2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE turn switch
[x] Cancel search: turn switchPage 1488 of 2199

(13) Remove the column coupler bolt (Fig. 13) and
slide the coupler off the column shaft.
(14) Remove the column mounting nuts (Fig. 13)
and lower column off mounting studs. Remove the
column from the vehicle.
(15) Remove the ignition switch, cylinder and
SKIM, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/LOCK
CYLINDER HOUSING - REMOVAL). (Fig. 14).INSTALLATION
WARNING: BEFORE SERVICING THE STEERING COL-
UMN THE AIRBAG SYSTEM MUST BE DISARMED.
FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL
DEPLOYMENT OF THE AIRBAG AND POSSIBLE PER-
SONAL INJURY. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
(1) Install the ignition switch, cylinder and SKIM-
,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/IGNITION
SWITCH - INSTALLATION).
(2) Install the column into the vehicle and lift the
column up onto the mounting studs. Install the
mounting nuts and tighten to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(3) Slid the coupler onto the column shaft and
install the coupler bolt. Tighten the coupler bolt to 49
N´m (36 ft. lbs.).
(4) Turn the ignition key to the on position then
release and install the shifter interlock cable (Fig.
12) into ignition lock cylinder housing.
(5) Verify ignition switch and shifter interlock
operation.,(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 42RE/GEAR SHIFT CABLE -
ADJUSTMENTS).
(6) Slide the multifuction switch and clock spring
onto the column as an assembly (Fig. 11).
(7) Install the multifuction switch mounting screw
(Fig. 10).
(8) Connect the multifuction switch (Fig. 9) and
ignition switch harness.
(9) Install the upper fixed shroud and mounting
screws (Fig. 8).
(10) Install the lower steering column shroud to
the steering column. Install and tighten the mount-
ing screw.
(11) Install the upper column shroud. Align the
upper shroud to the lower shroud and snap the two
shroud halves together.
(12) Install the knee blocker cover (Fig. 5),(Refer
to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL - INSTALLA-
TION).
(13) Install the cluster bezel by inserting it into
the instrument panel (Fig. 4).
(14) Align the steering wheel with the column
index spline and install the wheel on the column
shaft. Pull the clockspring wire harness through the
steering wheel armature spokes.
(15) Install and tighten the steering wheel mount-
ing nut to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(16) Connect the steering wheel wire harness con-
nector to the clock spring connector.
(17) Install the airbag,(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
(18) Connect the negative (ground) cable to the
battery.
Fig. 13 Column Coupler Bolt And Mounting Nuts
1 - COLUMN MOUNTING NUTS
2 - COUPLER BOLT
Fig. 14 Ignition Switch And SKIM
1 - SKIM
2 - IGNITION SWITCH
WJCOLUMN 19 - 11
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1530 of 2199

FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
overdrive control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
valve moves the overdrive piston into contact with
the overdrive clutch. The direct clutch is disengaged
before the overdrive clutch is engaged. The boost
valve provides increased fluid apply pressure to the
overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts, and when accel-
erating in fourth gear. The 3-4 accumulator cushions
overdrive clutch engagement to smooth 3-4 upshifts.
The accumulator is charged at the same time as
apply pressure acts against the overdrive piston.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Automatic transmission problems can be a result of
poor engine performance, incorrect fluid level, incor-
rect linkage or cable adjustment, band or hydraulic
control pressure adjustments, hydraulic system mal-
functions or electrical/mechanical component mal-
functions. Begin diagnosis by checking the easily
accessible items such as: fluid level and condition,
linkage adjustments and electrical connections. A
road test will determine if further diagnosis is neces-
sary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVEABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust throttle and gearshift linkage if com-
plaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift or
throttle linkage.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that diagnostic trouble
codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, band or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is advanced, an overhaul will be necessary
to restore normal operation.
A slipping clutch or band can often be determined
by comparing which internal units are applied in the
various gear ranges. The Clutch and Band Applica-
tion chart provides a basis for analyzing road test
results.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 11
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1532 of 2199

The rear servo and governor pressure ports are at
the right rear of the transmission case. The overdrive
clutch pressure port is at the left rear of the case.
