2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE radiator cap
[x] Cancel search: radiator capPage 393 of 2199

(6) Remove both horns and the mounting bracket
from the right extension of the radiator closure
assembly as a unit.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position both horns and the mounting bracket
onto the right extension of the radiator closure
assembly as a unit.
(2) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
horn mounting bracket to the right extension of the
radiator closure assembly. Tighten the screw to 11.3
N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(3) Reconnect the two right headlamp and dash
wire harness connectors to the horn connector recep-
tacles. Be certain to engage the connector lock tabs
after reconnecting them to the horn connector recep-
tacles.
(4) Install the lower front half of the inner liner to
the right front fender wheel house. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT FENDER - INSTALLA-
TION) for the procedure.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
HORN RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The horn relay is a electromechanical device that
switches battery current to the horn when the horn
switch grounds the relay coil. The horn relay is
located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) inthe engine compartment. If a problem is encountered
with a continuously sounding horn, it can usually be
quickly resolved by removing the horn relay from the
PDC until further diagnosis is completed. See the
fuse and relay layout label affixed to the inside sur-
face of the PDC cover for horn relay identification
and location.
The horn relay is a International Standards Orga-
nization (ISO) micro-relay. Relays conforming to the
ISO specifications have common physical dimensions,
current capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal
functions. The ISO micro-relay terminal functions
are the same as a conventional ISO relay. However,
the ISO micro-relay terminal pattern (or footprint) is
different, the current capacity is lower, and the phys-
ical dimensions are smaller than those of the conven-
tional ISO relay.
The horn relay cannot be repaired or adjusted and,
if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the
relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are
produced when the coil is de-energized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN RELAY
The horn relay (Fig. 2) is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) between the battery and the
right inner fender shield on the passenger side of the
engine compartment. If a problem is encountered
with a continuously sounding horn, it can usually be
quickly resolved by removing the horn relay from the
PDC until further diagnosis is completed. See the
fuse and relay layout label affixed to the inside sur-
face of the PDC cover for horn relay identification
and location. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
the appropriate wiring information. The wiring infor-
mation includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and
connector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
Fig. 1 Horns Remove/Install
1 - RADIATOR CLOSURE ASSEMBLY
2 - HORNS AND MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - RIGHT HEADLAMP AND DASH WIRE HARNESS
CONNECTORS
8H - 4 HORNWJ
HORN (Continued)
Page 547 of 2199

The ACM microprocessor continuously monitors all
of the supplemental restraint system electrical cir-
cuits to determine the system readiness. If the ACM
detects a monitored system fault, it sets an active
and stored Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and sends
electronic messages to the EMIC over the PCI data
bus to turn on the airbag indicator. An active fault
only remains for the duration of the fault or in some
cases the duration of the current ignition switch
cycle, while a stored fault causes a DTC to be stored
in memory by the ACM. For some DTCs, if a fault
does not recur for a number of ignition cycles, the
ACM will automatically erase the stored DTC. For
other internal faults, the stored DTC is latched for-
ever.
The ACM receives battery current through two cir-
cuits, on a fused ignition switch output (run) circuit
through a fuse in the Junction Block (JB), and on a
fused ignition switch output (start-run) circuit
through a second fuse in the JB. The ACM is
grounded through a ground circuit and take out of
the instrument panel floor wire harness. This take
out has a single eyelet terminal connector secured by
a nut to a ground stud located behind the ACM
mount on the floor panel transmission tunnel. These
connections allow the ACM to be operational when-
ever the ignition switch is in the Start or On posi-
tions. The ACM also contains an energy-storage
capacitor. When the ignition switch is in the Start or
On positions, this capacitor is continually being
charged with enough electrical energy to deploy the
airbags for up to one second following a battery dis-
connect or failure. The purpose of the capacitor is to
provide backup supplemental restraint system pro-
tection in case there is a loss of battery current sup-
ply to the ACM during an impact.
