2002 DODGE RAM oil level
[x] Cancel search: oil levelPage 2123 of 2255

The optional air conditioner for all models is
designed for the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant.
The air conditioning system has an evaporator to cool
and dehumidify the incoming air prior to blending it
with the heated air. This air conditioning system
uses a fixed orifice tube in the middle of the liquid
line to meter refrigerant flow to the evaporator coil.
To maintain minimum evaporator temperature and
prevent evaporator freezing, the a/c low pressure
switch on the accumulator cycles the compressor
clutch.
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
PORT
The high pressure service port is located on the liq-
uid line between the condenser and the evaporator,
near the front of the engine compartment. The low
pressure service port is located on the suction line,
near the accumulator outlet.
Each of the service ports has a threaded plastic
protective cap installed over it from the factory. After
servicing the refrigerant system, always reinstall
both of the service port caps.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE
The air conditioning system is designed to provide
the passenger compartment with low temperature
and low humidity air. The evaporator, located in the
HVAC housing on the dash panel below the instru-
ment panel, is cooled to temperatures near the freez-
ing point. As warm damp air passes through the
cooled evaporator, the air transfers its heat to the
refrigerant in the evaporator tubes and the moisture
in the air condenses on the evaporator fins. During
periods of high heat and humidity, an air condition-
ing system will be more effective in the recirculation
mode (Max-A/C). With the system in the recirculation
mode, only air from the passenger compartment
passes through the evaporator. As the passenger com-
partment air dehumidifies, the air conditioning sys-
tem performance levels improve.
Humidity has an important bearing on the temper-
ature of the air delivered to the interior of the vehi-
cle. It is important to understand the effect that
humidity has on the performance of the air condition-
ing system. When humidity is high, the evaporator
has to perform a double duty. It must lower the air
temperature, and it must lower the temperature of
the moisture in the air that condenses on the evapo-
rator fins. Condensing the moisture in the air trans-
fers heat energy into the evaporator fins and tubing.This reduces the amount of heat the evaporator can
absorb from the air. High humidity greatly reduces
the ability of the evaporator to lower the temperature
of the air.
However, evaporator capacity used to reduce the
amount of moisture in the air is not wasted. Wring-
ing some of the moisture out of the air entering the
vehicle adds to the comfort of the passengers.
Although, an owner may expect too much from their
air conditioning system on humid days. A perfor-
mance test is the best way to determine whether the
system is performing up to standard. This test also
provides valuable clues as to the possible cause of
trouble with the air conditioning system.
Before proceeding, (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - CAUTION). The air temperature in
the test room and in the vehicle must be a minimum
of 21É C (70É F) for this test.
(1) Connect a tachometer and a manifold gauge
set.
(2) Set the a/c heater mode control switch knob to
the recirculation mode (Max-A/C) position, the tem-
perature control knob to the full cool position, and
the blower motor switch to the highest speed posi-
tion.
(3) Start the engine and hold the idle speed at
1,000 rpm with the compressor clutch engaged. If the
compressor clutch does not engage, (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH COIL - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(4) The engine should be at operating temperature.
The doors and windows must be closed and the hood
must be mostly closed.
(5) Insert a thermometer in the driver side center
A/C (panel) outlet. Operate the engine for five min-
utes.
(6) The compressor clutch may cycle, depending
upon the ambient temperature and humidity. If the
clutch cycles, unplug the a/c low pressure switch wire
harness connector from the switch located on the
accumulator (Fig. 2). Place a jumper wire between
the two cavities of the a/c low pressure switch wire
harness connector.
24 - 2 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGBR/BE
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2125 of 2255

A/C Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
2. Faulty a/c low
pressure switch.2. (Refer to Controls/A/C Low Pressure Switch/Diagnosis
and Testing) in this group. Test the a/c low pressure
switch and replace, if required.
3. Faulty Powertrain
Control Module (PCM).3. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information) for testing
the PCM. Test the PCM and replace, if required.
EQUAL PRESSURES,
BUT THE
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
DOES NOT ENGAGE.1. No refrigerant in the
refrigerant system.1. (Refer to Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing - Refrigerant
System Leaks) in this group. Test the refrigerant system
for leaks. Repair, evacuate and charge the refrigerant
system, if required.
2. Faulty fuse. 2. Check the fuses in the Power Distribution Center and
the junction block. Repair the shorted circuit or
component and replace the fuses, if required.
