2002 DODGE RAM ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 1812 of 2255
GEAR CASE
(1) Position park pawl and spring in case and
install park pawl shaft. Verify that end of spring
with 90É bend is hooked to pawl and straight end of
spring is seated against case.
(2) Install pawl shaft retaining bolt. Tighten bolt
to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
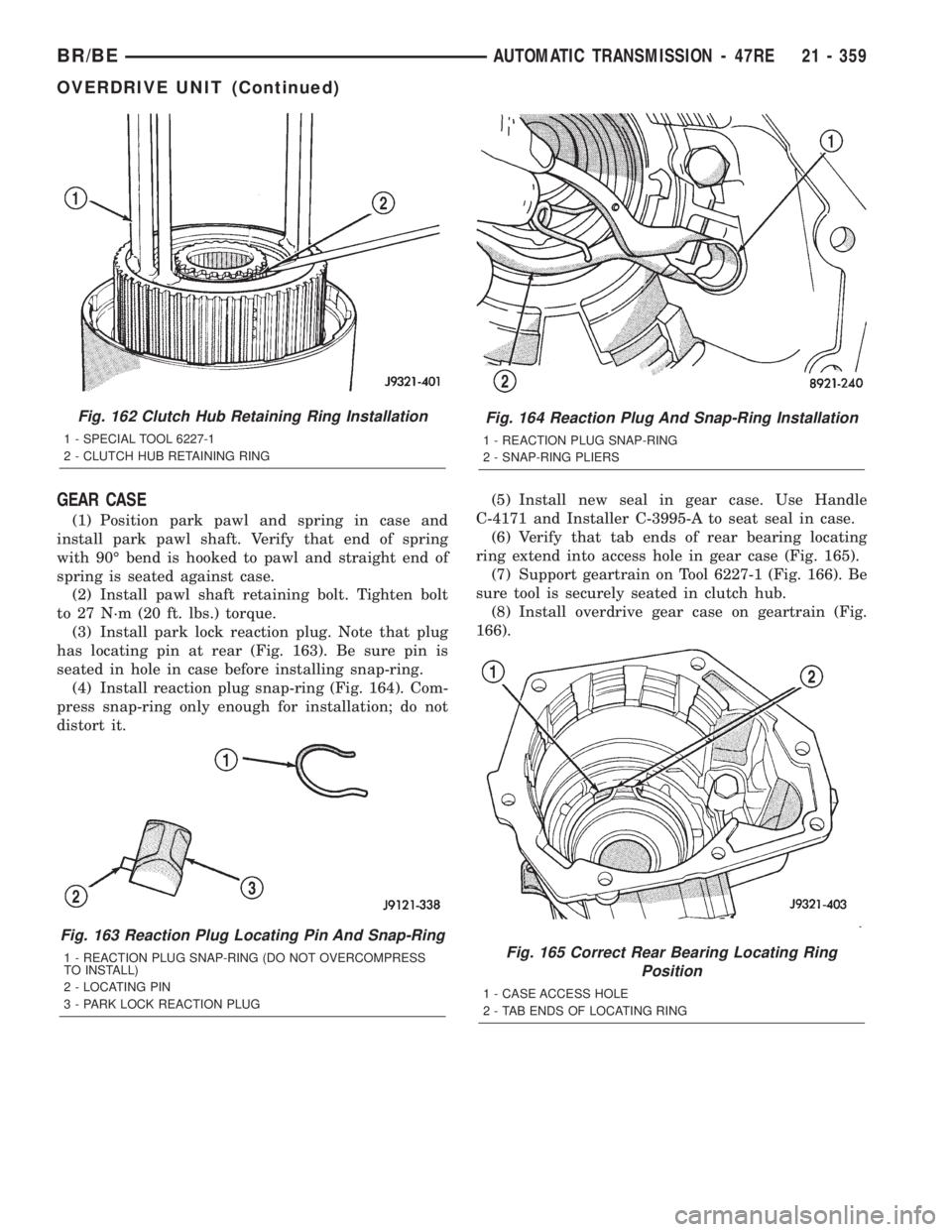
(3) Install park lock reaction plug. Note that plug
has locating pin at rear (Fig. 163). Be sure pin is
seated in hole in case before installing snap-ring.