Two sensors are contained within the ACM, an
electronic impact sensor and a safing sensor. The
ACM also monitors inputs from two remote front
impact sensors located on brackets on the inboard
sides of the right and left vertical members of the
radiator support near the front of the vehicle. The
electronic impact sensors are accelerometers that
sense the rate of vehicle deceleration, which provide
verification of the direction and severity of an
impact. On models equipped with optional side cur-
tain airbags, the ACM also monitors inputs from two
remote side impact sensors located near the base of
both the left and right inner B-pillars to control the
deployment of the side curtain airbag units.
The safing sensor is an electronic accelerometer
sensor within the ACM that provides an additional
logic input to the ACM microprocessor. The safingsensor is used to verify the need for an airbag
deployment by detecting impact energy of a lesser
magnitude than that of the primary electronic impact
sensors, and must exceed a safing threshold in order
for the airbags to deploy. The ACM also monitors a
Hall effect-type seat belt switch located in the buckle
of each front seat belt to determine whether the seat-
belts are buckled, and provides an input to the EMIC
over the PCI data bus to control the seatbelt indica-
tor operation based upon the status of the driver side
front seat belt switch. Vehicles with the optional side
curtain airbags feature a second safing sensor within
the ACM to provide confirmation to the ACM of side
impact forces. This second safing sensor is a bi-direc-
tional unit that detects impact forces from either side
of the vehicle.
Pre-programmed decision algorithms in the ACM
microprocessor determine when the deceleration rate
as signaled by the impact sensors and the safing sen-
sors indicate an impact that is severe enough to
require supplemental restraint system protection.
The ACM also determines the level of front airbag
deployment force required for each front seating posi-
tion based upon the status of the two seat belt switch
inputs and the severity of the monitored impact.
When the programmed conditions are met, the ACM
sends the proper electrical signals to deploy the mul-
tistage dual front airbags at the programmed force
levels, and to deploy either side curtain airbag.
The hard wired inputs and outputs for the ACM
may be diagnosed and tested using conventional
diagnostic tools and procedures. However, conven-
tional diagnostic methods will not prove conclusive in
the diagnosis of the ACM, the PCI data bus network,
or the electronic message inputs to and outputs from
the ACM. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate
means to diagnose the ACM, the PCI data bus net-
work, and the electronic message inputs to and out-
puts from the ACM requires the use of a DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
REMOVAL
Two different Airbag Control Modules (ACM) are
available for this vehicle. For vehicles equipped with
the optional side curtain airbags, both ACM connec-
tor receptacles are black in color and the ACM con-
tains a second bi-directional safing sensor for the
side airbags. For vehicles not equipped with the
optional side curtain airbags, the ACM connector
receptacles are gray.
8O - 10 RESTRAINTSWJ
AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 561 of 2199

OPERATION
The front impact sensors are electronic accelerom-
eters that sense the rate of vehicle deceleration,
which provides verification of the direction and sever-
ity of an impact. Each sensor also contains an elec-
tronic communication chip that allows the unit to
communicate the sensor status as well as sensor
fault information to the microprocessor in the Airbag
Control Module (ACM). The ACM microprocessor con-
tinuously monitors all of the passive restraint system
electrical circuits to determine the system readiness.
If the ACM detects a monitored system fault, it sets
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and controls the
airbag indicator operation accordingly.
