2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE engine coolant
[x] Cancel search: engine coolantPage 2122 of 2199

NOTE: The blend door sub-assembly is attached to
the housing with 2 screws, and may be removed for
service (Fig. 19).
ASSEMBLY
(1) Place the top half of the HVAC housing on the
bottom half. Be certain that each of the door pivot
pins align with the pivot holes in the HVAC housing.
(2) Install the 10 screws that secure the two hous-
ing halves to each other. Tighten the HVAC housing
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Attach the wire harness electrical connector(s)
to the mounts on the lower case at the blower motor
end of the unit.
(4) Install the 5 clips that secure the two housing
halves to each other. Check doors for binding after
replacement, and after assembly of housing.
(5) Install the screw with plastic washer holding
the lever assembly to the upper case section.
(6) Install the mode door actuator on the left side
of the housing.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN PLUMBING BEFORE PERFORMING THE
FOLLOWING OPERATION. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION)Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) Position the HVAC housing to the dash panel.
Be certain that the evaporator condensate drain tube
and the housing mounting studs are inserted into
their correct mounting holes.
(2) Install the HVAC housing mounting nuts to the
studs on the passenger compartment side of the dash
panel. Tighten the nuts to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the HVAC housing wire harness con-
nectors.
(4) Reinstall the rear floor heat ducts to the center
floor heat duct outlets.
(5) Install and tighten the nuts onto the HVAC
housing mounting studs on the engine compartment
side of the dash panel. Tighten the nuts to 7 N´m (60
in. lbs.).
(6) Reinstall the PCM to the passenger side dash
panel in the engine compartment. Refer to Electronic
Control Modules for the procedures.
(7) Reinstall the coolant reserve/overflow bottle to
the passenger side inner fender shield. Refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures.
(8) If the vehicle is equipped with the manual tem-
perature control system, connect the HVAC system
vacuum supply line connector to the tee fitting near
the heater core tubes.
(9) Unclamp/unplug the heater core hoses and
tubes. Connect the heater hoses to the heater core
tubes and fill the engine cooling system. Refer to
Cooling for the procedures.
(10) Unplug or remove the tape from the suction
line and the evaporator outlet tube fittings. Connect
the suction line to the evaporator outlet tube.
Tighten retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(11) Unplug or remove the tape from the liquid
line and the evaporator inlet tube fittings. Connect
the liquid line to the evaporator inlet tube. Tighten
retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(12) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
Fig. 19 BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY (AZC)
1 - PASSENGER SIDE BLEND DOOR
2 - BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY
3 - DOOR PIVOT SHAFT BUSHING
4 - DOOR SHAFT LEVER
5 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR
WJDISTRIBUTION 24 - 45
HVAC HOUSING (Continued)
Page 2148 of 2199

HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The heater core is located in the HVAC housing,
under the instrument panel. It is a heat exchanger
made of rows of tubes and fins.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through heater hoses
to the heater core at all times. As the coolant flows
through the heater core, heat removed from the
engine is transferred to the heater core fins and
tubes. Air directed through the heater core picks up
the heat from the heater core fins. The temperature
control door allows control of the heater output air
temperature by controlling how much of the air flow-
ing through the HVAC housing is directed through
the heater core. The blower motor speed controls the
volume of air flowing through the HVAC housing.
The heater core cannot be repaired and, if faulty or
damaged, it must be replaced. Refer to Cooling for
more information on the engine cooling system, the
engine coolant and the heater hoses.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
(1) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the foam gasket surrounding the core
tubes.
NOTE: Notice the orientation of the irregularly
shaped gasket on the tubes. The gasket must be
placed correctly to ensure proper sealing against
the body during reinstallation.(3)
Remove the screws and retainers that secure the
heater core and tubes to the HVAC housing (Fig. 12).
(4) Remove the mode door actuator if necessary,
for clearance to remove the core.
(5) Lift the heater core straight up and out of the
HVAC housing (Fig. 13).
(6) When replacing individual tubes, loosen and
remove the round tube-to-core clamp, and pull tube
from core.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
Fig. 12 HEATER CORE, TUBES, AND RETAINERS
1 - TUBE-TO-CORE CLAMPS
2 - GROUND STRAP
3 - HVAC HOUSING
4 - TUBE RETAINERS AND SCREWS
5 - HEATER CORE
WJPLUMBING 24 - 71
Page 2153 of 2199

VISCOUS HEATER
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The diesel engine has an engine mounted mechan-
ical device called a Viscous Heater that is used to
heat the coolant coming from the engine to the
heater core. The Viscous Heater is driven by the
engine fan belt and has a electro-mechanical clutch
which is controlled by the HVAC control unit.
