2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Wiring transmission
[x] Cancel search: Wiring transmissionPage 1453 of 2199

(8) Inspect system body grounds for loose or dirty
connections. Refer to Group 8, Wiring for ground
locations.
(9) Verify crankcase ventilation (CCV) operation.
Refer to Emission Control System for additional
information.
(10) Inspect all fuel line quick-connect fittings for
damage or leaks.
(11) Verify hose connections to all ports of vacuum
fittings on intake manifold, and for emission system
are tight and not leaking.
(12) Inspect accelerator cable, transmission throt-
tle cable (if equipped) and speed control cable connec-
tions (if equipped). Check their connections to
throttle body linkage for any binding or restrictions.
(13) Verify vacuum booster hose is firmly con-
nected to fitting on intake manifold. Also check con-
nection to brake vacuum booster.(14) Inspect air cleaner inlet and air cleaner ele-
ment for dirt or restrictions.
(15) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and
air conditioning condenser for restrictions.
(16) 4.0L Engine: Verify MAP, Intake Manifold Air
Temperature (IAT) sensor, TPS and Idle Air Control
(IAC) motor connectors are firmly connected (Fig. 9).
Be sure throttle body mounting bolts (Fig. 9)are
tight.
(17) 4.7L Engine: Verify Intake Manifold Air Tem-
perature (IAT) sensor, TPS and Idle Air Control (IAC)
motor connectors are firmly connected (Fig. 10). Be
sure throttle body mounting bolts (Fig. 10)are tight.
Fig. 8 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.7L V-8 Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2-STARTER
3 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
Fig. 9 IAT, MAP, IAC, TPS Sensor LocationsÐ4.0L
Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - THROTTLE BODY
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
5 - TPS
6 - MAP SENSOR
7 - ELEC. CONN.
8 - IAT SENSOR
9 - ELEC. CONN.
14 - 34 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1460 of 2199

The sensor is a hall effect device combined with an
internal magnet. It is also sensitive to steel within a
certain distance from it.
On 4.0L 6-cylinder engines, the flywheel/drive
plate has 3 sets of four notches at its outer edge (Fig.
19).
The notches cause a pulse to be generated when
they pass under the sensor. The pulses are the input
to the PCM. For each engine revolution there are 3
sets of four pulses generated.
The trailing edge of the fourth notch, which causes
the pulse, is four degrees before top dead center
(TDC) of the corresponding piston.
The engine will not operate if the PCM does not
receive a crankshaft position sensor input.
OPERATION - 4.7L
Engine speed and crankshaft position are provided
through the crankshaft position sensor. The sensor
generates pulses that are the input sent to the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM). The PCM interprets
the sensor input to determine the crankshaft posi-
tion. The PCM then uses this position, along with
other inputs, to determine injector sequence and igni-
tion timing.
The sensor is a hall effect device combined with an
internal magnet. It is also sensitive to steel within a
certain distance from it.On the 4.7L V±8 engine, a tonewheel is bolted to
the engine crankshaft (Fig. 20). This tonewheel has
sets of notches at its outer edge (Fig. 20).
The notches cause a pulse to be generated when
they pass under the sensor. The pulses are the input
to the PCM.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted
to the transmission bellhousing at the left/rear side
of the engine block (Fig. 21). The sensoris adjust-
ableand is attached with one bolt. A wire shield/
router is attached to the sensor (Fig. 21).
(1) Disconnect sensor pigtail harness (3±way con-
nector) from main engine wiring harness.
(2) Remove sensor mounting bolt.
(3) Remove wire shield and sensor.
REMOVAL - 4.7L
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is bolted to
the side of the engine cylinder block above the
starter motor (Fig. 22). It is positioned into a
machined hole at the side of the engine block.
(1) Remove starter motor. Refer to Starter Remov-
al/Installation.
Fig. 19 CKP Sensor OperationÐ4.0L 6-Cyl. Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - FLYWHEEL
3 - FLYWHEEL NOTCHES
Fig. 20 CKP Sensor Operation and TonewheelÐ4.7L
V±8 Engine
1 - TONEWHEEL
2 - NOTCHES
3 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
4 - CRANKSHAFT
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 41
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1489 of 2199
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Steering Column
Steering Wheel Nut61 45 Ð
Steering Column
Column Bracket Nuts12 Ð 105
Steering Column
Shaft Coupler Bolts49 36 Ð
SPECIAL TOOLS
STEERING COLUMN
IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The electrical ignition switch is located on the
steering column. It is used as the main on/off switch-
ing device for most electrical components. The
mechanical key lock cylinder is used to engage/disen-
gage the electrical ignition switch.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - IGNITION SWITCH
ELECTRICAL DIAGNOSIS
For ignition switch electrical schematics, refer to
Ignition Switch in Wiring Diagrams.
MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS (KEY DIFFICULT TO
ROTATE)
Vehicles equipped with an automatic trans-
mission and a floor mounted shifter:a cable is
used to connect the interlock device in the steering
column assembly, to the transmission floor shift
lever. This interlock device is used to lock the trans-
mission shifter in the PARK position when the key
lock cylinder is rotated to the LOCKED or ACCES-
SORY position. The interlock device within the steer-
ing column is not serviceable. If repair is necessary,the steering column assembly must be replaced,(Re-
fer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN - REMOVAL).
If the ignition key is difficult to rotate to or from
the LOCK or ACCESSORY position, it may not be
the fault of the key cylinder or the steering column
components. The brake transmission shift interlock
cable may be out of adjustment,(Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
44RE/SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM - ADJUST-
MENTS) .
Vehicles equipped with an automatic trans-
mission and a steering column mounted shifter:
an interlock device is located within the steering col-
umn. This interlock device is used to lock the trans-
mission shifter in the PARK position when the key
lock cylinder is in the LOCKED or ACCESSORY
position. If it is difficult to rotate the key to or from
the LOCK or ACCESSORY position, the interlock
device within the steering column may be defective.
This device is not serviceable. If repair is necessary,
the steering column assembly must be replaced,(Re-
fer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN - REMOVAL).
Vehicles equipped with a manual transmis-
sion and a floor mounted shifter:on certain mod-
els, a lever is located on the steering column behind
the ignition key lock cylinder. The lever must be
manually operated to allow rotation of the ignition
key lock cylinder to the LOCK or ACCESSORY posi-
tion. If it is difficult to rotate the key to the LOCK or
ACCESSORY position, the lever mechanism may be
defective. This mechanism is not serviceable. If
repair is necessary, the steering column assembly
must be replaced,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/COL-
UMN - REMOVAL).
On other models, the ignition key cylinder must be
depressed to allow it to be rotated into the LOCK or
ACCESSORY position. If it is difficult to rotate the
key to the LOCK or ACCESSORY position, the lock
mechanism within the steering column may be defec-
tive. This mechanism is not serviceable. If repair is
Puller C-3894-A
19 - 12 COLUMNWJ
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1491 of 2199

KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The key-in ignition switch is concealed within and
integral to the ignition switch, which is mounted on
the steering column. The key-in ignition switch is
actuated by the ignition lock cylinder mechanism,
and is hard wired between a body ground and the
Body Control Module (BCM) through the instrument
panel wire harness.
The key-in ignition switch cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the entire igni-
tion switch unit must be replaced,(Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
- REMOVAL). For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
Body Control Modulein the Contents of Wiring
Diagrams.
OPERATION
The key-in ignition switch closes a path to ground
for the BCM when the ignition key is inserted in the
ignition lock cylinder, and opens the ground path
when the key is removed from the ignition lock cyl-
inder. The BCM monitors the key-in ignition switch
status through an internal pull-up, then sends the
proper switch status messages to other electronic
modules over the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus network. The key-in ignition
switch status is also used by the BCM as an input
for chime warning system operation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toBody Con-
trol Modulein the Contents of Wiring Diagrams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO GROUP 8M - PASSIVE
RESTRAINT SYSTEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector from the key-in ignition switch connector
receptacle on the ignition switch. Check for continu-
ity between the key-in ignition switch sense and
ground terminals of the key-in ignition switch con-
nector receptacle. There should be continuity with
the key inserted in the ignition lock cylinder, and no
continuity with the key removed from the ignition
lock cylinder. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, replace
the faulty ignition switch unit.
(2) Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit cavity of the instrument panel wire harness con-
nector for the key-in ignition switch and a good
ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(3) Disconnect the gray 26-way instrument panel
wire harness connector from the Body Control Mod-
ule (BCM) connector receptacle. Check for continuity
between the key-in ignition switch sense circuit cav-
ity of the instrument panel wire harness connector
for the key-in ignition switch and a good ground.
There should be no continuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair the shorted key-in ignition switch
sense circuit as required.
(4) Check for continuity between the key-in igni-
tion switch sense circuit cavities of the instrument
panel wire harness connector for the key-in ignition
switch and the gray 26-way instrument panel wire
harness connector for the BCM. There should be con-
tinuity. If OK, use a DRB scan tool and the proper
Diagnostic Procedures manual to test the BCM. If
not OK, repair the open key-in ignition switch sense
circuit as required.
