2002 DODGE RAM radiator
[x] Cancel search: radiatorPage 1332 of 2255

(11) Inspect accelerator cable, transmission throt-
tle cable (if equipped) and cruise control cable con-
nections (if equipped). Check their connections to the
throttle arm of throttle body for any binding or
restrictions.
(12) If equipped with vacuum brake booster, verify
that vacuum booster hose is firmly connected to fit-
ting on intake manifold. Also check connection to
brake vacuum booster.
(13) Inspect the air cleaner inlet and air cleaner
element for dirt or restrictions.
(14) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and
air conditioning condenser for restrictions.
(15) Verify that the intake manifold air tempera-
ture sensor wire connector is firmly connected to har-
ness connector (Fig. 15).(16) Verify that MAP sensor electrical connector is
firmly connected to MAP sensor (Fig. 16).
(17) Verify that fuel injector wire harness connec-
tors are firmly connected to injectors in the correct
order. Each harness connector is numerically tagged
with the injector number (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.) of its
corresponding fuel injector and cylinder number.
(18) Verify harness connectors are firmly con-
nected to idle air control (IAC) motor and throttle
position sensor (TPS).
(19) Verify that wire harness connector is firmly
connected to the engine coolant temperature sensor
(Fig. 17).
Fig. 14 Ignition Coil PackÐ8.0L Engine
Fig. 15 Air Temperature SensorÐ8.0L Engine
1 - INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMP. SENSOR
2 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
Fig. 16 Map Sensor Ð8.0L Engine
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - THROTTLE BODY
Fig. 17 Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐ8.0L
Engine
1 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMP. SENSOR
2 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
3 - GENERATOR
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 33
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1348 of 2255

INSTALLATION - 8.0L
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM).
(1) Clean the mating surfaces of the throttle body
and the intake manifold.
(2) Install new throttle body-to-intake manifold
gasket.
(3) Install throttle body to intake manifold.
(4) Install four mounting nuts. Tighten nuts to 22
N´m (192 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install control cables.
(6) Install electrical connectors.
(7) Install air cleaner housing to throttle body.
(8) Install 4 air cleaner housing mounting nuts.
Tighten nuts to 11 N´m (96 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install air cleaner housing cover.
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage or kink the
cable core wire (within the cable sheathing) while
servicing accelerator pedal or cables.
(1) From inside the vehicle, hold up the accelerator
pedal. Remove the plastic cable retainer and throttle
cable core wire from upper end of pedal arm (Fig.
21). The plastic cable retainer snaps into pedal the
arm.
(2) Remove the cable core wire at the pedal arm.
(3) Remove the air cleaner housing.
(4) From inside the vehicle, pinch both sides of the
plastic cable housing retainer tabs at the dash panel
(Fig. 21).
(5) Remove cable housing from dash panel and
pull the cable into the engine compartment.
(6)5.9L Engines:Disconnect the cable from the
routing/holddown clip at the radiator fan shroud.
(7)8.0L V-10 Engine:Remove the throttle cable
socket at throttle lever ball. (Fig. 44) (snaps off).
(8)5.9L Engines:Slip the cable end rearward
from pin on throttle body (Fig. 43).
(9) Remove cable housing at throttle body mount-
ing bracket by pressing on release tab with a small
screwdriver (Fig. 45) or (Fig. 44).To prevent cable
housing breakage, press on the tab only enough
to release the cable from the bracket.Lift the
cable housing straight up from bracket while press-
ing on release tab. Remove throttle cable from vehi-
cle.
Fig. 43 Throttle Cable at Throttle BodyÐ5.9L
EnginesÐTypical
1 - THROTTLE LEVER PIN
2 - CAM (V-8 ENGINE ONLY)
3 - THROTTLE CABLE END
Fig. 44 Throttle Cable at Throttle BodyÐ8.0L V-10
Engine
1 - PRESS TAB FOR CABLE REMOVAL
2 - THROTTLE CABLE
3 - CABLE SOCKET
4 - LEVER BALL
5 - MOUNTING BRACKET
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 49
THROTTLE BODY (Continued)
Page 1610 of 2255

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has two primary causes.
