2002 CHRYSLER CARAVAN oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: oil pressurePage 1411 of 2399

(4) Using special tool VM.1059, push oil pressure
relief valve cap in untill flush with engine block (Fig.
77).
(5) Install oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
OIL COOLER & LINES
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove oil filter cap and filter (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove oil filter housing retaining nut and
housing (Fig. 78).
(5) Disconnect coolant hoses at cooler (Fig. 79).
(6) Remove oil cooler retaining bolt at engine block
(Fig. 79).
(7) Remove oil cooler retaining stud and remove oil
cooler from engine block (Fig. 79).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean oil cooler and engine block sealing sur-
faces.
Fig. 77 OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
INSTALLATION
1 - VM.1059
2 - OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
4 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 78 OIL FILTER HOUSING RETAINING NUT
1 - OIL FILTER HOUSING
2 - OIL FILTER HOUSING RETAINING NUT
3 - OIL COOLER
Fig. 79 WATER PUMP AND OIL COOLER
ASSEMBLIES
1 - WATER PUMP HOUSING STUDS
2 - WATER PUMP
3 - RETAINING NUTS
4 - OIL COOLER RETAINING STUD
5 - OIL COOLER TO ENGINE BLOCK RETAINING BOLT
6 - OIL COOLER COOLANT HOSE
7 - ENGINE BLOCK
9a - 50 ENGINERG
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1435 of 2399

TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: The turbocharger is a performance part
and must not be tampered with. The wastegate
bracket is an integral part of the turbocharger. Tam-
pering with the wastegate components can reduce
durability by increasing cylinder pressure and ther-
mal loading due to incorrect inlet and exhaust man-
ifold pressure. Poor fuel economy and failure to
meet regulatory emissions laws may result. Increas-
ing the turbocharger boost WILL NOT increase
engine power.
The turbocharger is an exhaust-driven super-
charger which increases the pressure and density of
the air entering the engine. With the increase of air
entering the engine, more fuel can be injected into
the cylinders, which creates more power during com-
bustion.
The turbocharger assembly consists of four (4)
major component systems (Fig. 1) (Fig. 2):
²Turbine section
²Compressor section
²Bearing housing
²Wastegate
OPERATION
Exhaust gas pressure and energy drive the tur-
bine, which in turn drives a centrifugal compressor
that compresses the inlet air, and forces the air into
the engine through the charge air cooler and plumb-
ing. Since heat is a by-product of this compression,
the air must pass through a charge air cooler to cool
the incoming air and maintain power and efficiency.
Increasing air flow to the engine provides:
²Improved engine performance
²Lower exhaust smoke density
²Improved operating economy
²Altitude compensation
²Noise reduction.
The turbocharger also uses a wastegate (Fig. 3),
which regulates intake manifold air pressure and
prevents over boosting at high engine speeds. When
the wastegate valve is closed, all of the exhaust gases
flow through the turbine wheel. As the intake mani-
fold pressure increases, the wastegate actuator opens
the valve, diverting some of the exhaust gases away
from the turbine wheel. This limits turbine shaft
speed and air output from the impeller.
The turbocharger is lubricated by engine oil that is
pressurized, cooled, and filtered. The oil is delivered
to the turbocharger by a supply line that is tapped
into the oil filter head. The oil travels into the bear-
ing housing, where it lubricates the shaft and bear-
ings (Fig. 4). A return pipe at the bottom of the
Fig. 1 Turbocharger Operation
1 - TURBINE SECTION
2 - EXHAUST GAS
3 - BEARING HOUSING
4 - COMPRESSOR SECTION
5 - INLET AIR
6 - COMPRESSED AIR TO ENGINE
7 - EXHAUST GAS
8 - EXHAUST GAS TO EXHAUST PIPE
Fig. 2 Turbocharger Wastegate Actuator
1 - TURBOCHARGER
2 - DIAPHRAGM
3 - WASTE GATE ACTUATOR
11a - 2 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND TURBOCHARGERRG
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1449 of 2399

REMOVAL
The front cradle crossmember must be installed in
the design location to achieve proper front end sus-
pension alignment. If the cradle crossmember is
removed without applying reference marks on the
frame rails, align the cradle crossmember according
to the dimensions provided in this group.