The impact sensors each receive battery current
and ground through dedicated left and right sensor
plus and minus circuits from the ACM. The impact
sensors and the ACM communicate by modulating
the voltage in the sensor plus circuit. The hard wired
circuits between the front impact sensors and the
ACM may be diagnosed and tested using conven-
tional diagnostic tools and procedures. However, con-
ventional diagnostic methods will not prove
conclusive in the diagnosis of the ACM or the impact
sensors. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate
means to diagnose the impact sensors, the ACM, and
the electronic message communication between the
sensors and the ACM requires the use of a DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
REMOVAL
The front and side impact sensors are interchange-
able except that the front impact sensors are serviced
with a right or left mounting bracket, while the side
impact sensors use no mounting bracket. If a front
impact sensor is faulty, but not damaged, the sensor
may be removed from the sensor mounting bracket
and replaced with a side impact sensor. If the front
impact sensor or the sensor mounting bracket are
damaged in any way, or if proper tightening torque of
the screws that secure the sensor to the bracket can-
not be achieved, the front impact sensor and bracket
must be replaced as a unit.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, FRONT IMPACT SENSOR,
SIDE IMPACT SENSOR, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BAT-
TERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT
TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO
DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHERDIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE
WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
WARNING: THE FRONT IMPACT SENSOR ENABLES
THE SYSTEM TO DEPLOY THE FRONT SUPPLE-
MENTAL RESTRAINTS. NEVER STRIKE OR DROP
THE FRONT IMPACT SENSOR, AS IT CAN DAMAGE
THE IMPACT SENSOR OR AFFECT ITS CALIBRA-
TION. IF AN IMPACT SENSOR IS ACCIDENTALLY
DROPPED DURING SERVICE, THE SENSOR MUST
BE SCRAPPED AND REPLACED WITH A NEW UNIT.
FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS WARNING COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL, INCOMPLETE, OR
IMPROPER FRONT SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE OCCUPANT INJU-
RIES.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Wait two minutes for the system capacitor to
discharge before further service.
(2) From the engine compartment, disconnect the
right or left headlamp and dash wire harness connec-
tor for the front impact sensor from the sensor con-
nector receptacle (Fig. 25).
Fig. 25 Front Impact Sensor Remove/Install (Right
Side Shown, Left Side Similar)
1 - BRACKET
2 - IMPACT SENSOR
3 - RADIATOR SUPPORT
4 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
5 - SCREW (2)
8O - 24 RESTRAINTSWJ
FRONT IMPACT SENSOR (Continued)
Page 562 of 2199

(3) From the engine compartment, remove the two
screws that secure the right or left front impact sen-
sor to the sensor mounting bracket on the right or
left radiator support vertical member.
(4) Remove the front impact sensor from the sen-
sor mounting bracket.
INSTALLATION
The front and side impact sensors are interchange-
able except that the front impact sensors are serviced
with a right or left mounting bracket, while the side
impact sensors use no mounting bracket. If a front
impact sensor is faulty, but not damaged, the sensor
may be removed from the sensor mounting bracket
and replaced with a side impact sensor. If the front
impact sensor or the sensor mounting bracket are
damaged in any way, or if proper tightening torque of
the screws that secure the sensor to the bracket can-
not be achieved, the front impact sensor and bracket
must be replaced as a unit.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, FRONT IMPACT SENSOR,
SIDE IMPACT SENSOR, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BAT-
TERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT
TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO
DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE
WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
WARNING: THE FRONT IMPACT SENSOR ENABLES
THE SYSTEM TO DEPLOY THE FRONT SUPPLE-
MENTAL RESTRAINTS. NEVER STRIKE OR DROP
THE FRONT IMPACT SENSOR, AS IT CAN DAMAGE
THE IMPACT SENSOR OR AFFECT ITS CALIBRA-
TION. IF AN IMPACT SENSOR IS ACCIDENTALLY
DROPPED DURING SERVICE, THE SENSOR MUST
BE SCRAPPED AND REPLACED WITH A NEW UNIT.
FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS WARNING COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL, INCOMPLETE, OR
IMPROPER FRONT SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE OCCUPANT INJU-
RIES.(1) Position the right or left front impact sensor to
the sensor mounting bracket on the right or left radi-
ator support vertical member in the engine compart-
ment (Fig. 25).
(2) Install and tighten the two screws that secure
the right or left front impact sensor to the sensor
mounting bracket. Tighten the screws to 10 N´m (85
in. lbs.).
(3) Reconnect the right or left headlamp and dash
wire harness connector for the front impact sensor to
the sensor connector receptacle.
