2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE can bus
[x] Cancel search: can busPage 1639 of 2199

INSPECTION
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the fac-
ing is flaking off. Replace the top and bottom pres-
sure plates if scored, warped, or cracked. Be sure the
driving lugs on the pressure and clutch plates are
also in good condition. The lugs must not be bent,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
clutch and pressure plates should slide freely in the
slots. Replace the retainer if the grooves are worn or
damaged. Also check action of the check balls in the
retainer and piston. Each check ball must move
freely and not stick.
Replace the retainer bushing if worn, scored, or
doubt exists about bushing condition.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
Check condition of the fiber thrust washer and
metal output shaft thrust washer. Replace either
washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the seal rings on the input shaft
and clutch retainer hub. Replace the seal rings only
if worn, distorted, or damaged. The input shaft front
seal ring is teflon with chamfered ends. The rear ring
is metal with interlocking ends.
Check the input shaft for wear, or damage. Replace
the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any way.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Soak clutch discs in transmission fluid while
assembling other clutch parts.
(2) Install new seal rings on clutch retainer hub
and input shaft, if necessary, (Fig. 227) and (Fig.
228).
(a) Be sure clutch hub seal ring is fully seated in
groove and is not twisted.
(3) Lubricate splined end of input shaft and clutch
retainer with transmission fluid. Then press input
shaft into retainer (Fig. 229). Use a suitably sized
press tool to support retainer as close to input shaft
as possible.
(4) Install input shaft snap-ring (Fig. 226).
(5) Invert retainer and press input shaft in oppo-
site direction until snap-ring is seated.
(6) Install new seals on clutch piston. Be sure lip
of each seal faces interior of clutch retainer.
(7) Lubricate lip of piston seals with generous
quantity of MopartDoor Ease. Then lubricate
retainer hub and bore with light coat of transmission
fluid.
(8) Install clutch piston in retainer. Use twisting
motion to seat piston in bottom of retainer. A thin
strip of plastic (about 0.0209thick), can be used to
guide seals into place if necessary.
CAUTION: Never push the clutch piston straight in.
This will fold the seals over causing leakage and
clutch slip. In addition, never use any type of metal
tool to help ease the piston seals into place. Metal
tools will cut, shave, or score the seals.
(9) Install piston spring in retainer and on top of
piston (Fig. 230). Concave side of spring faces down-
ward (toward piston).
(10) Install wave spring in retainer (Fig. 230). Be
sure spring is completely seated in retainer groove.
(11) Install bottom pressure plate (Fig. 225).
Ridged side of plate faces downward (toward piston)
and flat side toward clutch pack.
(12) Install first clutch disc in retainer on top of
bottom pressure plate. Then install a clutch plate fol-
lowed by a clutch disc until entire clutch pack is
installed (4 discs and 3 plates are required) (Fig.
225).
(13) Install top pressure plate.
(14) Install selective snap-ring. Be sure snap-ring
is fully seated in retainer groove.
(15) Using a suitable gauge bar and dial indicator,
measure clutch pack clearance (Fig. 231).
(a) Position gauge bar across the clutch drum
with the dial indicator pointer on the pressure
plate (Fig. 231).
(b) Using two small screw drivers, lift the pres-
sure plate and release it.
Fig. 226 Removing Input Shaft Snap-Ring
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING
3 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
21 - 120 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1771 of 2199

(9) Remove the oil pump valve retainers and asso-
ciated valve and spring one at a time (Fig. 93) (Fig.
94). Mark the combination of components as a group
and tag them as to the location from which they were
removed.
CLEANING
Clean pump and support components with solvent
and dry them with compressed air.
INSPECTION
Check condition of the seal rings and thrust
washer on the reaction shaft support. The seal rings
do not need to be replaced unless cracked, broken, or
severely worn.