(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
sludge and/or debris. The torque converter should
also be replaced at the same time.
Failure to flush the cooler and lines will result in
recontamination. Flushing applies to auxiliary coolers
as well. The torque converter should also be replaced
whenever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing procedures
will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
Fig. 88 Installing Overdrive Housing Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A OR C-3972-A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4471
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 157
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL (Continued)
Page 1670 of 2255

CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 245). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The drainback valve is located in the transmission
cooler outlet (pressure) line.
OPERATION
The valve prevents fluid from draining from the
converter into the cooler and lines when the vehicle
is shut down for lengthy periods. Production valves
have a hose nipple at one end, while the opposite end
is threaded for a flare fitting. All valves have an
arrow (or similar mark) to indicate direction of flow
through the valve.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
The converter drainback check valve is located in
the cooler outlet (pressure) line near the radiator
tank. The valve prevents fluid drainback when the
vehicle is parked for lengthy periods. The valve check
ball is spring loaded and has an opening pressure of
approximately 2 psi.
Fig. 245 Checking Torque Converter Seating -
Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 217
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1780 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Place seal in position on overdrive housing.
(2) Drive seal into overdrive housing with Seal
Installer C-3995-A (Fig. 82).
(3) Carefully guide propeller shaft slip yoke into
housing and onto output shaft splines. Align marks
made at removal and connect propeller shaft to rear
axle pinion yoke.
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluidexpansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has two primary causes.
(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
Fig. 81 Removing Overdrive Housing Yoke Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3985-B
2 - SEAL
Fig. 82 Installing Overdrive Housing Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A OR C-3972-A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4471
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 327
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL (Continued)
Page 1843 of 2255

TORQUE CONVERTER
DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The drainback valve is located in the transmission
cooler outlet (pressure) line.
OPERATION
The valve prevents fluid from draining from the
converter into the cooler and lines when the vehicle
is shut down for lengthy periods. Production valves
have a hose nipple at one end, while the opposite end
is threaded for a flare fitting. All valves have an
arrow (or similar mark) to indicate direction of flow
through the valve.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
The converter drainback check valve is located in
the cooler outlet (pressure) line near the radiator
tank. The valve prevents fluid drainback when the
vehicle is parked for lengthy periods. The valve check
ball is spring loaded and has an opening pressure of
approximately 2 psi.
The valve is serviced as an assembly; it is not
repairable. Do not clean the valve if restricted, or
contaminated by sludge, or debris. If the valve fails,
or if a transmission malfunction occurs that gener-
ates significant amounts of sludge and/or clutch par-ticles and metal shavings, the valve must be
replaced.
The valve must be removed whenever the cooler
and lines are reverse flushed. The valve can be flow
tested when necessary. The procedure is exactly the
same as for flow testing a cooler.
If the valve is restricted, installed backwards, or in
the wrong line, it will cause an overheating condition
and possible transmission failure.