(4) Install reaction plug snap-ring (Fig. 164). Com-
press snap-ring only enough for installation; do not
distort it.(5) Install new seal in gear case. Use Handle
C-4171 and Installer C-3995-A to seat seal in case.
(6) Verify that tab ends of rear bearing locating
ring extend into access hole in gear case (Fig. 165).
(7) Support geartrain on Tool 6227-1 (Fig. 166). Be
sure tool is securely seated in clutch hub.
(8) Install overdrive gear case on geartrain (Fig.
166).
Fig. 162 Clutch Hub Retaining Ring Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6227-1
2 - CLUTCH HUB RETAINING RING
Fig. 163 Reaction Plug Locating Pin And Snap-Ring
1 - REACTION PLUG SNAP-RING (DO NOT OVERCOMPRESS
TO INSTALL)
2 - LOCATING PIN
3 - PARK LOCK REACTION PLUG
Fig. 164 Reaction Plug And Snap-Ring Installation
1 - REACTION PLUG SNAP-RING
2 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
Fig. 165 Correct Rear Bearing Locating Ring
Position
1 - CASE ACCESS HOLE
2 - TAB ENDS OF LOCATING RING
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 359
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1813 of 2255
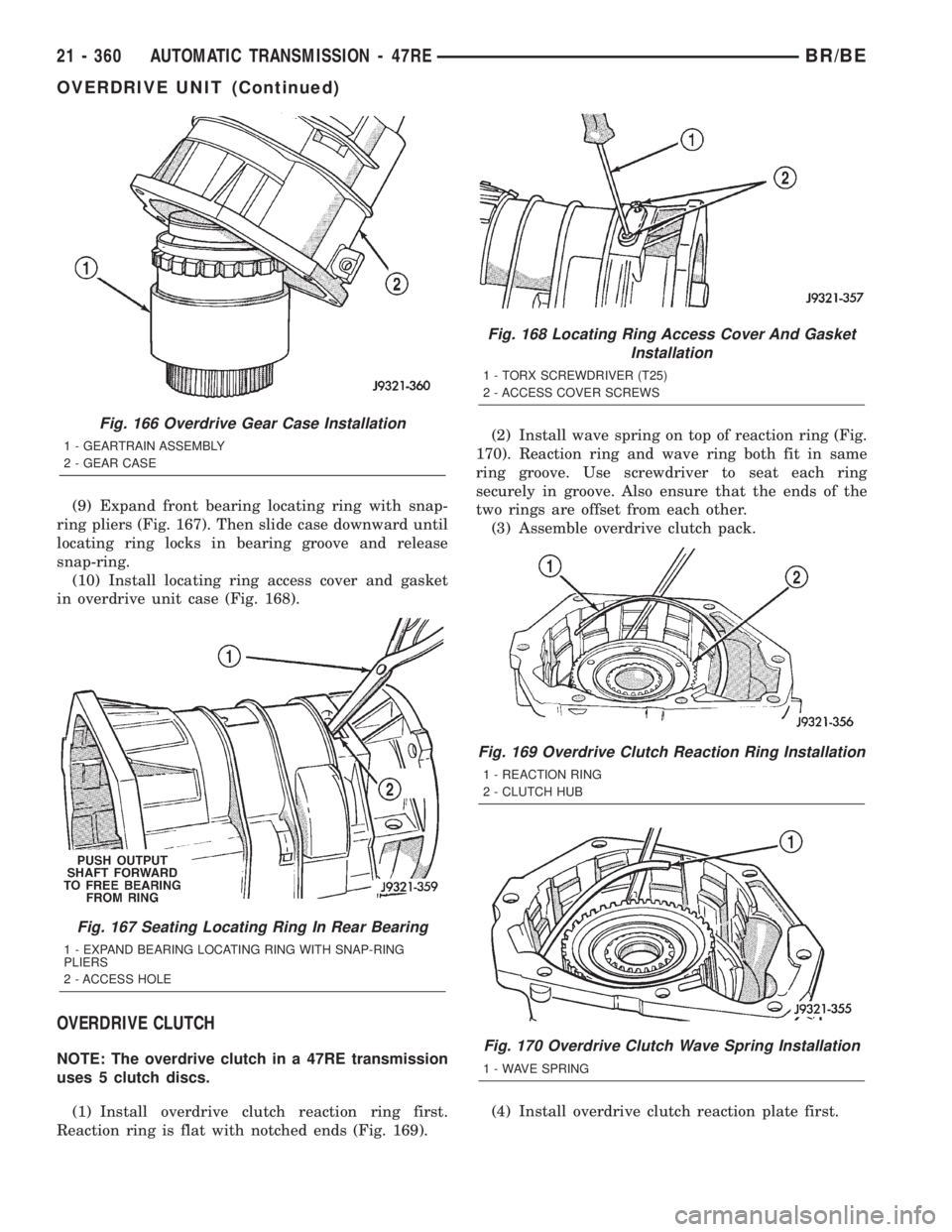
(9) Expand front bearing locating ring with snap-
ring pliers (Fig. 167). Then slide case downward until
locating ring locks in bearing groove and release
snap-ring.