3. Faulty a/c compressor
clutch coil.3. (Refer to Controls/A/C Compressor Clutch Coil/
Diagnosis and Testing) in this group. Test the compressor
clutch coil and replace, if required.
4. Faulty a/c compressor
clutch relay.4. (Refer to Controls/A/C Compressor Clutch Relay/
Diagnosis and Testing) in this group. Test the compressor
clutch relay and relay circuits. Repair the circuits or
replace the relay, if required.
5. Improperly installed or
faulty a/c low pressure
switch.5. (Refer to Controls/A/C Low Pressure Switch/Diagnosis
and Testing) in this group. Test the a/c low pressure
switch and tighten or replace, if required.
6. Faulty a/c high
pressure switch.6. (Refer to Controls/A/C High Pressure Switch/Diagnosis
and Testing) in this group. Test the a/c high pressure
switch and replace, if required.
7. Faulty Powertrain
Control Module (PCM).7. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information) for testing
the PCM. Test the PCM and replace, if required.
8. Faulty a/c heater
control.8. (Refer to Controls/A/C Heater Control/Diagnosis and
Testing) in this group. Test the a/c heater control and
replace, if required.
NORMAL PRESSURES,
BUT A/C
PERFORMANCE TEST
AIR TEMPERATURES AT
CENTER PANEL
OUTLET ARE TOO
HIGH.1. Excessive refrigerant
oil in system.1. (Refer to Plumbing/Refrigerant Oil/Standard Procedure
- Refrigerant Oil Level) in this group. Recover the
refrigerant from the refrigerant system and inspect the
refrigerant oil content. Restore the refrigerant oil to the
proper level, if required.
2. Blend door actuator
inoperative or faulty.2. Check the Blend Door Actuator operation. Replace as
required.
3. Blend door
inoperative, obstructed or
sealing improperly.3. (Refer to Distribution/Blend Door/Removal/Installation)
in this group. Inspect the blend door for proper operation
and sealing and correct, if required.
LOW SIDE PRESSURE
IS NORMAL OR
SLIGHTLY LOW, AND
HIGH SIDE PRESSURE
IS TOO LOW.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. (Refer to Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing - Refrigerant
System Leaks) in this group. Test the refrigerant system
for leaks. Repair, evacuate and charge the refrigerant
system, if required.
24 - 4 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGBR/BE
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2141 of 2255

(4) Reinstall the cluster bezel to the instrument
panel(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
CLUSTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION).
(5) Reach under the instrument panel to reinstall
the a/c heater control vacuum harness retainer to the
side of the center distribution duct.
(6) Plug in the two halves of the a/c heater control
to HVAC housing vacuum harness connector.
(7) Connect the battery negative cable.
A/C HIGH PRESSURE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The a/c high pressure switch is located on the dis-
charge line near the compressor. The switch is
screwed onto a fitting that contains a Schrader-type
valve, which allows the switch to be serviced without
discharging the refrigerant system. The discharge
line fitting is equipped with an O-ring to seal the
switch connection.
OPERATION
The a/c high pressure switch is connected in series
electrically with the a/c low pressure switch between
ground and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The switch contacts open and close causing the PCM
to turn the compressor clutch on and off. This pre-
vents compressor operation when the discharge line
pressure approaches high levels.
The a/c high pressure switch contacts are open
when the discharge line pressure rises above about3100 to 3375 kPa (450 to 490 psi). The switch con-
tacts will close when the discharge line pressure
drops to about 1860 to 2275 kPa (270 to 330 psi).
When checking refrigerant system pressures with a
manifold gauge set, keep in mind that the indicated
pressures will be about 172 kpa (25 psi) below the
actual switch pressure values due to the pressure
drop that occurs in the refrigerant system between
the switch and the high pressure service port.
The a/c high pressure switch is a factory-calibrated
unit. The switch cannot be adjusted or repaired and,
if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C HIGH
PRESSURE SWITCH
Before performing diagnosis of the a/c high pres-
sure switch, verify that the refrigerant system has
the correct refrigerant charge. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the a/c high pressure switch wire har-
ness connector from the switch on the refrigerant
system fitting.
(3) On the four terminal high pressure switch,
check for continuity between terminals C and D. On
the two terminal switch, check for continuity
between both terminals of the a/c high pressure
switch. There should be continuity. If OK, test and
repair the A/C switch sense circuit as required. If not
OK, replace the faulty switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the wire harness connector from the a/c
high pressure switch, which is mounted to a fitting
on the discharge line between the compressor and
the condenser inlet.
