2002 CHRYSLER CARAVAN fuel filter
[x] Cancel search: fuel filterPage 1363 of 2399

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION.......................47
INSTALLATION.......................48
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................48
REMOVAL.............................48
INSTALLATION.........................48
OIL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................48
REMOVAL.............................48
INSTALLATION.........................48
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
DESCRIPTION.........................49
REMOVAL.............................49
INSTALLATION.........................49
OIL COOLER & LINES
REMOVAL.............................50
INSTALLATION.........................50
OIL FILTER
DESCRIPTION.........................51
REMOVAL.............................51
INSTALLATION.........................51
OIL JET
DESCRIPTION.........................52
REMOVAL.............................52
INSTALLATION.........................52
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION.........................52
REMOVAL.............................52INSTALLATION.........................52
VALVE TIMING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - LOCKING ENGINE
90É AFTER TDC.......................53
BALANCE SHAFT
DESCRIPTION.........................54
OPERATION...........................54
REMOVAL.............................55
INSTALLATION.........................55
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - TIMING BELT OUTER COVER . . 56
REMOVAL - TIMING BELT INNER COVER . . . 56
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - TIMING BELT OUTER
COVER.............................56
INSTALLATION - TIMING BELT INNER
COVER.............................57
TIMING BELT IDLER PULLEY
REMOVAL.............................58
INSTALLATION.........................58
TMNG BELT/CHAIN TENSIONER
REMOVAL.............................59
INSTALLATION.........................59
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - TIMING BELT TENSIONER . 60
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL.............................60
INSTALLATION.........................61
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 2.5L COMMON RAIL DIESEL
ENGINE
This 2.5 Liter (2500cc) four-cylinder ªcommon railº
direct injection engine is an in-line overhead valve
diesel engine. This engine utilizes a cast iron cylin-
der block and an aluminum cylinder head. The
engine is turbocharged and intercooled. The engine
also has four valves per cylinder and dual overhead
camshafts (Fig. 1).
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Displacement 2.5L (2499 cc)
Bore 92.00
Stroke 94.00
Compression Ratio 17.5:1
Vacuum at Idle 685.8 mm/Hg (27.0
In/Hg)
Belt Tension Automatic Belt Tensioner
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Thermostat Opening 80ÉC 2ÉC
Generator Rating Denso 12V-95A
Cooling System Capacity 13.8 Liters W/O Auxiliary
Heater
16.6 Liters With Auxiliary
Heater
Engine Oil Capacity 6.0L W/Filter Change
Timing System Belt Driven Camshafts In
Cylinder Head Cover
Air Intake Dry Filter
Fuel Feed Vane Pump Incorporated
In Injection Pump
Fuel System Direct Fuel Injection
Combustion Cycle 4 Stroke
Cooling System Water Cooling
Injection Pump Rotary Pump and
Electronically Managed
Lubrication Pressure Lubricated By
Rotary Pump
Engine Rotation Clockwise Viewed From
Front Cover
9a - 2 ENGINERG
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1435 of 2399

TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: The turbocharger is a performance part
and must not be tampered with. The wastegate
bracket is an integral part of the turbocharger. Tam-
pering with the wastegate components can reduce
durability by increasing cylinder pressure and ther-
mal loading due to incorrect inlet and exhaust man-
ifold pressure. Poor fuel economy and failure to
meet regulatory emissions laws may result. Increas-
ing the turbocharger boost WILL NOT increase
engine power.
The turbocharger is an exhaust-driven super-
charger which increases the pressure and density of
the air entering the engine. With the increase of air
entering the engine, more fuel can be injected into
the cylinders, which creates more power during com-
bustion.
The turbocharger assembly consists of four (4)
major component systems (Fig. 1) (Fig. 2):
²Turbine section
²Compressor section
²Bearing housing
²Wastegate
OPERATION
Exhaust gas pressure and energy drive the tur-
bine, which in turn drives a centrifugal compressor
that compresses the inlet air, and forces the air into
the engine through the charge air cooler and plumb-
ing. Since heat is a by-product of this compression,
the air must pass through a charge air cooler to cool
the incoming air and maintain power and efficiency.
Increasing air flow to the engine provides:
²Improved engine performance
²Lower exhaust smoke density
²Improved operating economy
²Altitude compensation
²Noise reduction.
