2002 DODGE RAM power
[x] Cancel search: powerPage 278 of 2255

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISE (Objectional squeal, spueak,
or rumble is heard or felt while drive
belt is in operation)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Bearing noise 2. Locate and repair
3. Belt misalignment 3. Align belt/pulley(s)
4. Belt to pulley mismatch 4. Install correct belt
5. Driven component induced
vibration5. Locate defective driven
component and repair
TENSION SHEETING FABRIC
FAILURE
(Woven fabric on outside,
circumference of belt has cracked or
separated from body of belt)1. Tension sheeting contacting
stationary object1. Correct rubbing condition
2. Excessive heat causing woven
fabric to age2. Replace belt
3. Tension sheeting splice has
fractured3. Replace belt
CORD EDGE FAILURE
(Tensile member exposed at edges
of belt or separated from belt body)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Belt contacting stationary object 2. Replace belt
3. Pulley(s) out of tolerance 3. Replace pulley
4. Insufficient adhesion between
tensile member and rubber matrix4. Replace belt
REMOVAL
Drive belts are equipped with a spring loaded auto-
matic belt tensioner (Fig. 16). This belt tensioner will
be used on all belt configurations, such as with or
without power steering or air conditioning. For more
information, refer to Automatic Belt Tensioner, pro-
ceeding in this group.
(1) Attach a socket/wrench to pulley mounting bolt
of automatic tensioner (Fig. 16). The threads on the
pulley mounting bolt are left- hand.
(2) Relax the tension from the belt by rotating the
tensioner counterclockwise (as viewed from front)
(Fig. 16). When all belt tension has been relaxed,
remove belt from tensioner pulley first and other pul-
leys last.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: When installing the accessory drive belt,
the belt must be routed correctly. If not, engine may
overheat due to water pump rotating in wrong
direction. Refer to (Fig. 17) (Fig. 18) for correct
engine belt routing. The correct belt with correct
length must be used.
CAUTION: If the pulley is to be removed from the
tensioner, its mounting bolt has left-hand threads.
Fig. 16 Belt Tensioner
1 - PULLEY BOLT
2 - IDLER PULLEY
3 - TENSIONER PULLEY
4 - TENSIONER
5 - TENSIONER MOUNTING BOLT
BR/BEACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 29
DRIVE BELTS - 8.0L (Continued)
Page 279 of 2255

(1) Position drive belt over all pulleysexceptten-
sioner pulley.
(2) Attach a socket/wrench to pulley mounting bolt
of automatic tensioner (Fig. 16).
(3) Rotate socket/wrench counterclockwise. Install
belt over tensioner pulley. Let tensioner rotate back
into place. Remove wrench. Be sure belt is properly
seated on all pulleys.
DRIVE BELTS - 5.9L DIESEL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐACCESSORY
DRIVE BELT
VISUAL DIAGNOSIS
When diagnosing serpentine accessory drive belts,
small cracks that run across the ribbed surface of the
belt from rib to rib (Fig. 19), are considered normal.
These are not a reason to replace the belt. However,
cracks running along a rib (not across) arenotnor-
mal. Any belt with cracks running along a rib must
be replaced (Fig. 19). Also replace the belt if it has
excessive wear, frayed cords or severe glazing.
Refer to ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT DIAGNOSIS
CHART for further belt diagnosis.
Fig. 17 Belt RoutingÐWith A/C
1 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
2 - GENERATOR PULLEY
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - A/C COMPRESSOR PUMP PULLEY
5 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
6 - WATER PUMP AND FAN PULLEY
7 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
8 - AIR PUMP (A.I.R.) PULLEY
Fig. 18 Belt RoutingÐWithout A/C
1 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
2 - GENERATOR PULLEY
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
5 - WATER PUMP AND FAN PULLEY
6 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
7 - AIR PUMP (A.I.R.) PULLEY
Fig. 19 Belt Wear Patterns
1 - NORMAL CRACKS BELT OK
2 - NOT NORMAL CRACKS REPLACE BELT
7 - 30 ACCESSORY DRIVEBR/BE
DRIVE BELTS - 8.0L (Continued)
Page 282 of 2255
(3) Rotate ratchet and belt tensioner counterclock-
wise. Place belt over water pump pulley. Let ten-
sioner rotate back into place. Remove ratchet. Be
sure belt is properly seated on all pulleys.
