2002 DODGE RAM key
[x] Cancel search: keyPage 1360 of 2255

STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURES - WATER DRAINING
AT FUEL FILTER
Refer to Fuel Filter/Water Separator removal/in-
stallation for procedures.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - CLEANING FUEL
SYSTEM PARTS
CAUTION: Cleanliness cannot be overemphasized
when handling or replacing diesel fuel system com-
ponents. This especially includes the fuel injectors,
high-pressure fuel lines and fuel injection pump.
Very tight tolerances are used with these parts. Dirt
contamination could cause rapid part wear and pos-
sible plugging of fuel injector nozzle tip holes. This
in turn could lead to possible engine misfire.
Always wash/clean any fuel system component
thoroughly before disassembly and then air dry.
Cap or cover any open part after disassembly.
Before assembly, examine each part for dirt, grease
or other contaminants and clean if necessary. When
installing new parts, lubricate them with clean
engine oil or clean diesel fuel only.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - AIR BLEED
A certain amount of air becomes trapped in the
fuel system when fuel system components on the
supply and/or high-pressure side are serviced or
replaced. Primary air bleeding is accomplished using
the electric fuel transfer (lift) pump. If the vehicle
has been allowed to run completely out of fuel, the
fuel injectors must also be bled as the fuel injection
pumpis notself-bleeding (priming).
Servicing or replacing components on the fuel
return side will not require air bleeding.
WARNING: DO NOT BLEED AIR FROM THE FUEL
SYSTEM OF A HOT ENGINE.
(1) Loosen, but do not remove, banjo bolt (test port
fitting) holding low-pressure fuel supply line to side
of fuel injection pump (Fig. 11). Place a shop towel
around banjo fitting to catch excess fuel.
The fuel transfer (lift) pump is self-priming: When
the key is first turned on (without cranking engine),
the pump operates for approximately 2 seconds and
then shuts off. The pump will also operate for up to
25 seconds after the starter is quickly engaged, and
then disengaged without allowing the engine to start.
The pump shuts off immediately if the key is on and
the engine stops running.
(2) Turn key to CRANK position and quickly
release key to ON position before engine starts. Thiswill operate fuel transfer pump for approximately 25
seconds.
(3) If fuel is not present at fuel supply line after
25 seconds, turn key OFF. Repeat previous step until
fuel is exiting at fuel supply line.
(4) Tighten banjo bolt at fuel supply line to 24 N´m
(18 ft. lbs.) torque. Primary air bleeding is now com-
pleted.
(5) Attempt to start engine. If engine will not
start, proceed to following steps.If engine does
start, it may run erratically and be very noisy
for a few minutes. This is a normal condition.
(6)Continue to next step if:
²The vehicle fuel tank has been allowed to run
empty
²The fuel injection pump has been replaced
²High-pressure fuel lines have been replaced
²Vehicle has not been operated after an extended
period
CAUTION: Do not engage the starter motor for more
than 30 seconds at a time. Allow two minutes
between cranking intervals.
(7) Perform previous air bleeding procedure steps
using fuel transfer pump. Be sure fuel is present at
fuel supply line (Fig. 11) before proceeding.
Fig. 11 Fuel Supply Line Banjo Bolt
1 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE
2 - FUEL RETURN LINE
3 - BANJO BOLT (TEST PORT FITTING)
4 - OVERFLOW VALVE
5 - BANJO FITTING
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 61
FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1363 of 2255

REMOVAL
Refer to maintenance schedules in this manual for
recommended fuel filter replacement intervals.
Draining water from fuel filter/water separa-
tor housing:
The housing drain valve (Fig. 14) serves two pur-
poses. One is topartiallydrain filter housing of
excess water. The other is tocompletelydrain hous-
ing for fuel filter, drain valve, heater element or
water-in-fuel sensor replacement.
The filter housing should be partially drained
whenever water-in-fuel warning lamp remains illumi-
nated. (Note that lamp will be illuminated for
approximately two seconds when ignition key is ini-
tially placed in ON position for a bulb check).