(4) Do not reconnect the battery negative cable at
this time. The supplemental restraint system verifi-
cation test procedure should be performed following
service of any supplemental restraint system compo-
nent. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VERIFICATION TEST).
FRONT IMPACT SENSOR &
BRACKET
REMOVAL
The front and side impact sensors are interchange-
able except that the front impact sensors are serviced
with a right or left mounting bracket, while the side
impact sensors use no mounting bracket. If a front
impact sensor is faulty, but not damaged, the sensor
may be removed from the sensor mounting bracket
and replaced with a side impact sensor. If the front
impact sensor or the sensor mounting bracket are
damaged in any way, or if proper tightening torque of
the screws that secure the sensor to the bracket can-
not be achieved, the front impact sensor and bracket
must be replaced as a unit.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, FRONT IMPACT SENSOR,
SIDE IMPACT SENSOR, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BAT-
TERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT
TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO
DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE
WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
WJRESTRAINTS 8O - 25
FRONT IMPACT SENSOR (Continued)
Page 563 of 2199

WARNING: THE FRONT IMPACT SENSOR ENABLES
THE SYSTEM TO DEPLOY THE FRONT SUPPLE-
MENTAL RESTRAINTS. NEVER STRIKE OR DROP
THE FRONT IMPACT SENSOR, AS IT CAN DAMAGE
THE IMPACT SENSOR OR AFFECT ITS CALIBRA-
TION. IF AN IMPACT SENSOR IS ACCIDENTALLY
DROPPED DURING SERVICE, THE SENSOR MUST
BE SCRAPPED AND REPLACED WITH A NEW UNIT.
FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS WARNING COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL, INCOMPLETE, OR
IMPROPER FRONT SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE OCCUPANT INJU-
RIES.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Wait two minutes for the system capacitor to
discharge before further service.
(2) Remove the headlamp mounting module from
the front of the vehicle. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTE-
RIOR/HEADLAMP MOUNTING MODULE -
REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the right or left headlamp and dash
wire harness connector for the front impact sensor
from the sensor connector receptacle.
(4) Remove the three screws that secure the right
or left front impact sensor and bracket unit to the
right or left radiator support vertical member (Fig.
26).
(5) Remove the right or left front impact sensor
and bracket unit from the front of the vehicle.INSTALLATION
The front and side impact sensors are interchange-
able except that the front impact sensors are serviced
with a right or left mounting bracket, while the side
impact sensors use no mounting bracket. If a front
impact sensor is faulty, but not damaged, the sensor
may be removed from the sensor mounting bracket
and replaced with a side impact sensor. If the front
impact sensor or the sensor mounting bracket are
damaged in any way, or if proper tightening torque of
the screws that secure the sensor to the bracket can-
not be achieved, the front impact sensor and bracket
must be replaced as a unit.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, FRONT IMPACT SENSOR,
SIDE IMPACT SENSOR, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BAT-
TERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT
TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO
DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE
WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
WARNING: THE FRONT IMPACT SENSOR ENABLES
THE SYSTEM TO DEPLOY THE FRONT SUPPLE-
MENTAL RESTRAINTS. NEVER STRIKE OR DROP
THE FRONT IMPACT SENSOR, AS IT CAN DAMAGE
THE IMPACT SENSOR OR AFFECT ITS CALIBRA-
TION. IF AN IMPACT SENSOR IS ACCIDENTALLY
DROPPED DURING SERVICE, THE SENSOR MUST
BE SCRAPPED AND REPLACED WITH A NEW UNIT.
FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS WARNING COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL, INCOMPLETE, OR
IMPROPER FRONT SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE OCCUPANT INJU-
RIES.
(1) Position the right or left front impact sensor
and bracket unit to the front of the vehicle (Fig. 26).
(2) Position the right or left front impact sensor
and bracket unit to the right or left radiator support
vertical member.
