2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE check transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: check transmission fluidPage 199 of 2199

OPERATION
The master cylinder bore contains a primary and
secondary piston. The primary piston supplies
hydraulic pressure to the front brakes. The secondary
piston supplies hydraulic pressure to the rear brakes.
The master cylinder reservoir stores reserve brake
fluid for the hydraulic brake circuits.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MASTER
CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER
NOTE: Inspect and repair any external fluid leaks
before performing test.
(1) Start engine and check booster vacuum hose
connections. A hissing noise indicates vacuum leak.
Correct any vacuum leak before proceeding.
(2)
Stop engine and shift transmission into Neutral.
(3) Pump brake pedal until all vacuum reserve in
booster is depleted.
(4) Press and hold brake pedal under light foot
pressure. The pedal should hold firm, if the pedal
falls away the master cylinder or HCU may be faulty
(internal leakage).
(5) Start engine and note pedal action. It should
fall away slightly under light foot pressure then hold
firm. If no pedal action is discernible, power booster,
vacuum supply, or vacuum check valve is faulty. Pro-
ceed to the POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST.
(6) If the POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
passes, rebuild booster vacuum reserve as follows:
Release brake pedal. Increase engine speed to 1500
rpm, close the throttle and turn off the engine.
(7) Wait a minimum of 90 seconds and try brake
action again. Booster should provide two or more vac-
uum assisted pedal applications. If vacuum assist is
not provided, some component of the booster is faulty.
POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
(1) Connect vacuum gauge to booster check valve
with short length of hose and T-fitting (Fig. 48).
(2) Start and run engine at curb idle speed for one
minute.
(3) Observe the vacuum supply. If vacuum supply
is not adequate, repair vacuum supply.
(4) Clamp hose shut between vacuum source and
check valve.
(5) Stop engine and observe vacuum gauge.
(6) If vacuum drops more than one inch HG (33
millibars) within 15 seconds, booster diaphragm,
check valve or check valve seal/grommet is faulty.
POWER BOOSTER CHECK VALVE TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose from check valve.
(2)
Remove check valve and valve seal from booster.
(3) Use a hand operated vacuum pump for test.(4) Apply 51-67 kPa (15-20 in.) vacuum at large
end of check valve (Fig. 49).
(5) Vacuum should hold steady. If gauge on pump
indicates vacuum loss the check valve and seal
should be replaced.
Fig. 48 Typical Booster Vacuum Test Connections
1 - TEE FITTING
2 - SHORT CONNECTING HOSE
3 - CHECK VALVE
4 - CHECK VALVE HOSE
5 - CLAMP TOOL
6 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
7 - VACUUM GAUGE
Fig. 49 Vacuum Check Valve And Seal
1 - BOOSTER CHECK VALVE
2 - APPLY TEST VACUUM HERE
3 - VALVE SEAL
5 - 24 BRAKES - BASEWJ
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 234 of 2199

Carefully remove radiator pressure cap from filler
neck and check coolant level. Push down on cap to
disengage it from stop tabs. Wipe inside of filler neck
and examine lower inside sealing seat for nicks,
cracks, paint, dirt and solder residue. Inspect radia-
tor-to- reserve/overflow tank hose for internal
obstructions. Insert a wire through the hose to be
sure it is not obstructed.
Inspect cams on outside of filler neck. If cams are
damaged, seating of pressure cap valve and tester
seal will be affected.
Attach pressure tester (7700 or an equivalent) to
radiator filler neck (Fig. 6).
Operate tester pump to apply 103.4 kPa (15 psi)
pressure to system. If hoses enlarge excessively or
bulges while testing, replace as necessary. Observe
gauge pointer and determine condition of cooling sys-
tem according to following criteria:
Holds Steady:If pointer remains steady for two
minutes, serious coolant leaks are not present in sys-
tem. However, there could be an internal leak that
does not appear with normal system test pressure. If
it is certain that coolant is being lost and leaks can-
not be detected, inspect for interior leakage or per-
form Internal Leakage Test.
Drops Slowly:Indicates a small leak or seepage
is occurring. Examine all connections for seepage or
slight leakage with a flashlight. Inspect radiator,
hoses, gasket edges and heater. Seal small leak holes
with a Sealer Lubricant (or equivalent). Repair leak
holes and inspect system again with pressure
applied.
Drops Quickly:Indicates that serious leakage is
occurring. Examine system for external leakage. If
leaks are not visible, inspect for internal leakage.