(1) A drain hose is located at bottom of drain valve
(Fig. 14). Place drain pan under drain hose.
(2)With engine not running,pull drain valve
handle upward to OPEN (DRAIN) position (Fig. 14).
Hold drain valve open until all water and contami-
nants have been removed and clean fuel exits drain
hose.
(3) If drain valve, fuel heater element or Water-In-
Fuel (WIF) sensor is being replaced, drain housing
completely. Dispose of mixture in drain pan according
to applicable regulations.
(4) After draining operation, push valve handle
downward to CLOSE position (Fig. 14).
(5)Fuel Filter Replacement:The fuel filter is
located inside of the fuel filter housing (Fig. 15).
(a) Unscrew and remove fuel filter cap at top of
fuel filter housing (Fig. 14). To unscrew, attach tool
to 6±sided hex center of cap. Do not attempt to
loosen cap at outer edge. The fuel filter cap is
designed to remove filter while pulling up on cap.
(b) Remove o-ring (Fig. 15) from filter cap and
discard.
(c) The filter is retained to the cap with a series
of locking fingers. Carefully pry back a few of the
fingers to unlock filter from cap.
(6)Water-In-Fuel (WIF) Sensor Replacement:
The WIF sensor is located on the side of the fuel fil-
ter housing (Fig. 15).
(a) Disconnect electrical connector at sensor
(Fig. 16).
(b) Unscrew sensor from filter housing.
Fig. 14 Water Drain Valve and Drain Hose
1 - FUEL FILTER CAP
2 - DRAIN VALVE HANDLE
3 - DRAIN HOSE
4 - FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR
Fig. 15 Fuel Filter/Water Separator Components
1 - CAP
2 - O-RING
3 - FUEL FILTER
4 - FUEL HEATER ELEMENT
5 - HOUSING
6 - O-RINGS
7 - DRAIN VALVE
8 - FUEL HEATER THERMOSTAT
9 - WATER-IN-FUEL SENSOR
14 - 64 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL FILTER / WATER SEPARATOR (Continued)
Page 1366 of 2255

Voltage to operate the fuel heater element is sup-
plied from the ignition switch, through the fuel
heater relay (also refer to Fuel Heater Relay), to the
fuel temperature sensor and on to the fuel heater ele-
ment.
The heater element operates on 12 volts, 300 watts
at 0 degrees F. As temperature increases, power
requirements decrease.
A minimum of 7 volts is required to operate the
fuel heater. The resistance value of the heater ele-
ment is less than 1 ohm (cold) and up to 1000 ohms
warm.
TESTING
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at sensor (Fig.
19).
Turn key to ON position. 12 volts should be
present at red wire. If not, check fuel heater relay
and related wiring. Refer to Relay TestÐFuel Heater.
If OK, proceed.
Turn key OFF. Check black wire in connector for
ground continuity with an ohmmeter. If continuity is
not present, correct open ground circuit. This test can
also be performed with a voltmeter by backprobing
black wire with it connected to sensor. Reconnect elec-
trical connector and turn key ON. Voltage drop should
not exceed 2 volts (2 volts lower than checked at 12V+
connector). If voltage is lower, check for dirty or cor-
roded ground connection and repair. If OK, proceed.
(2) With electrical connector disconnected at sen-
sor and key OFF, check electrical/mechanical opera-
tion of fuel temperature sensor. Proceed to next step:
(3) Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity across
two terminals in electrical connector at side of sen-
sor. Sensor circuit should be open if fuel temperature
has risen above 75 degrees 8 degrees F. Sensor cir-
cuit should be closed if fuel temperature has dropped
below 45 degrees 8 degrees F. If not, replace fuel
heater assembly. This same test can also be per-
formed using a voltmeter, with key ON, and by back-
probing connector.
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
The fuel heater/element/sensor assembly is located
inside of the fuel filter housing. Refer to Fuel Filter/
Water Separator Removal/Installation for procedures.
