2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE oil temperature
[x] Cancel search: oil temperaturePage 330 of 2199
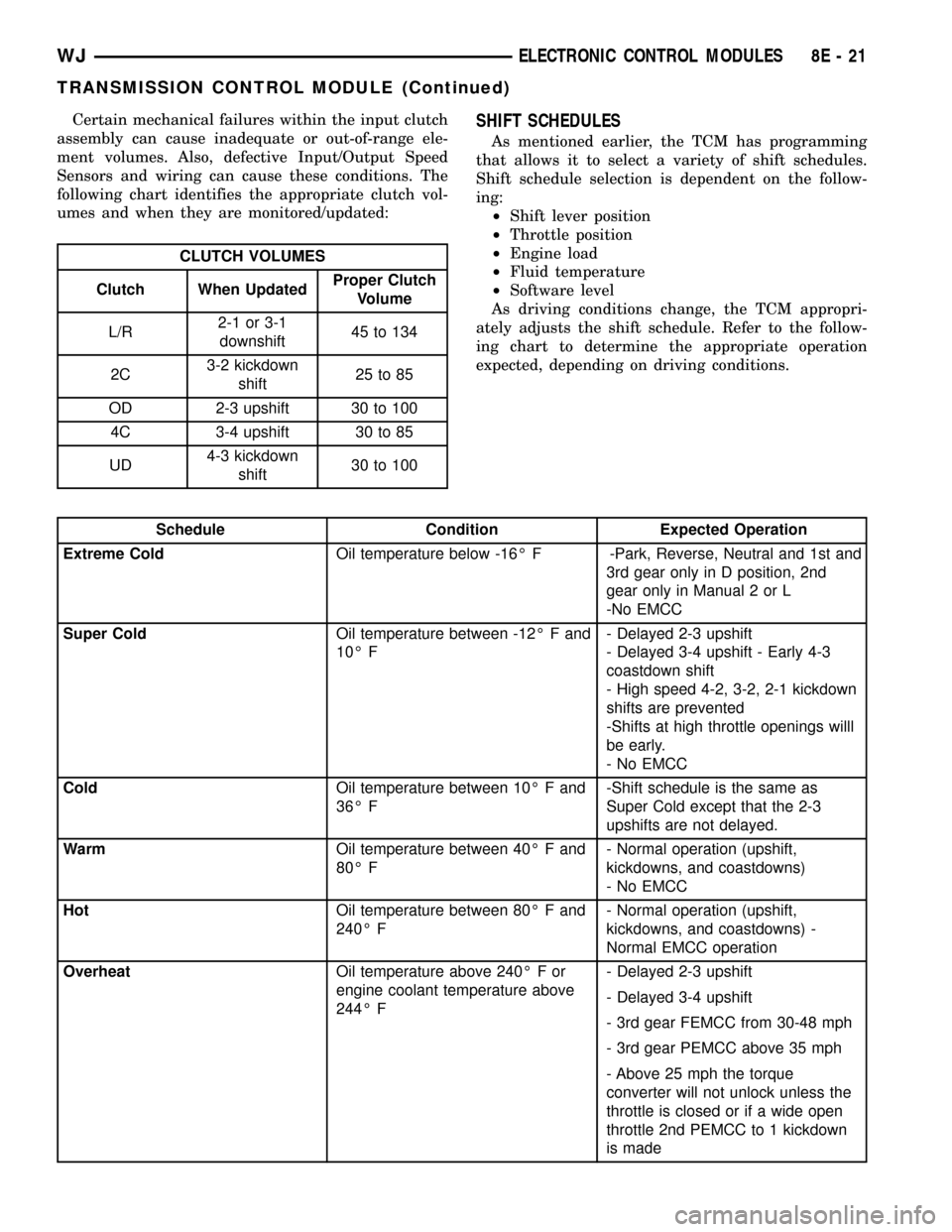
Certain mechanical failures within the input clutch
assembly can cause inadequate or out-of-range ele-
ment volumes. Also, defective Input/Output Speed
Sensors and wiring can cause these conditions. The
following chart identifies the appropriate clutch vol-
umes and when they are monitored/updated:
CLUTCH VOLUMES
Clutch When UpdatedProper Clutch
Volume
L/R2-1 or 3-1
downshift45 to 134
2C3-2 kickdown
shift25 to 85
OD 2-3 upshift 30 to 100
4C 3-4 upshift 30 to 85
UD4-3 kickdown
shift30 to 100
SHIFT SCHEDULES
As mentioned earlier, the TCM has programming
that allows it to select a variety of shift schedules.