Large radiator leak holes should be repaired by a
reputable radiator repair shop.INTERNAL LEAKAGE INSPECTION
Remove engine oil pan drain plug and drain a
small amount of engine oil. If coolant is present in
the pan, it will drain first because it is heavier than
oil. An alternative method is to operate engine for a
short period to churn the oil. After this is done,
remove engine dipstick and inspect for water glob-
ules. Also inspect transmission dipstick for water
globules and transmission fluid cooler for leakage.
WARNING: WITH RADIATOR PRESSURE TESTER
TOOL INSTALLED ON RADIATOR, DO NOT ALLOW
PRESSURE TO EXCEED 110 KPA (20 PSI). PRES-
SURE WILL BUILD UP QUICKLY IF A COMBUSTION
LEAK IS PRESENT. TO RELEASE PRESSURE,
ROCK TESTER FROM SIDE TO SIDE. WHEN
REMOVING TESTER, DO NOT TURN TESTER MORE
THAN 1/2 TURN IF SYSTEM IS UNDER PRESSURE.
Operate engine without pressure cap on radiator
until thermostat opens. Attach a Pressure Tester to
filler neck. If pressure builds up quickly it indicates a
combustion leak exists. This is usually the result of a
cylinder head gasket leak or crack in engine. Repair
as necessary.
If there is not an immediate pressure increase,
pump the Pressure Tester. Do this until indicated
pressure is within system range of 110 kPa (16 psi).
Fluctuation of gauge pointer indicates compression or
combustion leakage into cooling system.
Because the vehicle is equipped with a catalytic
converter,do notremove spark plug cables or short
out cylinders to isolate compression leak.
If the needle on dial of pressure tester does not
fluctuate, race engine a few times to check for an
abnormal amount of coolant or steam. This would be
emitting from exhaust pipe. Coolant or steam from
exhaust pipe may indicate a faulty cylinder head gas-
ket, cracked engine cylinder block or cylinder head.
A convenient check for exhaust gas leakage into
cooling system is provided by a commercially avail-
able Block Leak Check tool. Follow manufacturers
instructions when using this product.
COMBUSTION LEAKAGE TEST - WITHOUT
PRESSURE TESTER
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE CYLINDER BLOCK
DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAIN-
COCK WITH SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
Drain sufficient coolant to allow thermostat
removal. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE
COOLANT THERMOSTAT - REMOVAL). Remove
Fig. 6 Pressure Testing Cooling SystemÐTypical
1 - TYPICAL COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE TESTER
WJCOOLING 7 - 11
COOLING (Continued)
Page 1252 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐREAR SEAL AREA
LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs, oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as outlined in (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICA-
TION - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks or
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is specially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled. Refer to the service DiagnosisÐMechani-
cal, under the Oil Leak row, for components
inspections on possible causes and corrections.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL
SEAL - REAR - REMOVAL), for proper replacement
procedures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANT
MopartGasket Sealant is a slow drying, perma-
nently soft sealer. This material is recommended for
sealing threaded fittings and gaskets against leakage
of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 9
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1317 of 2199
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Coil Over Plugs
(10) Install generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(11) Install radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR - INSTALLATION).
(12) Install A/C condenser (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C CON-
DENSER - INSTALLATION).
(13) Connect radiator lower hose at the thermostat
housing.
(14) Connect the transmission oil cooler lines to
the radiator.
(15) Install A/C compressor. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - INSTALLATION).
(16) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION) and radiator fan (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(17) Install breathers, then connect tube to both
crankcase breathers (Fig. 5).
(18) Connect throttle and speed control cables.
(19) Install throttle body resonator assembly and
inlet hose.
(20) Raise vehicle.
(21) Connect two ground straps on the lower left
hand side of the engine and one ground strap on the
lower right side.
(22) Install torque converter bolts.
(23) Connect crankshaft position sensor (Fig. 4).
(24) Install starter.
(25) Install rubber splash shield.
CAUTION: The structural cover requires a specific
torque sequence. Failure to follow this sequence
may cause severe damage to the cover.
(26) Install structural cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER - INSTAL-
LATION).
(27) Install exhaust crossover pipe.
(28) Install engine block heater power cable, If
equipped.
(29) Lower vehicle.
(30) Check and fill engine oil (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES - SPECIFI-
CATIONS).
(31) Recharge the A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(32) Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(33) Connect the battery negative cable.