FUEL HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel heater relay is located in Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC) (Fig. 20). Refer to label on inside
of PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
Battery voltage to operate the fuel heater element
is supplied from the ignition switch through the fuel
heater relay.The fuel heater element and fuel
heater relay are not computer controlled.
Fig. 19 Fuel Heater Location
1 - FUEL HEATER AND TEMP. SENSOR
2 - FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR
3 - FUEL HEATER ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 20 Power Distribution Center Location
1 - CLIP
2 - BATTERY
3 - TRAY
4 - NEGATIVE CABLE
5 - POSITIVE CABLE
6 - CLIP
7 - FENDER INNER SHIELD
8 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 67
FUEL HEATER (Continued)
Page 1369 of 2255

OPERATION
The Bosch VP44 fuel injection pump (Fig. 25) is a
solenoid-valve controlled-radial-piston-distributor
type pump.The injection pump is driven by the engine cam-
shaft. A gear on the end of the pump shaft meshes
with the camshaft gear. The pump is timed to the
engine. The VP44 is controlled by an integral (and
non-serviceable) Fuel Pump Control Module (FPCM)
(Fig. 24). The FPCM can operate the engine as an
engine controller if a Crankshaft Position Sensor
(CKP) signal is not present.
Fuel from the transfer (lift) pump enters the VP44
where it is pressurized and then distributed through
high-pressure lines to the fuel injectors. The VP44 is
cooled by the fuel that flows through it. A greater
quantity of fuel is required for cooling the VP44 than
what is necessary for engine operation. Because of
this, approximately 70 percent of fuel entering the
pump is returned to the fuel tank through the over-
flow valve and fuel return line. Refer to Overflow
Valve Description/Operation for additional informa-
tion.
The VP44 is not self-priming. At least two fuel
injectors must be bled to remove air from the system.
When servicing the fuel system, disconnecting compo-
nents up to the pump will usually not require air
bleeding from the fuel system. However, removal of
the high-pressure lines, removal of the VP44 pump,
or allowing the vehicle to completely run out of fuel,
will require bleeding air from the high-pressure lines
at the fuel injectors.
VP44 timing is matched to engine timing by an off-