Inspect the pump and support components. Replace
the pump or support if the seal ring grooves or
machined surfaces are worn, scored, pitted, or dam-
aged. Replace the pump gears if pitted, worn
chipped, or damaged.Inspect the pump reaction shaft support bushings.
Replace either bushing only if heavily worn, scored or
damaged. It is not necessary to replace the bushings
unless they are actually damaged.
Inspect the valves and plugs for scratches, burrs,
nicks, or scores. Minor surface scratches on steel
valves and plugs can be removed with crocus cloth
butdo not round off the edges of the valve or
plug lands.Maintaining sharpness of these edges is
vitally important. The edges prevent foreign matter
from lodging between the valves and plugs and the
bore.
Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the oil
pump cover. Use a penlight to view the bore interi-
ors. Replace the oil pump if any bores are distorted
or scored. Inspect all of the valve springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Trial fit each valve and plug in its bore to check
freedom of operation. When clean and dry, the valves
and plugs should drop freely into the bores.
Fig. 93 Oil Pump Valve Body
1 - T/C REGULATOR VALVE
2 - T/C LIMIT VALVE
3 - REGULATOR VALVE
4 - OIL PUMP VALVE BODY
Fig. 94 T/C Switch Valve
1 - RETAINER
2 - T/C SWITCH VALVE
3 - OIL PUMP VALVE BODY
21 - 252 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1779 of 2199
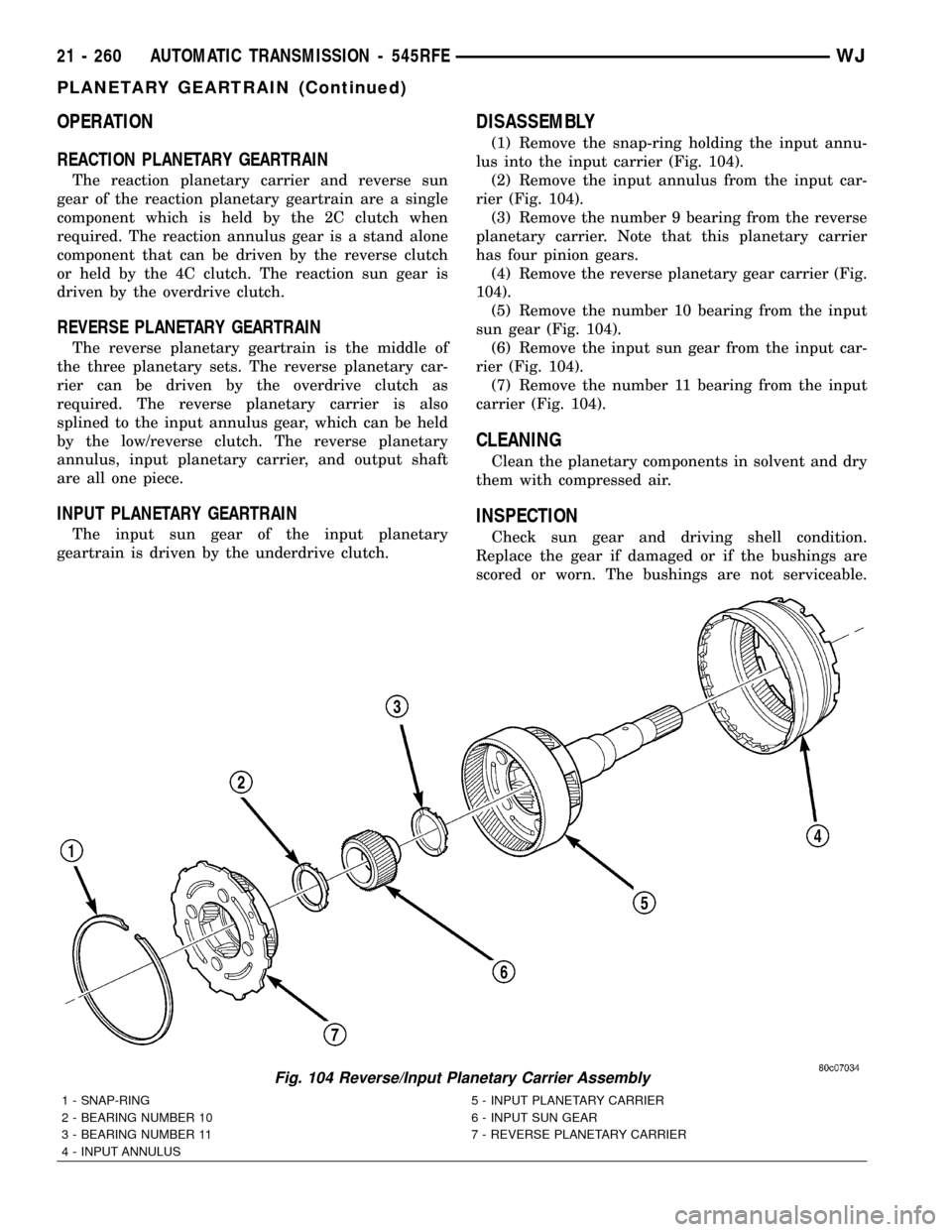
OPERATION
REACTION PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
The reaction planetary carrier and reverse sun
gear of the reaction planetary geartrain are a single