Test One - Transmission In Manual Low
NOTE: This test checks pump output, pressure reg-
ulation, and condition of the rear clutch and servo
circuit. Both test gauges are required for this test.
(1) Connect tachometer to engine. Position tachom-
eter so it can be observed from driver seat if helper
will be operating engine. Raise vehicle on hoist that
will allow rear wheels to rotate freely.
(2) Connect 100 psi Gauge C-3292 to accumulator
port. Then connect 300 psi Gauge C-3293-SP to rear
servo port.
(3) Disconnect throttle and gearshift cables from
levers on transmission valve body manual shaft.
(4) Have helper start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(5) Move transmission shift lever fully forward
into 1 range.(6) Gradually move transmission throttle lever
from full forward to full rearward position and note
pressures on both gauges:
²Line pressure at accumulator port should be
54-60 psi (372-414 kPa) with throttle lever forward
and gradually increase to 90-96 psi (621-662 kPa) as
throttle lever is moved rearward.
²Rear servo pressure should be same as line pres-
sure within 3 psi (20.68 kPa).
Test Two - Transmission In 2 Range
NOTE: This test checks pump output, line pressure
and pressure regulation. Use 100 psi Test Gauge
C-3292 for this test.
(1) Leave vehicle in place on hoist and leave Test
Gauge C-3292 connected to accumulator port.
(2) Have helper start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(3) Move transmission shift lever one detent rear-
ward from full forward position. This is 2 range.
(4) Move transmission throttle lever from full for-
ward to full rearward position and read pressure on
gauge.
(5) Line pressure should be 54-60 psi (372-414
kPa) with throttle lever forward and gradually
increase to 90-96 psi (621-662 kPa) as lever is moved
rearward.
Test Three - Transmission In D Range Third Gear
NOTE: This test checks pressure regulation and
condition of the clutch circuits. Both test gauges
are required for this test.
(1) Turn OD switch off.
(2) Leave vehicle on hoist and leave Gauge C-3292
in place at accumulator port.
(3) Move Gauge C-3293-SP over to front servo port
for this test.
(4) Have helper start and run engine at 1600 rpm
for this test.
(5) Move transmission shift lever two detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is D range.
(6) Read pressures on both gauges as transmission
throttle lever is gradually moved from full forward to
full rearward position:
²Line pressure at accumulator in D range third
gear, should be 54-60 psi (372-414 kPa) with throttle
lever forward and increase as lever is moved rear-
ward.
²Front servo pressure in D range third gear,
should be within 3 psi (21 kPa) of line pressure up to
kickdown point.
Fig. 9 Pressure Test Port Locations
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH TEST PORT
2 - GOVERNOR TEST PORT
3 - ACCUMULATOR TEST PORT
4 - FRONT SERVO TEST PORT
5 - REAR SERVO TEST PORT
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 13
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1533 of 2199

Test Four - Transmission In Reverse
NOTE: This test checks pump output, pressure reg-
ulation and the front clutch and rear servo circuits.
Use 300 psi Test Gauge C-3293-SP for this test.
(1) Leave vehicle on hoist and leave gauge C-3292
in place at accumulator port.
(2) Move 300 psi Gauge C-3293-SP back to rear
servo port.
(3) Have helper start and run engine at 1600 rpm
for test.
(4) Move transmission shift lever four detents
rearward from full forward position. This is Reverse
range.
(5) Move transmission throttle lever fully forward
then fully rearward and note reading at Gauge
C-3293-SP.
(6) Pressure should be 145 - 175 psi (1000-1207
kPa) with throttle lever forward and increase to 230 -
280 psi (1586-1931 kPa) as lever is gradually moved
rearward.
Test Five - Governor Pressure
NOTE: This test checks governor operation by mea-
suring governor pressure response to changes in
vehicle speed. It is usually not necessary to check
governor operation unless shift speeds are incor-
rect or if the transmission will not downshift. The
test should be performed on the road or on a hoist
that will allow the rear wheels to rotate freely.
(1) Move 100 psi Test Gauge C-3292 to governor
pressure port.
(2) Move transmission shift lever two detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is D range.