DESCRIPTION - VISCOUS HEATER CLUTCH
The basic viscous heater clutch assembly consists
of a stationary electromagnetic coil, a hub bearing
and pulley assembly and a clutch plate. The electro-
magnetic coil unit and the hub bearing and pulley
assembly are each retained on the nose of the com-
pressor front housing with snap rings (Fig. 17). The
clutch plate is keyed to the viscous heater shaft and
secured with a nut. These components provide the
means to engage and disengage the viscous heater
from the engine accessory drive belt.
OPERATION
OPERATION - VISCOUS HEATER
The Viscous Heater is driven by the engine fan
belt. The Viscous Heater has an electro-mechanical
clutch that receives a signal from the HVAC control
head and the Viscous Heater controller that ener-
gizes and engages the clutch. Once engaged theclutch allows the Viscous Heater to increase the tem-
perature of the coolant flowing to the heater core,
which provides heat the passenger compartment
quicker than normal engines without the Viscous
Heater. The Viscous Heater generates heat by means
of friction which heats a special Silicon Oil within its
housing which is then transferred to the engine cool-
ant when the coolant passes over fins within the
pump. Please note that the coolant is isolated from
the silicon oil within the pump housing. When
demand for passenger compartment heat decreases
the Viscous Heater clutch will receive an input from
the Viscous heater controller to disengage.
OPERATION - VISCOUS HEATER CLUTCH
When the clutch coil is energized, it magnetically
draws the clutch into contact with the pulley and
drives the viscous heater shaft. When the coil is not
energized the pulley freewheels on the clutch hub
bearing, which is part of the pulley. The viscous
heater clutch and coil are the only serviced parts on
the viscous heater assembly. If the viscous heater is
inoperative or damaged the entire assembly must be
replaced. The viscous heater clutch engagement is
controlled by several components: the viscous heater
controller, the engine powertrain control module and
the HVAC control head.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - VISCOUS HEATER
(1) Drain the engine coolant(Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Remove the engine accessory drive belt(Refer to
7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the heater hose clamps at the Viscous
Heater.
(4) Remove the heater hoses from the Viscous
Heater.
(5) Unplug the Viscous Heater clutch electrical
connector.
(6) Remove the bolts holding the Viscous Heater to
the mounting bracket.
(7) Remove the Viscous Heater from the vehicle.
REMOVAL - VISCOUS HEATER CLUTCH
(1) The viscous heater clutch can be serviced in
the vehicle and the cooling system does not have to
be drained.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove the serpentine drive belt(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
Fig. 17 CLUTCH ASSEMBLY- typical
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - SHAFT KEY
3 - PULLEY
4 - COIL
5 - CLUTCH SHIMS
6 - SNAP RING
7 - SNAP RING
24 - 76 PLUMBINGWJ
Page 2155 of 2199

(14) Remove the snap ring from the hub and
remove the clutch field coil (Fig. 22). Slide the clutch
field coil off of the hub.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
(1) Install Viscous Heater to engine mounting
bracket.
(2) Install the Viscous Heater mounting bolts and
tighten to 33 N´m ( 25 ft. lbs.).
(3) Plug the wiring harness electrical connector to
the Viscous Heater clutch.
(4) Install heater hoses to the Viscous Heater con-
nections.
(5) Install heater hose clamps to Viscous Heater
connections.
(6) Install the engine accessory drive belt(Refer to
7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(7) Refill the engine cooling system(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(9) Operate vehicle and check for any coolant
leaks, repair as required.
INSTALLATION - VISCOUS HEATER CLUTCH
(1) Install the clutch field coil and snap ring.
(2) Install the screw and retainer on the clutch coil
lead wire harness on the viscous heater housing.
Tighten the screw to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.)
(3) Align the rotor assembly squarely on the front
housing hub.
(4) Install the rotor bearing asembly with the
installer (Special Tool C-6871 or equalivent). Threadthe installer on the shaft, then turn the nut until the
rotor asembly is seated.