(3) Loosely install the three screws that secure the
right or left front impact sensor and bracket unit
right or left radiator support vertical member.
Fig. 26 Front Impact Sensor & B Remove/Install
1 - RADIATOR SUPPORT
2 - SCREW (3)
3 - BRACKET
4 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
5 - IMPACT SENSOR
8O - 26 RESTRAINTSWJ
FRONT IMPACT SENSOR & BRACKET (Continued)
Page 1251 of 2199
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise, the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
REMOVAL).
(3) Secure the throttle in the wide-open position.
(4) Disconnect the ignition coil.
(5) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(6) Record the compression pressure on the third
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the
correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing)
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM HOT COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn OFF the
engine.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
Perform the test procedure on each cylinder accord-
ing to the tester manufacturer's instructions. While
testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through
the throttle body, tailpipe or oil filler cap opening.
Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART .
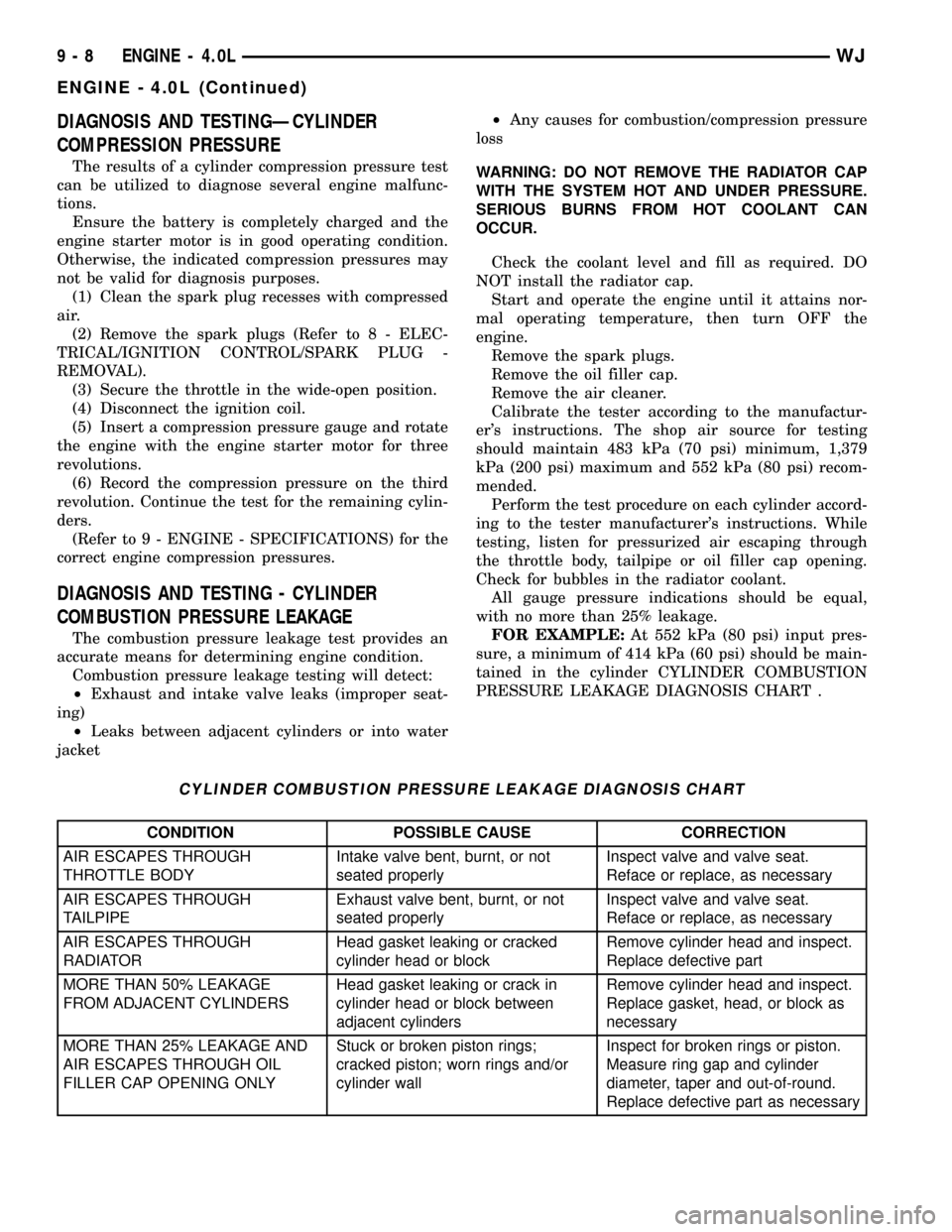
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLYStuck or broken piston rings;
cracked piston; worn rings and/or
cylinder wallInspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
9 - 8 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1254 of 2199

CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 40É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 3).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 4).CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Mark the hinge locations on the hood panel for
alignment reference during installation. Remove the
engine compartment lamp. Remove the hood.