(3) Have helper start and run engine at curb idle
speed. Then firmly apply service brakes so wheels
will not rotate.
(4) Note governor pressure:
²Governor pressure should be no more than 20.6
kPa (3 psi) at curb idle speed and wheels not rotat-
ing.
²If pressure exceeds 20.6 kPa (3 psi), a fault
exists in governor pressure control system.
(5) Release brakes, slowly increase engine speed,
and observe speedometer and pressure test gauge (do
not exceed 30 mph on speedometer). Governor pres-
sure should increase in proportion to vehicle speed.
Or approximately 6.89 kPa (1 psi) for every 1 mph.
(6) Governor pressure rise should be smooth and
drop back to no more than 20.6 kPa (3 psi), after
engine returns to curb idle and brakes are applied to
prevent wheels from rotating.
(7) Compare results of pressure test with analysis
chart.Test Six - Transmission In Overdrive Fourth Gear
NOTE: This test checks line pressure at the over-
drive clutch in fourth gear range. Use 300 psi Test
Gauge C-3293-SP for this test. The test should be
performed on the road or on a chassis dyno.
(1) Remove tachometer; it is not needed for this
test.
(2) Move 300 psi Gauge to overdrive clutch pres-
sure test port. Then remove other gauge and reinstall
test port plug.
(3) Lower vehicle.
(4) Turn OD switch on.
(5) Secure test gauge so it can be viewed from
drivers seat.
(6) Start engine and shift into D range.
(7) Increase vehicle speed gradually until 3-4 shift
occurs and note gauge pressure.
(8) Pressure should be 469-496 kPa (68-72 psi)
with closed throttle and increase to 620-827 kPa (90-
120 psi) at 1/2 to 3/4 throttle. Note that pressure can
increase to around 896 kPa (130 psi) at full throttle.
(9) Return to shop or move vehicle off chassis
dyno.
PRESSURE TEST ANALYSIS CHART
TEST CONDITION INDICATION
Line pressure OK during
any one testPump and regulator
valve OK
Line pressure OK in R
but low in D, 2, 1Leakage in rear clutch
area (seal rings, clutch
seals)
Pressure low in D Fourth
Gear RangeOverdrive clutch piston
seal, or check ball
problem
Pressure OK in 1, 2 but
low in D3 and RLeakage in front clutch
area