Shift schedule selection is dependent on the follow-
ing:
²Shift lever position
²Throttle position
²Engine load
²Fluid temperature
²Software level
As driving conditions change, the TCM appropri-
ately adjusts the shift schedule. Refer to the follow-
ing chart to determine the appropriate operation
expected, depending on driving conditions.
Schedule Condition Expected Operation
Extreme ColdOil temperature below -16É F -Park, Reverse, Neutral and 1st and
3rd gear only in D position, 2nd
gear only in Manual 2 or L
-No EMCC
Super ColdOil temperature between -12É F and
10É F- Delayed 2-3 upshift
- Delayed 3-4 upshift - Early 4-3
coastdown shift
- High speed 4-2, 3-2, 2-1 kickdown
shifts are prevented
-Shifts at high throttle openings willl
be early.
- No EMCC
ColdOil temperature between 10É F and
36É F-Shift schedule is the same as
Super Cold except that the 2-3
upshifts are not delayed.
WarmOil temperature between 40É F and
80É F- Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
- No EMCC
HotOil temperature between 80É F and
240É F- Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns) -
Normal EMCC operation
OverheatOil temperature above 240É F or
engine coolant temperature above
244É F- Delayed 2-3 upshift
- Delayed 3-4 upshift
- 3rd gear FEMCC from 30-48 mph
- 3rd gear PEMCC above 35 mph
- Above 25 mph the torque
converter will not unlock unless the
throttle is closed or if a wide open
throttle 2nd PEMCC to 1 kickdown
is made
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 21
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 331 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TCM QUICK LEARN
The quick learn procedure requires the use of the
DRBIIItscan tool.
This program allows the electronic transmission
system to recalibrate itself. This will provide the
proper transmission operation. The quick learn pro-
cedure should be performed if any of the following
procedures are performed:
²Transmission Assembly Replacement
²Transmission Control Module Replacement
²Solenoid Pack Replacement
²Clutch Plate and/or Seal Replacement
²Valve Body Replacement or ReconditionTo perform the Quick Learn Procedure, the follow-
ing conditions must be met:
²The brakes must be applied
²The engine speed must be above 500 rpm
²The throttle angle (TPS) must be less than 3
degrees
²The shift lever position must stay in PARK until
prompted to shift to overdrive
²The shift lever position must stay in overdrive
after the Shift to Overdrive prompt until the DRBt
indicates the procedure is complete
²The calculated oil temperature must be above
60É and below 200É
8E - 22 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESWJ
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 340 of 2199

to determine its cranking capacity. A battery that is
fully-charged, but does not pass the load test, is
faulty and must be replaced.
NOTE: Completely discharged batteries may take
several hours to accept a charge. Refer to Standard
Procedures for the proper battery charging proce-
dures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BATTERY
CHARGING
Battery charging is the means by which the bat-
tery can be restored to its full voltage potential. A
battery is fully-charged when:
²Micro 420 electrical system tester indicates bat-
tery is OK.
²All of the battery cells are gassing freely during
battery charging.
²Three hydrometer tests, taken at one-hour inter-
vals, indicate no increase in the temperature-cor-
rected specific gravity of the battery electrolyte.
²Open-circuit voltage of the battery is 12.4 volts
or above.
WARNING: NEVER EXCEED TWENTY AMPERES
WHEN CHARGING A COLD (-1É C [30É F] OR
LOWER) BATTERY. THE BATTERY MAY ARC INTER-
NALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR
VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, DO NOT
TEST, ASSIST-BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY
MAY ARC INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE,
USE FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BAT-
TERY. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.WARNING: IF THE BATTERY IS EQUIPPED WITH
REMOVABLE CELL CAPS, BE CERTAIN THAT EACH
OF THE CELL CAPS IS IN PLACE AND TIGHT
BEFORE THE BATTERY IS RETURNED TO SER-
VICE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT FROM LOOSE OR MISSING
CELL CAPS.
CAUTION: Always disconnect and isolate the bat-
tery negative cable before charging a battery. Do
not exceed sixteen volts while charging a battery.
Damage to the vehicle electrical system compo-
nents may result.
CAUTION: Battery electrolyte will bubble inside the
battery case during normal battery charging. Elec-
trolyte boiling or being discharged from the battery
vents indicates a battery overcharging condition.
Immediately reduce the charging rate or turn off the
charger to evaluate the battery condition. Damage
to the battery may result from overcharging.