LOCK CYLINDER
REMOVAL
The ignition key must be in the key cylinder for
cylinder removal. The key cylinder must be removed
first before removing ignition switch.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) If equipped with an automatic transmission,
place shifter in PARK position.
(3) Rotate key to ON position.
19 - 14 COLUMNWJ
Page 1531 of 2199
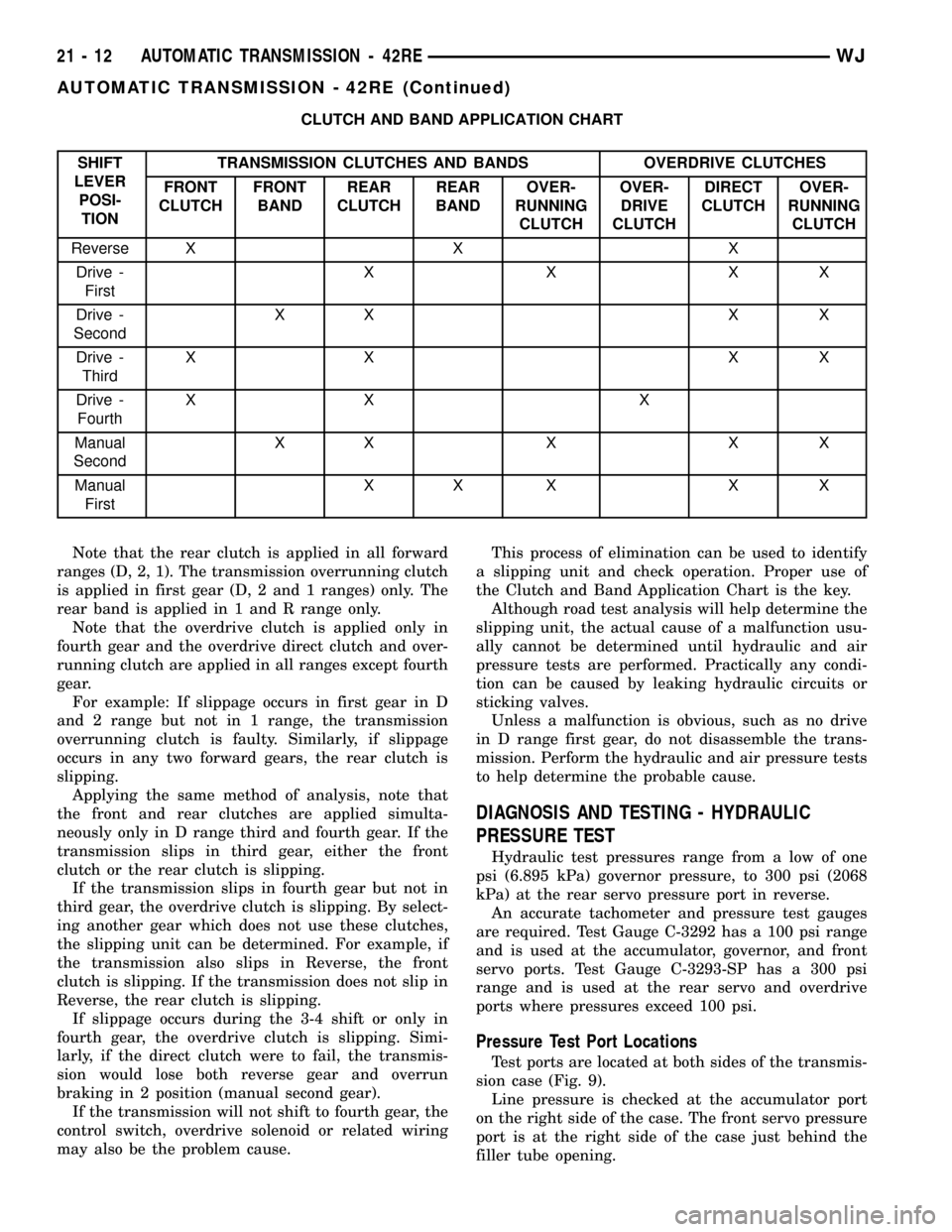
CLUTCH AND BAND APPLICATION CHART
SHIFT
LEVER
POSI-
TIONTRANSMISSION CLUTCHES AND BANDS OVERDRIVE CLUTCHES
FRONT
CLUTCHFRONT
BANDREAR
CLUTCHREAR
BANDOVER-
RUNNING
CLUTCHOVER-
DRIVE
CLUTCHDIRECT
CLUTCHOVER-
RUNNING
CLUTCH
Reverse X X X
Drive -
FirstXXXX
Drive -
SecondXX X X
Drive -
ThirdXX XX
Drive -
FourthXX X
Manual
SecondXXXXX
Manual
FirstXX X X X
Note that the rear clutch is applied in all forward
ranges (D, 2, 1). The transmission overrunning clutch
is applied in first gear (D, 2 and 1 ranges) only. The
rear band is applied in 1 and R range only.
