2002 DODGE RAM light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 237 of 2255
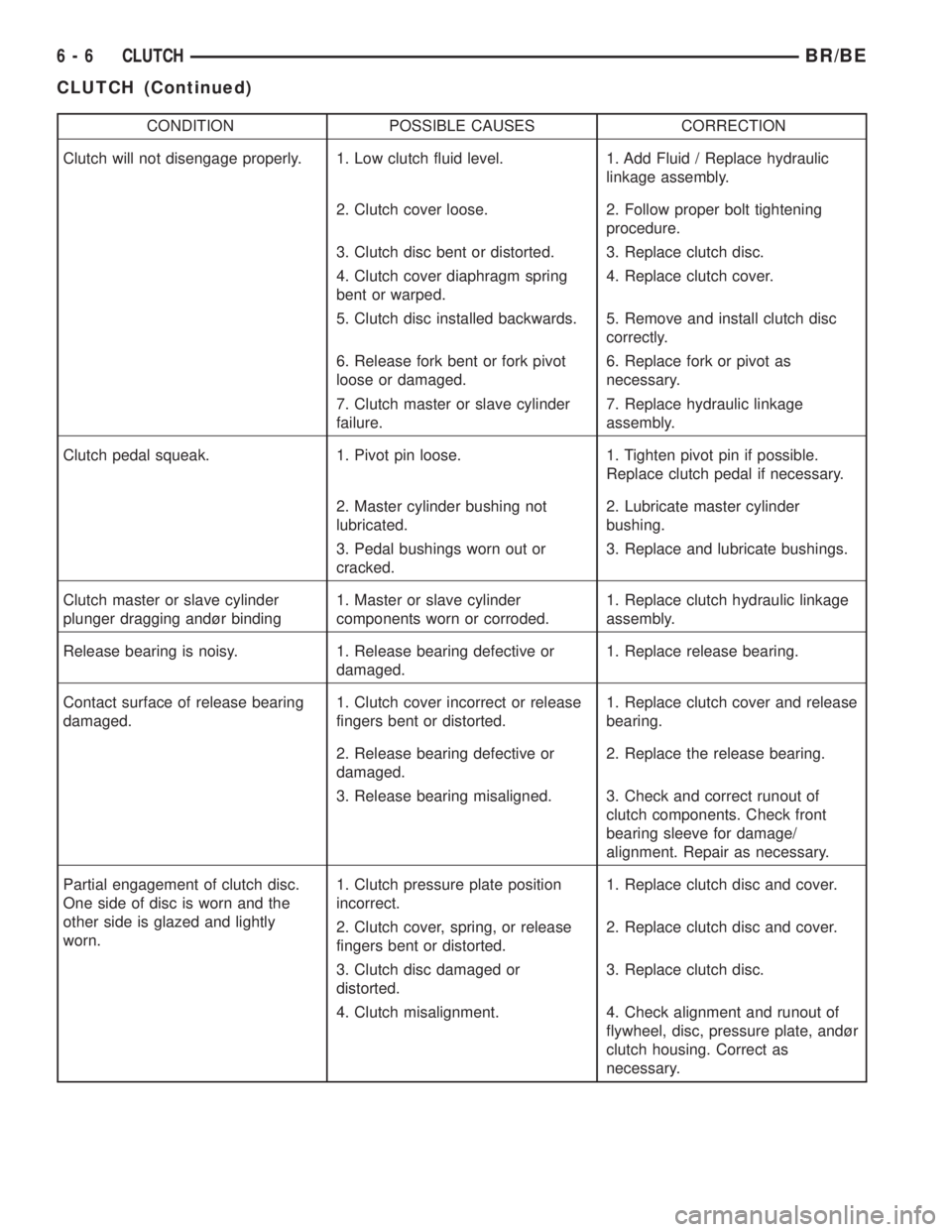
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Clutch will not disengage properly. 1. Low clutch fluid level. 1. Add Fluid / Replace hydraulic
linkage assembly.
2. Clutch cover loose. 2. Follow proper bolt tightening
procedure.
3. Clutch disc bent or distorted. 3. Replace clutch disc.
4. Clutch cover diaphragm spring
bent or warped.4. Replace clutch cover.