CAUTION: The battery should not be hot to the
touch. If the battery feels hot to the touch, turn off
the charger and let the battery cool before continu-
ing the charging operation. Damage to the battery
may result.
After the battery has been charged to 12.4 volts or
greater, perform a load test to determine the battery
cranking capacity. Refer to Standard Procedures for
the proper battery load test procedures. If the battery
will endure a load test, return the battery to service.
If the battery will not endure a load test, it is faulty
and must be replaced.
Clean and inspect the battery hold downs, tray,
terminals, posts, and top before completing battery
service. Refer to Battery System Cleaning for the
proper battery system cleaning procedures, and Bat-
tery System Inspection for the proper battery system
inspection procedures.
CHARGING A COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY
The following procedure should be used to recharge
a completely discharged battery. Unless this proce-
dure is properly followed, a good battery may be
needlessly replaced.
(1) Measure the voltage at the battery posts with a
voltmeter, accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt (Fig. 5). If the
reading is below ten volts, the battery charging cur-
rent will be low. It could take some time before the
battery accepts a current greater than a few milliam-
peres. Such low current may not be detectable on the
ammeters built into many battery chargers.
WJBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 9
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 355 of 2199

CHARGING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM............................24
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS - GAS POWERED . . 25
TORQUE - GAS POWERED.............25
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................26
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................26OPERATION...........................26
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................27
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................28
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION
The charging system consists of:
²Generator
²Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry
within the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Ignition switch
²Battery (refer to 8, Battery for information)
²Battery temperature sensor
²Generator Lamp (if equipped)
²Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped)
²Voltmeter (refer to 8, Instrument Cluster for
information)
²Wiring harness and connections (refer to 8, Wir-
ing for information)
OPERATION
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. The system is on when the engine is
running and the ASD relay is energized. When the
ASD relay is on, voltage is supplied to the ASD relay
sense circuit at the PCM. This voltage is connected
through the PCM and supplied to one of the genera-
tor field terminals (Gen. Source +) at the back of the
generator.
The amount of DC current produced by the gener-
ator is controlled by the EVR (field control) circuitry
contained within the PCM. This circuitry is con-
nected in series with the second rotor field terminal
and ground.
A battery temperature sensor, located in the bat-
tery tray housing, is used to sense battery tempera-
ture. This temperature data, along with data from
monitored line voltage, is used by the PCM to vary
the battery charging rate. This is done by cycling theground path to control the strength of the rotor mag-
netic field. The PCM then compensates and regulates
generator current output accordingly.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including EVR
(field control) circuitry, are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for certain failures it detects. Refer to
Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain Control
Module; Electronic Control Modules for more DTC
information.
The Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped) monitors:
charging system voltage,engine coolant tempera-
ture and engine oil pressure. If an extreme condition
is indicated, the lamp will be illuminated. This is
done as reminder to check the three gauges. The sig-
nal to activate the lamp is sent via the CCD bus cir-
cuits. The lamp is located on the instrument panel.
Refer to 8, Instrument Cluster for additional infor-
mation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM
The following procedures may be used to diagnose
the charging system if:
²the check gauges lamp (if equipped) is illumi-
nated with the engine running
²the voltmeter (if equipped) does not register
properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²accessories being left on with the engine not
running
8F - 24 CHARGINGWJ
Page 366 of 2199

SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - STARTER
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Stater Motor (B+) Terminal
(Diesel)27 20
Stater Motor (B+) Terminal
(Except Diesel)11.3 100
Starter Motor Retaining Bolts
(Diesel)27 20
Starter Motor Retaining Bolt
(Forward Facing 4.0L)41 30
Starter Motor Retaining Bolt
(Forward Facing 4.7L)54 40
Starter Motor Retaining Bolt
(Rearward Facing 4.7L)54 40
STARTER MOTOR - GAS POWERED
Starter Motor and Solenoid
Manufacturer Mitsubishi
Engine Application 4.0L/4.7L
Power Rating 1.4 Kilowatt (1.9 Horsepower)
Voltage12 Volts
Number of Fields 4
Number of Poles 4
Number of Brushes 4
Drive Type Planetary Gear Reduction
Free Running Test Voltage 11.2 Volts
Free Running Test Maximum Amperage Draw 90 Amperes
Free Running Test Minimum Speed 2400 rpm
Solenoid Closing Maximum Voltage Required 7.8 Volts
*Cranking Amperage Draw Test 160 Amperes
*Test at operating temperature. Cold engine, tight (new) engine, or heavy oil will increase starter amperage draw.