The turbocharger also uses a wastegate (Fig. 3),
which regulates intake manifold air pressure and
prevents over boosting at high engine speeds. When
the wastegate valve is closed, all of the exhaust gases
flow through the turbine wheel. As the intake mani-
fold pressure increases, the wastegate actuator opens
the valve, diverting some of the exhaust gases away
from the turbine wheel. This limits turbine shaft
speed and air output from the impeller.
The turbocharger is lubricated by engine oil that is
pressurized, cooled, and filtered. The oil is delivered
to the turbocharger by a supply line that is tapped
into the oil filter head. The oil travels into the bear-
ing housing, where it lubricates the shaft and bear-
ings (Fig. 4). A return pipe at the bottom of the
Fig. 1 Turbocharger Operation
1 - TURBINE SECTION
2 - EXHAUST GAS
3 - BEARING HOUSING
4 - COMPRESSOR SECTION
5 - INLET AIR
6 - COMPRESSED AIR TO ENGINE
7 - EXHAUST GAS
8 - EXHAUST GAS TO EXHAUST PIPE
Fig. 2 Turbocharger Wastegate Actuator
1 - TURBOCHARGER
2 - DIAPHRAGM
3 - WASTE GATE ACTUATOR
11a - 2 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND TURBOCHARGERRG
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1452 of 2399

FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY..........................1FUEL INJECTION........................16
FUEL DELIVERY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION........................2
DESCRIPTION - FFV REPLACEMENT
PARTS...............................2
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL DELIVERY
SYSTEM.............................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.......2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
FUEL TANK...........................2
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE..............3
TORQUE.............................3
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL................................3
FUEL FILTER
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................4
OPERATION............................4
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................6
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION - FUEL LINES/HOSES AND
CLAMPS.............................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HOSES AND
CLAMP..............................6
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
OPERATION............................7REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................7
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................8
OPERATION............................8
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................9
FUEL RAIL
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L.......................9
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L....................9
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L..................10
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L................10
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
FUEL TANK FILLER TUBE
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS...........................13
RSFUEL SYSTEM14-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1453 of 2399

FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The front wheel drive car uses a plastic fuel tank
located rear center of the vehicle.
The Fuel Delivery System consists of: the following
items:
²Electric fuel pump module
²Fuel filter
²Tubes/lines/hoses
²Fuel injectors
The in-tank fuel pump module contains the fuel
pump. The pump is serviced as part of the fuel pump
module. Refer to Fuel Pump Module.
The fuel filter is replaceable, it is mounted on the
outside, on top of, the fuel tank. Refer to the Main-
tenance Schedules in the Introduction section of this
manual for recommended fuel filter replacement
intervals.
DESCRIPTION - FFV REPLACEMENT PARTS
Many components in a Flexible Fuel Vehicle (FFV)
are designed to be compatible with ethanol. Always
be sure that the vehicle is serviced with correct etha-
nol compatible parts.
CAUTION: Replacing fuel system components with
non-ethanol compatible components can damage
your vehicle and may void the warranty.
OPERATION
The fuel system provides fuel pressure by an
in-tank pump module. The PCM controls the opera-
tion of the fuel system by providing battery voltage
to the fuel pump through the fuel pump relay. The
PCM requires only three inputs and a good ground to
operate the fuel pump relay. The three inputs are:²Ignition voltage
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL DELIVERY
SYSTEM
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information)
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
(1) Remove Fuel Pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.
(2) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(3) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(4) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
(5) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(6) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRB IIItscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING FUEL
TANK
(1) Release fuel system pressure, refer to the Fuel
System Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Insert a 1/4 inch siphon (max. O. D. 5/16) hose
from a portable fuel siphoning tank through the fuel
filler neck opening into the fuel tank. Hose most
have a 30 degree angle cut on the end to bypass the
check valve in the end of the filler neck. Refer to the
siphoning tank's Manufacturing Instructions.
(3) Drain fuel from fuel tank into siphoning tank.