Note that the overdrive clutch is applied only in
fourth gear and the overdrive direct clutch and over-
running clutch are applied in all ranges except fourth
gear.
For example: If slippage occurs in first gear in D
and 2 range but not in 1 range, the transmission
overrunning clutch is faulty. Similarly, if slippage
occurs in any two forward gears, the rear clutch is
slipping.
Applying the same method of analysis, note that
the front and rear clutches are applied simulta-
neously only in D range third and fourth gear. If the
transmission slips in third gear, either the front
clutch or the rear clutch is slipping.
If the transmission slips in fourth gear but not in
third gear, the overdrive clutch is slipping. By select-
ing another gear which does not use these clutches,
the slipping unit can be determined. For example, if
the transmission also slips in Reverse, the front
clutch is slipping. If the transmission does not slip in
Reverse, the rear clutch is slipping.
If slippage occurs during the 3-4 shift or only in
fourth gear, the overdrive clutch is slipping. Simi-
larly, if the direct clutch were to fail, the transmis-
sion would lose both reverse gear and overrun
braking in 2 position (manual second gear).
If the transmission will not shift to fourth gear, the
control switch, overdrive solenoid or related wiring
may also be the problem cause.This process of elimination can be used to identify
a slipping unit and check operation. Proper use of
the Clutch and Band Application Chart is the key.
Although road test analysis will help determine the
slipping unit, the actual cause of a malfunction usu-
ally cannot be determined until hydraulic and air
pressure tests are performed. Practically any condi-
tion can be caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or
sticking valves.
Unless a malfunction is obvious, such as no drive
in D range first gear, do not disassemble the trans-
mission. Perform the hydraulic and air pressure tests
to help determine the probable cause.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST
Hydraulic test pressures range from a low of one
psi (6.895 kPa) governor pressure, to 300 psi (2068
kPa) at the rear servo pressure port in reverse.
An accurate tachometer and pressure test gauges
are required. Test Gauge C-3292 has a 100 psi range
and is used at the accumulator, governor, and front
servo ports. Test Gauge C-3293-SP has a 300 psi
range and is used at the rear servo and overdrive
ports where pressures exceed 100 psi.