STARTER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The starter motors used for both the 4.0L and the
4.7L engines available in this model are very similar,
but are not interchangeable. Both starter motors are
mounted with two screws to the automatic transmis-
sion torque converter housing and are located on the
right side of the engine.
Each of these starter motors incorporates several
of the same features to create a reliable, efficient,compact, lightweight and powerful unit. The electric
motors of both starters feature four electromagnetic
field coils wound around four pole shoes, and four
brushes contact the motor commutator. Both starter
motors are rated at 1.4 kilowatts (about 1.9 horse-
power) output at 12 volts.
Both of these starter motors are serviced only as a
unit with their starter solenoids, and cannot be
repaired. If either component is faulty or damaged,
the entire starter motor and starter solenoid unit
must be replaced.
WJSTARTING 8F - 35
STARTING (Continued)
Page 405 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
SENSOR ONLY - 4.0L
The Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) on the 4.0L
6±cylinder engine is bolted to the top of the oil pump
drive shaft assembly (Fig. 6). The sensor and drive
shaft assembly is located on the right side of the
engine near the oil filter (Fig. 7).
(1) Install sensor to oil pump drive.
(2) Install 2 sensor mounting bolts and tighten to
2 N´m (15 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to CMP sensor.
OIL PUMP DRIVE AND SENSOR - 4.0L
(1) Clean oil pump drive mounting hole area of
engine block.
(2) Install new oil pump drive-to-engine block gas-
ket.
(3) Temporarily install a toothpick or similar tool
through access hole at side of oil pump drive housing.
Align toothpick into mating hole on pulse ring (Fig.
8).(4) Install oil pump drive into engine while align-
ing into slot on oil pump. Rotate oil pump drive back
to its original position and install hold-down clamp
and bolt. Finger tighten bolt. Do not do a final tight-
ening of bolt at this time.
(5) If engine crankshaft or camshaft has been
rotated, such as during engine tear-down, CMP sen-
sor relationship must be reestablished.
(a) Remove ignition coil rail assembly. Refer to
Ignition Coil Removal/Installation.
(b) Remove cylinder number 1 spark plug.
(c) Hold a finger over the open spark plug hole.
Rotate engine at vibration dampener bolt until
compression (pressure) is felt.
(d) Slowly continue to rotate engine. Do this
until timing index mark on vibration damper pul-
ley aligns with top dead center (TDC) mark (0
degree) on timing degree scale (Fig. 9). Always
rotate engine in direction of normal rotation. Do
not rotate engine backward to align timing marks.
(e) Install oil pump drive into engine while
aligning into slot on oil pump. If pump drive will
not drop down flush to engine block, the oil pump
slot is not aligned. Remove oil pump drive and
align slot in oil pump to shaft at bottom of drive.
Install into engine. Rotate oil pump drive back to
its original position and install hold-down clamp
and bolt. Finger tighten bolt. Do not do a final
tightening of bolt at this time.
(f) Remove toothpick from housing.
(6) Install sensor to oil pump drive. After installa-
tion, the CMP sensor should face rear of engine 0É.
(7) Install 2 sensor mounting bolts and tighten to
2 N´m (15 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Connect electrical connector to CMP sensor.
(9) If removed, install spark plug and ignition coil
rail.
To verify correct rotational position of oil pump
drive, the DRB scan tool must be used.
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING
TEST, THE ENGINE WILL BE RUNNING. BE CARE-
FUL NOT TO STAND IN LINE WITH THE FAN
BLADES OR FAN BELT. DO NOT WEAR LOOSE
CLOTHING.
(10) Connect DRB scan tool to data link connector.
The data link connector is located in passenger com-
partment, below and to left of steering column.
(11) Gain access to SET SYNC screen on DRB.
(12) Follow directions on DRB screen and start
engine. Bring to operating temperature (engine must
be in ªclosed loopº mode).
(13) With engine running atidle speed, the words
IN RANGE should appear on screen along with 0É.
This indicates correct position of oil pump drive.