(3) Unscrew the a/c high pressure switch from the
discharge line fitting.
(4) Remove the a/c high pressure switch from the
vehicle.
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the discharge line
fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate a new O-ring seal with clean refrig-
erant oil and install it on the discharge line fitting.
Use only the specified O-rings as they are made of a
special material for the R-134a system. Use only
refrigerant oil of the type recommended for the com-
pressor in the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
Fig. 19 A/C HEATER CONTROL REMOVE/INSTALL
1 - HEATED MIRROR WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
3 - SCREW
4 - HEATER-A/C CONTROL
24 - 20 CONTROLSBR/BE
A/C-HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2161 of 2255

PLUMBING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION..........................40
OPERATION............................41
WARNING..............................42
CAUTION..............................42
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM LEAKS.......................43
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE
COUPLERS...........................44
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE EQUIPMENT...........45
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY...........................45
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM EVACUATE....................46
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE......................46
SPECIFICATIONS........................46
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................46
OPERATION............................46
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
COMPRESSOR........................47
REMOVAL..............................47
INSTALLATION..........................48
A/C CONDENSER
DESCRIPTION..........................49
OPERATION............................49
REMOVAL..............................49
INSTALLATION..........................50
SUCTION AND DISCHARGE LINE
REMOVAL..............................51
INSTALLATION..........................52LIQUID LINE
REMOVAL..............................52
INSTALLATION..........................52
A/C EVAPORATOR
DESCRIPTION..........................53
OPERATION............................53
REMOVAL..............................53
INSTALLATION..........................53
A/C ORIFICE TUBE
DESCRIPTION..........................54
OPERATION............................54
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FIXED
ORIFICE TUBE.........................54
REMOVAL..............................54
INSTALLATION..........................54
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION..........................55
OPERATION............................55
REMOVAL..............................55
INSTALLATION..........................55
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION..........................56
OPERATION............................56
REMOVAL..............................56
INSTALLATION..........................56
REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION..........................56
OPERATION............................57
REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION..........................57
OPERATION............................57
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
OIL LEVEL............................57
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION - A/C LINE COUPLERS
Spring-lock type refrigerant line couplers are used
to connect many of the refrigerant lines and other
components to the refrigerant system. These couplers
require a special tool for disengaging the two coupler
halves.
DESCRIPTION- REFRIGERANT LINES
The refrigerant lines and hoses are used to carry
the refrigerant between the various air conditioning
system components. A barrier hose design with a
nylon tube, which is sandwiched between rubber lay-
ers, is used for the R-134a air conditioning system on
this vehicle. This nylon tube helps to further contain
the R-134a refrigerant, which has a smaller molecu-
lar structure than R-12 refrigerant. The ends of the
refrigerant hoses are made from lightweight alumi-
num or steel, and commonly use braze-less fittings.
24 - 40 PLUMBINGBR/BE
Page 2167 of 2255

STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM EVACUATE
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
If the refrigerant system has been open to the
atmosphere, it must be evacuated before the system
can be charged. If moisture and air enters the system
and becomes mixed with the refrigerant, the com-
pressor head pressure will rise above acceptable
operating levels. This will reduce the performance of
the air conditioner and damage the compressor.
Evacuating the refrigerant system will remove the
air and boil the moisture out of the system at near
room temperature. To evacuate the refrigerant sys-
tem, use the following procedure:
(1) Connect a R-134a refrigerant recovery/recy-
cling/charging station that meets SAE Standard
J2210 and a manifold gauge set to the refrigerant
system of the vehicle.
(2) Open the low and high side valves and start
the charging station vacuum pump. When the suc-
tion gauge reads 88 kPa (26 in. Hg.) vacuum or
greater, close all of the valves and turn off the vac-
uum pump.
(a) If the refrigerant system fails to reach the
specified vacuum, the system has a leak that must
be corrected. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAKS)
(b) If the refrigerant system maintains the spec-
ified vacuum for five minutes, restart the vacuum
pump, open the suction and discharge valves and
evacuate the system for an additional ten minutes.
(3) Close all of the valves, and turn off the charg-
ing station vacuum pump.
(4) The refrigerant system is now ready to be
charged with R-134a refrigerant. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)After the refrigerant system has been tested for
leaks and evacuated, a refrigerant charge can be
injected into the system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - SPECIFICA-
TIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY)
A R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging
station that meets SAE Standard J2210 must be
used to charge the refrigerant system with R-134a
refrigerant. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for proper care
and use of this equipment.