(5) Install the external front housing snap ring
with snap ring pliers. The bevel side of the snap ring
must be facing outward. Press the snap ring to make
sure it is properly seated in the groove.
CAUTION: If the snap ring is not fully seated in the
groove it will vibrate out, resulting in a clutch fail-
ure and severe damage to the front housing of the
compressor.
(6) Install the original clutch shims on the shaft.
(7) Install the clutch plate. Install the shaft hex
nut and tighten to 15±20 N´m (11±15 ft. lbs.).
(8) Check the clutch air gap with a feeler gauge
(Fig. 23). If the gap does not meet specification, add
or substract shims as required. The air gap specifica-
tion if 0.41 to 0.79 millimeters (0.016 to 0.031 inch-
es).
NOTE: The air gap is determined by the spacer
shims. When installing an original, or a new clutch
assembly, try the original shims first. When install-
ing a new clutch (and not having the old shims
available) use a 1.0, 0.50 and 0.13 millimeter (0.040,
0.020 and 0.005 inch) shim from the new clutch
hardware package that is provided with the new
clutch.
(9) Reinstall the viscous heater to the mounting
bracket. Tighten the mounting screws to 33 N´m (25
ft. lbs.).
(10) Reinstall the battery negative cable.
Fig. 22 CLUTCH FIELD COIL SNAP RING REMOVE-
typical
1 - COIL
2 - SNAP RING PLIERS
Fig. 23 CHECK CLUTCH AIR GAP-typical
1 - FEELER GAUGE
24 - 78 PLUMBINGWJ
VISCOUS HEATER (Continued)
Page 2158 of 2199

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0057 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0058 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0071 (M) Amb/Bat Temp Sensor Performance
P0106 Barometric Pressure Out of Range MAP sensor input voltage out of an acceptable range
detected during reading of barometric pressure at key-on.
P0107 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0108 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
PO111 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Performance
P0112 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0113 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0116 Coolant Temp Sensor Performance A rationatilty error has been detected in the coolant temp
sensor.
P0117 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0118 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0121 (M) TPS Voltage Does Not Agree With
MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor signal.
P0121 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0122 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage Low Throttle position sensor input below the acceptable
voltage range.
P0122 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0123 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
P0123 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too HighAPPS voltage input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
P0125 (M) Closed Loop Temp Not Reached Time to enter Closed Loop Operation (Fuel Control) is
excessive.
P0125 (M) Engine is Cold Too Long Engine does not reach operating temperature.
P0130 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0131 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0132 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0133 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0134 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor input.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 3
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2166 of 2199
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