Fig. 10 CMP LocationÐ4.7L Engine
1 - RIGHT CYLINDER HEAD
2 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
3 - MOUNTING BOLT
4 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
8I - 8 IGNITION CONTROLWJ
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 416 of 2199

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER............................7
REMOVAL.............................9
DISASSEMBLY.........................10
ASSEMBLY............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
ABS INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
AIRBAG INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
BRAKE/PARK BRAKE INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
INDICATOR..........................16
CHECK GAUGES INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................17
COOLANT LOW INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................17
OPERATION...........................18
CRUISE INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
ENGINE TEMPERATURE GAUGE
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
FRONT FOG LAMP INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................20
OPERATION...........................20
FUEL GAUGE
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................21
HIGH BEAM INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................22
OPERATION...........................22
LOW FUEL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................22
OPERATION...........................23
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL)
DESCRIPTION.........................23OPERATION...........................23
ODOMETER
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................25
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
DESCRIPTION.........................25
OPERATION...........................26
OVERDRIVE OFF INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................26
OPERATION...........................26
REAR FOG LAMP INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................27
SEATBELT INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
SHIFT INDICATOR (TRANSFER CASE)
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
SKIS INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
SPEEDOMETER
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................31
TACHOMETER
DESCRIPTION.........................31
OPERATION...........................31
TRANS TEMP INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................32
OPERATION...........................32
TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................33
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TURN SIGNAL
INDICATOR..........................33
VOLTAGE GAUGE
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34
WAIT-TO-START INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
WATER-IN-FUEL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................36
OPERATION...........................36
WJINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 1
Page 418 of 2199

EMIC also uses several hard wired inputs in order to
perform its many functions. The EMIC module incor-
porates a blue-green digital Vacuum Fluorescent Dis-
play (VFD) for displaying odometer and trip
odometer information.
The EMIC houses six analog gauges and has pro-
visions for up to twenty indicators (Fig. 2). The
EMIC includes the following analog gauges:
²Coolant Temperature Gauge
²Fuel Gauge
²Oil Pressure Gauge
²Speedometer
²Tachometer
²Voltage Gauge
Some of the EMIC indicators are automatically
configured when the EMIC is connected to the vehi-
cle electrical system for compatibility with certain
optional equipment or equipment required for regula-
tory purposes in certain markets. While each EMIC
may have provisions for indicators to support every
available option, the configurable indicators will not
be functional in a vehicle that does not have the
equipment that an indicator supports. The EMIC
includes provisions for the following indicators (Fig.
2):
²Airbag Indicator (with Airbags only)
²Antilock Brake System (ABS) Indicator
²Brake Indicator
²Check Gauges Indicator
²Coolant Low Indicator (with Diesel Engine
only)
²Cruise Indicator
²Four-Wheel Drive Part Time Indicator
(with Selec-Trac NVG-242 Transfer Case only)
²Front Fog Lamp Indicator (with Front Fog
Lamps only)
²High Beam Indicator
²Low Fuel Indicator
²Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
²Overdrive-Off Indicator (except Diesel
Engine)
²Rear Fog Lamp Indicator (with Rear Fog
Lamps only)
²Seatbelt Indicator
²Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS)
Indicator
²Transmission Overtemp Indicator (except
Diesel Engine)²Turn Signal (Right and Left) Indicators
²Wait-To-Start Indicator (with Diesel Engine
only)
²Water-In-Fuel Indicator (with Diesel Engine
only)
Many indicators in the EMIC are illuminated by a
dedicated Light Emitting Diode (LED) that is sol-
dered onto the EMIC electronic circuit board. The
LEDs are not available for service replacement and,
if damaged or faulty, the entire EMIC must be
replaced. Base cluster illumination is accomplished
by dimmable incandescent back lighting, which illu-
minates the gauges for visibility when the exterior
lighting is turned on. Premium cluster illumination
is accomplished by a dimmable electro-luminescent
lamp that is serviced only as a unit with the EMIC.
Each of the incandescent bulbs is secured by an inte-
gral bulb holder to the electronic circuit board from
the back of the cluster housing. The incandescent
bulb/bulb holder units are available for service
replacement.
Hard wired circuitry connects the EMIC to the
electrical system of the vehicle. These hard wired cir-
cuits are integral to several wire harnesses, which
are routed throughout the vehicle and retained by
many different methods. These circuits may be con-
nected to each other, to the vehicle electrical system
and to the EMIC through the use of a combination of
soldered splices, splice block connectors, and many
different types of wire harness terminal connectors
and insulators. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-
grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
further details on wire harness routing and reten-
tion, as well as pin-out and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
The EMIC modules for this model are serviced only
as complete units. The EMIC module cannot be
adjusted or repaired. If a gauge, an LED indicator,
the VFD, the electronic circuit board, the circuit
board hardware, the cluster overlay, the electro-lumi-
nescent lamp (premium model only) or the EMIC
housing are damaged or faulty, the entire EMIC mod-
ule must be replaced. The cluster lens, hood and
mask unit and the individual incandescent lamp
bulbs with holders are available for service replace-
ment.
WJINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 3
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)