CAUTION: The drainback valve is a one-way flow
device. It must be properly oriented in terms of flow
direction for the cooler to function properly. The
valve must be installed in the pressure line. Other-
wise flow will be blocked and would cause an over-
heating condition and eventual transmission failure.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 238). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
Fig. 237 Typical Method Of Checking Converter
Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
Fig. 238 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
21 - 390 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2060 of 2255
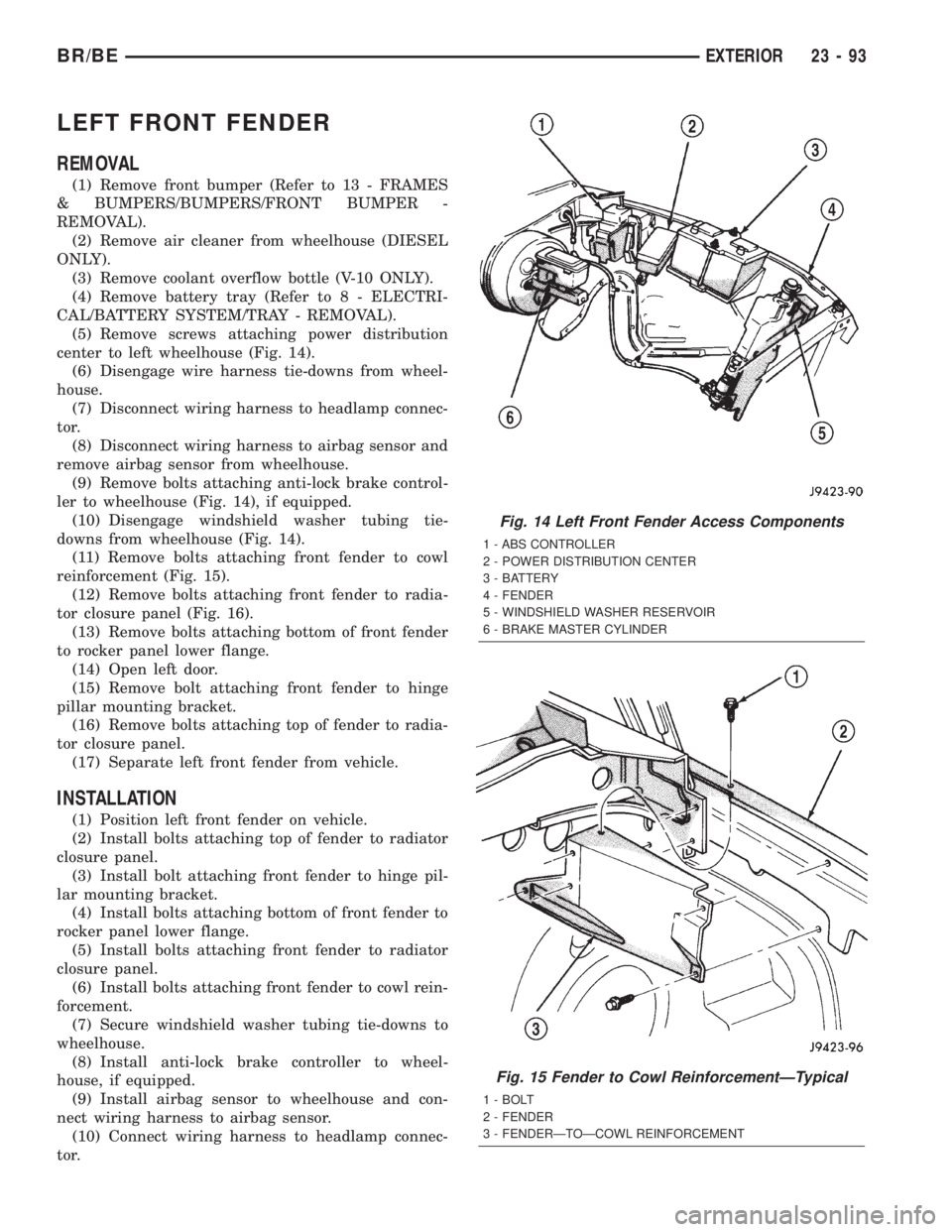
LEFT FRONT FENDER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove front bumper (Refer to 13 - FRAMES
& BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove air cleaner from wheelhouse (DIESEL
ONLY).
(3) Remove coolant overflow bottle (V-10 ONLY).
(4) Remove battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove screws attaching power distribution
center to left wheelhouse (Fig. 14).
(6) Disengage wire harness tie-downs from wheel-
house.
(7) Disconnect wiring harness to headlamp connec-
tor.
(8) Disconnect wiring harness to airbag sensor and
remove airbag sensor from wheelhouse.
(9) Remove bolts attaching anti-lock brake control-
ler to wheelhouse (Fig. 14), if equipped.
(10) Disengage windshield washer tubing tie-
downs from wheelhouse (Fig. 14).