Pressure OK in 2 but low
in R and 1Leakage in rear servo
Front servo pressure in 2 Leakage in servo; broken
servo ring or cracked
servo piston
Pressure low in all
positionsClogged filter, stuck
regulator valve, worn or
faulty pump, low oil level
Governor pressure too
high at idle speedGovernor pressure
solenoid valve system
fault. Refer to diagnostic
book.
21 - 14 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1541 of 2199
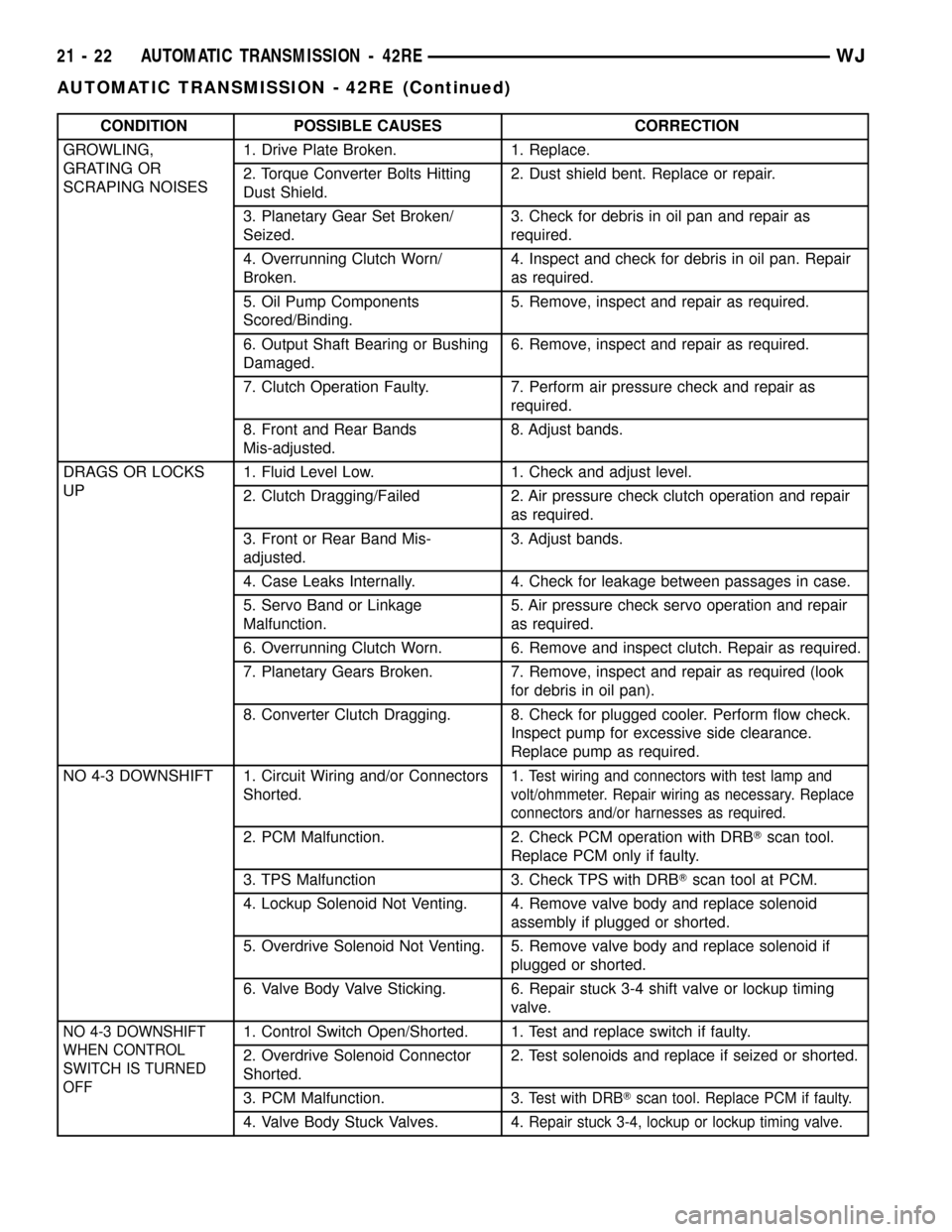
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
GROWLING,
GRATING OR
SCRAPING NOISES1. Drive Plate Broken. 1. Replace.
2. Torque Converter Bolts Hitting
Dust Shield.2. Dust shield bent. Replace or repair.
3. Planetary Gear Set Broken/
Seized.3. Check for debris in oil pan and repair as
required.
4. Overrunning Clutch Worn/
Broken.4. Inspect and check for debris in oil pan. Repair
as required.
5. Oil Pump Components
Scored/Binding.5. Remove, inspect and repair as required.
6. Output Shaft Bearing or Bushing
Damaged.6. Remove, inspect and repair as required.
7. Clutch Operation Faulty. 7. Perform air pressure check and repair as
required.
8. Front and Rear Bands
Mis-adjusted.8. Adjust bands.
DRAGS OR LOCKS
UP1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Check and adjust level.
2. Clutch Dragging/Failed 2. Air pressure check clutch operation and repair
as required.
3. Front or Rear Band Mis-
adjusted.3. Adjust bands.
4. Case Leaks Internally. 4. Check for leakage between passages in case.
5. Servo Band or Linkage
Malfunction.5. Air pressure check servo operation and repair
as required.
6. Overrunning Clutch Worn. 6. Remove and inspect clutch. Repair as required.
7. Planetary Gears Broken. 7. Remove, inspect and repair as required (look
for debris in oil pan).
8. Converter Clutch Dragging. 8. Check for plugged cooler. Perform flow check.
Inspect pump for excessive side clearance.
Replace pump as required.
NO 4-3 DOWNSHIFT 1. Circuit Wiring and/or Connectors
Shorted.1.
Test wiring and connectors with test lamp and
volt/ohmmeter. Repair wiring as necessary. Replace
connectors and/or harnesses as required.