5. Clutch disc installed backwards. 5. Remove and install clutch disc
correctly.
6. Release fork bent or fork pivot
loose or damaged.6. Replace fork or pivot as
necessary.
7. Clutch master or slave cylinder
failure.7. Replace hydraulic linkage
assembly.
Clutch pedal squeak. 1. Pivot pin loose. 1. Tighten pivot pin if possible.
Replace clutch pedal if necessary.
2. Master cylinder bushing not
lubricated.2. Lubricate master cylinder
bushing.
3. Pedal bushings worn out or
cracked.3. Replace and lubricate bushings.
Clutch master or slave cylinder
plunger dragging andùr binding1. Master or slave cylinder
components worn or corroded.1. Replace clutch hydraulic linkage
assembly.
Release bearing is noisy. 1. Release bearing defective or
damaged.1. Replace release bearing.
Contact surface of release bearing
damaged.1. Clutch cover incorrect or release
fingers bent or distorted.1. Replace clutch cover and release
bearing.
2. Release bearing defective or
damaged.2. Replace the release bearing.
3. Release bearing misaligned. 3. Check and correct runout of
clutch components. Check front
bearing sleeve for damage/
alignment. Repair as necessary.
Partial engagement of clutch disc.
One side of disc is worn and the
other side is glazed and lightly
worn.1. Clutch pressure plate position
incorrect.1. Replace clutch disc and cover.
2. Clutch cover, spring, or release
fingers bent or distorted.2. Replace clutch disc and cover.
3. Clutch disc damaged or
distorted.3. Replace clutch disc.
4. Clutch misalignment. 4. Check alignment and runout of
flywheel, disc, pressure plate, andùr
clutch housing. Correct as
necessary.
6 - 6 CLUTCHBR/BE
CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 239 of 2255

(6) If pressure plate will be reused, loosen cover
bolts evenly only few threads at a time in a diagonal
pattern (Fig. 6). This relieves cover spring tension
evenly to avoid warping.
(7) Remove bolts completely and remove plate, disc
and alignment tool.
INSTALLATION
(1) Check runout and free operation of new clutch
disc.
(2) Insert clutch alignment tool in pressure plate
and clutch disc.
(3) Insert alignment tool in pilot bearing and posi-
tion plate and disc on flywheel (Fig. 7).
NOTE: Raised side of disc hub faces away from the
flywheel.
(4) Iinstall cover bolts finger tight.
(5) Tighten cover bolts evenly and a few threads at
a time.
CAUTION: Cover bolts must be tightened evenly to
avoid distorting cover.
(6) Tighten clutch cover bolts to:
²5/16 in. diameter bolts to 23 N´m (17 ft. lbs.).
²3/8 in. diameter bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.).(7) Remove release lever and release bearing from
clutch housing. Apply Mopar high temperature bear-
ing grease or equivalent to bore of release bearing,
release lever contact surfaces and release lever pivot
stud (Fig. 8).
(8) Apply light coat of Mopar high temperature
bearing grease or equivalent to splines of transmis-
sion input shaft (or drive gear) and to release bearing
slide surface of the transmission front bearing
retainer (Fig. 9).
CAUTION: Do not over lubricate shaft splines. This
can result in grease contamination of disc.
(9) Install release lever and bearing in clutch
housing. Be sure spring clips that retain fork on
pivot ball and release bearing on fork are secure (Fig.
10). Also verify that the release lever is installed
properly.
NOTE: Release lever is installed correctly, when
lever part number is toward the bottom of the trans-
mission. Also a stamped ªIº in the lever goes
towards the pivot ball side of the transmission.
(10) Install transmission. Refer to 21 Transmission
and Transfer Case for procedures.
(11) Check fluid level in clutch master cylinder.