(10) Install locating ring access cover and gasket
in overdrive unit case (Fig. 168).
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
NOTE: The overdrive clutch in a 47RE transmission
uses 5 clutch discs.
(1) Install overdrive clutch reaction ring first.
Reaction ring is flat with notched ends (Fig. 169).(2) Install wave spring on top of reaction ring (Fig.
170). Reaction ring and wave ring both fit in same
ring groove. Use screwdriver to seat each ring
securely in groove. Also ensure that the ends of the
two rings are offset from each other.
(3) Assemble overdrive clutch pack.
(4) Install overdrive clutch reaction plate first.
Fig. 166 Overdrive Gear Case Installation
1 - GEARTRAIN ASSEMBLY
2 - GEAR CASE
Fig. 167 Seating Locating Ring In Rear Bearing
1 - EXPAND BEARING LOCATING RING WITH SNAP-RING
PLIERS
2 - ACCESS HOLE
Fig. 168 Locating Ring Access Cover And Gasket
Installation
1 - TORX SCREWDRIVER (T25)
2 - ACCESS COVER SCREWS
Fig. 169 Overdrive Clutch Reaction Ring Installation
1 - REACTION RING
2 - CLUTCH HUB
Fig. 170 Overdrive Clutch Wave Spring Installation
1 - WAVE SPRING
21 - 360 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1815 of 2255
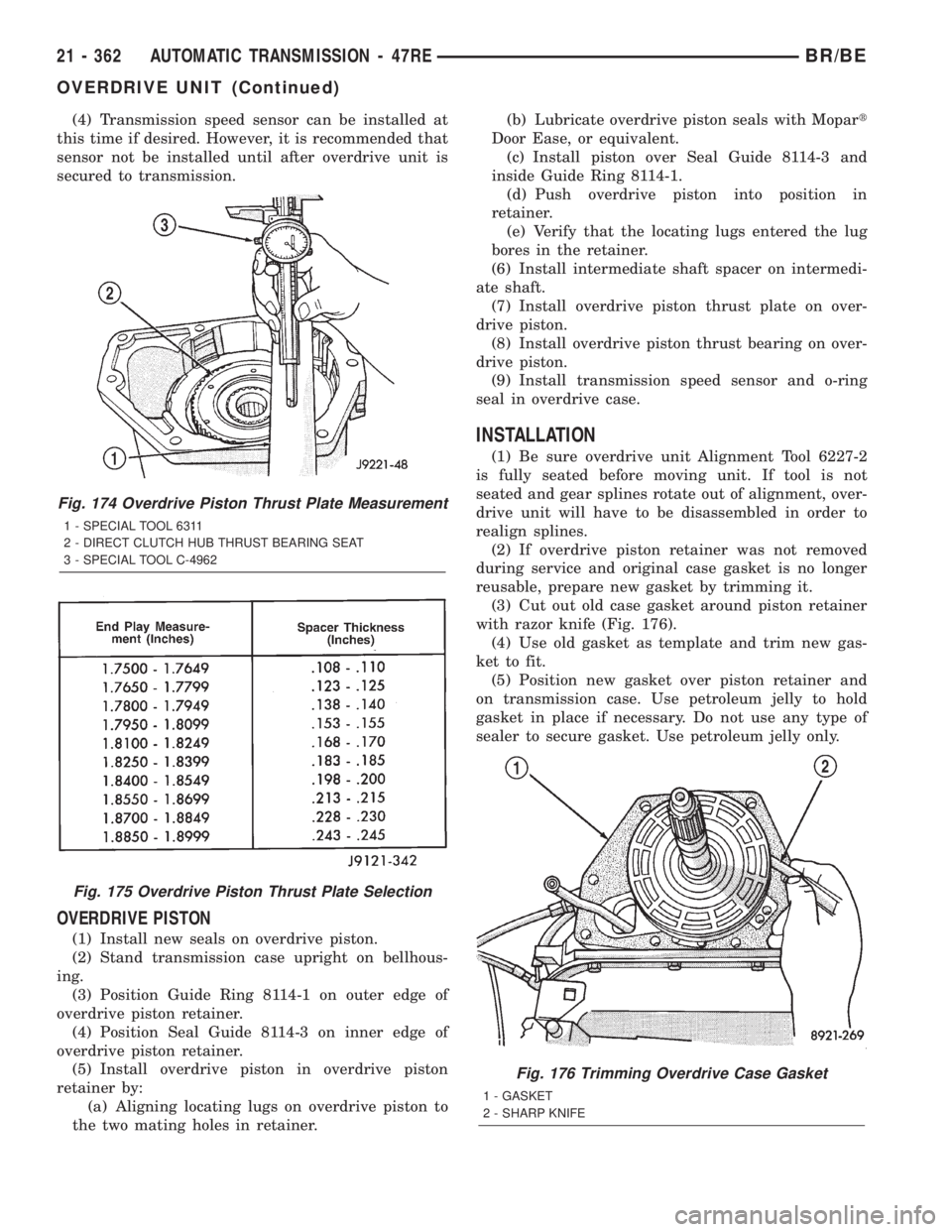
(4) Transmission speed sensor can be installed at
this time if desired. However, it is recommended that
sensor not be installed until after overdrive unit is
secured to transmission.
OVERDRIVE PISTON
(1) Install new seals on overdrive piston.
(2) Stand transmission case upright on bellhous-
ing.
(3) Position Guide Ring 8114-1 on outer edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(4) Position Seal Guide 8114-3 on inner edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(5) Install overdrive piston in overdrive piston
retainer by:
(a) Aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston to
the two mating holes in retainer.(b) Lubricate overdrive piston seals with Mopart
Door Ease, or equivalent.
(c) Install piston over Seal Guide 8114-3 and
inside Guide Ring 8114-1.