2. PCM Malfunction. 2. Check PCM operation with DRBTscan tool.
Replace PCM only if faulty.
3. TPS Malfunction 3. Check TPS with DRBTscan tool at PCM.
4. Lockup Solenoid Not Venting. 4. Remove valve body and replace solenoid
assembly if plugged or shorted.
5. Overdrive Solenoid Not Venting. 5. Remove valve body and replace solenoid if
plugged or shorted.
6. Valve Body Valve Sticking. 6. Repair stuck 3-4 shift valve or lockup timing
valve.
NO 4-3 DOWNSHIFT
WHEN CONTROL
SWITCH IS TURNED
OFF1. Control Switch Open/Shorted. 1. Test and replace switch if faulty.
2. Overdrive Solenoid Connector
Shorted.2. Test solenoids and replace if seized or shorted.
3. PCM Malfunction. 3.
Test with DRBTscan tool. Replace PCM if faulty.
4. Valve Body Stuck Valves. 4.Repair stuck 3-4, lockup or lockup timing valve.
21 - 22 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1542 of 2199
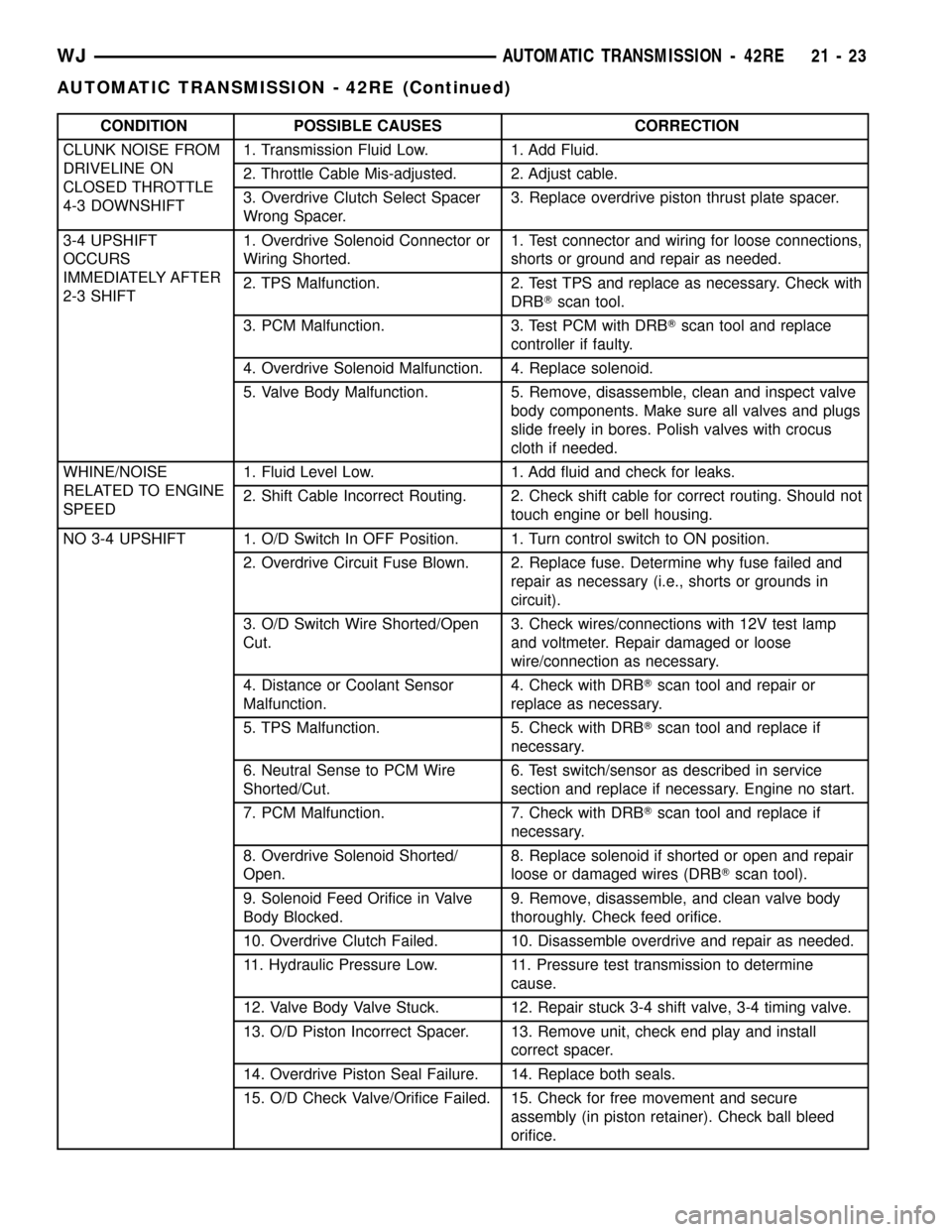
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUNK NOISE FROM
DRIVELINE ON
CLOSED THROTTLE
4-3 DOWNSHIFT1. Transmission Fluid Low. 1. Add Fluid.