Fig. 6 Bolt Loosening/Tightening Pattern
Fig. 7 Pressure Plate And Disc Alignment
1 - FLYWHEEL
2 - PRESSURE PLATE AND DISC
3 - CLUTCH DISC ALIGNMENT TOOL
6 - 8 CLUTCHBR/BE
CLUTCH DISC (Continued)
Page 247 of 2255
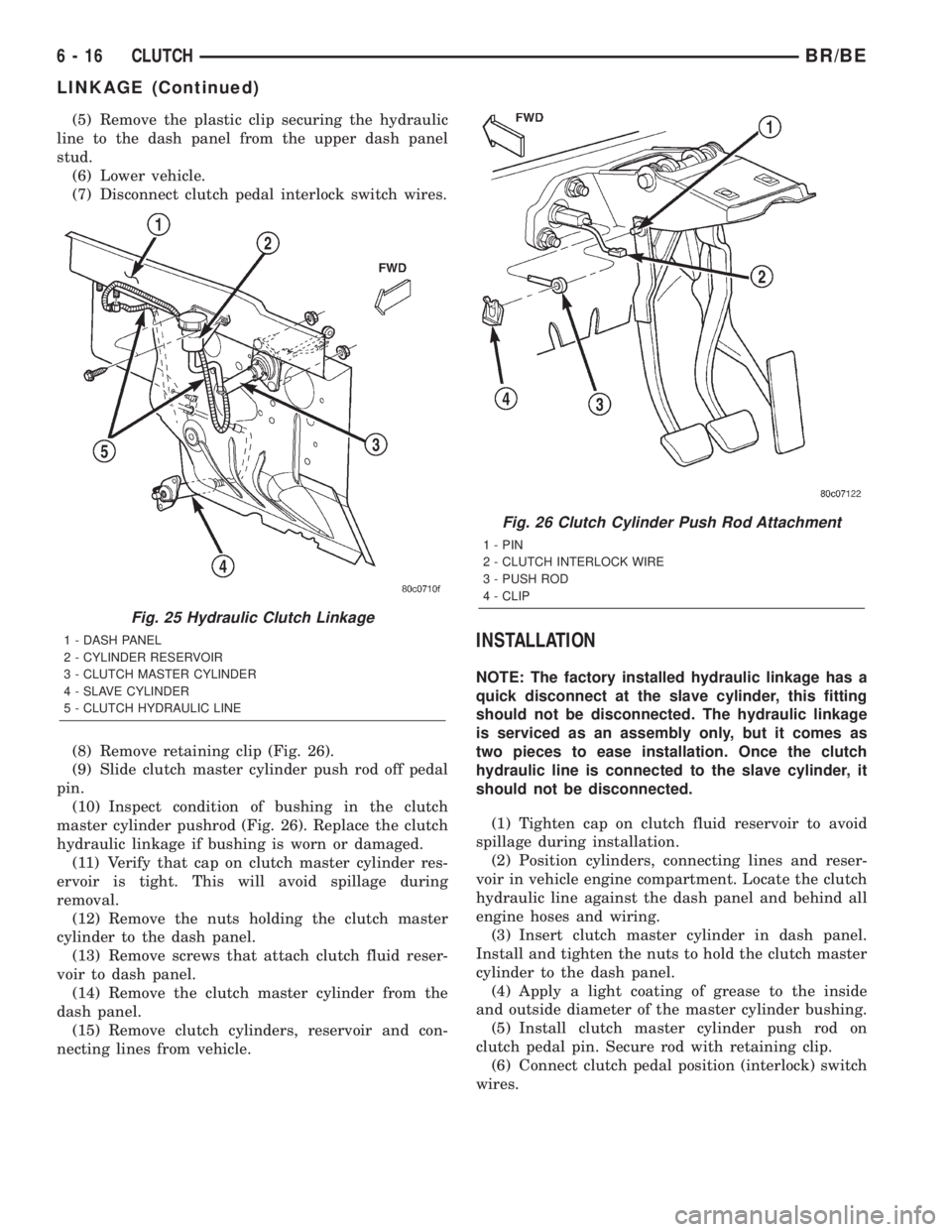
(5) Remove the plastic clip securing the hydraulic
line to the dash panel from the upper dash panel
stud.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Disconnect clutch pedal interlock switch wires.
(8) Remove retaining clip (Fig. 26).
(9) Slide clutch master cylinder push rod off pedal
pin.
(10) Inspect condition of bushing in the clutch
master cylinder pushrod (Fig. 26). Replace the clutch
hydraulic linkage if bushing is worn or damaged.
(11) Verify that cap on clutch master cylinder res-
ervoir is tight. This will avoid spillage during
removal.
