2002 DODGE RAM ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 1396 of 2255

(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Remove cable cover (Fig. 6). Cable cover is
attached with 2 Phillips screws, 2 plastic retention
clips and 2 push tabs (Fig. 6). Remove 2 Phillips
screws and carefully pry out 2 retention clips. After
clip removal, push rearward on front tab, and
upward on lower tab for cover removal.
(3) Using finger pressure only, disconnect end of
speed control servo cable from throttle lever pin by
pulling forward on connector while holding lever
rearward (Fig. 7).DO NOT try to pull connector
off perpendicular to lever pin. Connector will
be broken.
(4) Using two small screwdrivers, pry throttle
cable connector socket from throttle lever ball (Fig.
7).Be very careful not to bend throttle lever
arm.
(5) Disconnect transmission control cable at lever
arm (if equipped). Refer to 21, Transmission.
(6) Squeeze pinch tabs on speed control cable (Fig.
7) and pull cable rearward to remove from cable
mounting bracket.
(7) Squeeze pinch tabs on throttle cable (Fig. 7)
and pull cable rearward to remove from cable mount-
ing bracket.
(8) If equipped with an automatic transmission,
refer to 21, Transmission for transmission control
cable removal procedures.
(9) Disconnect wiring harness clip (Fig. 8) at bot-
tom of bracket.
(10) Remove 6 mounting bolts (Fig. 8) and par-
tially remove APPS assembly from engine. After
assembly is partially removed, disconnect electrical
connector from bottom of sensor by pushing on con-
nector tab (Fig. 9).
(11) Remove APPS assembly from engine.
INSTALLATION
The APPS is serviced (replaced) as one assembly
including the lever, brackets and sensor. The APPS is
calibrated to its mounting bracket. The APPS assem-
bly is located at left-front of engine below plastic
cable/lever/linkage cover (Fig. 6) .
(1) Snap electrical connector into bottom of sensor.
(2) Position APPS assembly to engine and install 6
bolts. Tighten bolts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect wiring harness clip (Fig. 8) at bottom
of bracket.
(4) If equipped with an automatic transmission,
refer to Group 21, Transmission for transmission con-
trol cable installation procedures.
(5) Install speed control cable into mounting
bracket. Be sure pinch tabs (Fig. 7) have secured
cable.(6) Install throttle cable into mounting bracket. Be
sure pinch tabs (Fig. 7) have secured cable.
(7) Connect throttle cable at lever (snaps on).
(8) Connect speed control cable to lever by pushing
cable connector rearward onto lever pin while hold-
ing lever forward.
(9) Install cable cover.
(10) Connect both negative battery cables to both
batteries.
(11)ECM Calibration:Turn key to ON position.
Without starting engine, slowly press throttle pedal
to floor and then slowly release. This step must be
done (one time) to ensure accelerator pedal position
sensor calibration has been learned by ECM. If not
done, possible DTC's may be set.
(12) Use DRB scan tool to erase any DTC's from
ECM/PCM.
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION
Six individual, high-pressure fuel injectors are
used. The injectors are vertically mounted (Fig. 10)
into a bored hole in the top of the cylinder head. This
bored hole is located between the intake/exhaust
valves.
Fig. 10 Fuel Injector Location
1 - CLAMP
2 - FUEL INJECTOR
3 - BORED HOLE
4 - SHIM
5 - BOLTS
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 97
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1408 of 2255

THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) From inside vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Remove plastic cable retainer and throttle cable core
wire from upper end of pedal arm (Fig. 39). The plas-
tic cable retainer snaps into pedal arm.
(3) Remove cable core wire at pedal arm.
(4) From inside vehicle, pinch both sides of plastic
cable housing retainer tabs at dash panel.
(5) Remove cable housing from dash panel and
pull cable into engine compartment.
(6) Remove cable cover (Fig. 36). Cable cover is
attached with 2 Phillips screws, 2 plastic retention
clips and 2 push tabs (Fig. 36). Remove 2 Phillips
screws and carefully pry out 2 retention clips. After
clip removal, push rearward on front tab, and
upward on lower tab for cover removal.