NOTE: If the caged nuts in the frame rails become
damaged and cannot be reused, a replacement nut
can be obtained through MoparT.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove steering column lower cover from
instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRU-
MENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPENING
COVER - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove steering column cover backing plate
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN COVER BACKING PLATE - REMOV-
AL).
(4) Position steering so front wheels are straight
ahead.
CAUTION: Do not rotate steering wheel after disen-
gaging lower coupling from steering gear, damage
to air bag clock spring can result.
(5) Remove clinch bolt attaching steering column
coupling to steering gear shaft (Fig. 10).(6) Remove steering column coupling from tele-
scoping steering gear shaft.
(7) Hoist vehicle and support on safety stands.
(8) Position a drain pan under power steering
pump and oil return hose coupling.
(9) Using a hose pinch-off pliers (C-4390), pinch
power steering oil return hose off between the cross-
member coupling and the pump.
(10) Loosen hose clamp at the cradle crossmember
coupling.
(11) Disconnect return hose from metal tube.
(12) While holding pressure relief valve nut on
back of power steering pump, Remove flare nut
attaching high pressure hose to back of pump.
(13) Remove high pressure hose from pump.
(14) Allow power steering fluid to drain into pan.
(15) Remove bolts attaching anti-lock brake sensor
leads to cradle crossmember.
(16) Position anti-lock brake leads out of the way.
(17) Disconnect stabilizer bar links from ends of
stabilizer bar.
(18) Disconnect lower ball joints from lower steer-
ing knuckles (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/
LOWER BALL JOINT - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove the rear engine mount heat shield
(Fig. 11).
(20) Remove through bolt attaching rear engine
mount to cradle crossmember (Fig. 12).
(21) Using paint or grease pencil, mark outline of
cradle crossmember on frame rails to aid installation.
(22) Support cradle crossmember on suitable lift-
ing device (Fig. 14).
(23) Remove bolts attaching crossmember to front
frame rails (Fig. 13).
Fig. 10 STEERING COUPLING
1 - STEERING SHAFT BOOT
2 - STEERING SHAFT
3 - CROSSMEMBER
4 - STEERING GEAR
5 - MOUNT
6 - TRANSAXLE
Fig. 11 REAR MOUNT HEAT SHIELD
1 - BOLT
2 - HEAT SHIELD
3 - CLIP
4 - REAR ENGINE MOUNT
13 - 10 FRAME & BUMPERSRS
FRONT CRADLE CROSSMEMBER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1458 of 2399

leaks are not present. The component should be
replaced immediately if there is any evidence of deg-
radation that could result in failure.
Never attempt to repair a plastic fuel line/tube.
Replace as necessary.
Avoid contact of any fuel tubes/hoses with other
vehicle components that could cause abrasions or
scuffing. Be sure that the plastic fuel lines/tubes are
properly routed to prevent pinching and to avoid heat
sources.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
OPERATION
The fuel system uses a nonadjustable pressure reg-
ulator that maintains fuel system pressure at
approximately 400 34 kPa (58 5 psi). The fuel
pressure regulator contains a diaphragm, calibrated
spring and a fuel return valve. The spring pushes
down on the diaphragm and closes off the fuel return
port. System fuel pressure reflects the amount of fuel
pressure required to open the return port.
The pressure regulator is a mechanical device that
is NOT controlled by the PCM or engine vacuum.
REMOVAL
The fuel pressure regulator is part of the fuel
pump module (Fig. 9). Remove the fuel pump module
from the fuel tank to access the fuel pressure regula-
tor. Refer to the Fuel Pump Module removal in this
section.
(1) Spread tangs on pressure regulator retainer.
(2) Pry fuel pressure regulator out of housing.
(3) Ensure both upper and lower O-rings were
removed with regulator.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pressure regulator is part of the fuel
pump module. Remove the fuel pump module from
the fuel tank to access the fuel pressure regulator.
Refer to the Fuel Pump Module removal in this sec-
tion.
(1) Lightly lubricate the O-rings with clean engine
oil and place them into opening in pump module (Fig.
9).
(2) Push regulator into opening in pump module.
(3) Fold tangs on regulator retainer over tabs on
housing.