Pressure Test Port Locations
Test ports are located at both sides of the transmis-
sion case (Fig. 9).
Line pressure is checked at the accumulator port
on the right side of the case. The front servo pressure
port is at the right side of the case just behind the
filler tube opening.
21 - 12 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1541 of 2199
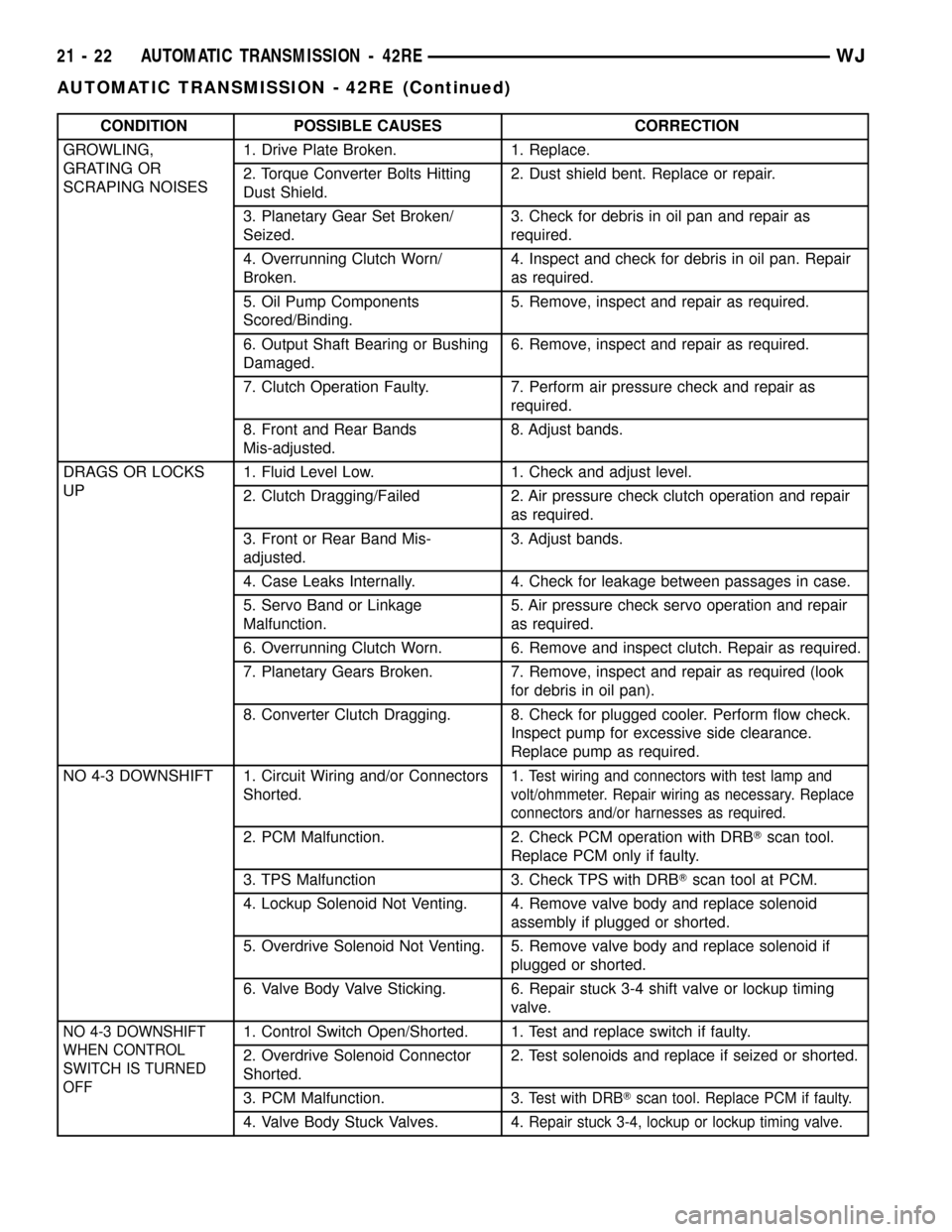
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
GROWLING,
GRATING OR
SCRAPING NOISES1. Drive Plate Broken. 1. Replace.
2. Torque Converter Bolts Hitting
Dust Shield.2. Dust shield bent. Replace or repair.
3. Planetary Gear Set Broken/
Seized.3. Check for debris in oil pan and repair as
required.
4. Overrunning Clutch Worn/
Broken.4. Inspect and check for debris in oil pan. Repair
as required.
5. Oil Pump Components
Scored/Binding.5. Remove, inspect and repair as required.
6. Output Shaft Bearing or Bushing
Damaged.6. Remove, inspect and repair as required.
7. Clutch Operation Faulty. 7. Perform air pressure check and repair as
required.
8. Front and Rear Bands
Mis-adjusted.8. Adjust bands.
DRAGS OR LOCKS
UP1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Check and adjust level.
2. Clutch Dragging/Failed 2. Air pressure check clutch operation and repair
as required.
3. Front or Rear Band Mis-
adjusted.3. Adjust bands.
4. Case Leaks Internally. 4. Check for leakage between passages in case.
5. Servo Band or Linkage
Malfunction.5. Air pressure check servo operation and repair
as required.
6. Overrunning Clutch Worn. 6. Remove and inspect clutch. Repair as required.
7. Planetary Gears Broken. 7. Remove, inspect and repair as required (look
for debris in oil pan).
8. Converter Clutch Dragging. 8. Check for plugged cooler. Perform flow check.
Inspect pump for excessive side clearance.
Replace pump as required.
NO 4-3 DOWNSHIFT 1. Circuit Wiring and/or Connectors
Shorted.1.
Test wiring and connectors with test lamp and
volt/ohmmeter. Repair wiring as necessary. Replace
connectors and/or harnesses as required.
2. PCM Malfunction. 2. Check PCM operation with DRBTscan tool.
Replace PCM only if faulty.
3. TPS Malfunction 3. Check TPS with DRBTscan tool at PCM.
4. Lockup Solenoid Not Venting. 4. Remove valve body and replace solenoid
assembly if plugged or shorted.
5. Overdrive Solenoid Not Venting. 5. Remove valve body and replace solenoid if
plugged or shorted.
6. Valve Body Valve Sticking. 6. Repair stuck 3-4 shift valve or lockup timing
valve.