(7) Using 2 screwdrivers, pry cable connector
socket from throttle lever ball (Fig. 37).Be very
careful not to bend throttle lever arm.
(8) Squeeze 2 pinch tabs on sides of throttle cable
at mounting bracket (Fig. 38) and push cable rear-
ward out of bracket.
Fig. 36 Cable/Lever/Throttle Linkage Cover
1 - CABLE/LEVER/LINKAGE COVER
2 - PUSH UP LOWER TAB
3 - SCREWS/CLIPS (2)
4 - TAB PUSH HERE
Fig. 37 Throttle Cable at Throttle Lever
1 - PINCH (2) TABS
2 - CABLE MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - PINCH TABS (2)
4 - OFF
5 - THROTTLE CABLE
6 - THROTTLE LEVER
7 - THROTTLE LEVER PIN
8 - OFF
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
Fig. 38 Cable Release
1-TAB
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 109
Page 1409 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Install cable through mounting hole on cable
mounting bracket (Fig. 37). Cable snaps into bracket.
Be sure 2 pinch tabs are secure.
(2) Using large pliers, connect cable end socket to
throttle lever ball (snaps on).
(3) Install remaining cable housing end into and
through dash panel opening (snaps into position).
The two plastic pinch tabs should lock cable to dash
panel.
(4) From inside vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Install throttle cable core wire and plastic cable
retainer into and through upper end of pedal arm
(the plastic retainer is snapped into pedal arm).
When installing plastic retainer to accelerator pedal
arm, note index tab on pedal arm (Fig. 39). Align
index slot on plastic cable retainer to this index tab.
(5) Connect negative battery cables to both batter-
ies.
(6) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
(7) Install cable/lever cover.
Fig. 39 Cable Removal/Installation at Pedal
1 - PINCH TWO TABS FOR CABLE REMOVAL
2 - DASH PANEL
3 - CABLE CORE WIRE
4 - THROTTLE PEDAL ARM
5 - INDEX TAB
6 - CABLE RETAINER
7 - CABLE STOP
14 - 110 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE (Continued)
Page 1434 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Install pitman shaft bearing into housing with
a bearing driver and handle.
(2) Coat the oil seal and washer withspecial
greasesupplied with the new seal.
(3) Install the oil seal with a driver and handle.
(4) Install backup washer.
(5) Install the retainer ring with snap ring pliers.
(6) Coat the dust seal withspecial greasesup-
plied with the new seal.
(7) Install dust seal with a driver and handle.
(8) Install pitman shaft to side cover by screwing
shaft in until it fully seats to side cover.
(9) Install preload adjuster nut.Do not tighten
nut until after Over-Center Rotation Torque
adjustment has been made.
(10) Install gasket to side cover and bend tabs
around edges of side cover (Fig. 11).
(11) Install pitman shaft assembly and side cover
to housing.
(12) Install side cover bolts and tighten to 60 N´m
(44 ft. lbs.).
(13) Perform over-center rotation torque adjust-
ment, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/GEAR - ADJUST-
MENTS).
PITMAN SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Clean exposed end of pitman shaft and housing
with a wire brush.
(2) Remove preload adjuster nut (Fig. 19).
(3) Rotate the stub shaft with a 12 point socket
from stop to stop and count the number of turns.
(4) Center the stub shaft by rotating it from the
stop 1/2 of the total amount of turns.
(5) Remove side cover bolts and remove side cover,
gasket and pitman shaft as an assembly (Fig. 19).
NOTE: The pitman shaft will not clear the housing if
it is not centered.
(6) Remove pitman shaft from the side cover.
(7) Remove dust seal from the housing with a seal
pick (Fig. 20).
CAUTION: Use care not to score the housing bore
when prying out seals and washer.
(8) Remove retaining ring with snap ring pliers.
(9) Remove washer from the housing.