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located in and is part of
the fuel pump module. It is a positive displacement,
gerotor type, immersible pump with a permanent
magnet electric motor. The fuel pump module is sus-
pended in fuel in the fuel tank.
OPERATION
The pump draws fuel through a strainer and
pushes it through the motor to the outlet. The pump
contains a check valve. The valve, in the pump out-
let, maintains pump pressure during engine off con-
ditions, for a short while. It is normal for fuel
pressure to drop to zero after cooldown. The fuel
pump relay provides voltage to the fuel pump. The
fuel pump has a maximum deadheaded pressure out-
put of approximately 880 kPa (130 psi). The regula-
tor adjusts fuel system pressure to approximately
400 kpa 34 kpa (58 psi 5 psi).
NOTE: Checkvalve maintains volume of fuel in the
rail and lines, not pressure.
Fig. 9 Fuel Pressure Regulator O-rings
1 - UPPER O-RING
2 - LOWER 0-RING
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-7
FUEL LINES (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1462 of 2399
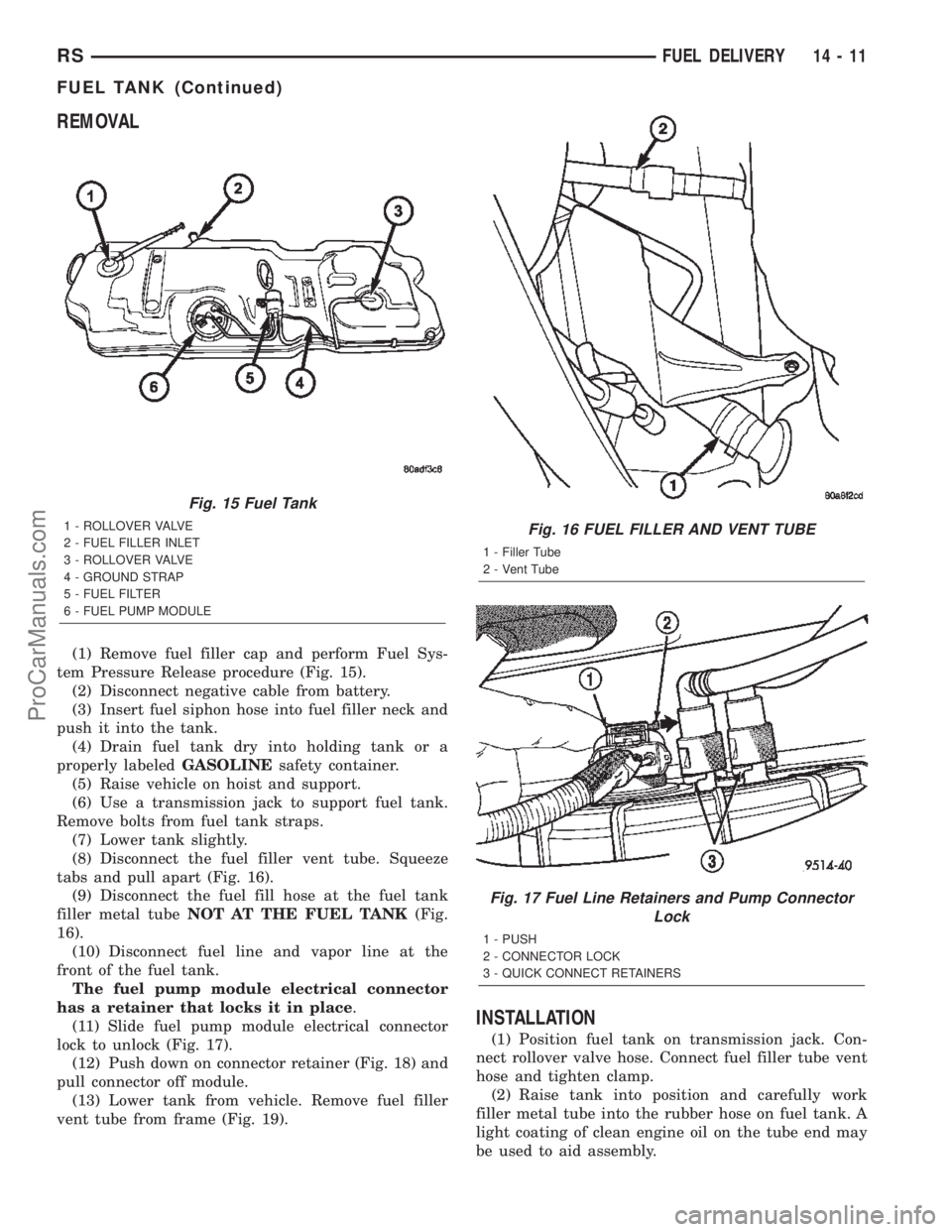
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure (Fig. 15).