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
The R-134a refrigerant system charge capacity for
this vehicle is: 0.907 kilograms (32 ounces).
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
The air conditioning system uses a Sanden
SD7H15 seven cylinder, reciprocating wobble plate-
type compressor on all models. This compressor has a
fixed displacement of 150 cubic centimeters (9.375
cubic inches), and has both the suction and discharge
ports located on the cylinder head. A label identifying
the use of R-134a refrigerant is located on the com-
pressor.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
A high pressure relief valve is located on the com-
pressor cylinder head, which is at the rear of the
compressor. This mechanical valve is designed to
vent refrigerant from the system to protect against
damage to the compressor and other system compo-
nents, caused by condenser air flow restriction or an
overcharge of refrigerant.
OPERATION
The compressor is driven by the engine through an
electric clutch, drive pulley and belt arrangement.
The compressor is lubricated by refrigerant oil that is
circulated throughout the refrigerant system with the
refrigerant.
The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant
vapor from the evaporator through its suction port. It
then compresses the refrigerant into a high-pressure,
high-temperature refrigerant vapor, which is then
pumped to the condenser through the compressor dis-
charge port.
The compressor cannot be repaired. If faulty or
damaged, the entire compressor assembly must be
24 - 46 PLUMBINGBR/BE
PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 2168 of 2255

replaced. The compressor clutch, pulley and clutch
coil are available for service.
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The high pressure relief valve vents the system
when a discharge pressure of 3445 to 4135 kPa (500
to 600 psi) or above is reached. The valve closes with
a minimum discharge pressure of 2756 kPa (400 psi)
is reached.
The high pressure relief valve vents only enough
refrigerant to reduce the system pressure, and then
re-seats itself. The majority of the refrigerant is con-
served in the system. If the valve vents refrigerant, it
does not mean the valve is faulty.
The high pressure relief valve is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The valve cannot be adjusted or
repaired, and must not be removed or otherwise dis-
turbed. The valve is only serviced as a part of the
compressor assembly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
When investigating an air conditioning related
noise, you must first know the conditions under
which the noise occurs. These conditions include:
weather, vehicle speed, transmission in gear or neu-
tral, engine speed, engine operating temperature,
and any other special conditions. Noises that develop
during air conditioning operation can often be mis-
leading. For example: What sounds like a failed front
bearing or connecting rod, may be caused by loose
bolts, nuts, mounting brackets, or a loose compressor
clutch assembly.
Drive belts are speed sensitive. At different engine
speeds and depending upon belt tension, belts can
develop noises that are mistaken for a compressor
noise. Improper belt tension can cause a misleading
noise when the compressor clutch is engaged, which
may not occur when the compressor clutch is disen-
gaged. Check the serpentine drive belt condition and
tension before beginning this procedure(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(1) Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate the
complaint conditions as much as possible. Switch the
compressor on and off several times to clearly iden-
tify the compressor noise. Listen to the compressor
while the clutch is engaged and disengaged. Probe
the compressor with an engine stethoscope or a long
screwdriver with the handle held to your ear to bet-
ter localize the source of the noise.
(2) Loosen all of the compressor mounting hard-
ware and retighten. Tighten the compressor clutch
mounting nut. Be certain that the clutch coil is
mounted securely to the compressor, and that the
clutch plate and pulley are properly aligned and have
the correct air gap. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIRCONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION)
(3) To duplicate a high-ambient temperature condi-
tion (high head pressure), restrict the air flow
through the condenser. Install a manifold gauge set
to be certain that the discharge pressure does not
exceed 2760 kPa (400 psi).
(4) Check the refrigerant system plumbing for
incorrect routing, rubbing or interference, which can
cause unusual noises. Also check the refrigerant lines
for kinks or sharp bends that will restrict refrigerant
flow, which can cause noises. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAU-
TION)
(5) If the noise is from opening and closing of the
high pressure relief valve, recover, evacuate, and
recharge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT RECOVERY)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIG-
ERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE) (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE) If the high pressure relief valve still
does not seat properly, replace the compressor.
(6) If the noise is from liquid slugging on the suc-
tion line, replace the accumulator. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/AC-
CUMULATOR - REMOVAL) Check the refrigerant oil
level and the refrigerant system charge. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
REFRIGERANT OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL) (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - SPECI-
FICATIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY) If the liquid
slugging condition continues following accumulator
replacement, replace the compressor.