(10) Remove oil seal from the housing with a seal
pick.
(11) Remove pitman shaft bearing from housing
with a bearing driver and handle (Fig. 21).
Fig. 19 Side Cover and Pitman Shaft
1 - SIDE COVER BOLTS
2 - PRELOAD ADJUSTER NUT
3 - SIDE COVER
4 - GASKET SEAL
5 - PITMAN SHAFT GEAR
6 - HOUSING ASSEMBLY
Fig. 20 Pitman Shaft Seals & Bearing
1 - BEARING
2 - WASHER
3 - DUST SEAL
4 - RETAINER
5 - OIL SEAL
BR/BEGEAR 19 - 25
PITMAN SHAFT (Continued)
Page 1480 of 2255
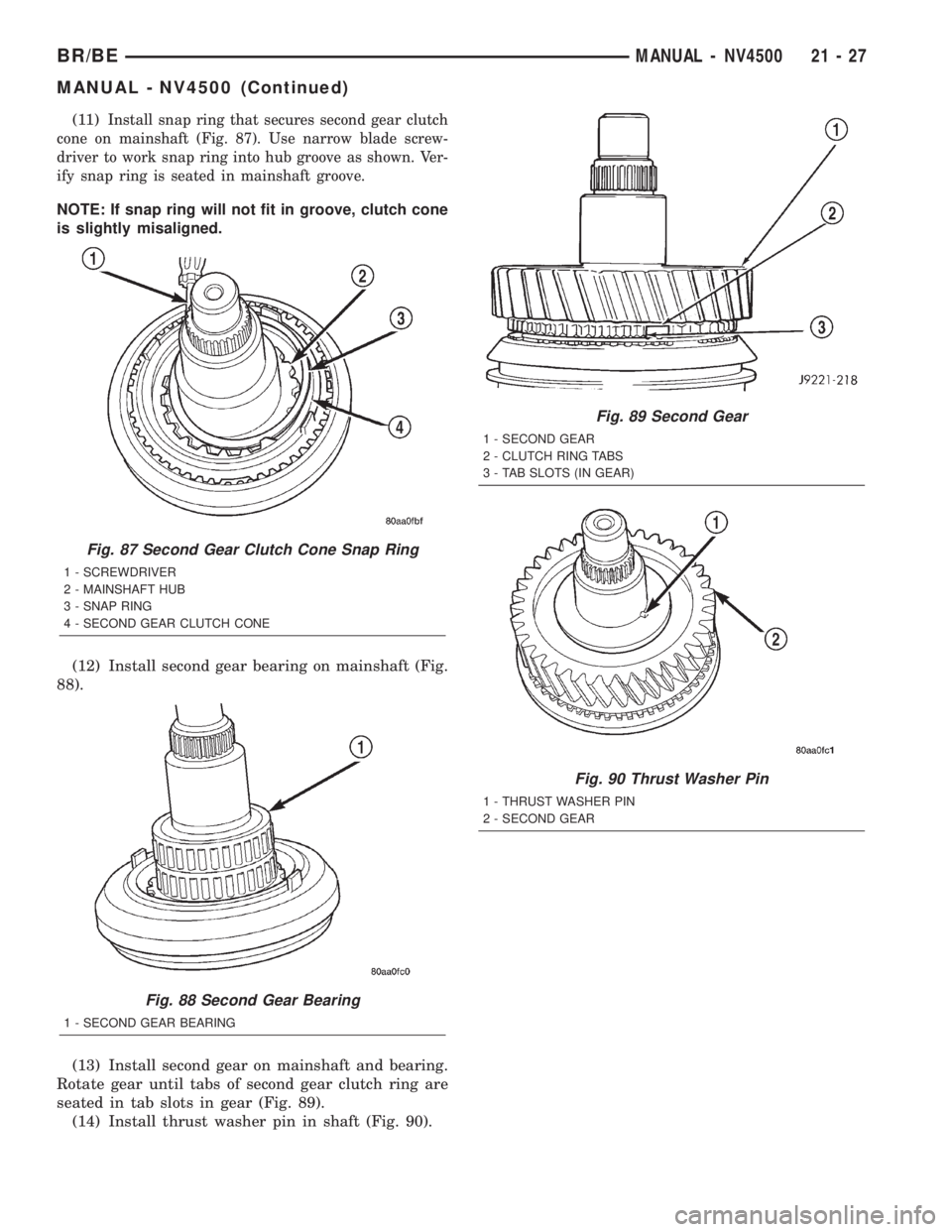
(11)Install snap ring that secures second gear clutch
cone on mainshaft (Fig. 87). Use narrow blade screw-
driver to work snap ring into hub groove as shown. Ver-
ify snap ring is seated in mainshaft groove.
