2002 DODGE RAM coolant
[x] Cancel search: coolantPage 1735 of 2255

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO 3-4 UPSHIFT 1. O/D Switch In OFF Position. 1. Turn control switch to ON position.
2. Overdrive Circuit Fuse Blown. 2. Replace fuse. Determine why fuse failed
and repair as necessary (i.e., shorts or
grounds in circuit).
3. O/D Switch Wire Shorted/Open
Cut.3. Check wires/connections with 12V test
lamp and voltmeter. Repair damaged or
loose wire/connection as necessary.
4. Distance or Coolant Sensor
Malfunction.4. Check with DRBTscan tool and repair or
replace as necessary.
5. TPS Malfunction. 5. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace
if necessary.
6. Neutral Sense to PCM Wire
Shorted/Cut.6. Test switch/sensor as described in
service section and replace if necessary.
Engine no start.
7. PCM Malfunction. 7. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace
if necessary.
8. Overdrive Solenoid Shorted/Open. 8. Replace solenoid if shorted or open and
repair loose or damaged wires (DRBTscan
tool).
9. Solenoid Feed Orifice in Valve
Body Blocked.9. Remove, disassemble, and clean valve
body thoroughly. Check feed orifice.
10. Overdrive Clutch Failed. 10. Disassemble overdrive and repair as
needed.
11. Hydraulic Pressure Low. 11. Pressure test transmission to determine
cause.
12. Valve Body Valve Stuck. 12. Repair stuck 3-4 shift valve, 3-4 timing
valve.
13. O/D Piston Incorrect Spacer. 13. Remove unit, check end play and install
correct spacer.
14. Overdrive Piston Seal Failure. 14. Replace both seals.
15. O/D Check Valve/Orifice Failed. 15. Check for free movement and secure
assembly (in piston retainer). Check ball
bleed orifice.
21 - 282 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE (Continued)