component which is held by the 2C clutch when
required. The reaction annulus gear is a stand alone
component that can be driven by the reverse clutch
or held by the 4C clutch. The reaction sun gear is
driven by the overdrive clutch.
REVERSE PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
The reverse planetary geartrain is the middle of
the three planetary sets. The reverse planetary car-
rier can be driven by the overdrive clutch as
required. The reverse planetary carrier is also
splined to the input annulus gear, which can be held
by the low/reverse clutch. The reverse planetary
annulus, input planetary carrier, and output shaft
are all one piece.
INPUT PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
The input sun gear of the input planetary
geartrain is driven by the underdrive clutch.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the snap-ring holding the input annu-
lus into the input carrier (Fig. 104).
(2) Remove the input annulus from the input car-
rier (Fig. 104).
(3) Remove the number 9 bearing from the reverse
planetary carrier. Note that this planetary carrier
has four pinion gears.
(4) Remove the reverse planetary gear carrier (Fig.
104).
(5) Remove the number 10 bearing from the input
sun gear (Fig. 104).
(6) Remove the input sun gear from the input car-
rier (Fig. 104).
(7) Remove the number 11 bearing from the input
carrier (Fig. 104).
CLEANING
Clean the planetary components in solvent and dry
them with compressed air.
INSPECTION
Check sun gear and driving shell condition.
Replace the gear if damaged or if the bushings are
scored or worn. The bushings are not serviceable.