(d) Push overdrive piston into position in
retainer.
(e) Verify that the locating lugs entered the lug
bores in the retainer.
(6) Install intermediate shaft spacer on intermedi-
ate shaft.
(7) Install overdrive piston thrust plate on over-
drive piston.
(8) Install overdrive piston thrust bearing on over-
drive piston.
(9) Install transmission speed sensor and o-ring
seal in overdrive case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure overdrive unit Alignment Tool 6227-2
is fully seated before moving unit. If tool is not
seated and gear splines rotate out of alignment, over-
drive unit will have to be disassembled in order to
realign splines.
(2) If overdrive piston retainer was not removed
during service and original case gasket is no longer
reusable, prepare new gasket by trimming it.
(3) Cut out old case gasket around piston retainer
with razor knife (Fig. 176).
(4) Use old gasket as template and trim new gas-
ket to fit.
(5) Position new gasket over piston retainer and
on transmission case. Use petroleum jelly to hold
gasket in place if necessary. Do not use any type of
sealer to secure gasket. Use petroleum jelly only.
Fig. 174 Overdrive Piston Thrust Plate Measurement
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6311
2 - DIRECT CLUTCH HUB THRUST BEARING SEAT
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4962
Fig. 175 Overdrive Piston Thrust Plate Selection
Fig. 176 Trimming Overdrive Case Gasket
1 - GASKET
2 - SHARP KNIFE
21 - 362 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1817 of 2255

DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the overdrive piston (Fig. 179).
(2) Remove the overdrive piston retainer bolts.
(3) Remove overdrive piston retainer.
(4) Remove case gasket.
(5) Tap old cam out of case with pin punch. Insert
punch through bolt holes at rear of case (Fig. 180).
Alternate position of punch to avoid cocking cam dur-
ing removal.
(6) Clean clutch cam bore and case. Be sure to
remove all chips/shavings generated during cam
removal.