Page 1780 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Place seal in position on overdrive housing.
(2) Drive seal into overdrive housing with Seal
Installer C-3995-A (Fig. 82).
(3) Carefully guide propeller shaft slip yoke into
housing and onto output shaft splines. Align marks
made at removal and connect propeller shaft to rear
axle pinion yoke.
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluidexpansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has two primary causes.
(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
Fig. 81 Removing Overdrive Housing Yoke Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3985-B
2 - SEAL
Fig. 82 Installing Overdrive Housing Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A OR C-3972-A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4471
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 327
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL (Continued)
Page 2060 of 2255
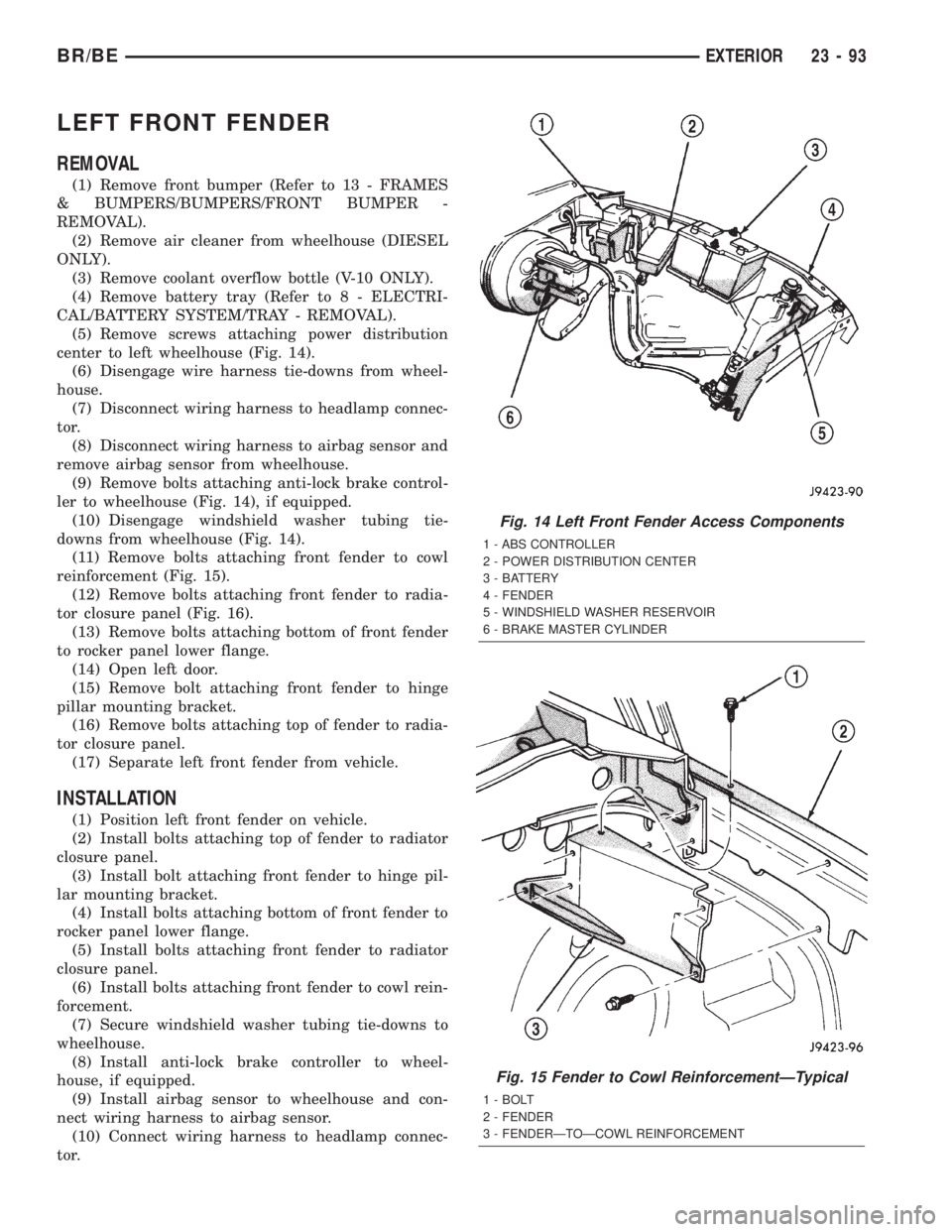
LEFT FRONT FENDER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove front bumper (Refer to 13 - FRAMES
& BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove air cleaner from wheelhouse (DIESEL
ONLY).
(3) Remove coolant overflow bottle (V-10 ONLY).
(4) Remove battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove screws attaching power distribution
center to left wheelhouse (Fig. 14).
(6) Disengage wire harness tie-downs from wheel-
house.
(7) Disconnect wiring harness to headlamp connec-
tor.
(8) Disconnect wiring harness to airbag sensor and
remove airbag sensor from wheelhouse.
(9) Remove bolts attaching anti-lock brake control-
ler to wheelhouse (Fig. 14), if equipped.
(10) Disengage windshield washer tubing tie-
downs from wheelhouse (Fig. 14).