Fig. 104 Reverse/Input Planetary Carrier Assembly
1 - SNAP-RING 5 - INPUT PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - BEARING NUMBER 10 6 - INPUT SUN GEAR
3 - BEARING NUMBER 11 7 - REVERSE PLANETARY CARRIER
4 - INPUT ANNULUS
21 - 260 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN (Continued)
Page 1799 of 2199
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION........................280
OPERATION..........................281
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV242.......................281
REMOVAL............................282
DISASSEMBLY........................282
CLEANING...........................292
INSPECTION.........................293
ASSEMBLY...........................295
INSTALLATION........................307
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN/
REFILL............................310FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................310
INSTALLATION........................310
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................311
OPERATION..........................311
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL -
NV242HD
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................313
INSTALLATION........................313
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
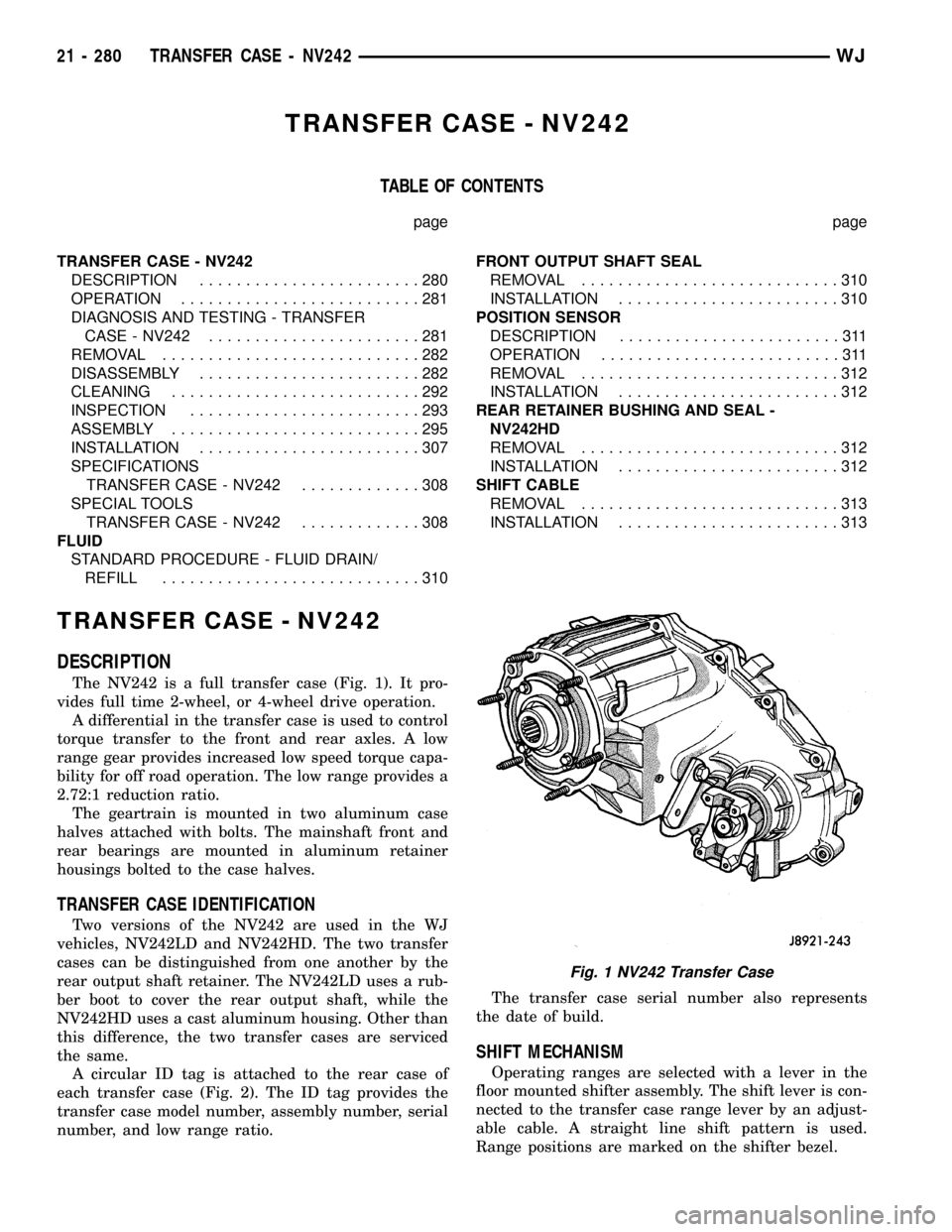
DESCRIPTION
The NV242 is a full transfer case (Fig. 1). It pro-
vides full time 2-wheel, or 4-wheel drive operation.
A differential in the transfer case is used to control
torque transfer to the front and rear axles. A low
range gear provides increased low speed torque capa-
bility for off road operation. The low range provides a
2.72:1 reduction ratio.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum retainer
housings bolted to the case halves.