(3) Remove the radiator drain cock and radiator
cap to drain the coolant. DO NOT waste usable cool-
ant. If the solution is clean, drain the coolant into a
clean container for reuse.
(4) Remove the upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose.
(5) Remove the lower radiator hose.
(6) Remove upper radiator support retaining bolts
and remove radiator support.
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
Fig. 4 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 11
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1255 of 2199

(7) Remove the fan assembly from the water pump
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the fan shroud.
(9) Disconnect the transmission fluid cooler lines
(automatic transmission).
(10) Discharge the A/C system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Remove the service valves and cap the com-
pressor ports.
(12) Remove the radiator or radiator/condenser (if
equipped with A/C).
(13) Disconnect the heater hoses at the engine
thermostat housing and water pump.
(14) Disconnect the accelerator cable, transmission
line pressure cable and speed control cable (if
equipped) from the throttle body.
(15) Remove cables from the bracket and secure
out of the way.
(16) Disconnect the body ground at the engine.
(17) Disconnect the following connectors and
secure their harness out of the way.
²Power steering pressure switch
²Coolant temperature sensor
²Six (6) fuel injector connectors
²Intake air temperature sensor
²Throttle position sensor
²Map sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Oxygen sensor
²Camshaft position sensor
²Generator connector and B+ terminal wire
(18) Disconnect the coil rail electrical connections
and the oil pressure switch connector.
(19) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(20) Disconnect the fuel supply line at the injector
rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/
QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(21) Remove the fuel line bracket from the intake
manifold.
(22) Remove the air cleaner assembly (Fig. 5).
(23) Disconnect the hoses from the fittings at the
steering gear.
(24) Drain the pump reservoir.
(25) Cap the fittings on the hoses and steering
gear to prevent foreign objects from entering the sys-
tem.
(26) Raise and support the vehicle.
(27) Disconnect the wires from the engine starter
motor solenoid.(28) Remove the engine starter motor (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR -
REMOVAL).
(29) Disconnect the oxygen sensor from the
exhaust pipe.
(30) Disconnect the exhaust pipe from the mani-
fold.
(31) Remove the exhaust pipe support.
(32) Remove the bending brace (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCT SUPPORT -
REMOVAL).
(33) Remove the engine flywheel/converter housing
access cover.
(34) Mark the converter and drive plate location.
(35) Remove the converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(36) Remove the upper engine flywheel/converter
housing bolts and loosen the bottom bolts.
(37) Remove the engine mount cushion-to-engine
compartment bracket bolts.
(38) Lower the vehicle.
(39) Attach a lifting device to the engine.
(40) Raise the engine off the front supports.
(41) Place a support or floor jack under the con-
verter (or engine flywheel) housing.
(42) Remove the remaining converter (or engine
flywheel) housing bolts.
(43) Lift the engine out of the engine compart-
ment.
Fig. 5 Air Cleaner Assembly
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP
2 - AIR CLEANER ASSEMBLY
9 - 12 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)