NO 4-3 DOWNSHIFT
WHEN CONTROL
SWITCH IS TURNED
OFF1. Control Switch Open/Shorted. 1. Test and replace switch if faulty.
2. Overdrive Solenoid Connector
Shorted.2. Test solenoids and replace if seized or shorted.
3. PCM Malfunction. 3.
Test with DRBTscan tool. Replace PCM if faulty.
4. Valve Body Stuck Valves. 4.Repair stuck 3-4, lockup or lockup timing valve.
21 - 22 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1542 of 2199
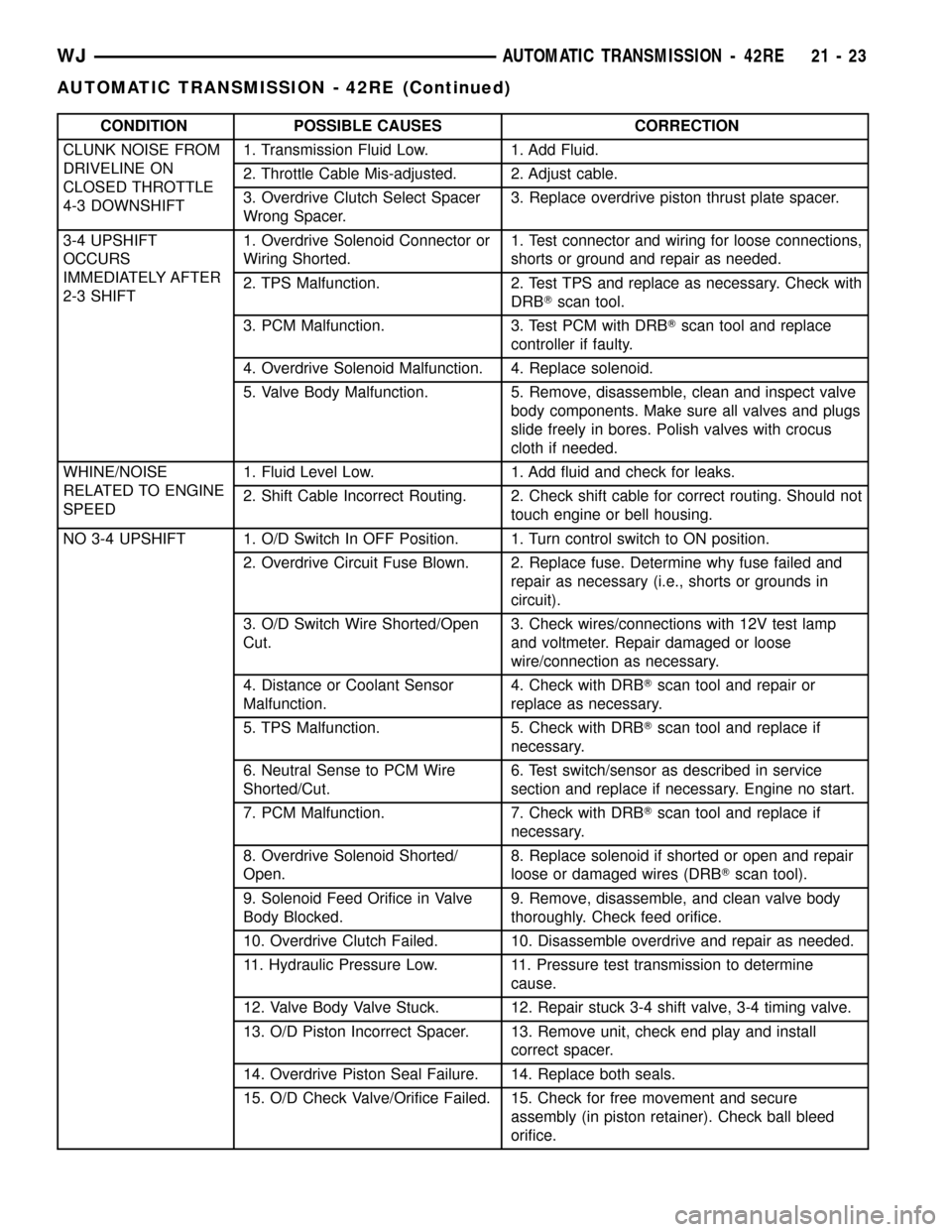
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUNK NOISE FROM
DRIVELINE ON
CLOSED THROTTLE
4-3 DOWNSHIFT1. Transmission Fluid Low. 1. Add Fluid.
2. Throttle Cable Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust cable.
3. Overdrive Clutch Select Spacer
Wrong Spacer.3. Replace overdrive piston thrust plate spacer.