set keyway that fits into the pump shaft. This key-
way has a stamped number on it that is matched to
a number on the VP44 pump (each keyway is cali-
brated to each pump).
When removing/installing the VP44, the same
numbered keyway must always be installed.
Also, the arrow on the top of the keyway should
be installed pointed rearward towards the
pump.
Because of electrical control, the injection pump
high and low idle speeds are not adjustable. Also,
adjustment of fuel pump timing is not required and
is not necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐFUEL INJECTION
PUMP TIMING
With the Bosch VP44 injection pump, there are no
mechanical adjustments needed for fuel injection tim-
ing. All timing and fuel adjustments are made by the
Engine Control Module (ECM). However, if a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) has been stored indicating
an ªengine sync errorº or a ªstatic timing errorº, per-
form the following.
Fig. 24 Fuel Injection Pump Location
1 - FPCM ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES
3 - FITTINGS
4 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
5 - FPCM
Fig. 25 Bosch VP44 Fuel Injection Pump
1 - BOSCH VP44 PUMP
14 - 70 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1370 of 2255
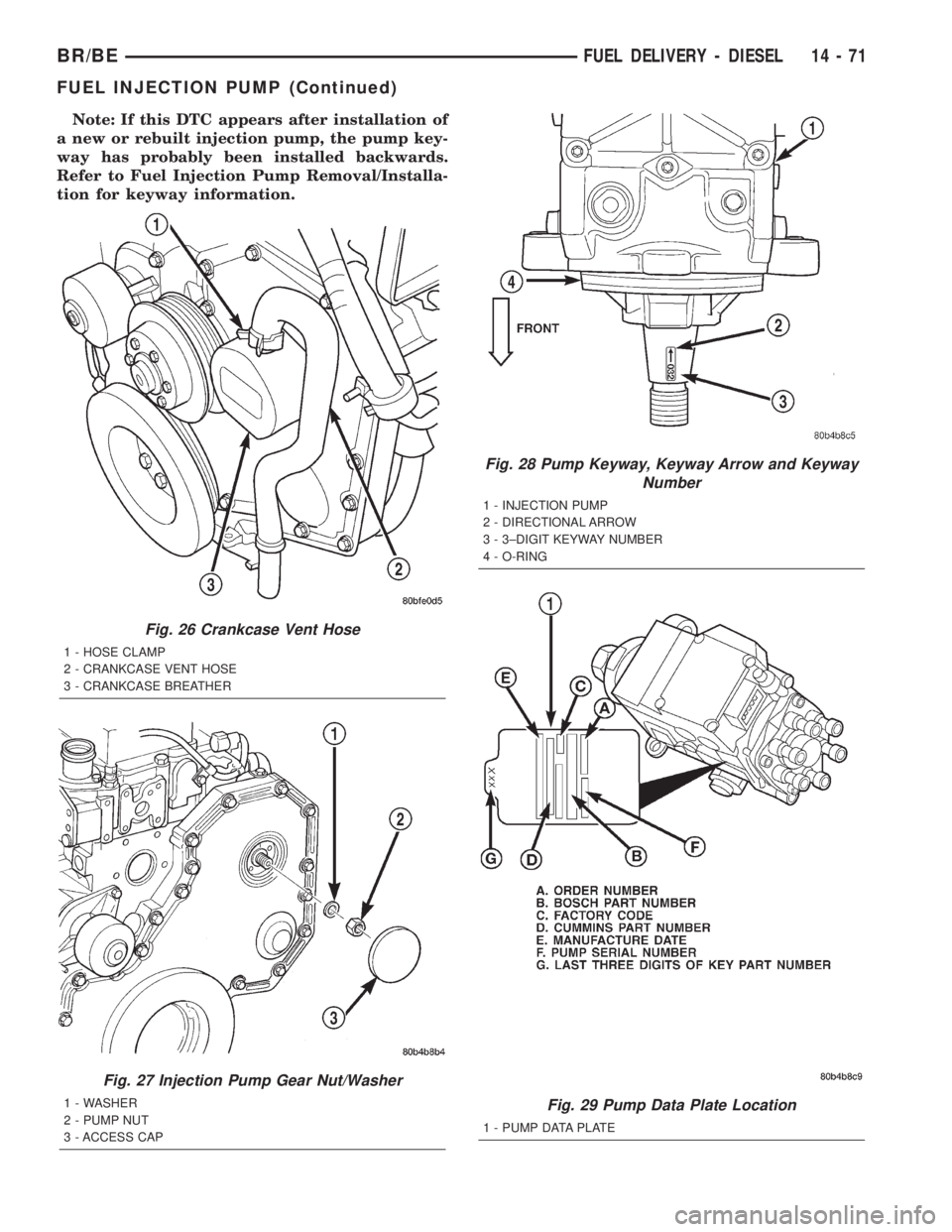
Note: If this DTC appears after installation of
a new or rebuilt injection pump, the pump key-
way has probably been installed backwards.
Refer to Fuel Injection Pump Removal/Installa-
tion for keyway information.
Fig. 26 Crankcase Vent Hose
1 - HOSE CLAMP
2 - CRANKCASE VENT HOSE
3 - CRANKCASE BREATHER
Fig. 27 Injection Pump Gear Nut/Washer
1 - WASHER
2 - PUMP NUT
3 - ACCESS CAP
Fig. 28 Pump Keyway, Keyway Arrow and Keyway
Number
1 - INJECTION PUMP
2 - DIRECTIONAL ARROW
3 - 3±DIGIT KEYWAY NUMBER
4 - O-RING
Fig. 29 Pump Data Plate Location
1 - PUMP DATA PLATE
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 71
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1371 of 2255

(1) Remove hose clamp and crankcase vent hose at
crankcase breather (Fig. 26). Remove crankcase
breather from gear cover. Breather threads into
cover.
(2) Remove injection pump nut and washer (Fig.
27). Locate keyway behind washer.
(3) Be sure keyway aligning fuel injection pump
shaft to injection pump gear is in proper position and
pump gear has not slipped on pump shaft.