TRANSFER CASE IDENTIFICATION
Two versions of the NV242 are used in the WJ
vehicles, NV242LD and NV242HD. The two transfer
cases can be distinguished from one another by the
rear output shaft retainer. The NV242LD uses a rub-
ber boot to cover the rear output shaft, while the
NV242HD uses a cast aluminum housing. Other than
this difference, the two transfer cases are serviced
the same.
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 2). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a lever in the
floor mounted shifter assembly. The shift lever is con-
nected to the transfer case range lever by an adjust-
able cable. A straight line shift pattern is used.
Range positions are marked on the shifter bezel.
Fig. 1 NV242 Transfer Case
21 - 280 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
Page 1844 of 2199

INPUT AND LOW RANGE GEARS
Inspect the low range gear pinions and pinion pins.
Replace the low range gear if any of the pins or pin-
ions are worn or damaged.
Inspect the thrust washers, retainer, and snap-
ring. Replace the snap-ring if bent, or distorted.
Replace the thrust washers and retainer if worn,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Examine the input gear carefully. Be sure the gear
teeth and bearing surfaces are in good condition.
Replace the gear if wear or damage is evident.
Check the input gear pilot bearing. Rotate the
bearing and check for roughness or noise. Also check
bearing position in the bore. The bearing should be
recessed approximately 2.5 mm (0.100 in.) below the
top edge of the bore. The bearing should not be
seated at the bottom of the bore. Replace the bearing
if worn, or roughness is evident. Replace both the
gear and bearing if the bearing is a loose fit in the
bore.
GEAR CASE AND RETAINERS
Examine both case halves and retainers carefully.
Replace any retainer or case half if wear, cracks, or
other damage is evident.
Check condition of the low range annulus gear and
the shift rail bushing in the front case (Fig. 32). The
low range annulus gear is not a serviceable part.
Replace the gear and case as an assembly if the gear
is loose, worn, or damaged. The shift rail bushing is
a serviceable part and can be replaced if necessary.
Check the bushing in the rear retainer. Replace the
bushing if worn or scored.
Examine the sealing surfaces of both case halves
and retainers. Small burrs, or scratches on these sur-
faces can be reduced with crocus cloth or a fine tooth
file.
Examine condition of the shift rail bushing in the
front case. If the bushing is worn or damaged, it can
be removed with a blind hole type puller. A replace-
ment bushing can be installed with a suitable size
driver. Recess the bushing slightly below the edge of
the bore but do not seat it all the into the case.
GEARTRAIN
Inspect the mainshaft splines, gear teeth and bear-
ing surfaces carefully for evidence of wear, or dam-
age. Replace the shaft if necessary. do not attempt to
salvage it if damaged.
The shift rail and range fork are an assembly.
Replace both parts if either is damaged. However, the
nylon pads in the fork can be replaced if worn, or
cracked.
Inspect the transfer case snap-rings closely. Do not
attempt to salvage a distorted snap-ring by straight-ening or reshaping it. Replace any snap-ring that is
distorted, or worn.
Inspect the low range gear, input gear and the gear
thrust washers retainer, and snap-ring. The low
range gear is serviced as an assembly only. Replace
the gear if the case or pinions are damaged.
During inspection, also make sure the seal surface
of the input gear is in good condition. Minor nicks on
this surface can be reduced with crocus cloth. How-
ever, replace the gear if the seal surface is severely
scored or worn.
OIL PUMP AND PROGRESSIVE COUPLING
The oil pump and progressive coupling are not ser-
viceable components. Replace the coupling as an
assembly if it is damaged. Replace the oil pump as
an assembly if the gear teeth are worn, or if the
pump has become damaged.
BEARINGS AND SEALS
The transfer case seals should be replaced during
overhaul. Use new seals in the input gear bearing
retainer, front case and rear retainer. Also replace
the yoke seal washer and the detent plug O-ring.
Check condition of each transfer case bearing.
Replace any bearing exhibiting signs of roughness,
wear, or damage.
