted to the side of the
throttle body (Fig. 40). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
31).
(1) Remove air cleaner duct and air resonator box
at throttle body.
14 - 48 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
Page 1468 of 2199

(2) Remove two MAP sensor mounting bolts
(screws) (Fig. 31).
(3) While removing MAP sensor, slide the rubber
L-shaped fitting (Fig. 31) from the throttle body.
(4) Remove rubber L-shaped fitting from MAP sen-
sor.
REMOVAL - 4.7L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
intake manifold (Fig. 32). An o-ring seals the sensor
to the intake manifold.
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at sensor.
(2) Clean area around MAP sensor.
(3) Remove 2 sensor mounting bolts (Fig. 32).
(4) Remove MAP sensor from intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted to the side of the
throttle body (Fig. 40). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
31).
(1) Install rubber L-shaped fitting to MAP sensor.
(2) Position sensor to throttle body while guiding
rubber fitting over throttle body vacuum nipple.
(3) Install MAP sensor mounting bolts (screws).
Tighten screws to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install air cleanerduct/air box.
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
intake manifold (Fig. 32). An o-ring seals the sensor
to the intake manifold.
(1) Clean MAP sensor mounting hole at intake
manifold.
(2) Check MAP sensor o-ring seal for cuts or tears.
(3) Position sensor into manifold.
(4) Install MAP sensor mounting bolts (screws).
Tighten screws to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect electrical connector.
O2S HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 2 oxygen (O2) sensor heater relays (upstream
and downstream) are located in the Powertrain Dis-
tribution Center (PDC).
OPERATION
Engines equipped with the California (NAE) Emis-
sions Package usefour O2 sensors.
Two of the four sensor heater elements (upstream
sensors 1/1 and 2/1) are controlled by the upstream
heater relay through output signals from the Power-
train Control Module (PCM).
Fig. 31 Rubber L-Shaped FittingÐMAP Sensor-to-
Throttle BodyÐ4.0L Engine
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - MAP SENSOR
3 - RUBBER FITTING
4 - MOUNTING SCREWS (2)Fig. 32 MAP and ECT Sensor LocationsÐ4.7L V±8
Engine
1 - ECT SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (2)
3 - MAP SENSOR
4 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 49
MAP SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1472 of 2199
(3) Remove all control cables from throttle body
(lever) arm. Refer to Accelerator Pedal and Throttle
Cable.
(4) Remove four throttle body mounting bolts.
(5) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
(6) Discard old throttle body-to-intake manifold
gasket.
REMOVAL - 4.7L
(1) Remove the air duct and air resonator box at
throttle body.
(2) Disconnect throttle body electrical connectors
at IAC motor and TPS (Fig. 36).
(3) Remove vacuum line at throttle body.
(4) Remove all control cables from throttle body
(lever) arm. Refer to Accelerator Pedal and Throttle
Cable.
(5) Remove three throttle body mounting bolts
(Fig. 36).
(6) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
(1) Clean the mating surfaces of the throttle body
and the intake manifold.
(2) Install new throttle body-to-intake manifold
gasket.
(3) Install throttle body to intake manifold.
(4) Install four mounting bolts. Tighten bolts to 11
N´m (100 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install control cables.
(6) Install electrical connectors.
(7) Install air duct and air box at throttle body.