NOTE: If snap ring will not fit in groove, clutch cone
is slightly misaligned.
(12) Install second gear bearing on mainshaft (Fig.
88).
(13) Install second gear on mainshaft and bearing.
Rotate gear until tabs of second gear clutch ring are
seated in tab slots in gear (Fig. 89).
(14) Install thrust washer pin in shaft (Fig. 90).
Fig. 87 Second Gear Clutch Cone Snap Ring
1 - SCREWDRIVER
2 - MAINSHAFT HUB
3 - SNAP RING
4 - SECOND GEAR CLUTCH CONE
Fig. 88 Second Gear Bearing
1 - SECOND GEAR BEARING
Fig. 89 Second Gear
1 - SECOND GEAR
2 - CLUTCH RING TABS
3 - TAB SLOTS (IN GEAR)
Fig. 90 Thrust Washer Pin
1 - THRUST WASHER PIN
2 - SECOND GEAR
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 27
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1482 of 2255
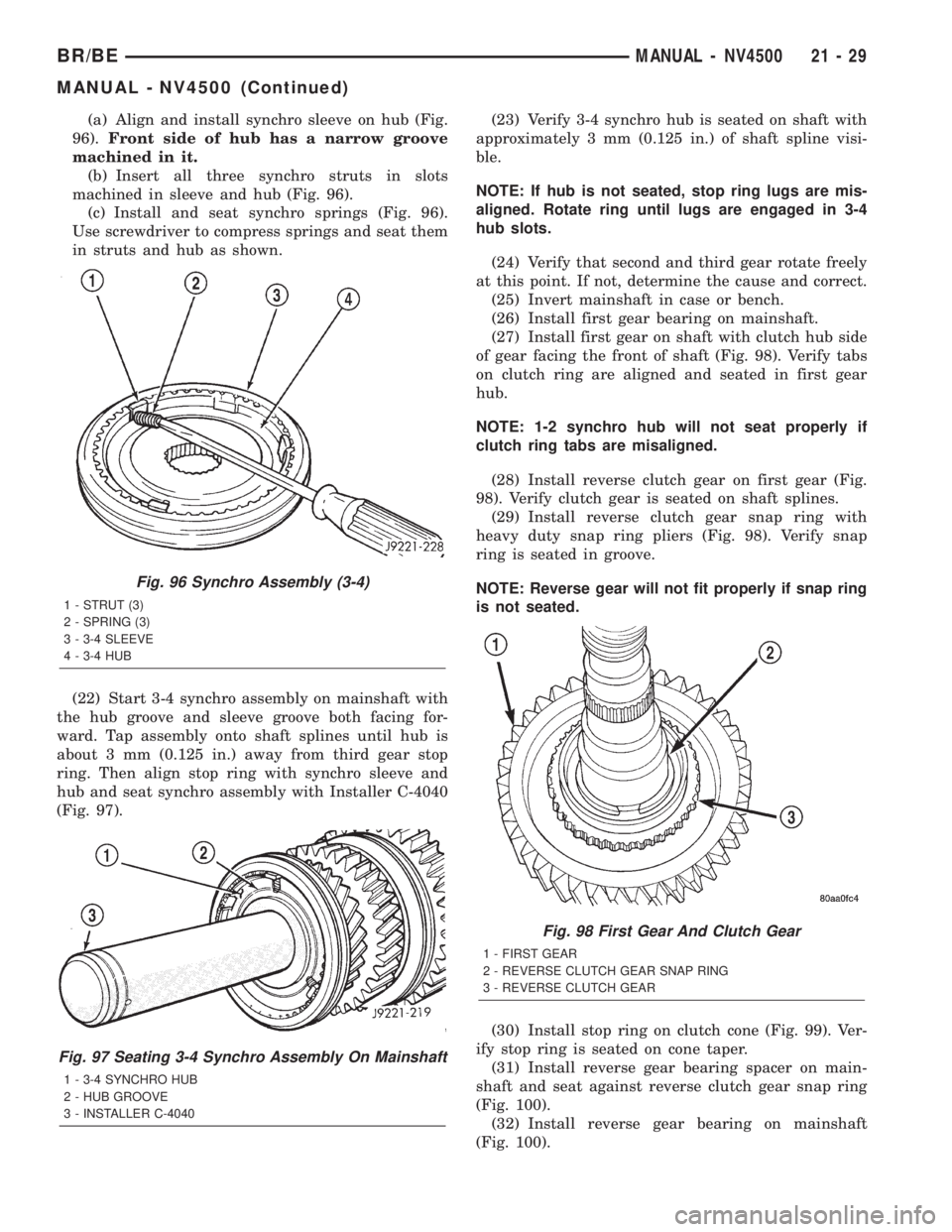
(a) Align and install synchro sleeve on hub (Fig.
96).Front side of hub has a narrow groove
machined in it.
(b) Insert all three synchro struts in slots
machined in sleeve and hub (Fig. 96).
(c) Install and seat synchro springs (Fig. 96).
Use screwdriver to compress springs and seat them
in struts and hub as shown.
(22) Start 3-4 synchro assembly on mainshaft with
the hub groove and sleeve groove both facing for-
ward. Tap assembly onto shaft splines until hub is
about 3 mm (0.125 in.) away from third gear stop
ring. Then align stop ring with synchro sleeve and
hub and seat synchro assembly with Installer C-4040
(Fig. 97).(23) Verify 3-4 synchro hub is seated on shaft with
approximately 3 mm (0.125 in.) of shaft spline visi-
ble.