The following steps will require removing timing
gear cover to gain access to timing gears. Refer to
Group 9, Engines for procedures.
(4) Use a T-type puller to separate injection pump
gear from pump shaft.
(5) Be sure keyway has been installed with arrow
pointed torearof pump (Fig. 28).
(6)Pump timing has been calibrated to pump
keyway. Be sure 3±digit number on pump key-
way (Fig. 28) matches 3±digit number on fuel
injection pump data plate. Plate is located on
side of injection pump (Fig. 29). Twenty±one dif-
ferent calibrated keyways/pumps are available.
(7) Verify timing marks on crank, cam and pump
are aligned (Fig. 30).
(8) Perform necessary gear alignment/repairs as
needed.
(9) Install crankcase breather to gear cover. Install
hose clamp and crankcase vent hose to breather (Fig.
26).
(10) After repairs are completed, erase DTC using
DRB Scan Tool.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Refer to Cleaning Fuel System Parts.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries. Cover and isolate ends of cables.
(2) Thoroughly clean fuel lines at cylinder head
and injection pump ends. Thoroughly clean fuel injec-
tion pump and supply/return lines at side of pump.
(3) Disconnect 9±way electrical connector at Fuel
Pump Control Module (FPCM) (Fig. 31).
(4) Remove fuel return line at side of injection
pump by removing overflow valve (Fig. 32). Place rag
beneath overflow valve to catch excess fuel.