2. Throttle Cable Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust cable.
3. Overdrive Clutch Select Spacer
Wrong Spacer.3. Replace overdrive piston thrust plate spacer.
3-4 UPSHIFT
OCCURS
IMMEDIATELY AFTER
2-3 SHIFT1. Overdrive Solenoid Connector or
Wiring Shorted.1.
Test connector and wiring for loose connections,
shorts or ground and repair as needed.
2. TPS Malfunction. 2. Test TPS and replace as necessary. Check with
DRBTscan tool.
3. PCM Malfunction. 3. Test PCM with DRBTscan tool and replace
controller if faulty.
4. Overdrive Solenoid Malfunction. 4. Replace solenoid.
5. Valve Body Malfunction. 5. Remove, disassemble, clean and inspect valve
body components. Make sure all valves and plugs
slide freely in bores. Polish valves with crocus
cloth if needed.
WHINE/NOISE
RELATED TO ENGINE
SPEED1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Incorrect Routing. 2. Check shift cable for correct routing. Should not
touch engine or bell housing.
NO 3-4 UPSHIFT 1. O/D Switch In OFF Position. 1. Turn control switch to ON position.
2. Overdrive Circuit Fuse Blown. 2. Replace fuse. Determine why fuse failed and
repair as necessary (i.e., shorts or grounds in
circuit).
3. O/D Switch Wire Shorted/Open
Cut.3. Check wires/connections with 12V test lamp
and voltmeter. Repair damaged or loose
wire/connection as necessary.
4. Distance or Coolant Sensor
Malfunction.4. Check with DRBTscan tool and repair or
replace as necessary.
5. TPS Malfunction. 5. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace if
necessary.
6. Neutral Sense to PCM Wire
Shorted/Cut.6. Test switch/sensor as described in service
section and replace if necessary. Engine no start.
7. PCM Malfunction. 7. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace if
necessary.
8. Overdrive Solenoid Shorted/
Open.8. Replace solenoid if shorted or open and repair
loose or damaged wires (DRBTscan tool).
9. Solenoid Feed Orifice in Valve
Body Blocked.9. Remove, disassemble, and clean valve body
thoroughly. Check feed orifice.
10. Overdrive Clutch Failed. 10. Disassemble overdrive and repair as needed.
11. Hydraulic Pressure Low. 11. Pressure test transmission to determine
cause.
12. Valve Body Valve Stuck. 12. Repair stuck 3-4 shift valve, 3-4 timing valve.
13. O/D Piston Incorrect Spacer. 13. Remove unit, check end play and install
correct spacer.
14. Overdrive Piston Seal Failure. 14. Replace both seals.
15. O/D Check Valve/Orifice Failed. 15. Check for free movement and secure
assembly (in piston retainer). Check ball bleed
orifice.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 23
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1545 of 2199

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL LEAKS. 1. Fluid Lines and Fittings
Loose/Leaks/Damaged.1. Tighten fittings. If leaks persist, replace fittings
and lines if necessary.
2. Fill Tube (where tube enters
case) Leaks/Damaged.2. Replace tube seal. Inspect tube for cracks in fill
tube.
3. Pressure Port Plug Loose
Loose/Damaged.3. Tighten to correct torque. Replace plug or
reseal if leak persists.