VACUUM PUMP - 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
The vacuum pump and the power steering pump
are combined into a single assembly on diesel engine
models (Fig. 23). Both pumps are operated by a drive
gear attached to the vacuum pump shaft. The shaft
gear is driven by the camshaft gear.
The vacuum pump is a constant displacement,
vane-type pump. Vacuum is generated by four vanes
mounted in the pump rotor. The rotor is located in
the pump housing and is pressed onto the pump
shaft.
The vacuum and steering pumps are operated by a
single drive gear pressed onto the vacuum pump
shaft. The drive gear is operated by the engine cam-
shaft gear.
The vacuum and power steering pump shafts are
connected by a coupling. Each pump shaft has an
adapter with drive lugs that engage in the coupling.
The vacuum pump rotating components are lubri-
cated by engine oil. Lubricating oil is supplied to the
pump through an oil line at the underside of the
pump housing.
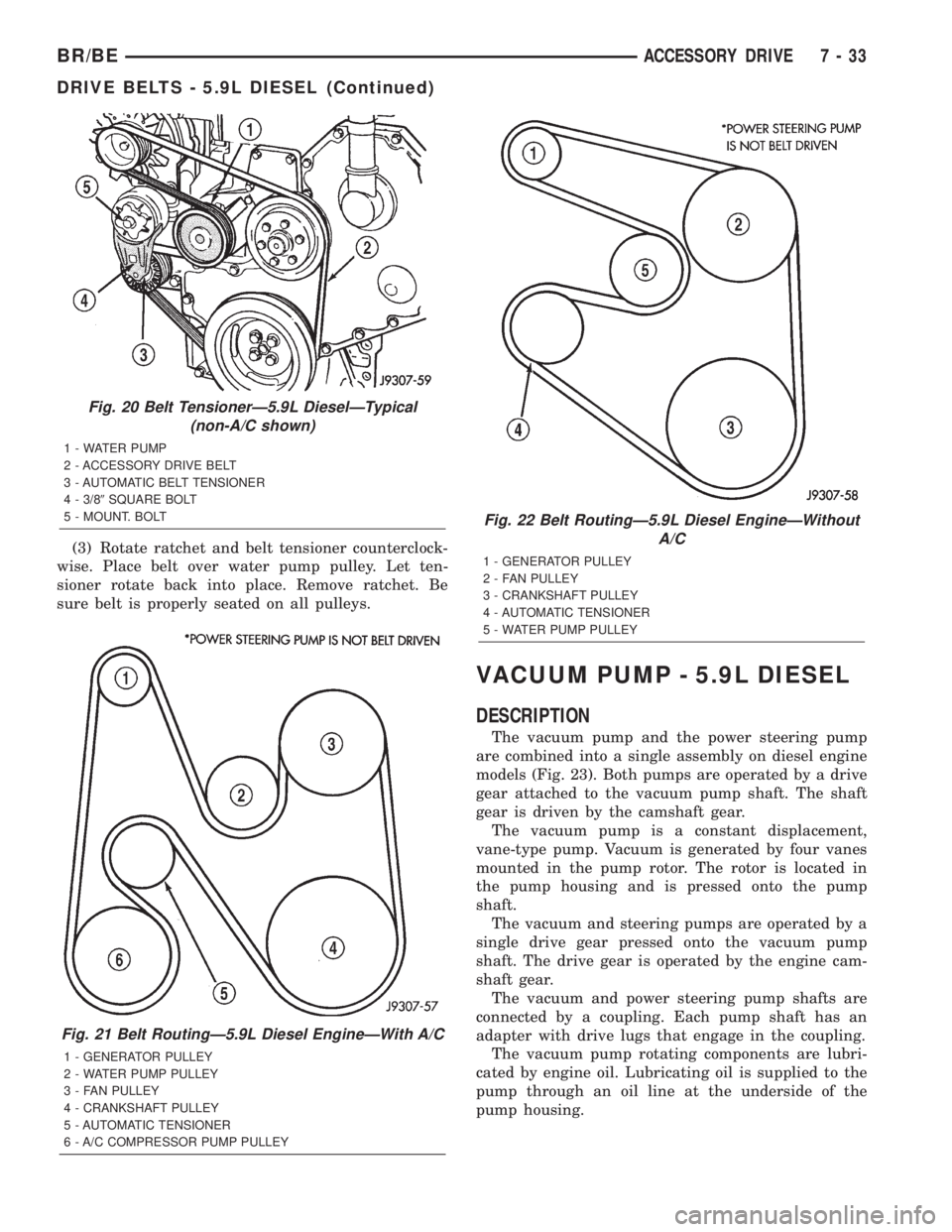
Fig. 20 Belt TensionerÐ5.9L DieselÐTypical
(non-A/C shown)
1 - WATER PUMP
2 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
3 - AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER
4 - 3/89SQUARE BOLT
5 - MOUNT. BOLT
Fig. 21 Belt RoutingÐ5.9L Diesel EngineÐWith A/C
1 - GENERATOR PULLEY
2 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
3 - FAN PULLEY
4 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
5 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
6 - A/C COMPRESSOR PUMP PULLEY
Fig. 22 Belt RoutingÐ5.9L Diesel EngineÐWithout
A/C
1 - GENERATOR PULLEY
2 - FAN PULLEY
3 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
4 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
5 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
BR/BEACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 33
DRIVE BELTS - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 283 of 2255

The complete assembly must be removed in order
to service either pump. However, the power steering