(7) If the noise continues, replace the compressor
and repeat Step 1.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
The compressor may be removed and repositioned
without disconnecting the refrigerant lines or dis-
charging the refrigerant system. Discharging is not
necessary if servicing the compressor clutch or clutch
coil, the engine, the cylinder head, or the generator.
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
BR/BEPLUMBING 24 - 47
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2169 of 2255
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY)
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove the serpentine drive belt(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL), (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY
DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - REMOVAL) or (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(4) Unplug the compressor clutch coil wire harness
connector.
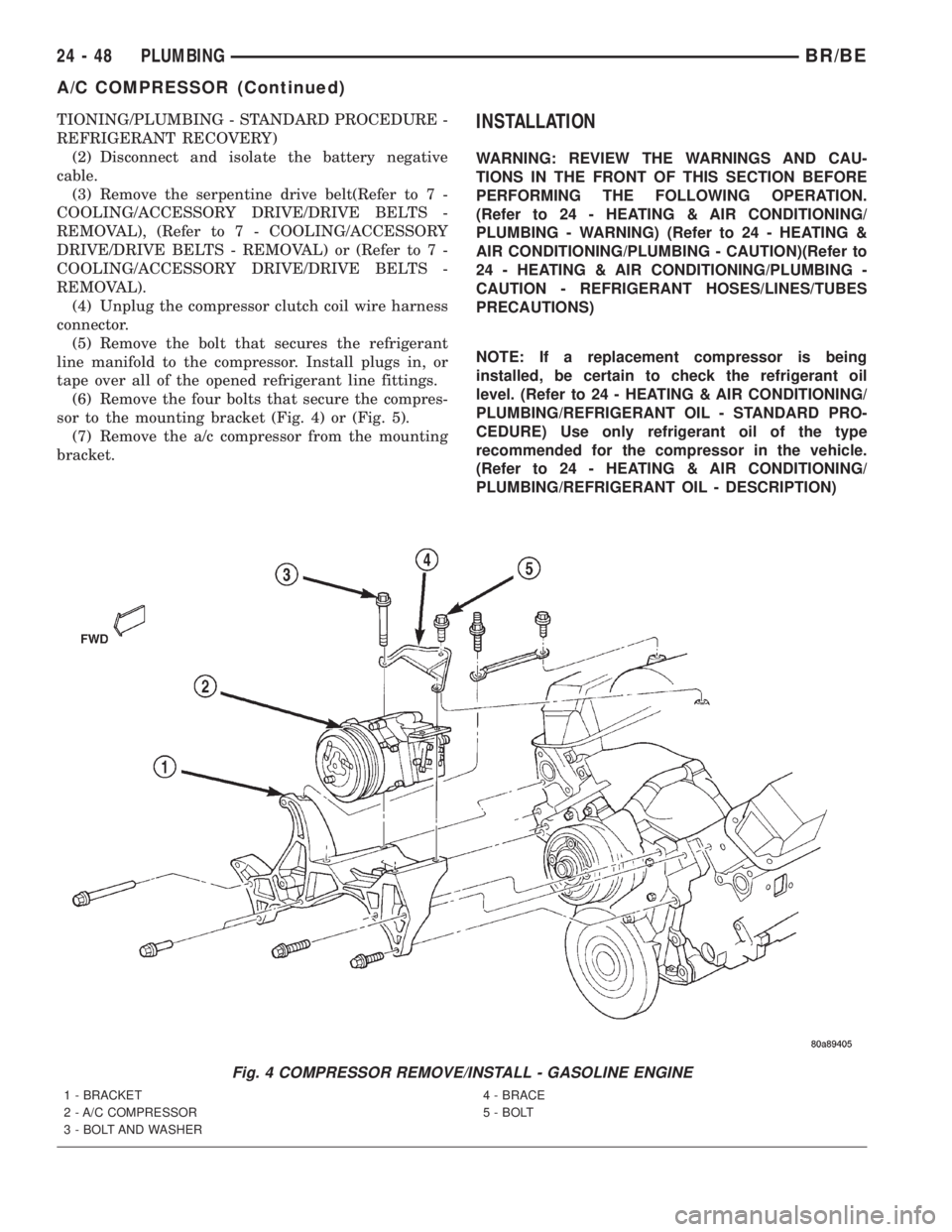
(5) Remove the bolt that secures the refrigerant
line manifold to the compressor. Install plugs in, or
tape over all of the opened refrigerant line fittings.