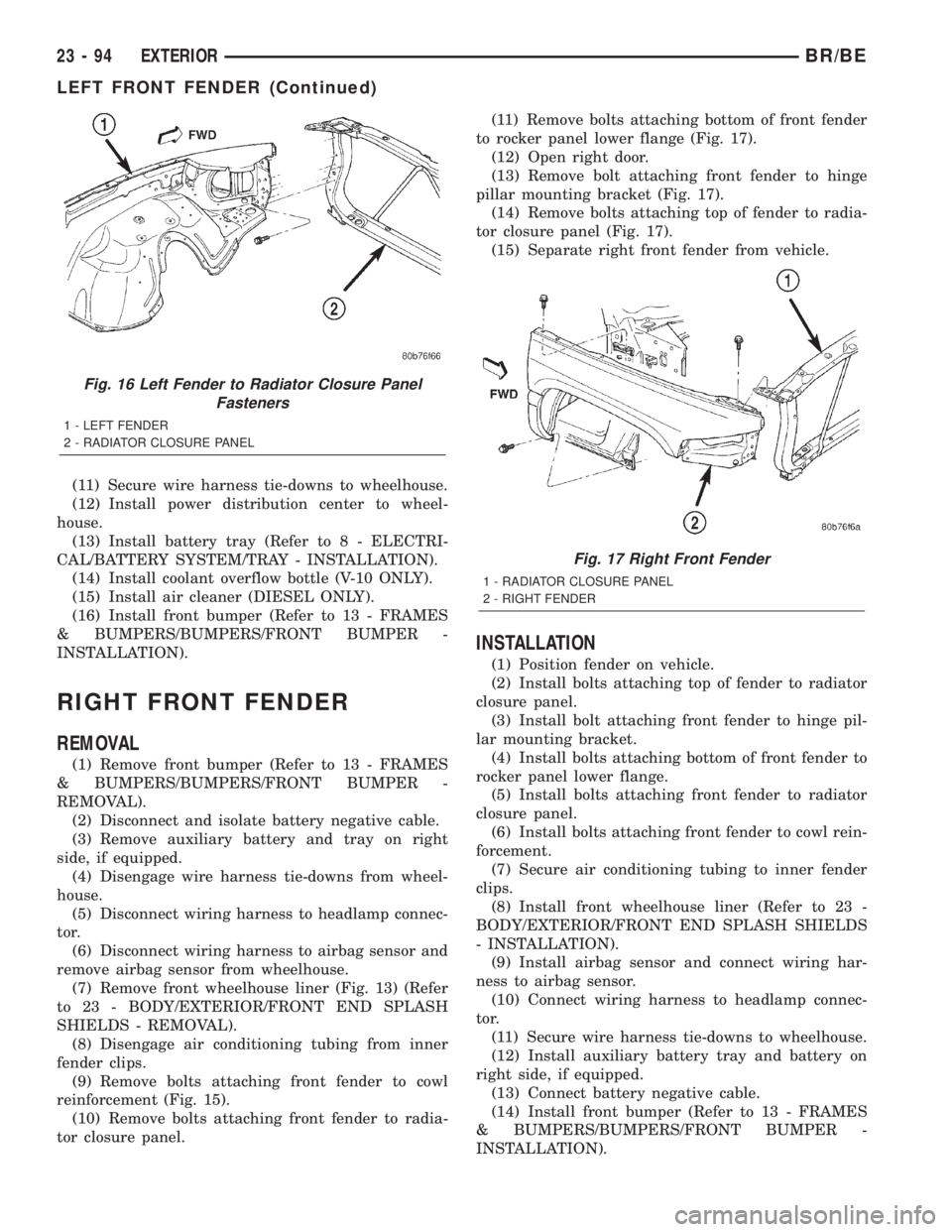
(11) Remove bolts attaching front fender to cowl
reinforcement (Fig. 15).
(12) Remove bolts attaching front fender to radia-
tor closure panel (Fig. 16).
(13) Remove bolts attaching bottom of front fender
to rocker panel lower flange.
(14) Open left door.
(15) Remove bolt attaching front fender to hinge
pillar mounting bracket.
(16) Remove bolts attaching top of fender to radia-
tor closure panel.
(17) Separate left front fender from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position left front fender on vehicle.
(2) Install bolts attaching top of fender to radiator
closure panel.
(3) Install bolt attaching front fender to hinge pil-
lar mounting bracket.
(4) Install bolts attaching bottom of front fender to
rocker panel lower flange.
(5) Install bolts attaching front fender to radiator
closure panel.
(6) Install bolts attaching front fender to cowl rein-
forcement.
(7) Secure windshield washer tubing tie-downs to
wheelhouse.