(12) Remove the nuts holding the clutch master
cylinder to the dash panel.
(13) Remove screws that attach clutch fluid reser-
voir to dash panel.
(14) Remove the clutch master cylinder from the
dash panel.
(15) Remove clutch cylinders, reservoir and con-
necting lines from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The factory installed hydraulic linkage has a
quick disconnect at the slave cylinder, this fitting
should not be disconnected. The hydraulic linkage
is serviced as an assembly only, but it comes as
two pieces to ease installation. Once the clutch
hydraulic line is connected to the slave cylinder, it
should not be disconnected.
(1) Tighten cap on clutch fluid reservoir to avoid
spillage during installation.
(2) Position cylinders, connecting lines and reser-
voir in vehicle engine compartment. Locate the clutch
hydraulic line against the dash panel and behind all
engine hoses and wiring.
(3) Insert clutch master cylinder in dash panel.
Install and tighten the nuts to hold the clutch master
cylinder to the dash panel.
(4) Apply a light coating of grease to the inside
and outside diameter of the master cylinder bushing.
(5) Install clutch master cylinder push rod on
clutch pedal pin. Secure rod with retaining clip.
(6) Connect clutch pedal position (interlock) switch
wires.
Fig. 25 Hydraulic Clutch Linkage
1 - DASH PANEL
2 - CYLINDER RESERVOIR
3 - CLUTCH MASTER CYLINDER
4 - SLAVE CYLINDER
5 - CLUTCH HYDRAULIC LINE
Fig. 26 Clutch Cylinder Push Rod Attachment
1 - PIN
2 - CLUTCH INTERLOCK WIRE
3 - PUSH ROD
4 - CLIP
6 - 16 CLUTCHBR/BE
LINKAGE (Continued)
Page 253 of 2255

DESCRIPTIONÐHOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system utilizes both worm drive and
spring type hose clamps. If a spring type clamp
replacement is necessary, replace with the original
Mopartequipment spring type clamp.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
OPERATIONÐHOSE CLAMPS
The worm type hose clamp uses a specified torque
value to maintain proper tension on a hose connec-
tion.
The spring type hose clamp applies constant ten-
sion on a hose connection. To remove a spring type
hose clamp, only use constant tension clamp pliers
designed to compress the hose clamp.
OPERATIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system regulates engine operating tem-
perature. It allows the engine to reach normal oper-
ating temperature as quickly as possible. It also
maintains normal operating temperature and pre-
vents overheating.
The cooling system also provides a means of heat-
ing the passenger compartment and cooling the auto-
matic transmission fluid (if equipped). The cooling
system is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water
pump to circulate coolant throughout the system.
An optional factory installed maximum duty cool-
ing package is available on most models. This pack-age will provide additional cooling capacity for
vehicles used under extreme conditions such as
trailer towing in high ambient temperatures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
CHECKS
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM OVERHEATING
Establish what driving conditions caused the com-
plaint. Abnormal loads on the cooling system such as
the following may be the cause:
²PROLONGED IDLE
²VERY HIGH AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
²SLIGHT TAIL WIND AT IDLE
²SLOW TRAFFIC
²TRAFFIC JAMS
²HIGH SPEED OR STEEP GRADES
Driving techniques that avoid overheating are:
²Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range.
²Increasing engine speed for more air flow is rec-
ommended.
TRAILER TOWING:
Consult Trailer Towing section of owners manual.
Do not exceed limits.
AIR CONDITIONING; ADD-ON OR AFTER MARKET:
A maximum cooling package should have been
ordered with vehicle if add-on or after market A/C is
installed. If not, maximum cooling system compo-
nents should be installed for model involved per
manufacturer's specifications.
RECENT SERVICE OR ACCIDENT REPAIR:
Determine if any recent service has been per-
formed on vehicle that may effect cooling system.
This may be:
²Engine adjustments (incorrect timing)
²Slipping engine accessory drive belt(s)
²Brakes (possibly dragging)
²Changed parts. Incorrect water pump or pump
rotating in wrong direction due to belt not correctly
routed
²Reconditioned radiator or cooling system refill-
ing (possibly under filled or air trapped in system).