NOTE: If hub is not seated, stop ring lugs are mis-
aligned. Rotate ring until lugs are engaged in 3-4
hub slots.
(24) Verify that second and third gear rotate freely
at this point. If not, determine the cause and correct.
(25) Invert mainshaft in case or bench.
(26) Install first gear bearing on mainshaft.
(27) Install first gear on shaft with clutch hub side
of gear facing the front of shaft (Fig. 98). Verify tabs
on clutch ring are aligned and seated in first gear
hub.
NOTE: 1-2 synchro hub will not seat properly if
clutch ring tabs are misaligned.
(28) Install reverse clutch gear on first gear (Fig.
98). Verify clutch gear is seated on shaft splines.
(29) Install reverse clutch gear snap ring with
heavy duty snap ring pliers (Fig. 98). Verify snap
ring is seated in groove.
NOTE: Reverse gear will not fit properly if snap ring
is not seated.
(30) Install stop ring on clutch cone (Fig. 99). Ver-
ify stop ring is seated on cone taper.
(31) Install reverse gear bearing spacer on main-
shaft and seat against reverse clutch gear snap ring
(Fig. 100).
(32) Install reverse gear bearing on mainshaft
(Fig. 100).
Fig. 96 Synchro Assembly (3-4)
1 - STRUT (3)
2 - SPRING (3)
3 - 3-4 SLEEVE
4 - 3-4 HUB
Fig. 97 Seating 3-4 Synchro Assembly On Mainshaft
1 - 3-4 SYNCHRO HUB
2 - HUB GROOVE
3 - INSTALLER C-4040
Fig. 98 First Gear And Clutch Gear
1 - FIRST GEAR
2 - REVERSE CLUTCH GEAR SNAP RING
3 - REVERSE CLUTCH GEAR
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 29
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1497 of 2255

(3) Clean all chips from shift cover and plug bores.