(8) Install anti-lock brake controller to wheel-
house, if equipped.
(9) Install airbag sensor to wheelhouse and con-
nect wiring harness to airbag sensor.
(10) Connect wiring harness to headlamp connec-
tor.
Fig. 14 Left Front Fender Access Components
1 - ABS CONTROLLER
2 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
3 - BATTERY
4 - FENDER
5 - WINDSHIELD WASHER RESERVOIR
6 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
Fig. 15 Fender to Cowl ReinforcementÐTypical
1 - BOLT
2 - FENDER
3 - FENDERÐTOÐCOWL REINFORCEMENT
BR/BEEXTERIOR 23 - 93
Page 2061 of 2255
(11) Secure wire harness tie-downs to wheelhouse.
(12) Install power distribution center to wheel-
house.
(13) Install battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install coolant overflow bottle (V-10 ONLY).
(15) Install air cleaner (DIESEL ONLY).
(16) Install front bumper (Refer to 13 - FRAMES
& BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER -
INSTALLATION).
RIGHT FRONT FENDER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove front bumper (Refer to 13 - FRAMES
& BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER -
REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect and isolate battery negative cable.
(3) Remove auxiliary battery and tray on right
side, if equipped.
(4) Disengage wire harness tie-downs from wheel-
house.
(5) Disconnect wiring harness to headlamp connec-
tor.
(6) Disconnect wiring harness to airbag sensor and
remove airbag sensor from wheelhouse.
(7) Remove front wheelhouse liner (Fig. 13) (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT END SPLASH
SHIELDS - REMOVAL).
(8) Disengage air conditioning tubing from inner
fender clips.
(9) Remove bolts attaching front fender to cowl
reinforcement (Fig. 15).
(10) Remove bolts attaching front fender to radia-
tor closure panel.(11) Remove bolts attaching bottom of front fender
to rocker panel lower flange (Fig. 17).
(12) Open right door.
(13) Remove bolt attaching front fender to hinge
pillar mounting bracket (Fig. 17).
(14) Remove bolts attaching top of fender to radia-
tor closure panel (Fig. 17).
(15) Separate right front fender from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fender on vehicle.
(2) Install bolts attaching top of fender to radiator
closure panel.
(3) Install bolt attaching front fender to hinge pil-
lar mounting bracket.
(4) Install bolts attaching bottom of front fender to
rocker panel lower flange.
(5) Install bolts attaching front fender to radiator
closure panel.
(6) Install bolts attaching front fender to cowl rein-
forcement.
(7) Secure air conditioning tubing to inner fender
clips.
(8) Install front wheelhouse liner (Refer to 23 -
BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT END SPLASH SHIELDS
- INSTALLATION).
(9) Install airbag sensor and connect wiring har-
ness to airbag sensor.
(10) Connect wiring harness to headlamp connec-
tor.
(11) Secure wire harness tie-downs to wheelhouse.
(12) Install auxiliary battery tray and battery on
right side, if equipped.
(13) Connect battery negative cable.
(14) Install front bumper (Refer to 13 - FRAMES
& BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER -
INSTALLATION).
Fig. 16 Left Fender to Radiator Closure Panel
Fasteners
1 - LEFT FENDER
2 - RADIATOR CLOSURE PANEL
Fig. 17 Right Front Fender
1 - RADIATOR CLOSURE PANEL
2 - RIGHT FENDER
23 - 94 EXTERIORBR/BE
LEFT FRONT FENDER (Continued)
Page 2127 of 2255

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE
Before performing the following tests, refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures to check the engine coolant
level and flow, engine coolant reserve/recovery sys-
tem operation, accessory drive belt condition and ten-
sion, radiator air flow and the fan drive operation.