NOTE: If investigation reveals none of the previous
items as a cause for an engine overheating com-
plaint, (Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
Fig. 4 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
7 - 4 COOLINGBR/BE
COOLING (Continued)
Page 254 of 2255

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
COOLING SYSTEM RELATED DIAGNOSTICS
The powertrain control module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor certain cooling system com-
ponents:
²If the engine has remained cool for too long a
period, such as with a stuck open thermostat, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
²If an open or shorted condition has developed in
the relay circuit controlling the electric radiator fan,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit
often enough to indicated an actual problem, a DTC
is stored. The DTC will be stored in the PCM mem-
ory for eventual display to the service technician.
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
To read DTC's and to obtain cooling system data,
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the DRB
scan tool to erase a DTC. Refer to the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service informa-
tion for operation of the DRB scan tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be added to cooling sys-
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate engine until radiator
upper hose is warm to touch. Aim the commercially
available black light tool at components to be
checked. If leaks are present, black light will cause
additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks
exist (Fig. 5).
PRESSURE TESTER METHOD
The engine should be at normal operating temper-
ature. Recheck the system cold if cause of coolant
loss is not located during the warm engine examina-
tion.WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING.
Carefully remove radiator pressure cap from filler
neck and check coolant level. Push down on cap to
disengage it from stop tabs. Wipe inside of filler neck
and examine lower inside sealing seat for nicks,
cracks, paint, dirt and solder residue. Inspect radia-
tor-to- reserve/overflow tank hose for internal
obstructions. Insert a wire through the hose to be
sure it is not obstructed.
Inspect cams on outside of filler neck. If cams are
damaged, seating of pressure cap valve and tester
seal will be affected.
Attach pressure tester (7700 or an equivalent) to
radiator filler neck (Fig. 6).
Operate tester pump to apply 103.4 kPa (15 psi)
pressure to system. If hoses enlarge excessively or
bulges while testing, replace as necessary. Observe
gauge pointer and determine condition of cooling sys-
tem according to following criteria:
Holds Steady:If pointer remains steady for two
minutes, serious coolant leaks are not present in sys-
tem. However, there could be an internal leak that
does not appear with normal system test pressure. If
it is certain that coolant is being lost and leaks can-
not be detected, inspect for interior leakage or per-
form Internal Leakage Test.
Drops Slowly:Indicates a small leak or seepage
is occurring. Examine all connections for seepage or
slight leakage with a flashlight. Inspect radiator,
Fig. 5 Leak Detection Using Black LightÐTypical
1 - TYPICAL BLACK LIGHT TOOL
BR/BECOOLING 7 - 5
COOLING (Continued)
Page 259 of 2255

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READING
IS INCONSISTENT (FLUCTUATES,
CYCLES OR IS ERRATIC)1. During cold weather operation,
with the heater blower in the high
position, the gauge reading may
drop slightly.1. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary.
2. Temperature gauge or engine
mounted gauge sensor defective or
shorted. Also, corroded or loose
wiring in this circuit.2. Check operation of gauge and
repair if necessary. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
3. Gauge reading rises when
vehicle is brought to a stop after
heavy use (engine still running)3. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary. Gauge should return
to normal range after vehicle is
driven.
4. Gauge reading high after
re-starting a warmed up (hot)
engine.4. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary. The gauge should
return to normal range after a few
minutes of engine operation.
5. Coolant level low in radiator (air
will build up in the cooling system
causing the thermostat to open
late).5. Check and correct coolant leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Cylinder head gasket leaking
allowing exhaust gas to enter
cooling system causing a
thermostat to open late.6. (a) Check for cylinder head
gasket leaks. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(b) Check for coolant in the engine
oil. Inspect for white steam emitting
from the exhaust system. Repair as
necessary.
7. Water pump impeller loose on
shaft.7. Check water pump and replace
as necessary. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/WATER PUMP -
REMOVAL).
8. Loose accessory drive belt.
(water pump slipping)8. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Check and correct as necessary.
9. Air leak on the suction side of
the water pump allows air to build
up in cooling system causing
thermostat to open late.9. Locate leak and repair as
necessary.