3-4 UPSHIFT
OCCURS
IMMEDIATELY AFTER
2-3 SHIFT1. Overdrive Solenoid Connector or
Wiring Shorted.1.
Test connector and wiring for loose connections,
shorts or ground and repair as needed.
2. TPS Malfunction. 2. Test TPS and replace as necessary. Check with
DRBTscan tool.
3. PCM Malfunction. 3. Test PCM with DRBTscan tool and replace
controller if faulty.
4. Overdrive Solenoid Malfunction. 4. Replace solenoid.
5. Valve Body Malfunction. 5. Remove, disassemble, clean and inspect valve
body components. Make sure all valves and plugs
slide freely in bores. Polish valves with crocus
cloth if needed.
WHINE/NOISE
RELATED TO ENGINE
SPEED1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Incorrect Routing. 2. Check shift cable for correct routing. Should not
touch engine or bell housing.
NO 3-4 UPSHIFT 1. O/D Switch In OFF Position. 1. Turn control switch to ON position.
2. Overdrive Circuit Fuse Blown. 2. Replace fuse. Determine why fuse failed and
repair as necessary (i.e., shorts or grounds in
circuit).
3. O/D Switch Wire Shorted/Open
Cut.3. Check wires/connections with 12V test lamp
and voltmeter. Repair damaged or loose
wire/connection as necessary.
4. Distance or Coolant Sensor
Malfunction.4. Check with DRBTscan tool and repair or
replace as necessary.
5. TPS Malfunction. 5. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace if
necessary.
6. Neutral Sense to PCM Wire
Shorted/Cut.6. Test switch/sensor as described in service
section and replace if necessary. Engine no start.
7. PCM Malfunction. 7. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace if
necessary.
8. Overdrive Solenoid Shorted/
Open.8. Replace solenoid if shorted or open and repair
loose or damaged wires (DRBTscan tool).
9. Solenoid Feed Orifice in Valve
Body Blocked.9. Remove, disassemble, and clean valve body
thoroughly. Check feed orifice.
10. Overdrive Clutch Failed. 10. Disassemble overdrive and repair as needed.
11. Hydraulic Pressure Low. 11. Pressure test transmission to determine
cause.
12. Valve Body Valve Stuck. 12. Repair stuck 3-4 shift valve, 3-4 timing valve.
13. O/D Piston Incorrect Spacer. 13. Remove unit, check end play and install
correct spacer.
14. Overdrive Piston Seal Failure. 14. Replace both seals.
15. O/D Check Valve/Orifice Failed. 15. Check for free movement and secure
assembly (in piston retainer). Check ball bleed
orifice.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 23
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1543 of 2199