4. Pan Gasket Leaks. 4. Tighten pan screws (150 in. lbs.). If leaks
persist, replace gasket.
5. Valve Body Manual Lever Shaft
Seal Leaks/Worn.5. Replace shaft seal.
6. Rear Bearing Access Plate
Leaks.6. Replace gasket. Tighten screws.
7. Gasket Damaged or Bolts are
Loose.7. Replace bolts or gasket or tighten both.
8. Adapter/Extension Gasket
Damaged Leaks/Damaged.8. Replace gasket.
9. Park/Neutral Switch, or
Transmission Range Sensor
Leaks/Damaged.9. Replace switch and gasket.
10. Converter Housing Area Leaks. 10. Check for leaks at seal caused by worn seal
or burr on converter hub (cutting seal), worn
bushing, missing oil return, oil in front pump
housing or hole plugged. Check for leaks past
O-ring seal on pump or past pump-to-case bolts;
pump housing porous, oil coming out vent due to
overfill or leak past front band shaft access plug.
11. Pump Seal Leaks/Worn/
Damaged.11. Replace seal.
12. Torque Converter Weld
Leak/Cracked Hub.12. Replace converter.
13. Case Porosity Leaks. 13. Replace case.
NOISY OPERATION
IN FOURTH GEAR
ONLY1. Overdrive Clutch Discs, Plates
or Snap Rings Damaged.1. Remove unit and rebuild clutch pack.
2. Overdrive Piston or Planetary
Thrust Bearing Damaged.2. Remove and disassemble unit. Replace either
thrust bearing if damaged.
3. Output Shaft Bearings
Scored/Damaged.3. Remove and disassemble unit. Replace either
bearing if damaged.
4. Planetary Gears Worn/Chipped. 4. Remove and overhaul overdrive unit.
5. Overdrive Unit Overrunning
Clutch Rollers Worn/Scored.5. Remove and overhaul overdrive unit.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR
Damaged or worn threads in the aluminum trans-
mission case and valve body can be repaired by the
use of Heli-CoilsŸ, or equivalent. This repair con-
sists of drilling out the worn-out damaged threads.
Then tap the hole with a special Heli-CoilŸ tap, or
equivalent, and installing a Heli-CoilŸ insert, orequivalent, into the hole. This brings the hole back to