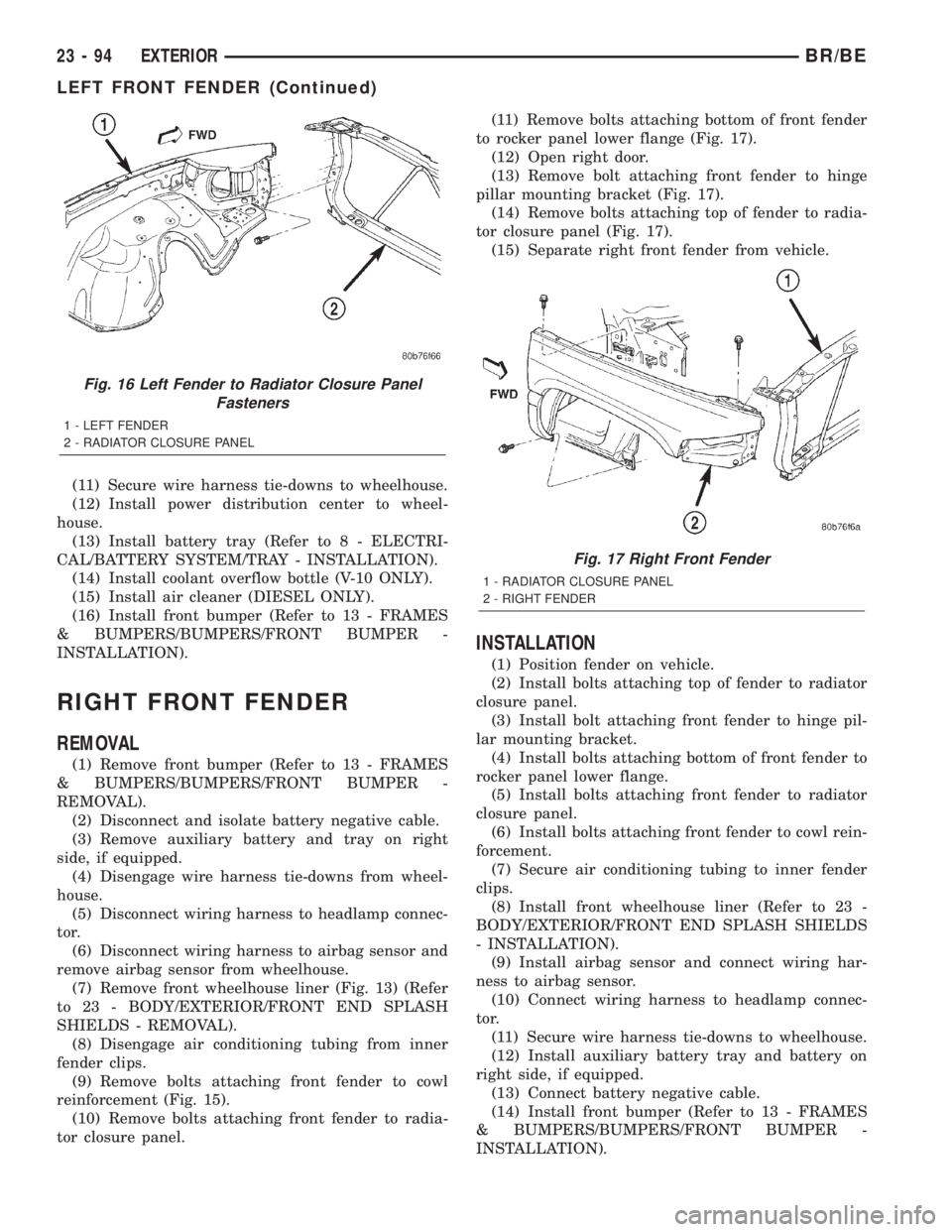
(11) Remove bolts attaching front fender to cowl
reinforcement (Fig. 15).
(12) Remove bolts attaching front fender to radia-
tor closure panel (Fig. 16).
(13) Remove bolts attaching bottom of front fender
to rocker panel lower flange.
(14) Open left door.
(15) Remove bolt attaching front fender to hinge
pillar mounting bracket.