Fig. 32 Low Range Annulus Gear Location
1 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
2 - SHIFT RAIL BUSHING
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV247 21 - 325
TRANSFER CASE - NV247 (Continued)
Page 1849 of 2199

(7) Install snap-ring to hold input/low range gear
into front bearing (Fig. 47).
(8) Clean gasket sealer residue from retainer and
inspect retainer for cracks or other damage.
(9) Applya3mm(1/8 in.) bead of Mopartgasket
maker or silicone adhesive to sealing surface of
retainer.
(10) Align cavity in seal retainer with fluid return
hole in front of case.
CAUTION: Do not block fluid return cavity on seal-
ing surface of retainer when applying MoparTgas-
ket maker or silicone adhesive sealer. Seal failure
and fluid leak can result.
(11) Install bolts to hold retainer to transfer case
(Fig. 48). Tighten to 21 N´m (16 ft. lbs.) of torque.SHIFT FORKS AND MAINSHAFT
(1) Install new sector shaft O-ring and bushing
(Fig. 49).
(2) Install shift sector (Fig. 50).
(3) Install locking clutch spring, locking clutch,
blockout spring, and range clutch sleeve, to main-
shaft as shown in (Fig. 51). Install snap ring.
(4) Install drive sprocket hub to mainshaft and
manually load the needle bearings.
(5) Install new pads on range fork, if necessary.
Fig. 47 Install Input Gear Snap-Ring
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - SNAP-RING
Fig. 48 Install Front Bearing Retainer
1 - FRONT BEARING RETAINER
Fig. 49 Sector O-Ring And Bushing Installation
1 - SECTOR BUSHING
2 - O-RING
Fig. 50 Shift Sector Installation
1 - SHIFT SECTOR
21 - 330 TRANSFER CASE - NV247WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV247 (Continued)
Page 1876 of 2199

(2) Apply silicone lubricant to a cloth and wipe it
on door seals to avoid over-spray that can soil pas-
senger's clothing.
(3) Before applying lubricant, the component
should be wiped clean. After lubrication, any excess
lubricant should be removed.
(4) The hood latch, latch release mechanism, latch
striker, and safety latch should be lubricated period-
ically.
(5) The door lock cylinders should be lubricated
twice each year (preferably autumn and spring).
(a) Spray a small amount of lock cylinder lubri-
cant directly into the lock cylinder.
(b) Apply a small amount to the key and insert
it into the lock cylinder.
(c) Rotate it to the locked position and then back
to the unlocked position several times.(d) Remove the key. Wipe the lubricant from it
with a clean cloth to avoid soiling of clothing.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRILLING AND
WELDING
When holes must be drilled or punched in an inner
body panel, verify depth of space to the outer body
panel, electrical wiring, or other components. Dam-
age to vehicle can result.
Do not weld exterior panels unless combustible
material on the interior of vehicle is removed from
the repair area. Fire or hazardous conditions, can
result.
Always have a fire extinguisher ready for use when
welding.