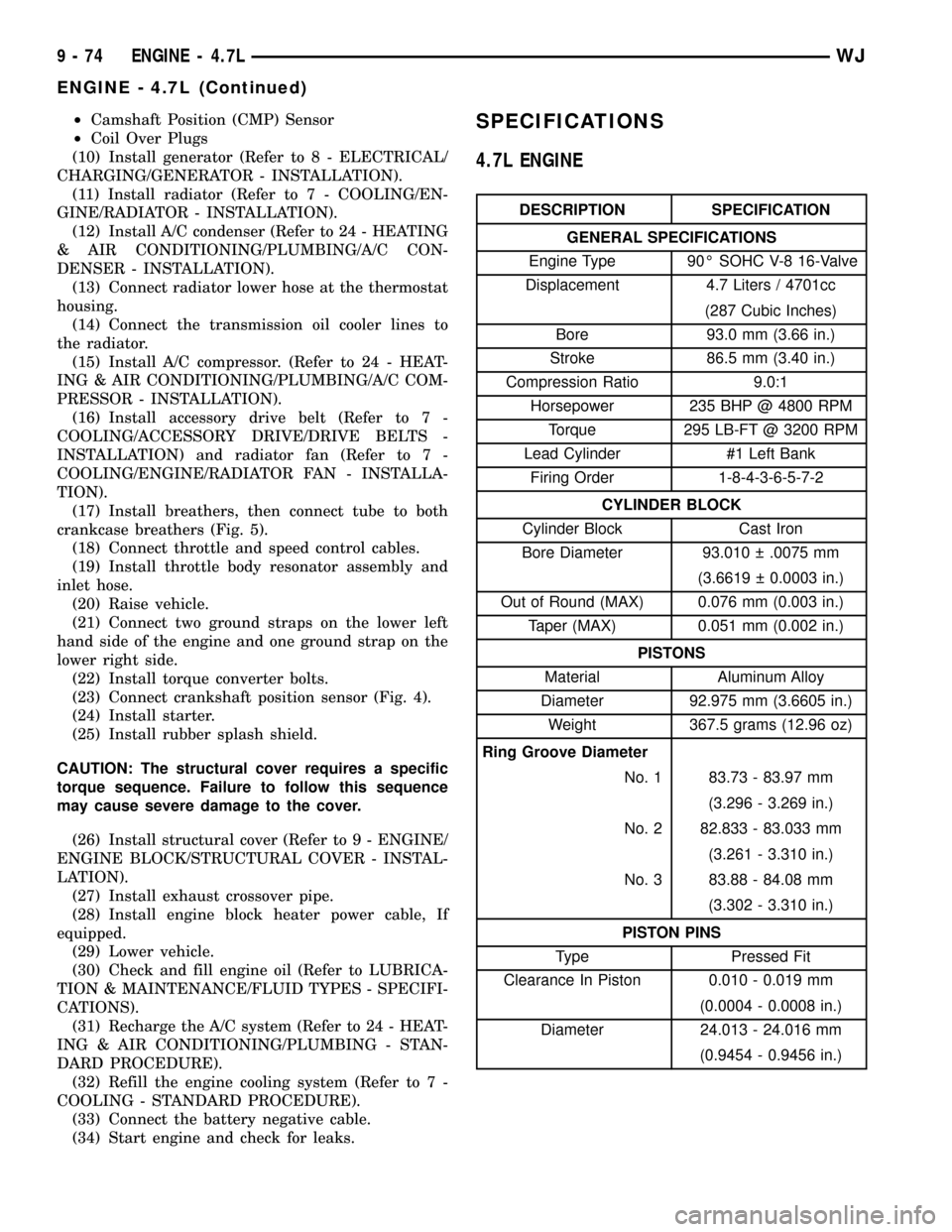
(34) Start engine and check for leaks.SPECIFICATIONS
4.7L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Engine Type 90É SOHC V-8 16-Valve
Displacement 4.7 Liters / 4701cc
(287 Cubic Inches)
Bore 93.0 mm (3.66 in.)
Stroke 86.5 mm (3.40 in.)
Compression Ratio 9.0:1
Horsepower 235 BHP @ 4800 RPM
Torque 295 LB-FT @ 3200 RPM
Lead Cylinder #1 Left Bank
Firing Order 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2
CYLINDER BLOCK
Cylinder Block Cast Iron
Bore Diameter 93.010 .0075 mm
(3.6619 0.0003 in.)
Out of Round (MAX) 0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Taper (MAX) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
PISTONS
Material Aluminum Alloy
Diameter 92.975 mm (3.6605 in.)