(5) Remove fuel supply line at side of injection
pump by removing banjo bolt (Fig. 32). Also remove
same line at top of fuel filter housing (banjo bolt).
(6) Remove all high-pressure fuel lines, intake air
tube, accelerator pedal position sensor, air intake
housing, engine oil dipstick tube, wiring clips, electri-
cal cables at intake heaters and engine lifting
bracket. Refer to High-Pressure Fuel Line Removal/
Installation. All of these items are covered in this
procedure.
(7) Remove hose clamp at crankcase vent hose
(Fig. 33) and remove hose from canister.
(8) Remove (unscrew) canister (Fig. 33) from gear
cover.
Fig. 30 Checking Fuel Injection Pump Gear Timing
1 - PUMP SHAFT
2 - KEYWAY
3 - PUMP GEAR
4 - CAM GEAR
5 - CRANKSHAFT GEAR
Fig. 31 FPCM 9±Way Connector
1 - FPCM ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES
3 - FITTINGS
4 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
5 - FPCM
14 - 72 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1372 of 2255
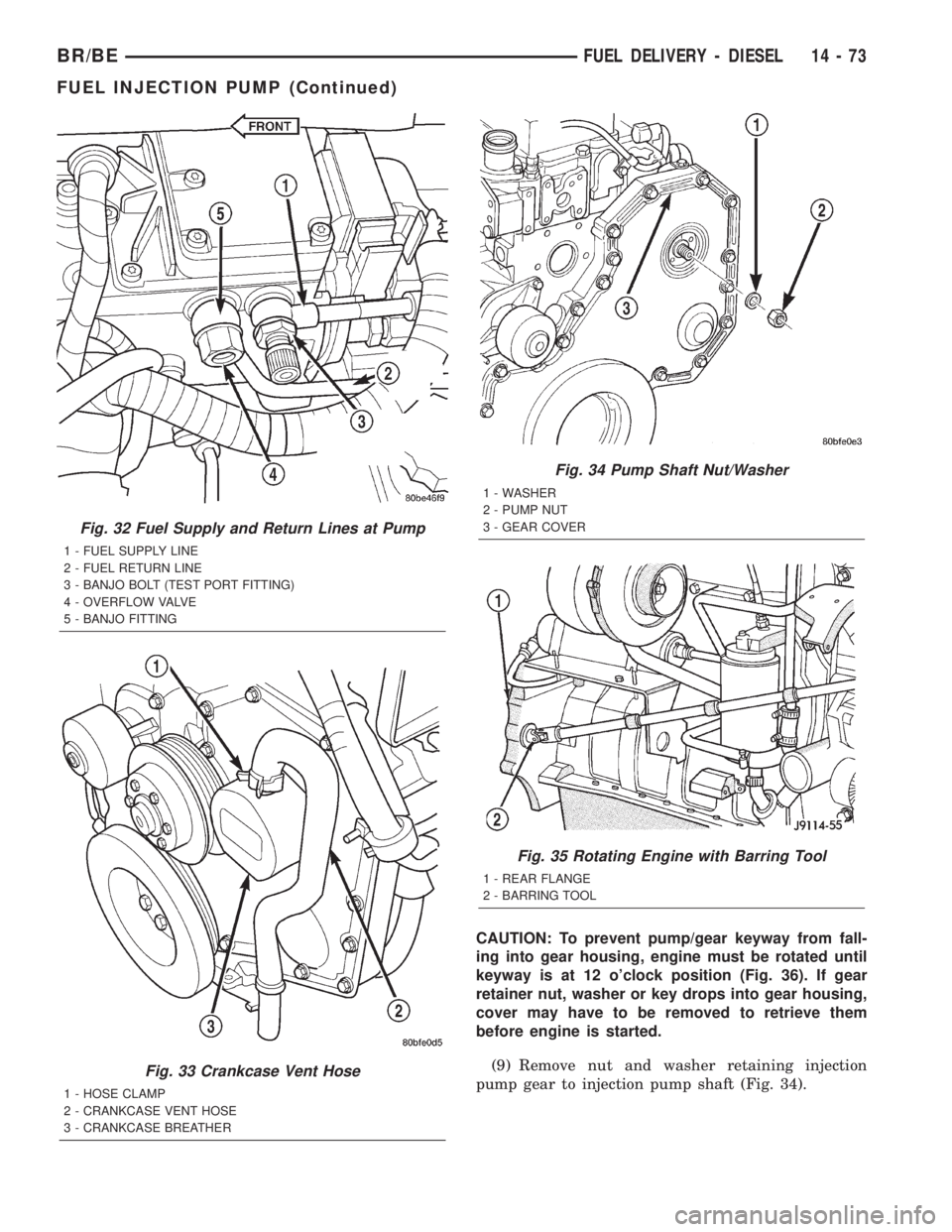
CAUTION: To prevent pump/gear keyway from fall-
ing into gear housing, engine must be rotated until
keyway is at 12 o'clock position (Fig. 36). If gear
retainer nut, washer or key drops into gear housing,
cover may have to be removed to retrieve them
before engine is started.
(9) Remove nut and washer retaining injection
pump gear to injection pump shaft (Fig. 34).
Fig. 32 Fuel Supply and Return Lines at Pump