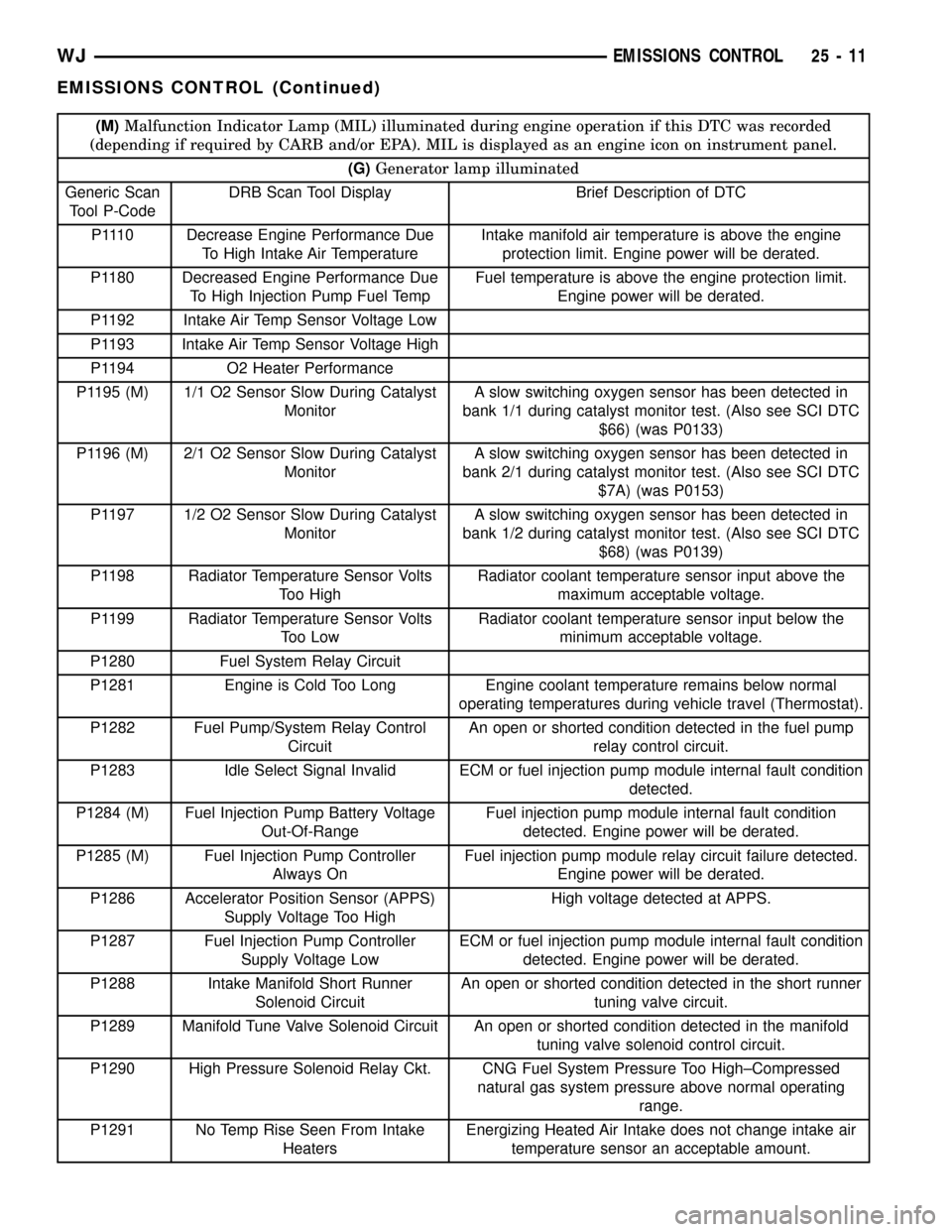
P1110 Decrease Engine Performance Due
To High Intake Air TemperatureIntake manifold air temperature is above the engine
protection limit. Engine power will be derated.
P1180 Decreased Engine Performance Due
To High Injection Pump Fuel TempFuel temperature is above the engine protection limit.
Engine power will be derated.
P1192 Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low
P1193 Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High
P1194 O2 Heater Performance
P1195 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 1/1 during catalyst monitor test. (Also see SCI DTC
$66) (was P0133)
P1196 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 2/1 during catalyst monitor test. (Also see SCI DTC
$7A) (was P0153)
P1197 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 1/2 during catalyst monitor test. (Also see SCI DTC
$68) (was P0139)
P1198 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too HighRadiator coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P1199 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too LowRadiator coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P1280 Fuel System Relay Circuit
P1281 Engine is Cold Too Long Engine coolant temperature remains below normal
operating temperatures during vehicle travel (Thermostat).
P1282 Fuel Pump/System Relay Control
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the fuel pump
relay control circuit.
P1283 Idle Select Signal Invalid ECM or fuel injection pump module internal fault condition
detected.
P1284 (M) Fuel Injection Pump Battery Voltage
Out-Of-RangeFuel injection pump module internal fault condition
detected. Engine power will be derated.
P1285 (M) Fuel Injection Pump Controller
Always OnFuel injection pump module relay circuit failure detected.
Engine power will be derated.
P1286 Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Supply Voltage Too HighHigh voltage detected at APPS.
P1287 Fuel Injection Pump Controller
Supply Voltage LowECM or fuel injection pump module internal fault condition
detected. Engine power will be derated.
P1288 Intake Manifold Short Runner
Solenoid CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the short runner
tuning valve circuit.
P1289 Manifold Tune Valve Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the manifold
tuning valve solenoid control circuit.
P1290 High Pressure Solenoid Relay Ckt. CNG Fuel System Pressure Too High±Compressed
natural gas system pressure above normal operating
range.
P1291 No Temp Rise Seen From Intake
HeatersEnergizing Heated Air Intake does not change intake air
temperature sensor an acceptable amount.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 11
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2174 of 2199

and deteriorate engine performance, driveability and
fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's sensor strategy is based on the fact that
as a catalyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity
and its efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring
the oxygen storage capacity of a catalyst, its effi-
ciency can be indirectly calculated. The upstream
O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION
The term ªTripº has different meanings depending
on what the circumstances are. If the MIL (Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp) is OFF, a Trip is defined as
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst
Monitor have been completed in the same drive cycle.