SPECIFICATIONS
BODY LUBRICANTS
COMPONENT SERVICE INTERVAL LUBRICANT
Door Hinges As RequiredMulti-Purpose Grease NLGI GC-LB
(Water Resistant) (1)
Door Latches As RequiredMulti-Purpose Grease NLGI GC-LB
(Water Resistant) (1)
Hood Latch, Release Mechanism and
Safety LatchAs Required
(When Performing Other
Underhood Service)Multi-Purpose Grease NLGI GC-LB 2
EP (2)
Hood Hinges As Required Engine Oil
Seat Track and Release Mechanism As RequiredMulti-Purpose Grease NLGI GC-LB 2
EP (2)
Liftgate Hinge As RequiredMulti-Purpose Grease NLGI GC-LB 2
EP (2)
Liftgate Support Arms As Required Engine Oil
Liftgate Latches As Required White Spray Lubricant (3)
Liftgate Release Handle (Pivot and Slide
Contact Surfaces)As RequiredMulti-Purpose Grease NLGI GC-LB 2
EP (2)
Window System Components As Required White Spray Lubricant (3)
Lock Cylinders Twice a Year Lock-Cylinder Lubricant (4)
Parking Brake Mechanism As RequiredMulti-Purpose Grease NLGI GC-LB 2
EP (1)
1 = Mopar Wheel Bearing Grease (High
Temp)
2 = Mopar Multi-Mileage Lubricant
3 = Mopar Spray White Lube
4 = Mopar Lock Cylinder Lubricant
WJBODY 23 - 3
BODY (Continued)
Page 2095 of 2199

Both the manual A/C Heater control panel and the
AZC control panel are serviced only as complete
units and cannot be repaired. If faulty or damaged,
the entire control panel unit must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC ZONE
CONTROL SYSTEM
The Automatic Zone Control (AZC) control module
has a system self-diagnostic mode which continuously
monitors various parameters during normal system
operation. If a system fault is detected, a current and
historical fault is recorded. When the current fault is
cleared, the historical fault remains until reset (man-
ually or automatically). Both the current and histor-
ical fault codes can be accessed through either the
front panel, or over the Programmable Communica-
tions Interface (PCI) bus using a DRBIIItscan tool,
and the appropriate diagnostic information.
The AZC control module is capable of three differ-
ent types of self-diagnostic tests, as follows:
²Fault Code Tests
²Input Circuit Tests
²Output Circuit/Actuator Tests
The information that follows describes:
²How to read the self-diagnostic display
²How to enter the AZC control module self-diag-
nostic test mode
²How to select the self-diagnostic test types
²How to perform the different tests
ENTERING THE AZC SELF-DIAGNOSTIC MODE
To enter the AZC self-diagnostic mode, perform the
following:
(1) Depress the a/c and recirc buttons at the same
time and hold. Rotate the left temperature control
knob clockwise (CW) one detent.
(2) If you continue to keep the a/c and recirc but-
tons depressed, the AZC control module will perform
a Segment Test of the Vacuum Fluorescent (VF) dis-
play. In the Segment Test you should see all of the
display segments illuminate as long as both buttons
are held. If a display segment fails to illuminate, the
vacuum fluorescent display is faulty and the a/c
heater control must be replaced.
(3) After viewing the Segment Test, release the
A/C and Recirc buttons and the display will clear
momentarily.Ifa0isdisplayed, then no faults
are set in the system.Should there be any faults,
either9current9or9historical9, all fault codes will be
displayed in ascending numerical sequence (note no
effort is made to display fault codes in chronological
order). Each fault code is displayed for one second
before the next code is displayed. Once all fault codes
have been displayed, the system will then repeat the
fault code numbers. This will continue until the left
side set temperature control is moved at least onedetent position in the CW direction or the ignition is
turned9OFF9.
FAULT CODE TESTS
Fault codes are two-digit numbers that identify a
circuit that is malfunctioning. There are two differ-
ent kinds of fault codes.
1.Current Fault Codes- Current means the
fault is present right now. There are two types of cur-
rent faults: input faults, and system faults.
2.Historical Fault Codes- Historical or stored
means that the fault occurred previously, but is not
present right now. A majority of historical fault codes
are caused by intermittent wire harness or wire har-
ness connector problems.
CURRENT FAULT CODES
Input faults 01 = IR thermister circuit
open
02 = IR thermister circuit
shorted
03 = Fan pot shorted
04 = Fan pot open
05 = Mode pot shorted
06 = Mode pot open
07 = IR sensor delta too
large
08 = Reserved
09 = Reserved
10 = One of four motor
drivers has drive9A9
shorted to ground
11 = Engine air intake
temperature Buss
message missing
12 = Country code Buss
message missing
24 - 18 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)