1 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE
2 - FUEL RETURN LINE
3 - BANJO BOLT (TEST PORT FITTING)
4 - OVERFLOW VALVE
5 - BANJO FITTING
Fig. 33 Crankcase Vent Hose
1 - HOSE CLAMP
2 - CRANKCASE VENT HOSE
3 - CRANKCASE BREATHER
Fig. 34 Pump Shaft Nut/Washer
1 - WASHER
2 - PUMP NUT
3 - GEAR COVER
Fig. 35 Rotating Engine with Barring Tool
1 - REAR FLANGE
2 - BARRING TOOL
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 73
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1373 of 2255
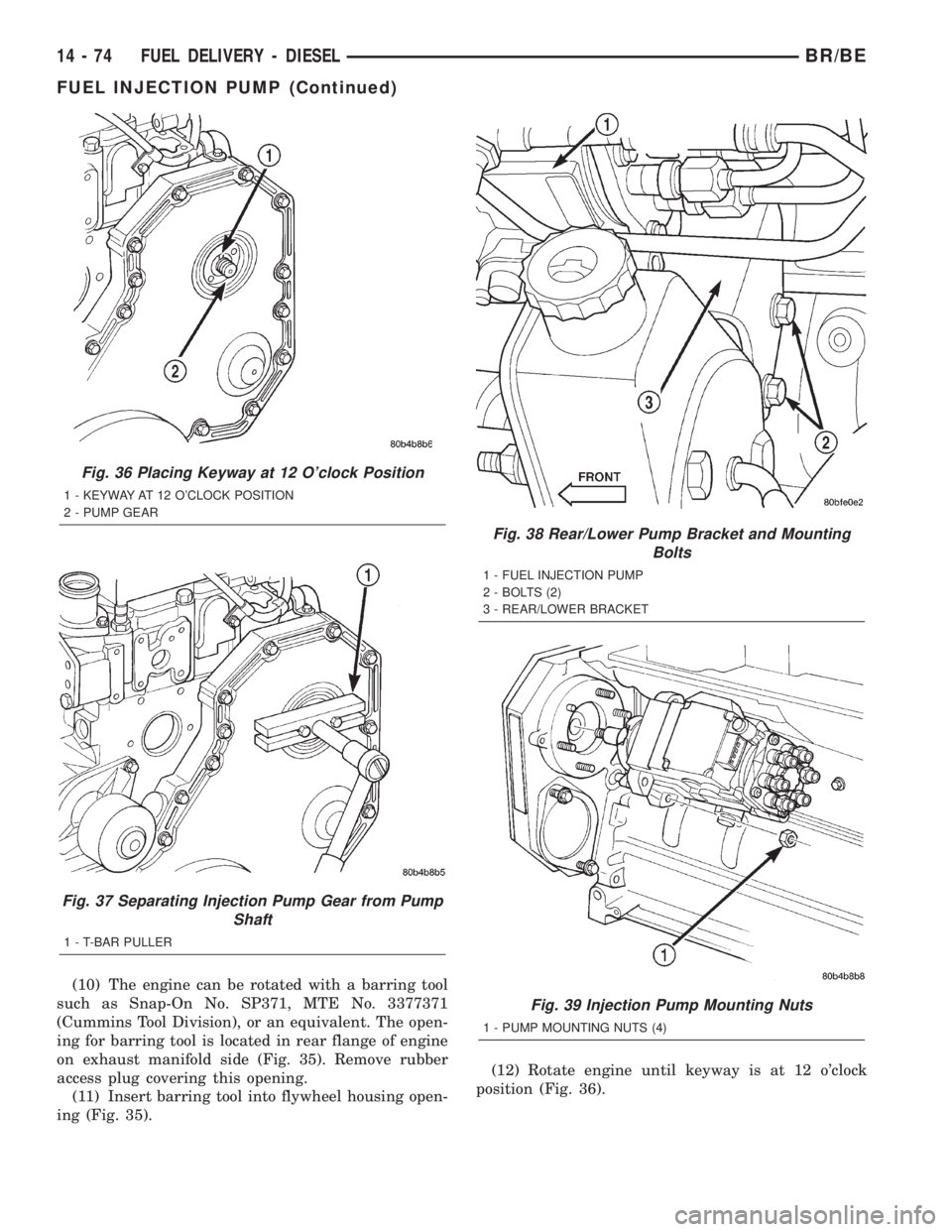
(10) The engine can be rotated with a barring tool
such as Snap-On No. SP371, MTE No. 3377371
(Cummins Tool Division), or an equivalent. The open-
ing for barring tool is located in rear flange of engine
on exhaust manifold side (Fig. 35). Remove rubber
access plug covering this opening.
(11) Insert barring tool into flywheel housing open-
ing (Fig. 35).(12) Rotate engine until keyway is at 12 o'clock
position (Fig. 36).
Fig. 36 Placing Keyway at 12 O'clock Position
1 - KEYWAY AT 12 O'CLOCK POSITION
2 - PUMP GEAR
Fig. 37 Separating Injection Pump Gear from Pump
Shaft
1 - T-BAR PULLER
Fig. 38 Rear/Lower Pump Bracket and Mounting
Bolts
1 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
2 - BOLTS (2)
3 - REAR/LOWER BRACKET
Fig. 39 Injection Pump Mounting Nuts
1 - PUMP MOUNTING NUTS (4)
14 - 74 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)