CLEANING
Clean the overrunning clutch assembly, clutch cam,
low-reverse drum, and overdrive piston retainer in
solvent. Dry them with compressed air after clean-
ing.
INSPECTION
Inspect condition of each clutch part after cleaning.
Replace the overrunning clutch roller and spring
assembly if any rollers or springs are worn or dam-
aged, or if the roller cage is distorted, or damaged.
Replace the cam if worn, cracked or damaged.
Replace the low-reverse drum if the clutch race,
roller surface or inside diameter is scored, worn or
damaged.Do not remove the clutch race from
the low-reverse drum under any circumstances.
Replace the drum and race as an assembly if
either component is damaged.
Examine the overdrive piston retainer carefully for
wear, cracks, scoring or other damage. Be sure the
retainer hub is a snug fit in the case and drum.
Replace the retainer if worn or damaged.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Temporarily install overdrive piston retainer in
case. Use 3-4 bolts to secure retainer.
(2) Align and start new clutch cam in the trans-
mission case. Be sure serrations on cam and in case
are aligned (Fig. 181). Then tap cam into case just
enough to hold it in place.
(3) Verify that cam is correctly positioned before
proceeding any further. Narrow ends of cam ramps
should be to left when cam is viewed from front end
of case (Fig. 181).
(4) Insert Adapter Tool SP-5124 into piston
retainer (Fig. 182).
(5) Assemble Puller Bolt SP-3701 and Press Plate
SP-3583-A (Fig. 183).
(6) Install assembled puller plate and bolt (Fig.
184). Insert bolt through cam, case and adapter tool.
Be sure plate is seated squarely on cam.
(7) Hold puller plate and bolt in place and install
puller nut SP-3701 on puller bolt (Fig. 185).
(8) Tighten puller nut to press clutch cam into
case (Fig. 185). Be sure cam is pressed into case
evenly and does not become cocked.
(9) Remove clutch cam installer tools.
(10) Stake case in 14 places around clutch cam to
help secure cam in case. Use blunt punch or chisel to
stake case.
Fig. 179 Overdrive Piston Removal
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH PISTON
2 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
3 - SELECTIVE SPACER
4 - PISTON RETAINER
Fig. 180 Overrunning Clutch Cam
1 - PIN PUNCH
2 - REAR SUPPORT BOLT HOLES
21 - 364 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1824 of 2255

INSPECTION
Inspect the planetary gear sets and annulus gears.
The planetary pinions, shafts, washers, and retaining
pins are serviceable. However, if a pinion carrier is
damaged, the entire planetary gear set must be
replaced as an assembly.
Replace the annulus gears if the teeth are chipped,
broken, or worn, or the gear is cracked. Replace the
planetary thrust plates and the tabbed thrust wash-
ers if cracked, scored or worn.Inspect the machined surfaces of the intermediate
shaft. Be sure the oil passages are open and clear.
Replace the shaft if scored, pitted, or damaged.
Inspect the sun gear and driving shell. If either
component is worn or damaged, remove the sun gear
rear retaining ring and separate the sun gear and
thrust plate from the driving shell. Then replace the
necessary component.
Replace the sun gear as an assembly if the gear
teeth are chipped or worn. Also replace the gear as
an assembly if the bushings are scored or worn. The
sun gear bushings are not serviceable. Replace the
thrust plate if worn, or severely scored. Replace the
driving shell if distorted, cracked, or damaged in any
way.
Replace all snap-rings during geartrain assembly.
Reusing snap-rings is not recommended.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate sun gear and planetary gears with
transmission fluid during assembly. Use petroleum
jelly to lubricate intermediate shaft bushing surfaces,
thrust washers and thrust plates and to hold these
parts in place during assembly.
(2) Install front snap-ring on sun gear and install
gear in driving shell. Then install thrust plate over
sun gear and against rear side of driving shell (Fig.
202). Install rear snap-ring to secure sun gear and
thrust plate in driving shell.
(3) Install rear annulus gear on intermediate shaft
(Fig. 203).
(4) Install thrust plate in annulus gear (Fig. 204).
Be sure plate is seated on shaft splines and against
gear.