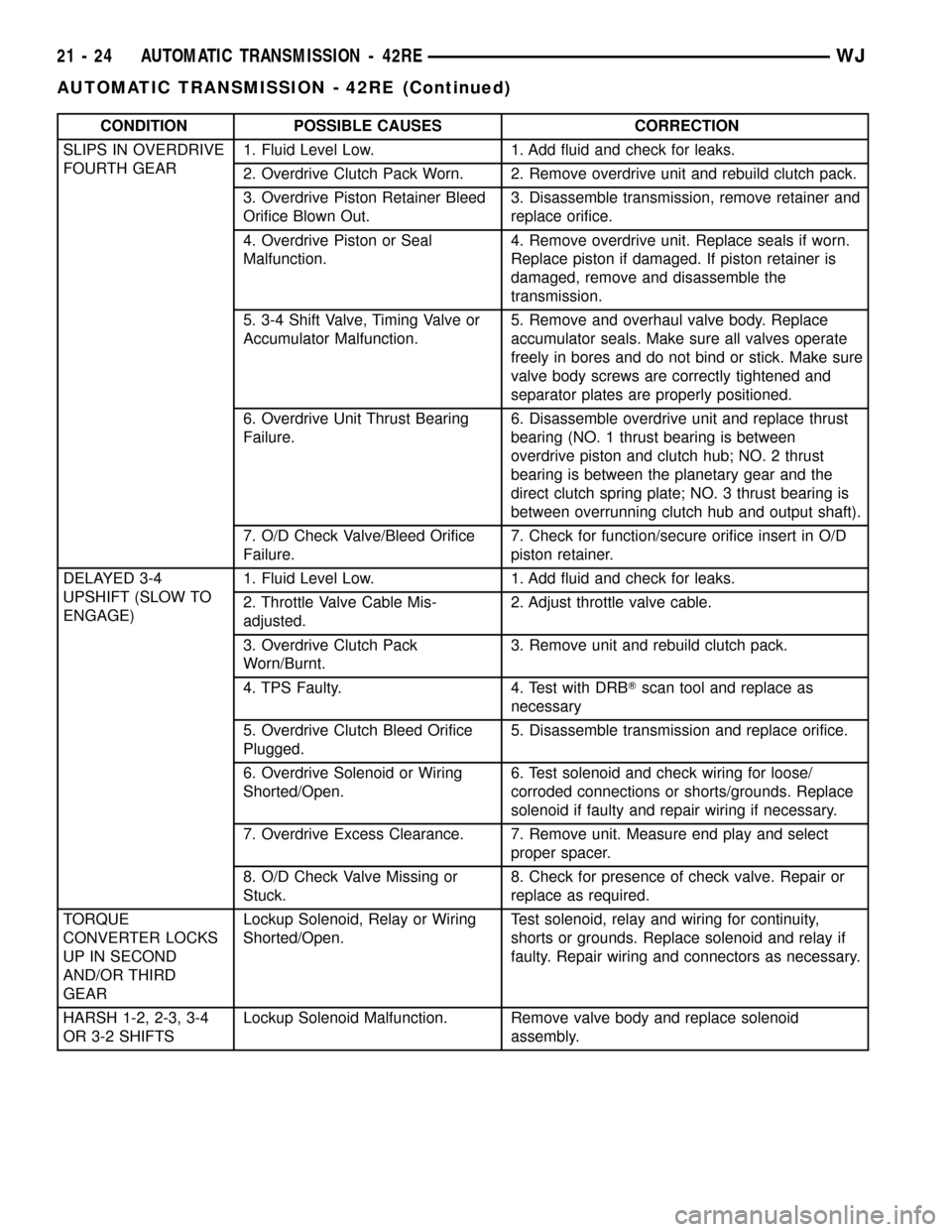
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SLIPS IN OVERDRIVE
FOURTH GEAR1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Overdrive Clutch Pack Worn. 2. Remove overdrive unit and rebuild clutch pack.
3. Overdrive Piston Retainer Bleed
Orifice Blown Out.3. Disassemble transmission, remove retainer and
replace orifice.
4. Overdrive Piston or Seal
Malfunction.4. Remove overdrive unit. Replace seals if worn.
Replace piston if damaged. If piston retainer is
damaged, remove and disassemble the
transmission.
5. 3-4 Shift Valve, Timing Valve or
Accumulator Malfunction.5. Remove and overhaul valve body. Replace
accumulator seals. Make sure all valves operate
freely in bores and do not bind or stick. Make sure
valve body screws are correctly tightened and
separator plates are properly positioned.
6. Overdrive Unit Thrust Bearing
Failure.6. Disassemble overdrive unit and replace thrust
bearing (NO. 1 thrust bearing is between
overdrive piston and clutch hub; NO. 2 thrust
bearing is between the planetary gear and the
direct clutch spring plate; NO. 3 thrust bearing is
between overrunning clutch hub and output shaft).
7. O/D Check Valve/Bleed Orifice
Failure.7. Check for function/secure orifice insert in O/D
piston retainer.
DELAYED 3-4
UPSHIFT (SLOW TO
ENGAGE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Throttle Valve Cable Mis-
adjusted.2. Adjust throttle valve cable.
3. Overdrive Clutch Pack
Worn/Burnt.3. Remove unit and rebuild clutch pack.
4. TPS Faulty. 4. Test with DRBTscan tool and replace as
necessary
5. Overdrive Clutch Bleed Orifice
Plugged.5. Disassemble transmission and replace orifice.
6. Overdrive Solenoid or Wiring
Shorted/Open.6. Test solenoid and check wiring for loose/
corroded connections or shorts/grounds. Replace
solenoid if faulty and repair wiring if necessary.
7. Overdrive Excess Clearance. 7. Remove unit. Measure end play and select
proper spacer.
8. O/D Check Valve Missing or
Stuck.8. Check for presence of check valve. Repair or
replace as required.
TORQUE
CONVERTER LOCKS
UP IN SECOND
AND/OR THIRD
GEARLockup Solenoid, Relay or Wiring
Shorted/Open.Test solenoid, relay and wiring for continuity,
shorts or grounds. Replace solenoid and relay if
faulty. Repair wiring and connectors as necessary.
HARSH 1-2, 2-3, 3-4
OR 3-2 SHIFTSLockup Solenoid Malfunction. Remove valve body and replace solenoid
assembly.
21 - 24 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)