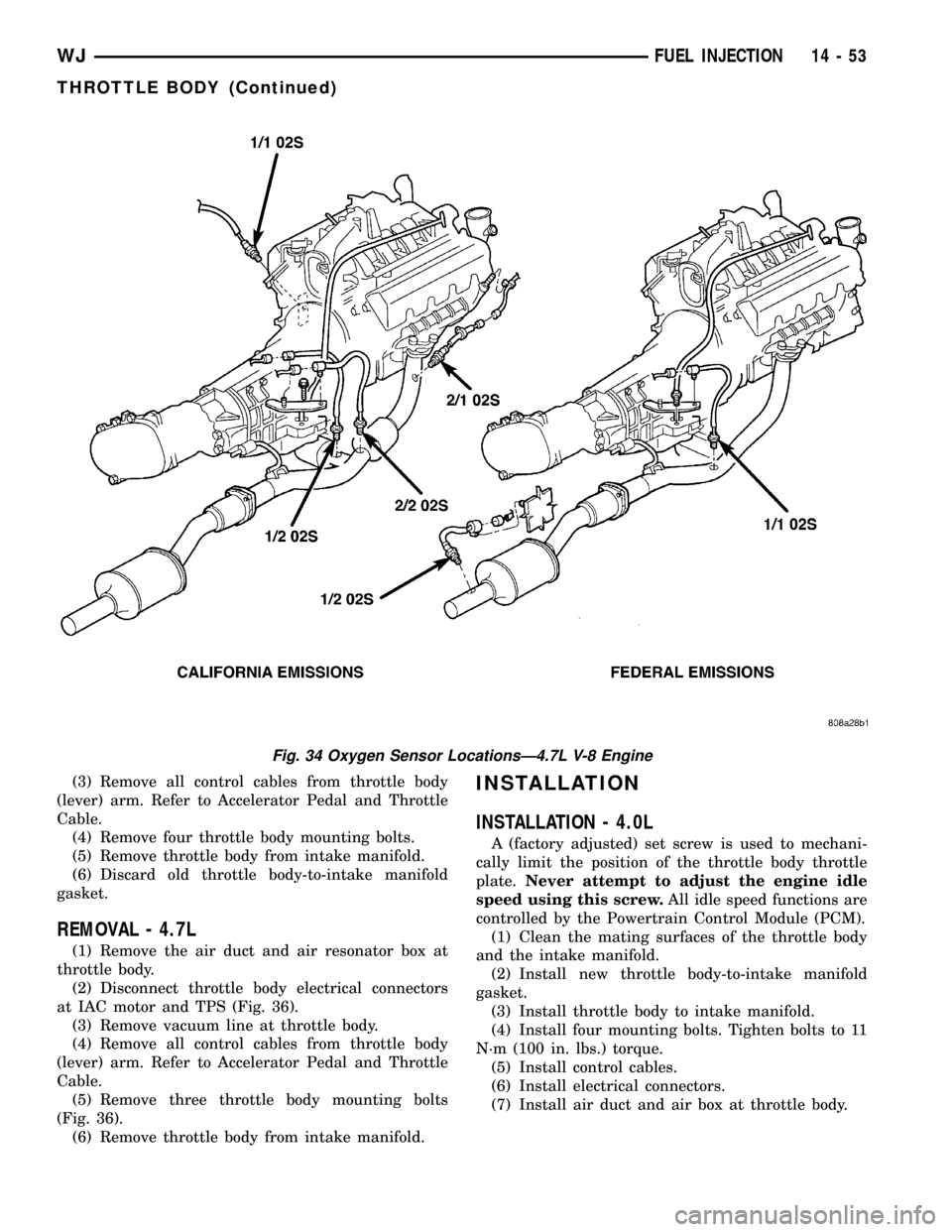
Fig. 34 Oxygen Sensor LocationsÐ4.7L V-8 Engine
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 53
THROTTLE BODY (Continued)
Page 1473 of 2199

INSTALLATION - 4.7L
(1) Clean throttle body-to-intake manifold o-ring.
(2) Clean mating surfaces of throttle body and
intake manifold.
(3) Install throttle body to intake manifold by posi-
tioning throttle body to manifold alignment pins.
(4) Install three mounting bolts. Tighten bolts to
12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install control cables.
(6) Install vacuum line to throttle body.
(7) Install electrical connectors.
(8) Install air duct/air box at throttle body.
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage or kink the
cable core wire (within the cable sheathing) while
servicing accelerator pedal or throttle cable.
(1) From inside vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Remove plastic cable retainer (clip) and throttle cable
core wire from upper end of pedal arm (Fig. 16).
Plastic cable retainer (clip) snaps into pedal arm.
(2) Remove cable core wire at pedal arm.
(3) From inside vehicle, remove clip holding cable
to dashpanel (Fig. 16).
(4) Remove cable housing from dash panel and
pull into engine compartment.
(5) Remove (unsnap) cable from routing clips on
engine valve cover.
(6) Remove cable connector at throttle body
bellcrank ball by unsnapping rearward (Fig. 37).