pump can be removed and serviced separately when
necessary.
The vacuum pump is not a serviceable component.
If diagnosis indicates a pump malfunction, the pump
must be replaced as an assembly. Do not disassemble
or attempt to repair the pump.
The combined vacuum and steering pump assem-
bly must be removed for access to either pump. How-
ever, the vacuum pump can be removed without
having to disassemble the power steering pump.
If the power steering pump requires service, simply
remove the assembly and separate the two pumps.
Refer to the pump removal and installation proce-
dures in this section.
OPERATION
Vacuum pump output is transmitted to the
HEVAC, speed control, systems through a supply
hose. The hose is connected to an outlet port on the
pump housing and uses an in-line check valve to
retain system vacuum when vehicle is not running.
Pump output ranges from a minimum of 8.5 to 25
inches vacuum.
The pump rotor and vanes are rotated by the pump
drive gear. The drive gear is operated by the cam-
shaft gear.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐVACUUM PUMP
OUTPUT
The vacuum pump supplies necessary vacuum to
components in the following systems:
²HEVAC system
²Speed Control System
A quick check to determine if the vacuum pump is
the cause of the problem in any of these systems is to
road test the vehicle and verify that all of these sys-
tems are fuctioning properly. If only one of these has
a vacuum related failure, then it is likely the vacuum
pump is not the cause.
A standard vacuum gauge can be used to check
pump output when necessary. Simply disconnect the
pump supply hose and connect a vacuum gauge to
the outlet port for testing purposes. With the engine
running, vacuum output should be a minimum of 25
inches, depending on engine speed.
DIAGNOSING LOW VACUUM OUTPUT CONDITION
If the vacuum pump is suspected of low vacuum
output, check the pump and vacuum harnesses as
follows:
(1) Visually inspect the vacuum harness for obvi-
ous failures (i.e. disconnected, cracks, breaks etc.)