(6) Remove the four bolts that secure the compres-
sor to the mounting bracket (Fig. 4) or (Fig. 5).
(7) Remove the a/c compressor from the mounting
bracket.INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)(Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION - REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES
PRECAUTIONS)
NOTE: If a replacement compressor is being
installed, be certain to check the refrigerant oil
level. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE) Use only refrigerant oil of the type
recommended for the compressor in the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
Fig. 4 COMPRESSOR REMOVE/INSTALL - GASOLINE ENGINE
1 - BRACKET
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - BOLT AND WASHER4 - BRACE
5 - BOLT
24 - 48 PLUMBINGBR/BE
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2178 of 2255

OPERATION
R-134a refrigerant is not compatible with R-12
refrigerant in an air conditioning system. Even a
small amount of R-12 added to an R-134a refrigerant
system will cause compressor failure, refrigerant oil
sludge or poor air conditioning system performance.
In addition, the PolyAlkylene Glycol (PAG) synthetic
refrigerant oils used in an R-134a refrigerant system
are not compatible with the mineral-based refriger-
ant oils used in an R-12 refrigerant system.
R-134a refrigerant system service ports, service
tool couplers and refrigerant dispensing bottles have
all been designed with unique fittings to ensure that
an R-134a system is not accidentally contaminated
with the wrong refrigerant (R-12). There are also
labels posted in the engine compartment of the vehi-
cle and on the compressor identifying to service tech-
nicians that the air conditioning system is equipped
with R-134a.
REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION
The refrigerant oil used in R-134a refrigerant sys-
tems is a synthetic-based, PolyAlkylene Glycol (PAG),
wax-free lubricant. Mineral-based R-12 refrigerant
oils are not compatible with PAG oils, and should
never be introduced to an R-134a refrigerant system.
There are different PAG oils available, and each
contains a different additive package. The SD7H15
compressor used in this vehicle is designed to use an
SP-20 PAG refrigerant oil. Use only refrigerant oil of
this same type to service the refrigerant system.
OPERATION
After performing any refrigerant recovery or recy-
cling operation, always replenish the refrigerant sys-
tem with the same amount of the recommended
refrigerant oil as was removed. Too little refrigerant
oil can cause compressor damage, and too much can
reduce air conditioning system performance.
PAG refrigerant oil is much more hygroscopic than
mineral oil, and will absorb any moisture it comes
into contact with, even moisture in the air. The PAG
oil container should always be kept tightly capped
until it is ready to be used. After use, recap the oil
container immediately to prevent moisture contami-
nation.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT OIL
LEVEL
When an air conditioning system is assembled at
the factory, all components except the compressor are
refrigerant oil free. After the refrigerant system has
been charged and operated, the refrigerant oil in the
compressor is dispersed throughout the refrigerant
system. The accumulator, evaporator, condenser, and
compressor will each retain a significant amount of
the needed refrigerant oil.
It is important to have the correct amount of oil in
the refrigerant system. This ensures proper lubrica-
tion of the compressor. Too little oil will result in
damage to the compressor. Too much oil will reduce
the cooling capacity of the air conditioning system.
It will not be necessary to check the oil level in the
compressor or to add oil, unless there has been an oil
loss. An oil loss may occur due to a rupture or leak
from a refrigerant line, a connector fitting, a compo-
nent, or a component seal. If a leak occurs, add 30
milliliters (1 fluid ounce) of refrigerant oil to the
refrigerant system after the repair has been made.
Refrigerant oil loss will be evident at the leak point
by the presence of a wet, shiny surface around the
leak.
Refrigerant oil must be added when a accumulator,
evaporator coil, or condenser are replaced. See the
Refrigerant Oil Capacities chart. When a compressor
is replaced, the refrigerant oil must be drained from
the old compressor and measured. Drain all of the
refrigerant oil from the new compressor, then fill the
new compressor with the same amount of refrigerant
oil that was drained out of the old compressor.
Refrigerant Oil Capacities
Component ml fl oz
A/C System 210 6.2
Accumulator 60 2
Condenser 30 1
Evaporator 60 2
Compressordrain and measure
the oil from the old
compressor - see
text.
BR/BEPLUMBING 24 - 57
REFRIGERANT (Continued)