(7) Remove throttle cable from bracket by com-
pressing release tabs (Fig. 37) and pushing cable
through hole in bracket.
(8) Remove throttle cable from vehicle.
Fig. 35 Throttle Body and Sensor LocationsÐ4.0L
Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - THROTTLE BODY
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
5 - TPS
6 - MAP SENSOR
7 - ELEC. CONN.
8 - IAT SENSOR
9 - ELEC. CONN.
Fig. 36 Throttle Body, Sensors and Electrical
ConnectorsÐ4.7L V-8 Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - THROTTLE BODY
3 - IAT SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - IAC MOTOR CONNECTOR
5 - TPS CONNECTOR
14 - 54 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
THROTTLE BODY (Continued)
Page 2179 of 2199

EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM............................24
DESCRIPTION - CCV SYSTEM...........25
DESCRIPTION - PCV SYSTEM...........25
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L CCV SYSTEM.........26
OPERATION - 4.7L PCV SYSTEM.........26
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - EVAPORATION SYSTEM.......27
CCV HOSE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CCV SYSTEM -
4.0L................................28
REMOVAL - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING........28
INSTALLATION - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING....29
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29REMOVAL.............................29
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................31
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENABLING
CONDITIONS TO RUN EVAP LEAK
DETECTION TEST.....................32
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
ORVR
DESCRIPTION.........................37
OPERATION...........................37
P C V VA LV E
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE/PCV
SYSTEM - 4.7L.......................37
REMOVAL - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.............39
INSTALLATION - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.........39
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION.........................39
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM
The evaporation control system prevents the emis-
sion of fuel tank vapors into the atmosphere. When
fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapors pass
through the control valve, through the fuel manage-
ment valve, and through vent hoses and tubes to a
charcoal filled evaporative canister. The canister tem-
porarily holds the vapors. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) allows intake manifold vacuum todraw vapors into the combustion chambers during
certain operating conditions.
Gas powered engines use a duty cycle purge sys-
tem. The PCM controls vapor flow by operating the
duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid. Refer to Duty Cycle
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid.
When equipped with certain emissions packages, a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) will be used as part of
the evaporative system for OBD II requirements.
Also refer to Leak Detection Pump.
Vehicles powered with gasoline engines are also
equipped with ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor
Recovery). Refer to ORVR for additional information.
25 - 24 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
Page 2181 of 2199

²a PCV valve mounted to the oil filler housing
(Fig. 3). The PCV valve is sealed to the oil filler
housing with an o-ring.
²the air cleaner housing
²two interconnected breathers threaded into the
rear of each cylinder head (Fig. 4).
²tubes and hose to connect the system compo-
nents.
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L CCV SYSTEM
The CCV system performs the same function as a
conventional PCV system, but does not use a vacuum
controlled PCV valve.
The fixed orifice fitting meters the amount of
crankcase vapors drawn out of the engine.
When the engine is operating, fresh air enters the
engine and mixes with crankcase vapors. Engine vac-uum draws the vapor/air mixture through the fixed
orifice and into the intake manifold. The vapors are
then consumed during engine combustion.
OPERATION - 4.7L PCV SYSTEM
The PCV system operates by engine intake mani-
fold vacuum. Filtered air is routed into the crankcase
through the air cleaner hose and crankcase breath-
ers. The metered air, along with crankcase vapors,
are drawn through the PCV valve and into a passage
in the intake manifold. The PCV system manages
crankcase pressure and meters blow-by gases to the
intake system, reducing engine sludge formation.
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
This plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum.
TYPICALPCV valves are shown in (Fig. 5), (Fig.
6) and (Fig. 7).
When the engine is not operating, or during an
engine pop-back, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat (Fig. 5). This will prevent vapors
from flowing through the valve.
Fig. 3 PCV Valve/Oil Filler Tube (Housing)Ð4.7L
Engine
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
Fig. 4 PCV System Hoses/TubesÐ4.7L Engine
1 - FRESH AIR FITTING
2 - CONNECTING TUBES/HOSES
3 - CRANKCASE BREATHERS (2)
4 - RUBBER HOSE
5 - AIR CLEANER RESONATOR
25 - 26 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)