(2) Disconnect the vacuum supply hose at the vac-
uum pump check valve. Connect vacuum gauge to
this valve and run engine at various throttle open-
ings. Output should be a minimum 25 inches of vac-
uum. If vacuum is consistently below 25 inches, the
vacuum pump should be replaced. If output is within
specified limits, the vacuum harness should be sus-
pected as the cause.
(3) Disconnect and isolate the vacuum supply har-
ness. Cap off open ends and apply roughly 15 inches
of vacuum to the harness. If the vacuum gauge does
not hold its reading, then there is an open in the har-
ness and it should be repaired or replaced.
(4) If the vacuum loss is still not detected at this
point, then the pump and harness are not the cause
of the low vacuum condition. Apply vacuum to the
related components of the vacuum supply system (i.e.
valves, servos, solenoids, etc.) to find the source of
the vacuum loss.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cables.
(2) Position drain pan under power steering pump.
(3) Disconnect vacuum and steering pump hoses.
(4) Disconnect lubricating oil feed line from fitting
at underside of vacuum pump (Fig. 24).
(5) Remove lower bolt that attaches pump assem-
bly to engine block (Fig. 25).
Fig. 23 Diesel Vacuum & Power Steering Pump
Assembly
1 - VACUUM PUMP
2 - POWER STEERING PUMP
3 - PUMP ADAPTER
4 - DRIVE GEAR
7 - 34 ACCESSORY DRIVEBR/BE
VACUUM PUMP - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 284 of 2255
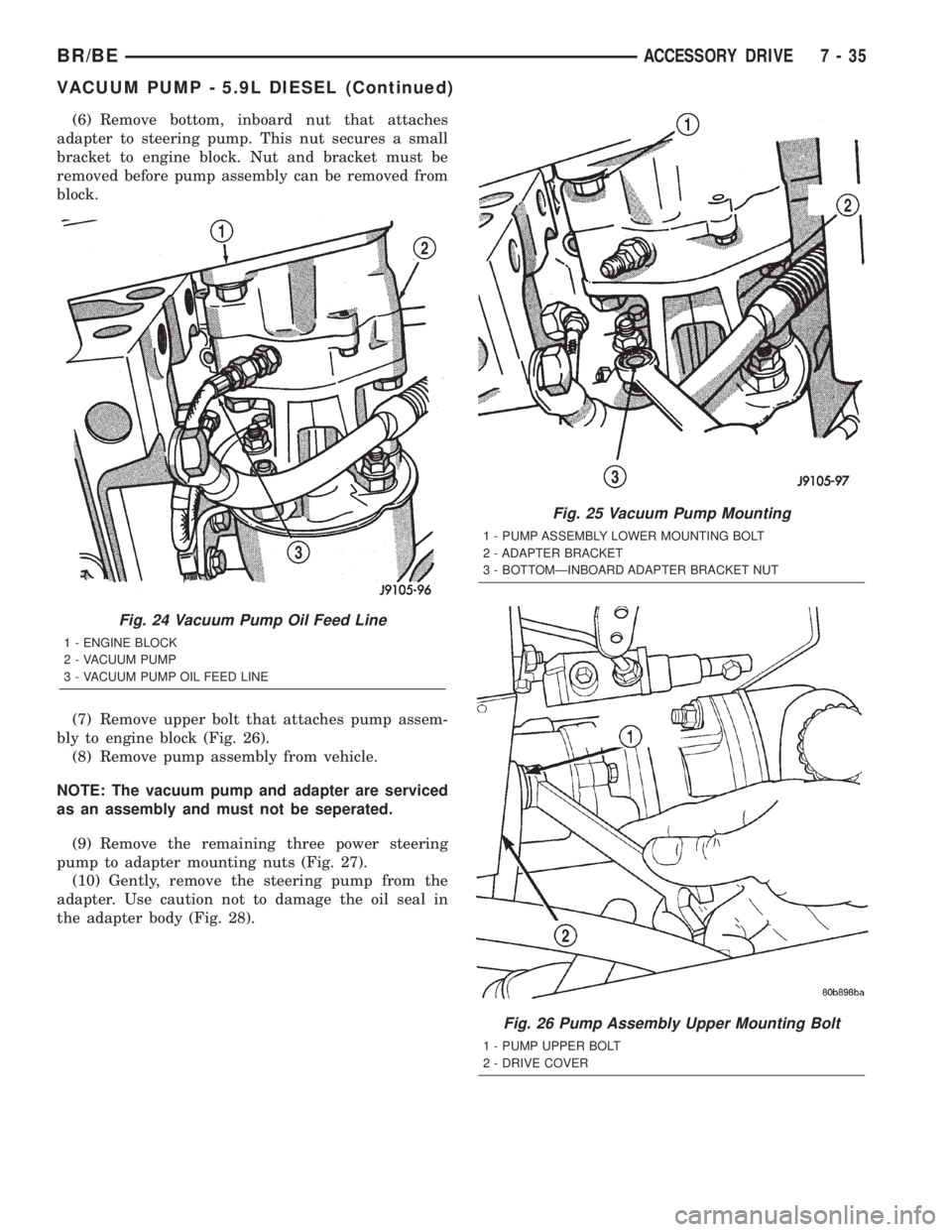
(6) Remove bottom, inboard nut that attaches
adapter to steering pump. This nut secures a small
bracket to engine block. Nut and bracket must be
removed before pump assembly can be removed from
block.
(7) Remove upper bolt that attaches pump assem-
bly to engine block (Fig. 26).
(8) Remove pump assembly from vehicle.
NOTE: The vacuum pump and adapter are serviced
as an assembly and must not be seperated.
(9) Remove the remaining three power steering
pump to adapter mounting nuts (Fig. 27).
(10) Gently, remove the steering pump from the
adapter. Use caution not to damage the oil seal in
the adapter body (Fig. 28).
Fig. 24 Vacuum Pump Oil Feed Line
1 - ENGINE BLOCK
2 - VACUUM PUMP
3 - VACUUM PUMP OIL FEED LINE
Fig. 25 Vacuum Pump Mounting
1 - PUMP ASSEMBLY LOWER MOUNTING BOLT
2 - ADAPTER BRACKET
3 - BOTTOMÐINBOARD ADAPTER BRACKET NUT