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1454 of 2399
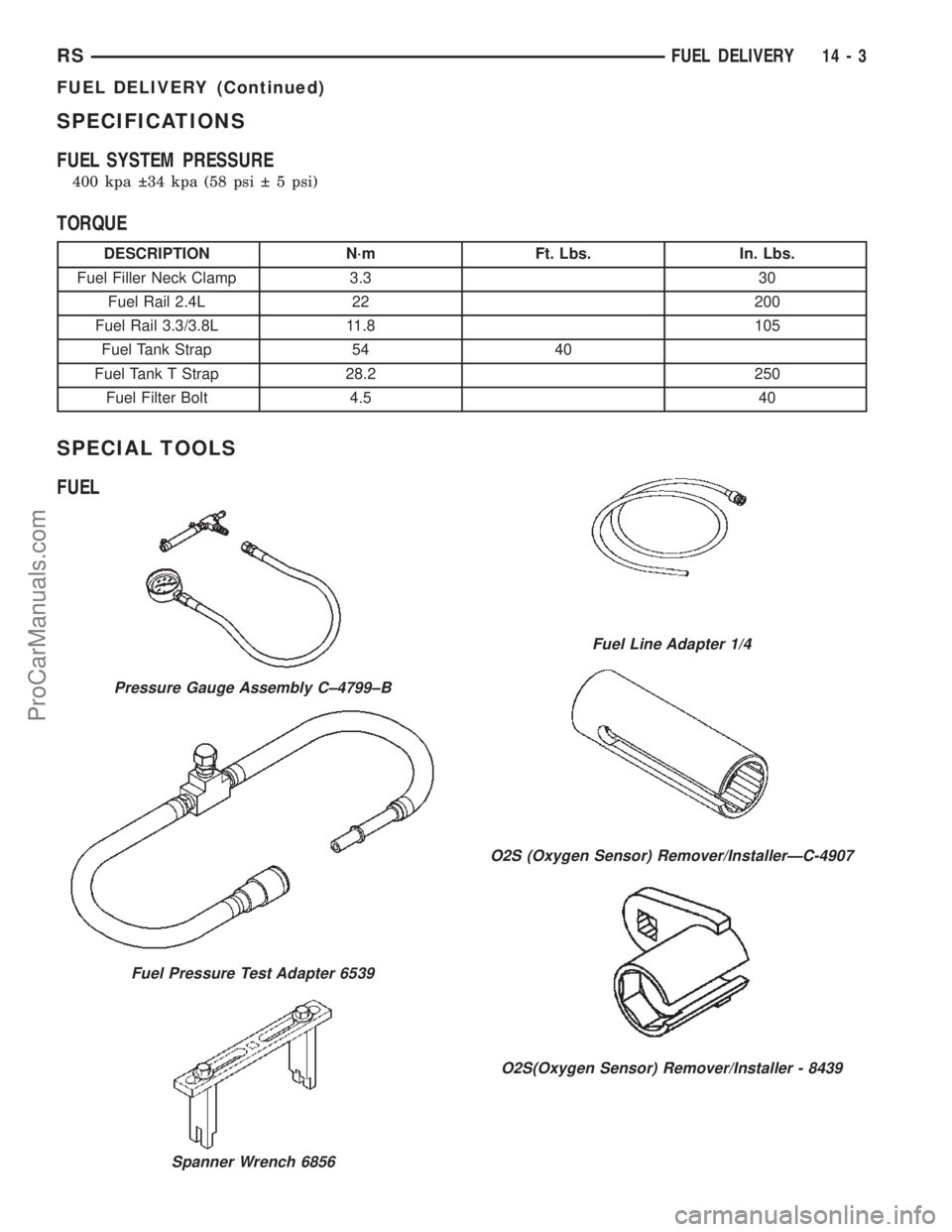
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
400 kpa 34 kpa (58 psi 5 psi)
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fuel Filler Neck Clamp 3.3 30
Fuel Rail 2.4L 22 200
Fuel Rail 3.3/3.8L 11.8 105
Fuel Tank Strap 54 40
Fuel Tank T Strap 28.2 250
Fuel Filter Bolt 4.5 40
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL
Pressure Gauge Assembly C±4799±B
Fuel Pressure Test Adapter 6539
Spanner Wrench 6856
Fuel Line Adapter 1/4
O2S (Oxygen Sensor) Remover/InstallerÐC-4907
O2S(Oxygen Sensor) Remover/Installer - 8439
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-3
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1455 of 2399

FUEL FILTER
REMOVAL
(1) Release fuel pressure, refer to the Fuel release
procedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(3) Raise vehicle and support.
(4) Support the fuel tank with a transmission jack.
(5) Remove fuel line from the front of the tank.
(6) Remove ground strap
(7) Remove the inboard side of the fuel tank straps
and front T strap fastner.