Weight 367.5 grams (12.96 oz)
Ring Groove Diameter
No. 1 83.73 - 83.97 mm
(3.296 - 3.269 in.)
No. 2 82.833 - 83.033 mm
(3.261 - 3.310 in.)
No. 3 83.88 - 84.08 mm
(3.302 - 3.310 in.)
PISTON PINS
Type Pressed Fit
Clearance In Piston 0.010 - 0.019 mm
(0.0004 - 0.0008 in.)
Diameter 24.013 - 24.016 mm
(0.9454 - 0.9456 in.)
9 - 74 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1376 of 2199

NOTE: When installing oil pan gasket/windage tray,
start four pan bolts at each corner before tightening
oil pickup tube. This will keep pan gasket in align-
ment.
(3) Install oil pump pick-up tube using a new
O-ring. First tighten bolt at O-ring end of tube to 28
N´m (20 ft. lbs.). Tighten remain tube support fasten-
ers to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install oil pan and tighten fasteners to 15 N´m
(11 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 95).
(5) Reconnect transmission oil cooler lines to oil
pan stud bolt.
(6) Install starter (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install exhaust system Y-pipe.
(8) Install structural cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER - INSTAL-
LATION).
(9) Lower vehicle.
(10) Fill engine with proper amount of oil (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
(11) Connect negative cable to battery.
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The 3±wire, solid-state engine oil pressure sensor
(sending unit) is located in an engine oil pressure
gallery.
OPERATION
The oil pressure sensor uses three circuits. They are:
²A 5±volt power supply from the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM)
²A sensor ground through the PCM's sensor
return
²
A signal to the PCM relating to engine oil pressure
The oil pressure sensor has a 3±wire electrical
function very much like the Manifold Absolute Pres-
sure (MAP) sensor. Meaning different pressures
relate to different output voltages.
A 5±volt supply is sent to the sensor from the PCM
to power up the sensor. The sensor returns a voltage
signal back to the PCM relating to engine oil pres-
sure. This signal is then transferred (bussed) to the
instrument panel on either a CCD or PCI bus circuit
(depending on vehicle line) to operate the oil pressure
gauge and the check gauges lamp. Ground for the
sensor is provided by the PCM through a low-noise
sensor return.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove front splash shield.
(4) Disconnect oil pressure sender wire (Fig. 96).
(5) Remove the pressure sender (Fig. 96).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install oil pressure sender.
(2) Connect oil pressure sender wire.
(3) Install front splash shield.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 95 Oil Pan Tightening Sequence
Fig. 96 Oil Pressure Sending Unit
1 - BELT
2 - OIL PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - OIL FILTER
4 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 133
OIL PAN (Continued)
Page 1510 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PUMP LEAKAGE
(1) Possible areas of pump leakage (Fig. 3).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INITIAL OPERATION
- 4.0L
WARNING: THE FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE
CHECKED WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY
FROM MOVING COMPONENTS.
CAUTION: Use MOPAR Power Steering Fluid or
equivalent. Do not use automatic transmission fluid
and do not overfill.
Wipe filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal ambient temperature.
(1) Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level
and let the fluid settle for at least two minutes.
(2) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds
then turn engine off.
(3) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above proce-
dure until the fluid level remains constant after run-
ning the engine.
(4) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(5) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops at least 20 times.(6) Check the fluid level add if necessary.
(7) Lower the vehicle, start the engine and turn
the steering wheel slowly from lock to lock.
(8) Stop the engine and check the fluid level and
refill as required.
(9) If the fluid is extremely foamy or milky look-
ing, allow the vehicle to stand a few minutes and
repeat the procedure.
CAUTION: Do not run a vehicle with foamy fluid for
an extended period. This may cause pump damage.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INITIAL OPERATION
- 4.7L
WARNING: THE FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE
CHECKED WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY
FROM MOVING COMPONENTS.
NOTE: Remove as much of the old fluid out of the
system as possible with a suction tool or by remov-
ing a hose, When a component has failed. Then
refill it with fresh fluid until it is clean. This may
have to be done more than once.
CAUTION: Use MOPAR Power Steering Fluid or
equivalent. Do not use automatic transmission fluid
and do not overfill.
Wipe filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal ambient temperature.
(1) Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level
and let the fluid settle for at least two minutes.
(2) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds
then turn engine off.
(3) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above proce-
dure until the fluid level remains constant after run-
ning the engine.
(4) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(5) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops at least 20 times.