Fig. 26 Pump Assembly Upper Mounting Bolt
1 - PUMP UPPER BOLT
2 - DRIVE COVER
BR/BEACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 35
VACUUM PUMP - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 285 of 2255
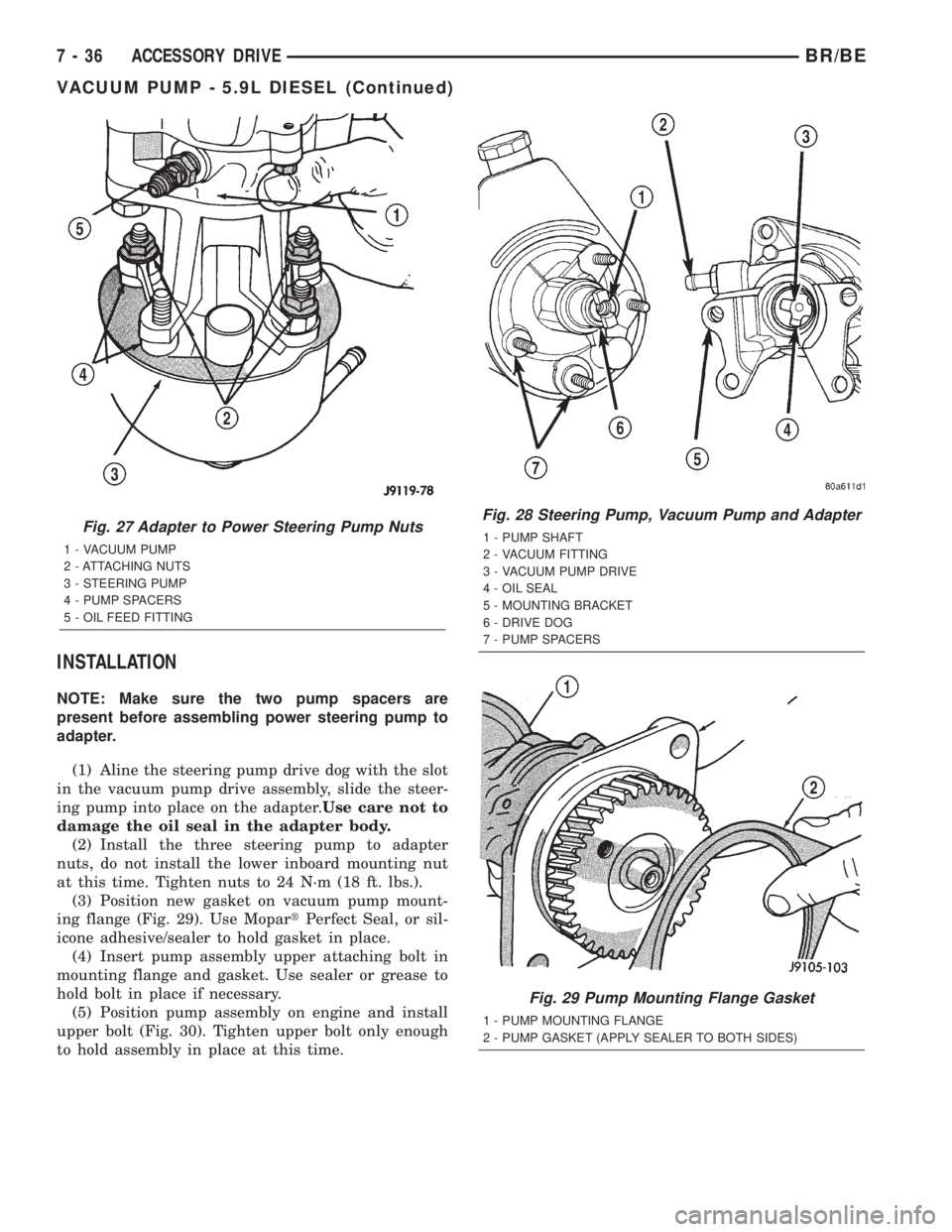
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Make sure the two pump spacers are
present before assembling power steering pump to
adapter.
(1) Aline the steering pump drive dog with the slot
in the vacuum pump drive assembly, slide the steer-
ing pump into place on the adapter.Use care not to
damage the oil seal in the adapter body.
(2) Install the three steering pump to adapter
nuts, do not install the lower inboard mounting nut
at this time. Tighten nuts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(3) Position new gasket on vacuum pump mount-
ing flange (Fig. 29). Use MopartPerfect Seal, or sil-
icone adhesive/sealer to hold gasket in place.
(4) Insert pump assembly upper attaching bolt in
mounting flange and gasket. Use sealer or grease to
hold bolt in place if necessary.
(5) Position pump assembly on engine and install
upper bolt (Fig. 30). Tighten upper bolt only enough
to hold assembly in place at this time.
