2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE can bus
[x] Cancel search: can busPage 1251 of 2199
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise, the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
REMOVAL).
(3) Secure the throttle in the wide-open position.
(4) Disconnect the ignition coil.
(5) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(6) Record the compression pressure on the third
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the
correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing)
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM HOT COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn OFF the
engine.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
Perform the test procedure on each cylinder accord-
ing to the tester manufacturer's instructions. While
testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through
the throttle body, tailpipe or oil filler cap opening.
Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART .
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLYStuck or broken piston rings;
cracked piston; worn rings and/or
cylinder wallInspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
9 - 8 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1262 of 2199

(2) Lift cover up and position to the side.
(3) Remove air cleaner element.
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
(1) Clean inside of air cleaner housing before
installing new element.
(2) Install air cleaner element into housing.
(3) Latch clips and clamp cover down to secure. Be
sure air cleaner cover is properly seated to air
cleaner housing.
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL - 4.0L
(1) Disconnect air cleaner cover-to-air duct clamp
(Fig. 6).
(2) Disconnect air duct at housing.
(3)Each of the 3 air cleaner housing mount-
ing bolts is attached with 2 nuts (an upper nut
and lower nut). DO NOT REMOVE BOLTS. To
prevent stripping bolts, only remove lower
nuts. The lower housing nuts are located under
left front inner fender (Fig. 6).
(a) To gain access to lower nuts, raise vehicle.
(b) Remove clips retaining rubber inner fender
shield.
(c) Pry back shield enough to gain access to
lower nuts.
(d) Remove 3 nuts.
(e) Remove air cleaner assembly from vehicle.
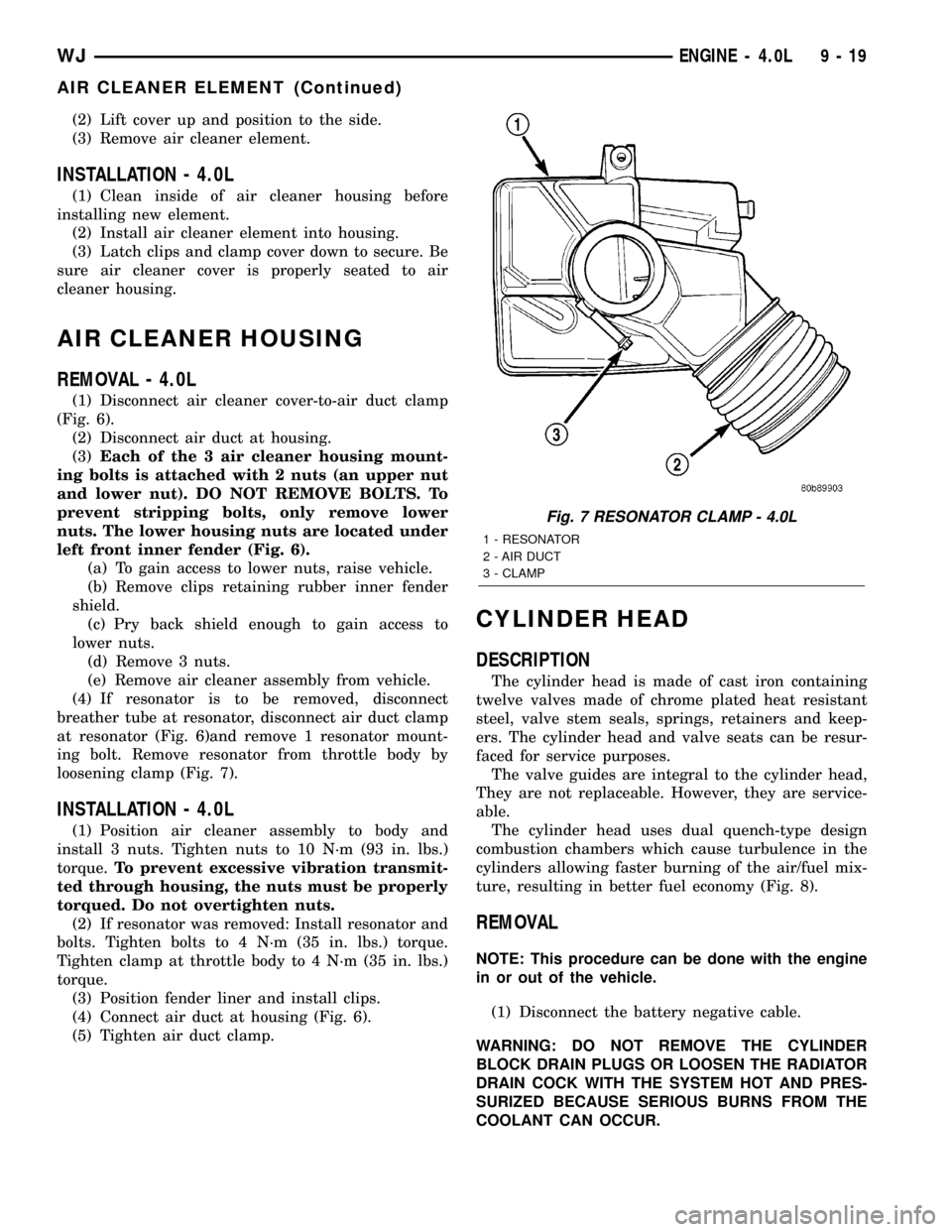
(4) If resonator is to be removed, disconnect
breather tube at resonator, disconnect air duct clamp
at resonator (Fig. 6)and remove 1 resonator mount-
ing bolt. Remove resonator from throttle body by
loosening clamp (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
(1) Position air cleaner assembly to body and
install 3 nuts. Tighten nuts to 10 N´m (93 in. lbs.)
torque.To prevent excessive vibration transmit-
ted through housing, the nuts must be properly
torqued. Do not overtighten nuts.
(2) If resonator was removed: Install resonator and
bolts. Tighten bolts to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
Tighten clamp at throttle body to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Position fender liner and install clips.
(4) Connect air duct at housing (Fig. 6).
(5) Tighten air duct clamp.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head is made of cast iron containing
twelve valves made of chrome plated heat resistant
steel, valve stem seals, springs, retainers and keep-
ers. The cylinder head and valve seats can be resur-
faced for service purposes.
The valve guides are integral to the cylinder head,
They are not replaceable. However, they are service-
able.
The cylinder head uses dual quench-type design
combustion chambers which cause turbulence in the
cylinders allowing faster burning of the air/fuel mix-
ture, resulting in better fuel economy (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure can be done with the engine
in or out of the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAIN COCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE
COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
Fig. 7 RESONATOR CLAMP - 4.0L
1 - RESONATOR
2 - AIR DUCT
3 - CLAMP
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 19
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT (Continued)
Page 1264 of 2199