(8) Lower the tank about 6 inches (Fig. 1).
(9) Remove fuel lines from the fuel pump module.
(10) Remove fuel filter from tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install fuel filter to tank. Tighten bolt to 4.5
N´m (40 in. lbs.)
(2) Install fuel lines to the fuel pump module (Fig.
1).
(3) Raise tank into position.
(4) Install the fuel tank straps.Tighten bolt for
main straps to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) and the T strap
bolt to 28.2 N´m (250 in. lbs.)
(5) Install the ground strap
(6) Connect the fuel line at the front of the tank.
(7) Lower vehicle.
(8) Connect the negative battery cable.
(9) Pressurize the fuel system with the DRBIIIt
and check for leaks.
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge level sending unit is attached to the
side of fuel pump module. The level sensor is a vari-
able resistor.
OPERATION
Its resistance changes with the amount of fuel in
the tank. The float arm attached to the sensor moves
as the fuel level changes.
The fuel level input is used as an input for OBD II.
If the fuel level is below 15% or above 85% of total
tank capacity several monitors are disabled. There
are diagnostics for the level circuit open and shorted.
REMOVAL
Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module in this section.
(1) Depress retaining tab and remove the fuel
pump/level sensor connector from theBOTTOMof
the fuel pump module electrical connector (Fig. 2) .
NOTE: The pump module harness on TOP of flange
is not serviceable or removable.
Fig. 1 FUEL FILTER
Fig. 2 Fuel Pump/Level Sensor Electrical Connector
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - RETAINING TAB
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERYRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1462 of 2399
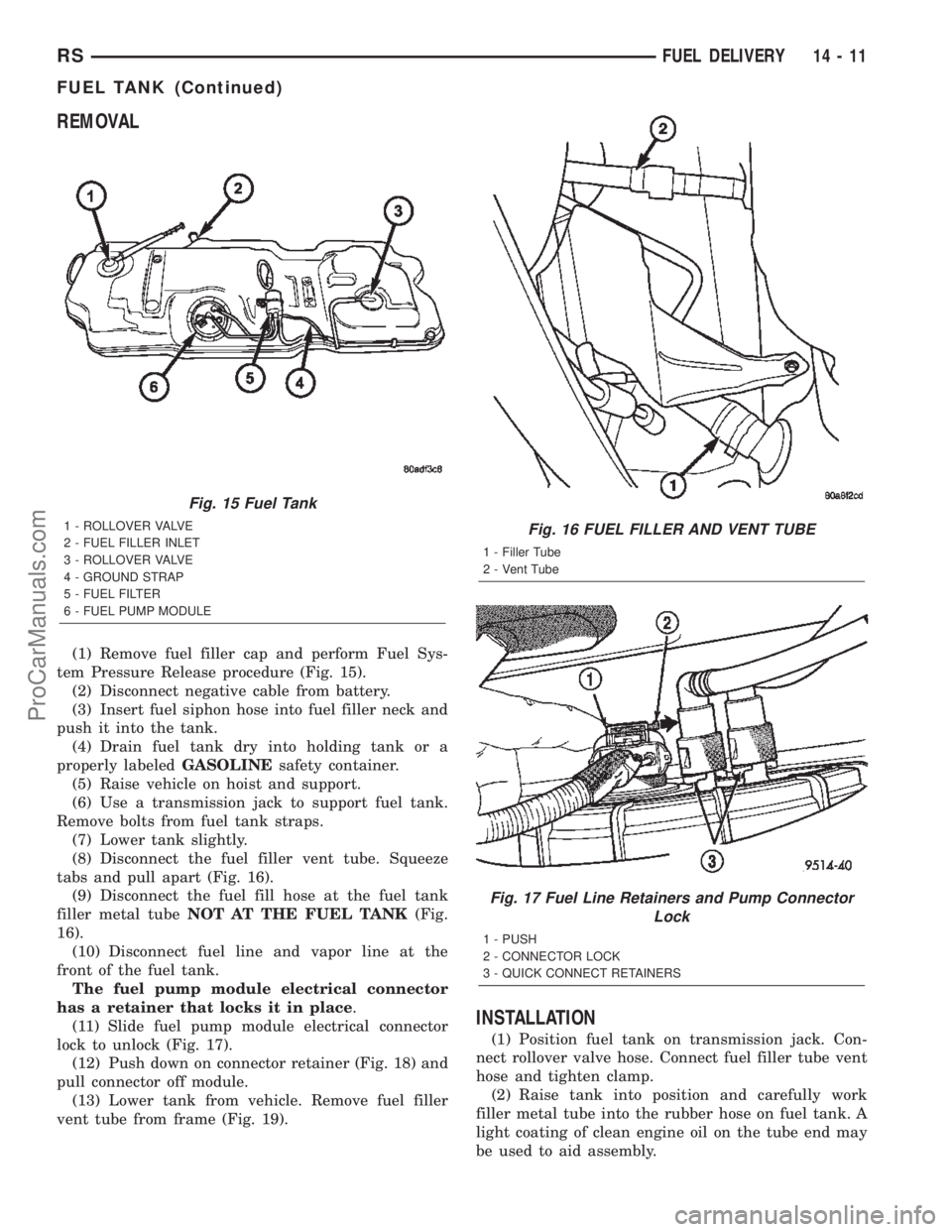
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure (Fig. 15).