Fig. 27 Adapter to Power Steering Pump Nuts
1 - VACUUM PUMP
2 - ATTACHING NUTS
3 - STEERING PUMP
4 - PUMP SPACERS
5 - OIL FEED FITTING
Fig. 28 Steering Pump, Vacuum Pump and Adapter
1 - PUMP SHAFT
2 - VACUUM FITTING
3 - VACUUM PUMP DRIVE
4 - OIL SEAL
5 - MOUNTING BRACKET
6 - DRIVE DOG
7 - PUMP SPACERS
Fig. 29 Pump Mounting Flange Gasket
1 - PUMP MOUNTING FLANGE
2 - PUMP GASKET (APPLY SEALER TO BOTH SIDES)
7 - 36 ACCESSORY DRIVEBR/BE
VACUUM PUMP - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 286 of 2255

(6) Working from under vehicle, install pump
assembly lower attaching bolt. Then tighten upper
and lower bolt to 77 N´m (57 ft. lbs.).
(7) Position bracket on steering pump inboard
stud. Then install remaining adapter attaching nut
on stud. Tighten nut to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(8) Connect oil feed line to vacuum pump connec-
tor and tighten line fitting.
(9) Connect steering pump pressure and return
lines to pump. Tighten pressure line fitting to 30
N´m (22 ft. lbs.).
(10) Connect vacuum hose to vacuum pump.
(11) Connect battery cables, if removed.
(12) Fill power steering pump reservoir and Purge
air from steering pump lines (Refer to 19 - STEER-
ING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 30 Installing Pump Assembly On Engine
1 - PUMP ASSEMBLY
2 - PUMP GASKET
3 - DRIVE GEAR
BR/BEACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 37
VACUUM PUMP - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 293 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Install fan blade assembly to viscous fan drive.
Tighten mounting bolts to 23 N´m (17 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Position the fan shroud and fan blade/viscous
fan drive to the vehicle as an assembly.
(3) Install viscous fan drive assembly on fan hub
shaft (Fig. 7). Tighten mounting nut to 57 N´m (42 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(4) Install fan shroud bolts into position and
tighten the mounting bolts to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.)
torque.
(5) Connect the battery negative cables.
NOTE:
Viscous Fan Drive Fluid Pump Out Requirement:
After installing a new viscous fan drive, bring the
engine speed up to approximately 2000 rpm and
hold for approximately two minutes. This will
ensure proper fluid distribution within the drive.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER - 5.9L
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE ENGINE UNLESS
BLOCK HEATER CORD HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED
FROM POWER SOURCE AND SECURED IN PLACE.
THE POWER CORD MUST BE SECURED IN ITS
RETAINING CLIPS AND ROUTED AWAY FROM
EXHAUST MANIFOLDS AND MOVING PARTS.
An optional engine block heater is available on all
models. The heater is equipped with a power cord.
The heater is mounted in a core hole of the engine
cylinder block (in place of a freeze plug) with the
heating element immersed in engine coolant. The
cord is attached to an engine compartment compo-
nent with tie-straps.
The 5.9L gas powered engine has the block heater
located on the right side of engine next to the oil fil-
ter (Fig. 8).
OPERATION
The heater warms the engine coolant providing
easier engine starting and faster warm-up in low
temperatures. Connecting the power cord to a
grounded 110-120 volt AC electrical outlet with a
grounded three wire extension cord provides the elec-
tricity needed to heat the element..
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Drain coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).(3) Remove power cord from heater by unplugging
(Fig. 9).
(4) Loosen (but do not completely remove) the
screw at center of block heater (Fig. 9).
(5) Remove block heater by carefully prying from
side-to-side. Note direction of heating element coil
(up or down). Element coil must be installed correctly
to prevent damage.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and inspect the block heater hole.
(2) Install new O-ring seal(s) to heater in gasoline
engines.
(3) Insert block heater into cylinder block.
(4) With heater fully seated, tighten center screw
to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(5) Fill cooling system with recommended coolant.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(6) Start and warm the engine.
(7) Check block heater for leaks.
Fig. 8 Engine Block Heater
1 - FREEZE PLUG HOLE
2 - BLOCK HEATER
3 - SCREW
4 - POWER CORD (120V AC)
5 - HEATING COIL
6 - OIL FILTER
7 - 44 ENGINEBR/BE
RADIATOR FAN - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)