Fig. 199 Rear Planetary Thrust Washer Removal
1 - SUN GEAR
2 - REAR PLANETARY THRUST WASHER
3 - DRIVING SHELL
Fig. 200 Rear Planetary And Annulus Gear Removal
1 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
2 - REAR ANNULUS GEAR
3 - REAR PLANETARY GEAR
Fig. 201 Rear Annulus Thrust Plate Removal
1 - REAR ANNULUS GEAR
2 - THRUST PLATE
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 371
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT (Continued)
Page 1833 of 2255

ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT
Check linkage adjustment by starting engine in
PARK and NEUTRAL. Adjustment is acceptable if
the engine starts in only these two positions. Adjust-
ment is incorrect if the engine starts in one position
but not both positions
If the engine starts in any other position, or if the
engine will not start in any position, the park/neutral
switch is probably faulty.
LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
Check condition of the shift linkage (Fig. 222). Do
not attempt adjustment if any component is loose,
worn, or bent. Replace any suspect components.
Replace the grommet securing the shift rod or
torque rod in place if either rod was removed from
the grommet. Remove the old grommet as necessary
and use suitable pliers to install the new grommet.
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Loosen lock bolt in front shift rod adjusting
swivel (Fig. 222).
(4) Ensure that the shift rod slides freely in the
swivel. Lube rod and swivel as necessary.
(5) Move transmission shift lever fully rearward to
the Park detent.
(6) Center adjusting swivel on shift rod.
(7) Tighten swivel lock bolt to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(8) Lower vehicle and verify proper adjustment.
SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
²Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
²Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
Fig. 222 Linkage Adjustment Components
1 - FRONT SHIFT ROD
2 - TORQUE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
3 - TORQUE SHAFT ARM
4 - ADJUSTING SWIVEL
5 - LOCK BOLT
21 - 380 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
SHIFT MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 1842 of 2255

STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 236).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the overrun-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The torque converter clutch is hydraulically
applied and is released when fluid is vented from the
hydraulic circuit by the torque converter control
(TCC) solenoid on the valve body. The torque con-
verter clutch is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The torque converter clutch engages
in fourth gear, and in third gear under various con-
ditions, such as when the O/D switch is OFF, when
the vehicle is cruising on a level surface after the
vehicle has warmed up. The torque converter clutch
will disengage momentarily when an increase in
engine load is sensed by the PCM, such as when thevehicle begins to go uphill or the throttle pressure is
increased.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 237). Surface of converter lugs
should be 19mm (0.75 in.) to the rear of the straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
Fig. 236 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 389
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1862 of 2255

(8) Remove bolts attaching valve body to transmis-
sion case.
(9) Lower valve body enough to remove accumula-
tor piston and springs.
(10) Work manual lever shaft and electrical con-
nector out of transmission case.
(11) Lower valve body, rotate valve body away
from case, pull park rod out of sprag, and remove
valve body (Fig. 264).DISASSEMBLY
CAUTION: Do not clamp any valve body component
in a vise. This practice can damage the component
resulting in unsatisfactory operation after assembly
and installation. Do not use pliers to remove any of
the valves, plugs or springs and do not force any of
the components out or into place. The valves and
valve body housings will be damaged if force is
used. Tag or mark the valve body springs for refer-
ence as they are removed. Do not allow them to
become intermixed.
(1) Disconnect wires from governor pressure sen-
sor and solenoid.
(2) Remove screws attaching governor body and
retainer plate to transfer plate.
(3) Remove retainer plate, governor body and gas-
ket from transfer plate.
(4) Remove governor pressure sensor from gover-
nor body.
(5) Remove governor pressure solenoid by pulling
it straight out of bore in governor body. Remove and
discard solenoid O-rings if worn, cut, or torn.
(6) Remove small shoulder bolt that secures sole-
noid harness case connector to 3-4 accumulator hous-
ing (Fig. 265). Retain shoulder bolt. Either tape it to
harness or thread it back into accumulator housing
after connector removal.
Fig. 263 Transmission Case Connector
1 - SOLENOID CASE CONNECTOR
2 - PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
Fig. 264 Valve Body
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - WIRE HARNESS
3 - PARK ROD
4 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
5 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
Fig. 265 Solenoid Harness Case Connector
Shoulder Bolt
1 - SOLENOID HARNESS CASE CONNECTOR
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 409
VALVE BODY (Continued)