(16) Remove bolts attaching top of fender to radia-
tor closure panel.
(17) Separate left front fender from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position left front fender on vehicle.
(2) Install bolts attaching top of fender to radiator
closure panel.
(3) Install bolt attaching front fender to hinge pil-
lar mounting bracket.
(4) Install bolts attaching bottom of front fender to
rocker panel lower flange.
(5) Install bolts attaching front fender to radiator
closure panel.
(6) Install bolts attaching front fender to cowl rein-
forcement.
(7) Secure windshield washer tubing tie-downs to
wheelhouse.
(8) Install anti-lock brake controller to wheel-
house, if equipped.
(9) Install airbag sensor to wheelhouse and con-
nect wiring harness to airbag sensor.
(10) Connect wiring harness to headlamp connec-
tor.
Fig. 14 Left Front Fender Access Components
1 - ABS CONTROLLER
2 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
3 - BATTERY
4 - FENDER
5 - WINDSHIELD WASHER RESERVOIR
6 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
Fig. 15 Fender to Cowl ReinforcementÐTypical
1 - BOLT
2 - FENDER
3 - FENDERÐTOÐCOWL REINFORCEMENT
BR/BEEXTERIOR 23 - 93
Page 2061 of 2255
(11) Secure wire harness tie-downs to wheelhouse.
(12) Install power distribution center to wheel-
house.
(13) Install battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install coolant overflow bottle (V-10 ONLY).
(15) Install air cleaner (DIESEL ONLY).
(16) Install front bumper (Refer to 13 - FRAMES
& BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER -
INSTALLATION).
RIGHT FRONT FENDER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove front bumper (Refer to 13 - FRAMES
& BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER -
REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect and isolate battery negative cable.
(3) Remove auxiliary battery and tray on right
side, if equipped.
(4) Disengage wire harness tie-downs from wheel-
house.
(5) Disconnect wiring harness to headlamp connec-
tor.
(6) Disconnect wiring harness to airbag sensor and
remove airbag sensor from wheelhouse.
(7) Remove front wheelhouse liner (Fig. 13) (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT END SPLASH
SHIELDS - REMOVAL).
(8) Disengage air conditioning tubing from inner
fender clips.
(9) Remove bolts attaching front fender to cowl
reinforcement (Fig. 15).
(10) Remove bolts attaching front fender to radia-
tor closure panel.(11) Remove bolts attaching bottom of front fender
to rocker panel lower flange (Fig. 17).
(12) Open right door.
(13) Remove bolt attaching front fender to hinge
pillar mounting bracket (Fig. 17).
(14) Remove bolts attaching top of fender to radia-
tor closure panel (Fig. 17).
(15) Separate right front fender from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fender on vehicle.
(2) Install bolts attaching top of fender to radiator
closure panel.
(3) Install bolt attaching front fender to hinge pil-
lar mounting bracket.
(4) Install bolts attaching bottom of front fender to
rocker panel lower flange.
(5) Install bolts attaching front fender to radiator
closure panel.
(6) Install bolts attaching front fender to cowl rein-
forcement.
(7) Secure air conditioning tubing to inner fender
clips.
(8) Install front wheelhouse liner (Refer to 23 -
BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT END SPLASH SHIELDS
- INSTALLATION).
(9) Install airbag sensor and connect wiring har-
ness to airbag sensor.
(10) Connect wiring harness to headlamp connec-
tor.
(11) Secure wire harness tie-downs to wheelhouse.
(12) Install auxiliary battery tray and battery on
right side, if equipped.
(13) Connect battery negative cable.
(14) Install front bumper (Refer to 13 - FRAMES
& BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER -
INSTALLATION).
Fig. 16 Left Fender to Radiator Closure Panel
Fasteners
1 - LEFT FENDER
2 - RADIATOR CLOSURE PANEL
Fig. 17 Right Front Fender
1 - RADIATOR CLOSURE PANEL
2 - RIGHT FENDER
23 - 94 EXTERIORBR/BE
LEFT FRONT FENDER (Continued)