CLEANING
Thoroughly clean the engine cylinder head and cyl-
inder block mating surfaces. Clean the intake and
engine exhaust manifold and engine cylinder head
mating surfaces. Remove all gasket material and car-
bon.
Check to ensure that no coolant or foreign material
has fallen into the tappet bore area.
Remove the carbon deposits from the combustion
chambers and top of the pistons.
INSPECTION
Use a straightedge and feeler gauge to check the
flatness of the engine cylinder head and block mating
surfaces.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: This procedure can be done with the engine
in or out of the vehicle.
The engine cylinder head gasket is a composition
gasket. The gasket is to be installed DRY.DO NOT
use a gasket sealing compound on the gasket.
If the engine cylinder head is to be replaced and
the original valves used, measure the valve stem
diameter. Only standard size valves can be used with
a service replacement engine cylinder head unless
the replacement head valve stem guide bores are
reamed to accommodate oversize valve stems.
Remove all carbon buildup and reface the valves.
(1) Remove the shop towels from the cylinder
bores. Coat the bores with clean engine oil.
(2) Position the engine cylinder head gasket (with
the numbers facing up) using the alignment dowels
in the cylinder block, to position the gasket.
CAUTION: Engine cylinder head bolts should be
reused only once. Replace the head bolts if they
were used before or if they have a paint dab on the
top of the bolt.
(3) With bolt No.14 held in place (tape around
bolt), install the engine cylinder head over the same
dowels used to locate the gasket. Remove the tape
from bolt No.14.
(4) Coat the threads of stud bolt No.11 with Loc-
tite 592 sealant, or equivalent.
(5) Tighten the engine cylinder head bolts in
sequence according to the following procedure (Fig.
10).
CAUTION: During the final tightening sequence,
bolt No.11 will be tightened to a lower torque than
the rest of the bolts. DO NOT overtighten bolt
No.11.(a) Tighten all bolts in sequence (1 through 14)
to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.) torque.
(b) Tighten all bolts in sequence (1 through 14)
to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(c) Check all bolts to verify they are set to 61
N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(d) Tighten bolts in sequence:
²Bolts 1 through 10 to 149 N´m (110 ft. lbs.)
torque.
²Bolt 11 to 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Bolts 12 through 14 to 149 N´m (110 ft. lbs.)
torque.
CYLINDER HEAD BOLTS
POSITION DESCRIPTION
1,4,5,12,13 1/2 in.-13 BOLT
8,9 1/2 in.-13 BOLT WITH DOWEL
POINT
2,3,6,7,10,11,14 1/2 in.-13 WITH 7/16 in.-14 STUD
END
All bolts are 12 point drives for rocker cover clearance
(e) Check all bolts in sequence to verify the cor-
rect torque.
(f) If not already done, clean and mark each bolt
with a dab of paint after tightening. Should you
encounter bolts which were painted in an earlier
service operation, replace them.
(6) Install the spark plugs (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG - INSTAL-
LATION).
(7) Connect the temperature sending unit wire
connector.
(8) Install the ignition coil rail (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/COIL RAIL -
INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the intake and exhaust manifolds (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the fuel line.
(11) Attach the power steering pump and bracket.
Fig. 10 Engine Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening
Sequence
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 21
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1271 of 2199

VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
The valve springs (Fig. 25) are made of high
strength silicon chrome spring steel. The springs are
common for both intake and exhaust valves.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VALVE SPRING
TENSION TEST
Clean all carbon deposits from the combustion
chambers, valve ports, valve stems, valve stem
guides and head.
Use a universal Valve Spring Tester and a torque
wrench to test each valve spring for the specified ten-
sion value (Fig. 26).
Replace valve springs that are not within specifica-
tions.
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure can be done with the engine
cylinder head installed on the block.
Inspect the valve stems, especially the grooves. An
Arkansas smooth stone should be used to remove
nicks and high spots.Each valve spring is held in place by a retainer
and a set of conical valve locks. The locks can be
removed only by compressing the valve spring.
(1) Remove the engine cylinder head cover (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
Fig. 24 Valve
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
Fig. 25 VALVE AND KEEPER CONFIGURATION 4.0L
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
Fig. 26 Valve Spring Tester
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - VALVE SPRING TESTER
9 - 28 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
VALVE STEM SEALS (Continued)
Page 1307 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING)ÐPERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fig. 1 Engine Identification Location
1 - VEHICLE VIN NUMBER LOCATION
2 - CYLINDER BLOCK RIGHT HAND SIDE
3 - CYLINDER BORE #2
9 - 64 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1328 of 2199

(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the left side
exhaust manifold.
(4) Drain the engine coolant. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove the intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove accessory drive belt. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(9) Remove the power steering pump and set
aside.
(10) Rotate the crankshaft until the damper tim-
ing mark is aligned with TDC indicator mark (Fig.
9).
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 85
CYLINDER HEAD - LEFT (Continued)
Page 1341 of 2199

VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negitive cable.
(2) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the right side
exhaust manifold.
(4) Drain the engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove oil fill housing from cylinder head.
(9) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(10) Rotate the crankshaft until the damper tim-
ing mark is aligned with TDC indicator mark (Fig.
9).
(11) Verify the V8 mark on the camshaft sprocket
is at the 12 o'clock position (Fig. 11). Rotate the
crankshaft one turn if necessary.
(12) Remove the crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(13) Remove the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(14) Lock the secondary timing chains to the idler
sprocket using Special Tool 8515 (Fig. 10).
NOTE: Mark the secondary timing chain prior to
removal to aid in installation.
(15) Mark the secondary timing chain, one link on
each side of the V8 mark on the camshaft drive gear
(Fig. 11).
(16) Remove the right side secondary chain ten-
sioner (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIM-
ING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(17) Remove the cylinder head access plug (Fig.
29).
(18) Remove the right side secondary chain guide
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
9 - 98 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT (Continued)
Page 1373 of 2199

If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks
in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
Use an engine oil that is API Service Grade Certi-
fied. MOPARtprovides engine oils that conform to
this service grade.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity of engine oil. Use only engine oils with multi-
ple viscosities such as 5W-30 or 10W-30 in the 4.7L
engines.The 4.7L H.O. uses 10W-30 oil only.These
are specified with a dual SAE viscosity grade which
indicates the cold-to-hot temperature viscosity range.
Select an engine oil that is best suited to your par-
ticular temperature range and variation (Fig. 90).
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. The designation of ENERGY CON-
SERVING is located on the label of an engine oil con-
tainer.
CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 91).
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator is located on the
right side of the the 4.7L engine. (Fig. 92).
Fig. 90 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity - 4.7L
Engine
9 - 130 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
LUBRICATION (Continued)