Then clean plug bores with solvent and dry with
clean shop towel.
INSTALLATION
EXPANSION PLUG
(1) Apply small bead of Mopar silicone sealer or
equivalent to outer edge of each new plug.
(2) Position each plug in bore and tap into place
with hammer and punch or socket.
FIFTH-REVERSE SHIFT FORK PADS
(1) Align pad locating tab.
(2) Snap pads into place and verify locating tabs
are locked-in.
SHIFT COVER
(1) Clean mating surfaces of shift cover and gear
case with wax and grease remover.(2) Apply a small amount of Mopar silicone sealer
or equivalent to sealing surface of shift cover.
CAUTION: Do not over-apply an excesive amount
sealer. Excess can squeezed into gear case and
could block lubricant feed holes in time.
(3) Lubricate synchro sleeves with CastroltSyn-
torq gear lubricant or equivalent. Then apply light
coat of petroleum jelly to shift fork contact surfaces.
(4) Verify shift fork pads (Fig. 137) are secure.
(5) Verify 1-2 and 3-4 synchro sleeves and forks in
shift cover are in neutral position.
(6) Align and seat shift cover on transmission.
NOTE: If cover will not seat, it may not be aligned
on gear case dowels or shift forks are not aligned
with sleeves and shift lug.
(7) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or equivalent to
threads of shift cover bolts.
(8) Install shift cover bolts and tighten to 27-31
N´m (216-276 in. lbs.).
(9) Apply sealer to backup lamp switch. Install
switch into cover and tighten to 22-34 N´m (193-265
in. lbs.).
(10) Install vent assembly if removed. Apply an
adhesive/sealer to vent tube to help secure it in cover.
(11) Install transmission.
Fig. 135 Shift Fork Pad Locations
1 - SHIFT FORK PADS
2 - FIFTH-REVERSE FORK
Fig. 136 Expansion Plug Location
1 - EXPANSION PLUGS
Fig. 137 Fifth-Reverse Shift Fork Pads
1 - SHIFT FORK PADS
2 - FIFTH-REVERSE FORK
21 - 44 MANUAL - NV4500BR/BE
SHIFT MECHANISM - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1606 of 2255

GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
There are four governor pressure curves pro-
grammed into the transmission control module. The
different curves allow the control module to adjust
governor pressure for varying conditions. One curve
is used for operation when fluid temperature is at, or
below, ±1ÉC (30ÉF). A second curve is used when fluid
temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absence
of sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to pro-
duce governor pressure. The average current sup-
plied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One
amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pres-
sure. Zero amps sets the maximum governor pres-
sure.The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts
(DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the sole-
noid using the governor pressure solenoid control cir-
cuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conven-
tional governor can delay shifts, resulting in higher
than normal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The elec-
tronically controlled low temperature governor pres-
sure curve is higher than normal to make the
transmission shift at normal speeds and sooner. The
PCM uses a temperature sensor in the transmission
oil sump to determine when low temperature gover-
nor pressure is needed.
NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous
stand-alone electronic module. This facilitated the
development of a load adaptive shift strategy - the
ability to alter the shift schedule in response to vehi-
cle load condition. One manifestation of this capabil-
ity is grade9hunting9prevention - the ability of the
transmission logic to delay an upshift on a grade if
the engine does not have sufficient power to main-
tain speed in the higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and
the potential for hunting between gears occurs with a
heavily loaded vehicle or on steep grades. When
hunting occurs, it is very objectionable because shifts
are frequent and accompanied by large changes in
noise and acceleration.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE OPERATION
In wide-open throttle (WOT) mode, adaptive mem-
ory in the PCM assures that up-shifts occur at the
preprogrammed optimum speed. WOT operation is
determined from the throttle position sensor, which
is also a part of the emission control system. The ini-
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 153
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)