When any Emission DTC is set, the MIL on the
dash is turned ON. When the MIL is ON, it takes 3
good trips to turn the MIL OFF. In this case, itdepends on what type of DTC is set to know what a
ªTripº is.
For the Fuel Monitor or Mis-Fire Monitor (contin-
uous monitor), the vehicle must be operated in the
ªSimilar Condition Windowº for a specified amount of
time to be considered a Good Trip.
If a Non-Contiuous OBDII Monitor fails twice in a
row and turns ON the MIL, re-running that monitor
which previously failed, on the next start-up and
passing the monitor, is considered to be a Good Trip.
These will include the following:
²Oxygen Sensor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Purge Flow Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
²EGR Monitor (if equipped)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
If any other Emission DTC is set (not an OBDII
Monitor), a Good Trip is considered to be when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Monitor have
been completed; or 2 Minutes of engine run time if
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor or Catalyst Monitor have
been stopped from running.
It can take up to 2 Failures in a row to turn on the
MIL. After the MIL is ON, it takes 3 Good Trips to
turn the MIL OFF. After the MIL is OFF, the PCM
will self-erase the DTC after 40 Warm-up cycles. A
Warm-up cycle is counted when the ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor) has crossed 160ÉF and
has risen by at least 40ÉF since the engine has been
started.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum if
the TPS indicates a small throttle opening.
All open/short circuit checks or any component that
has an associated limp in will set a fault after 1 trip
with the malfunction present. Components without
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 19
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2177 of 2199

Non-emissions related failures have no priority.
One trip failures of two trip faults have low priority.
Two trip failures or matured faults have higher pri-
ority. One and two trip failures of fuel system and
misfire monitor take precedence over non-fuel system
and non-misfire failures.
DTC Self Erasure
With one trip components or systems, the MIL is
illuminated upon test failure and DTCs are stored.
Two trip monitors are components requiring failure
in two consecutive trips for MIL illumination. Upon
failure of the first test, the Task Manager enters a
maturing code. If the component fails the test for a
second time the code matures and a DTC is set.
After three good trips the MIL is extinguished and
the Task Manager automatically switches the trip
counter to a warm-up cycle counter. DTCs are auto-
matically erased following 40 warm-up cycles if the
component does not fail again.
For misfire and fuel system monitors, the compo-
nent must pass the test under a Similar Conditions
Window in order to record a good trip. A Similar Con-
ditions Window is when engine RPM is within 375
RPM and load is within 10% of when the fault
occurred.
NOTE: It is important to understand that a compo-
nent does not have to fail under a similar window of
operation to mature. It must pass the test under a
Similar Conditions Window when it failed to record
a Good Trip for DTC erasure for misfire and fuel
system monitors.
DTCs can be erased anytime with a DRB III. Eras-
ing the DTC with the DRB III erases all OBD II
information. The DRB III automatically displays a
warning that erasing the DTC will also erase all
OBD II monitor data. This includes all counter infor-
mation for warm-up cycles, trips and Freeze Frame.
Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
²Specific Good Trip
²Fuel System Good Trip
²Misfire Good Trip
²Alternate Good Trip (appears as a Global Good
Trip on DRB III)
²Comprehensive Components
²Major Monitor
²Warm-Up CyclesSpecific Good Trip
The term Good Trip has different meanings
depending on the circumstances:
²If the MIL is OFF, a trip is defined as when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst Monitor
have been completed in the same drive cycle.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by the Fuel
Monitor or Misfire Monitor (both continuous moni-
tors), the vehicle must be operated in the Similar
Condition Window for a specified amount of time.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by a Task
Manager commanded once-per-trip monitor (such as
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst Monitor, Purge
Flow Monitor, Leak Detection Pump Monitor, EGR
Monitor or Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor), a good
trip is when the monitor is passed on the next start-
up.
²If the MIL is ON and any other emissions DTC
was set (not an OBD II monitor), a good trip occurs
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Mon-
itor have been completed, or two minutes of engine
run time if the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst
Monitor have been stopped from running.
Fuel System Good Trip
To count a good trip (three required) and turn off
the MIL, the following conditions must occur:
²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfire
Warm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
25 - 22 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)