PRESSURE CAP IS BLOWING
OFF STEAM AND/OR COOLANT
TO COOLANT TANK.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READING
MAY BE ABOVE NORMAL BUT
NOT HIGH. COOLANT LEVEL MAY
BE HIGH IN COOLANT RESERVE/
OVERFLOW TANK1. Pressure relief valve in radiator
cap is defective.1. Check condition of radiator cap
and cap seals. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). Replace cap as
necessary.
7 - 10 COOLINGBR/BE
COOLING (Continued)
Page 296 of 2255

ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR - 5.9L
DESCRIPTION
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is
used to sense engine coolant temperature. The sensor
protrudes into an engine water jacket.
The ECT sensor is a two-wire Negative Thermal
Coefficient (NTC) sensor. Meaning, as engine coolant
temperature increases, resistance (voltage) in the
sensor decreases. As temperature decreases, resis-
tance (voltage) in the sensor increases.
OPERATION
At key-on, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
sends out a regulated 5 volt signal to the ECT sensor.
The PCM then monitors the signal as it passes
through the ECT sensor to the sensor ground (sensor
return).
When the engine is cold, the PCM will operate in
Open Loop cycle. It will demand slightly richer air-
fuel mixtures and higher idle speeds. This is done
until normal operating temperatures are reached.
The PCM uses inputs from the ECT sensor for the
following calculations:
²for engine coolant temperature gauge operation
through CCD or PCI (J1850) communications
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance curves
²ASD relay shut-down times
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor key-on steps
²Pulse-width prime-shot during cranking
²O2 sensor closed loop times
²Purge solenoid on/off times
²EGR solenoid on/off times (if equipped)
²Leak Detection Pump operation (if equipped)
²Radiator fan relay on/off times (if equipped)²Target idle speed
REMOVAL
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. COOLING SYSTEM
MUST BE PARTIALLY DRAINED BEFORE REMOV-
ING THE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR.
REFER TO GROUP 7, COOLING.
(1) Partially drain cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(3) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor
(Fig. 14).
(4)Engines with air conditioning:When
removing the connector from sensor, do not pull
directly on wiring harness. Fabricate an L-shaped
hook tool from a coat hanger (approximately eight
inches long). Place the hook part of tool under the
connector for removal. The connector is snapped onto
the sensor. It is not equipped with a lock type tab.
(5) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install sensor.
(2) Tighten to 6±8 N´m (55±75 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to sensor. The sen-
sor connector is symmetrical (not indexed). It can be
installed to the sensor in either direction.
(4) Install air cleaner assembly.
(5) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 13 Block HeaterÐDiesel Engine
1 - BLOCK HEATER
Fig. 14 Engine Coolant Temperature
1 - GENERATOR
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
BR/BEENGINE 7 - 47
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 298 of 2255

(6) Remove generator. Position generator to gain
access for thermostat gasket removal.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER HPC-20)
MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. ALWAYSWEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING CON-
STANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps (Fig. 18). If
replacement is necessary, use only an original
equipment clamp with matching number or letter.
(7) Remove radiator upper hose clamp and upper
hose at thermostat housing.
(8) Position wiring harness (behind thermostat
housing) to gain access to thermostat housing.
(9) Remove thermostat housing mounting bolts,
thermostat housing, gasket and thermostat (Fig. 19).
Discard old gasket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean mating areas of intake manifold and
thermostat housing.
(2) Install thermostat (spring side down) into
recessed machined groove on intake manifold (Fig.
19).
(3) Install gasket on intake manifold and over
thermostat (Fig. 19).
(4) Position thermostat housing to intake manifold.
Note the word FRONT stamped on housing (Fig. 20).
For adequate clearance, thismustbe placed towards
front of vehicle. The housing is slightly angled for-
ward after installation to intake manifold.
(5) Install two housing-to-intake manifold bolts.
Tighten bolts to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install radiator upper hose to thermostat hous-
ing.
Fig. 16 Generator Support BracketÐ5.9L Engine
1 - IDLER PULLEY BUSHING
2 - A/C AND/OR GENERATOR MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - SCREW AND WASHER
Fig. 17 Automatic Belt TensionerÐ5.9L Engines
1 - IDLER PULLEY
2 - TENSIONER
3 - FAN BLADE
Fig. 18 SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
BR/BEENGINE 7 - 49
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - 5.9L (Continued)