(6) Check the fluid level add if necessary.
(7) Lower the vehicle, start the engine, and use
the DRB III to activate the hydraulic fan on full fan
operation.
(8)
Turn the steering wheel slowly from lock to lock.
(9) Stop the engine, check the fluid level and refill
as required and repeat the process
CAUTION: Do not run a vehicle with foamy fluid for
an extended period. This may cause pump damage.
(10) If the fluid is extremely foamy or milky look-
ing, allow the vehicle to stand a few minutes and
repeat the procedure.
Fig. 3 4.0L Power Steering Pump
WJPUMP 19 - 33
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1520 of 2199

TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE..........1
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE......177TRANSFER CASE - NV242................280
TRANSFER CASE - NV247................315
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION......................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY . 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD
TESTING............................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST.....................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH AND BAND
OPERATION.........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK.................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIAGNOSIS
CHARTS............................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR......................26
REMOVAL.............................27
DISASSEMBLY.........................29
CLEANING............................34
INSPECTION..........................34
ASSEMBLY............................34
INSTALLATION.........................41
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS..............43
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION......................55
SPECIAL TOOLS
RE TRANSMISSIONS..................57
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................60
OPERATION...........................60
INSPECTION..........................60BANDS
DESCRIPTION.........................61
OPERATION...........................61
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - BANDS................62
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION.........................63
OPERATION...........................63
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK.......63
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK....................64
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION.........................65
OPERATION...........................65
REMOVAL.............................67
INSTALLATION.........................67
EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING
REMOVAL.............................68
INSTALLATION.........................68
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL.............................69
INSTALLATION.........................69
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL..............69
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID........................69
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION.....................70
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK.............................70
WJTRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE 21 - 1
Page 1521 of 2199
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER REPLACEMENT................71
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL................................72
FRONT CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION.........................73
OPERATION...........................74
DISASSEMBLY.........................74
INSPECTION..........................74
ASSEMBLY............................74
FRONT SERVO
DESCRIPTION.........................77
OPERATION...........................77
DISASSEMBLY.........................77
CLEANING............................77
INSPECTION..........................77
ASSEMBLY............................77
GEARSHIFT CABLE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE..............................78
REMOVAL.............................78
INSTALLATION.........................79
ADJUSTMENTS - GEARSHIFT CABLE.......79
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................80
OPERATION...........................80
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP
VOLUME CHECK......................81
DISASSEMBLY.........................81
CLEANING............................83
INSPECTION..........................83
ASSEMBLY............................83
OUTPUT SHAFT FRONT BEARING
REMOVAL.............................85
INSTALLATION.........................85
OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING
REMOVAL.............................85
INSTALLATION.........................85
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION.........................86
OPERATION...........................86
OVERDRIVE OFF SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................86
OPERATION...........................86
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERDRIVE
ELECTRICAL CONTROLS...............87
OVERDRIVE UNIT
REMOVAL.............................87
DISASSEMBLY.........................88
CLEANING............................95
INSPECTION..........................95
ASSEMBLY............................95
INSTALLATION........................104
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE
PISTON RETAINER
DESCRIPTION........................105
OPERATION..........................105DISASSEMBLY........................106
CLEANING...........................106
INSPECTION.........................106
ASSEMBLY...........................106
PARK LOCK CABLE
REMOVAL............................108
INSTALLATION........................108
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PARK/NEUTRAL
POSITION SWITCH...................109
REMOVAL............................109
INSTALLATION........................109
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION........................110
OPERATION..........................110
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT
DESCRIPTION........................112
OPERATION..........................112
DISASSEMBLY........................112
INSPECTION..........................113
ASSEMBLY...........................113
REAR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION........................118
OPERATION..........................118
DISASSEMBLY........................119
CLEANING...........................119
INSPECTION.........................120
ASSEMBLY...........................120
REAR SERVO
DESCRIPTION........................122
OPERATION..........................122
DISASSEMBLY........................122
CLEANING...........................122
ASSEMBLY...........................123
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................123
OPERATION..........................123
REMOVAL............................123
INSTALLATION........................125
SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION........................125
OPERATION..........................126
SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................126
OPERATION..........................126
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION........................126
ADJUSTMENTS - TRANSMISSION THROTTLE
VALVE CABLE.......................126
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................128
OPERATION..........................132
REMOVAL............................133
INSTALLATION........................133
TORQUE CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION........................134
OPERATION..........................134
21 - 2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