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Insert fuel siphon hose into fuel filler neck and
push it into the tank.
(4) Drain fuel tank dry into holding tank or a
properly labeledGASOLINEsafety container.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist and support.
(6) Use a transmission jack to support fuel tank.
Remove bolts from fuel tank straps.
(7) Lower tank slightly.
(8) Disconnect the fuel filler vent tube. Squeeze
tabs and pull apart (Fig. 16).
(9) Disconnect the fuel fill hose at the fuel tank
filler metal tubeNOT AT THE FUEL TANK(Fig.
16).
(10) Disconnect fuel line and vapor line at the
front of the fuel tank.
The fuel pump module electrical connector
has a retainer that locks it in place.
(11) Slide fuel pump module electrical connector
lock to unlock (Fig. 17).
(12) Push down on connector retainer (Fig. 18) and
pull connector off module.
(13) Lower tank from vehicle. Remove fuel filler
vent tube from frame (Fig. 19).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fuel tank on transmission jack. Con-
nect rollover valve hose. Connect fuel filler tube vent
hose and tighten clamp.
(2) Raise tank into position and carefully work
filler metal tube into the rubber hose on fuel tank. A
light coating of clean engine oil on the tube end may
be used to aid assembly.
Fig. 15 Fuel Tank
1 - ROLLOVER VALVE
2 - FUEL FILLER INLET
3 - ROLLOVER VALVE
4 - GROUND STRAP
5 - FUEL FILTER
6 - FUEL PUMP MODULEFig. 16 FUEL FILLER AND VENT TUBE
1 - Filler Tube
2 - Vent Tube
Fig. 17 Fuel Line Retainers and Pump Connector
Lock
1 - PUSH
2 - CONNECTOR LOCK
3 - QUICK CONNECT RETAINERS
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-11
FUEL TANK (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1464 of 2399

(4) Install the 3 screws at the filler door.
(5) Install the canister from filler tube (Fig. 21).
(6) Install the splash shield.
(7) Install the left rear tire.
(8) lower vehicle.
(9) Connect the negative battery cable.
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal in this section.
(2) Using a thin straight blade screwdriver, pry
back the locking tabs on fuel pump reservoir and
remove the strainer (Fig. 22).
(3) Remove strainer O-ring from the fuel pump
reservoir body.
(4) Remove any contaminants in the fuel tank by
washing the inside of the fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the strainer O-ring with clean engine
oil.
(2) Insert strainer O-ring into outlet of strainer so
that it sits evenly on the step inside the outlet.
(3) Push strainer onto the inlet of the fuel pump
reservoir body. Make sure the locking tabs on the
reservoir body lock over the locking tangs on the
strainer.
(4) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Installation in this section.
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS
REMOVAL
When disconnecting a quick-connect fitting, the
retainer will remain on the fuel tube nipple.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE DISCONNECTING A QUICK-CONNECT FIT-
TINGS. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE.
(1) Perform Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery or aux-
iliary jumper terminal.
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Never install a quick-connect fitting with-
out the retainer being either on the fuel tube or
already in the quick-connect fitting. In either case,
ensure the retainer locks securely into the quick-
connect fitting by firmly pulling on fuel tube and fit-
ting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean engine oil.
Fig. 21 FUEL TUBE VENT CANISTER
Fig. 22 Inlet
1 - TABS
2 - INLET STRAINER
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-13
FUEL TANK FILLER TUBE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com