its original thread size.
Heli-CoilŸ, or equivalent, tools and inserts are
readily available from most automotive parts suppli-
ers.
21 - 26 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1575 of 2199
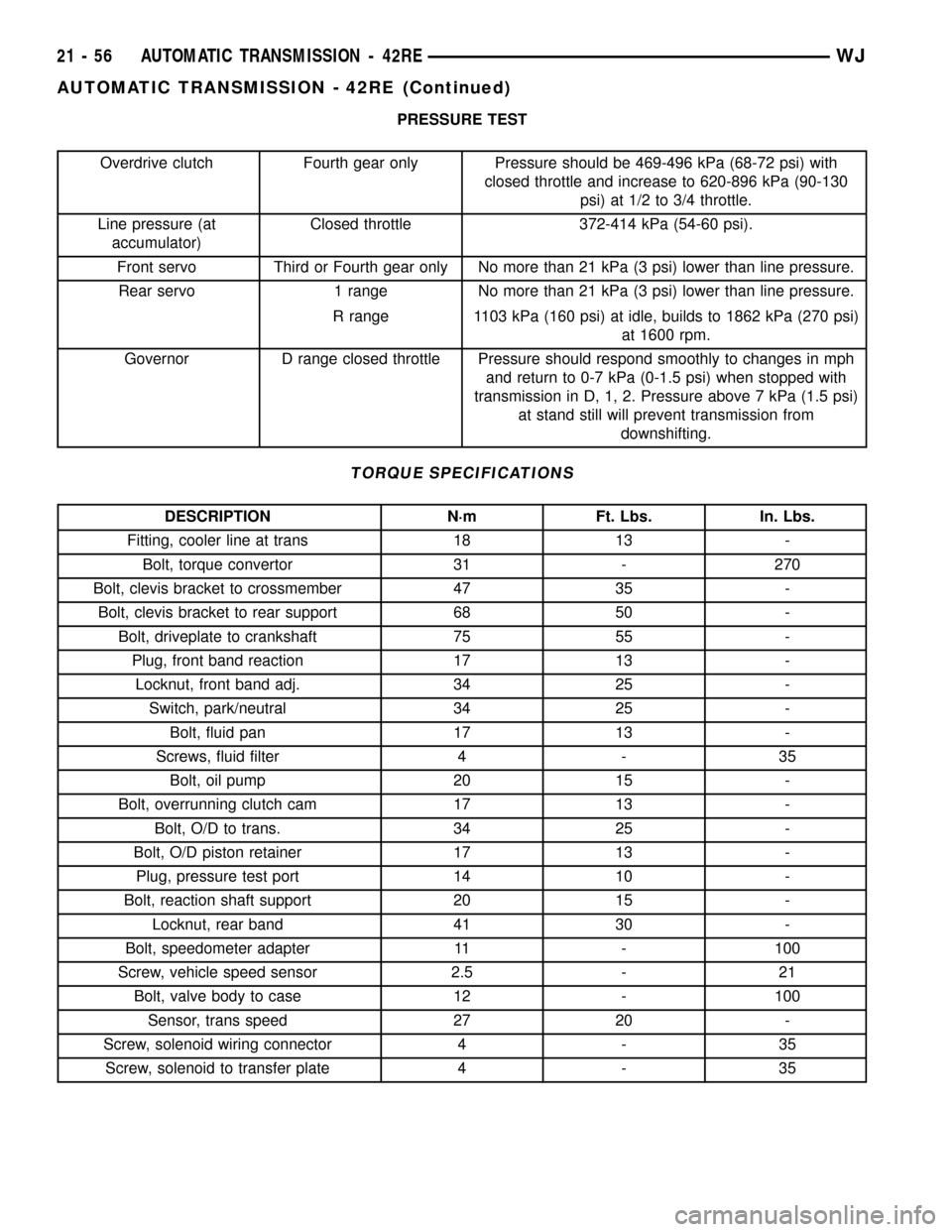
PRESSURE TEST
Overdrive clutch Fourth gear only Pressure should be 469-496 kPa (68-72 psi) with
closed throttle and increase to 620-896 kPa (90-130
psi) at 1/2 to 3/4 throttle.
Line pressure (at
accumulator)Closed throttle 372-414 kPa (54-60 psi).
Front servo Third or Fourth gear only No more than 21 kPa (3 psi) lower than line pressure.
Rear servo 1 range No more than 21 kPa (3 psi) lower than line pressure.
R range 1103 kPa (160 psi) at idle, builds to 1862 kPa (270 psi)
at 1600 rpm.
Governor D range closed throttle Pressure should respond smoothly to changes in mph
and return to 0-7 kPa (0-1.5 psi) when stopped with
transmission in D, 1, 2. Pressure above 7 kPa (1.5 psi)
at stand still will prevent transmission from
downshifting.
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fitting, cooler line at trans 18 13 -
Bolt, torque convertor 31 - 270
Bolt, clevis bracket to crossmember 47 35 -
Bolt, clevis bracket to rear support 68 50 -
Bolt, driveplate to crankshaft 75 55 -
Plug, front band reaction 17 13 -
Locknut, front band adj. 34 25 -
Switch, park/neutral 34 25 -
Bolt, fluid pan 17 13 -
Screws, fluid filter 4 - 35
Bolt, oil pump 20 15 -
Bolt, overrunning clutch cam 17 13 -
Bolt, O/D to trans. 34 25 -
Bolt, O/D piston retainer 17 13 -
Plug, pressure test port 14 10 -
Bolt, reaction shaft support 20 15 -
Locknut, rear band 41 30 -
Bolt, speedometer adapter 11 - 100
Screw, vehicle speed sensor 2.5 - 21
Bolt, valve body to case 12 - 100
Sensor, trans speed 27 20 -
Screw, solenoid wiring connector 4 - 35
Screw, solenoid to transfer plate 4 - 35
21 - 56 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)