Also be certain that the accessory vacuum supply
line is connected at the engine vacuum source.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT
Engine coolant is delivered to the heater core
through two heater hoses. With the engine idling atnormal operating temperature, set the temperature
control knob in the full hot position, the mode control
switch knob in the floor position, and the blower
motor switch knob in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged at the HVAC housing floor
outlets. Compare the test thermometer reading to the
Temperature Reference chart.
Temperature Reference
Ambient Air Temperature15.5É C
(60É F)21.1É C
(70É F)26.6É C
(80É F)32.2É C
(90É F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet62.2É C
(144É F)63.8É C
(147É F)65.5É C
(150É F)67.2É C
(153É F)
If the floor outlet air temperature is too low, refer
to Cooling to check the engine coolant temperature
specifications. Both of the heater hoses should be hot
to the touch. The coolant return heater hose should
be slightly cooler than the coolant supply heater
hose. If the return hose is much cooler than the sup-
ply hose, locate and repair the engine coolant flow
obstruction in the cooling system. Refer to Cooling
for the procedures.
An alternate method of checking heater perfor-
mance is to use a DRBIIItscan tool to monitor the
engine coolant temperature. The floor outlet air tem-
perature reading should be no more than 4.5É C (40É
F) lower than the engine coolant temperature read-
ing.
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW Possible loca-
tions or causes of obstructed coolant flow:
²Faulty water pump.
²Faulty thermostat.
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²A plugged heater core.If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is still
low, a mechanical problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS Possible locations or
causes of insufficient heat:
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²A faulty, obstructed or improperly installed
blend door.
²A faulty blower system.
²A faulty a/c heater control.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be
adjusted with the temperature control knob on the
a/c heater control panel, the following could require
service:
²A faulty a/c heater control.
²A faulty blend door actuator.
²A faulty, obstructed or improperly installed
blend door.
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²The engine cooling system.
Heater Diagnosis
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
INSUFFICIENT HEATER
OUTPUT.1. Incorrect engine
coolant level.1. Check the engine coolant level. Refer to Cooling for
the procedures.
2. Air trapped in engine
cooling system.2. Check the operation of the coolant reserve/recovery
system. Refer to Cooling for the procedures.
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGBR/BE
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2128 of 2255

Heater Diagnosis
3. Incorrect engine
coolant temperature.3. Check the performance and operation of the engine
cooling system including: thermostat, water pump, fan
drive, accessory drive belt, coolant flow (plugged radiator
or heater core, plugged or kinked coolant hoses), air flow
(missing or improperly installed radiator air seals or fan
shroud). Refer to Cooling for the procedures.
4. Blend door actuator
inoperative or defective.4. (Refer to Controls/Blend Door Actuator) in this group.
5. Blend door not
operating properly.5. Check for a damaged, obstructed or improperly
installed blend door or seals. (Refer to Controls/Blend
Door Actuator) in this group.
6. Insufficient air flow
through heater housing.6. Remove foreign material or obstructions from cowl air
intake.
7. Improper blower motor
operation.7. (Refer to Distribution/Blower Motor/ Diagnosis and
Testing) in this group.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable and iso-
late it.
(2) Locate the diode in the harness, and remove
the protective covering.
(3) Remove the diode from the harness, pay atten-
tion to the current flow direction (Fig. 3).
(4) Remove the insulation from the wires in the
harness. Only remove enough insulation to solder in
the new diode.
(5) Install the new diode in the harness, making
sure current flow is correct. If necessary refer to the
appropriate wiring diagram for current flow.
(6) Solder the connection together using rosin core
type solder only.Do not use acid core solder.(7) Tape the diode to the harness using electrical
tape making, sure the diode is completely sealed
from the elements.
(8) Re-connect the battery negative cable, and test
affected systems.
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE
Item Description Notes
Vehicle BR/BE - Ram
Pickup
System R134a w/orifice
tube
Compressor Sanden SD7H15 SP-20 PAG oil
Freeze±up
ControlA/C Low
Pressure Switchaccumulator
mounted
Low psi Control opens < 22-24
psi resets >
37-43 psi
High psi Control switch - opens >
450 - 490 psi,
resets < 270 -
330 psimounted on
discharge line,
near
compressor
A/C Heater
Control Headmanual type
Mode Door vacuum actuator
Blend Door electric actuator
Recirculation
Doorvacuum actuator
Fig. 3 DIODE IDENTIFICATION
1 - CURRENT FLOW
2 - BAND AROUND DIODE INDICATES CURRENT FLOW
3 - DIODE AS SHOWN IN THE DIAGRAMS
BR/BEHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 7
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2177 of 2255

(3) Tighten the accumulator retaining band screw
to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(4) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the suction line and the accumulator
outlet. Connect the suction line refrigerant line cou-
pler to the accumulator outlet. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE COUPLERS)
(5) Reinstall the a/c low pressure switch on the
accumulator. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C LOW PRESSURE
SWITCH - INSTALLATION)
(6) Connect the battery negative cable.
(7) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(8) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
NOTE: If the accumulator is replaced, add 60 milli-
liters (2 fluid ounces) of refrigerant oil to the refrig-
erant system. Use only refrigerant oil of the type
recommended for the compressor in the vehicle.
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The heater core is located in the HVAC housing,
under the instrument panel. It is a heat exchanger
made of rows of tubes and fins.
The heater core is not repairable and if damaged it
must be replaced.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through heater hoses
to the heater core at all times. As the coolant flows
through the heater core, heat removed from the
engine is transferred to the heater core fins and
tubes. Air directed through the heater core picks up
the heat from the heater core fins. The blend door
allows control of the heater output air temperature
by controlling how much of the air flowing through
the HVAC housing is directed through the heater
core. The blower motor speed controls the volume of
air flowing through the HVAC housing.
The heater core cannot be repaired and, if faulty or
damaged, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)(2) Remove the screws and retainers that secure
the heater core to the HVAC housing.
(3) Lift the heater core straight up and out of the
heater-A/C housing (Fig. 14).
INSTALLATION
(1) Lower the heater core into the HVAC housing.
(2) Position the retainers over the heater core
tubes. Install and tighten the screws that secure the
heater core and retainers to the HVAC housing.
Tighten the screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Reinstall the HVAC housing in the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLA-
TION)
REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION
The refrigerant used in this air conditioning sys-
tem is a HydroFluoroCarbon (HFC), type R-134a.
Unlike R-12, which is a ChloroFluoroCarbon (CFC),
R-134a refrigerant does not contain ozone-depleting
chlorine. R-134a refrigerant is a non-toxic, non-flam-
mable, clear, and colorless liquefied gas.
Even though R-134a does not contain chlorine, it
must be reclaimed and recycled just like CFC-type
refrigerants. This is because R-134a is a greenhouse
gas and can contribute to global warming.
Fig. 14 HEATER CORE REMOVE/INSTALL
1 - HEATER CORE LINES
2 - HEATER CORE
24 - 56 PLUMBINGBR/BE
ACCUMULATOR (Continued)
Page 2182 of 2255

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0031 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0032 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0037 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0038 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0043 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0044 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0051 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0052 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0057 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0058 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0071 (M) Amb/Bat Temp Sensor Performance
P0106 Barometric Pressure Out of Range MAP sensor input voltage out of an acceptable range
detected during reading of barometric pressure at key-on.
P0107 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0108 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
PO111 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Performance
P0112 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0113 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0116 Coolant Temp Sensor Performance A rationatilty error has been detected in the coolant temp
sensor.
P0117 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below the minimum
acceptable voltage.
P0118 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0121 (M) TPS Voltage Does Not Agree With
MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor signal.
P0121 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable voltage.
P0122 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage Low Throttle position sensor input below the acceptable voltage
range.
P0122 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable voltage.
P0123 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage High Throttle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
P0123 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too HighAPPS voltage input above the maximum acceptable voltage.
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 3
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)