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Insert fuel siphon hose into fuel filler neck and
push it into the tank.
(4) Drain fuel tank dry into holding tank or a
properly labeledGASOLINEsafety container.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist and support.
(6) Use a transmission jack to support fuel tank.
Remove bolts from fuel tank straps.
(7) Lower tank slightly.
(8) Disconnect the fuel filler vent tube. Squeeze
tabs and pull apart (Fig. 16).
(9) Disconnect the fuel fill hose at the fuel tank
filler metal tubeNOT AT THE FUEL TANK(Fig.
16).
(10) Disconnect fuel line and vapor line at the
front of the fuel tank.
The fuel pump module electrical connector
has a retainer that locks it in place.
(11) Slide fuel pump module electrical connector
lock to unlock (Fig. 17).
(12) Push down on connector retainer (Fig. 18) and
pull connector off module.
(13) Lower tank from vehicle. Remove fuel filler
vent tube from frame (Fig. 19).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fuel tank on transmission jack. Con-
nect rollover valve hose. Connect fuel filler tube vent
hose and tighten clamp.
(2) Raise tank into position and carefully work
filler metal tube into the rubber hose on fuel tank. A
light coating of clean engine oil on the tube end may
be used to aid assembly.
Fig. 15 Fuel Tank
1 - ROLLOVER VALVE
2 - FUEL FILLER INLET
3 - ROLLOVER VALVE
4 - GROUND STRAP
5 - FUEL FILTER
6 - FUEL PUMP MODULEFig. 16 FUEL FILLER AND VENT TUBE
1 - Filler Tube
2 - Vent Tube
Fig. 17 Fuel Line Retainers and Pump Connector
Lock
1 - PUSH
2 - CONNECTOR LOCK
3 - QUICK CONNECT RETAINERS
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-11
FUEL TANK (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1464 of 2399

(4) Install the 3 screws at the filler door.
(5) Install the canister from filler tube (Fig. 21).
(6) Install the splash shield.
(7) Install the left rear tire.
(8) lower vehicle.
(9) Connect the negative battery cable.
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal in this section.
(2) Using a thin straight blade screwdriver, pry
back the locking tabs on fuel pump reservoir and
remove the strainer (Fig. 22).
(3) Remove strainer O-ring from the fuel pump
reservoir body.
(4) Remove any contaminants in the fuel tank by
washing the inside of the fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the strainer O-ring with clean engine
oil.
(2) Insert strainer O-ring into outlet of strainer so
that it sits evenly on the step inside the outlet.
(3) Push strainer onto the inlet of the fuel pump
reservoir body. Make sure the locking tabs on the
reservoir body lock over the locking tangs on the
strainer.
(4) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Installation in this section.
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS
REMOVAL
When disconnecting a quick-connect fitting, the
retainer will remain on the fuel tube nipple.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE DISCONNECTING A QUICK-CONNECT FIT-
TINGS. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE.
(1) Perform Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery or aux-
iliary jumper terminal.
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Never install a quick-connect fitting with-
out the retainer being either on the fuel tube or
already in the quick-connect fitting. In either case,
ensure the retainer locks securely into the quick-
connect fitting by firmly pulling on fuel tube and fit-
ting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean engine oil.
Fig. 21 FUEL TUBE VENT CANISTER
Fig. 22 Inlet
1 - TABS
2 - INLET STRAINER
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-13
FUEL TANK FILLER TUBE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1466 of 2399

(6) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(7) Insert quick-connect fitting to component being
serviced and into plastic retainer. When a connection
is made, a click will be heard.
(8) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(9) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
(10) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting can be identified by the use of a
full-round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 25) usually black
in color.CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers, retainers) of this type of quick-connect fitting
are not serviced separately. Do not attempt to repair
damaged fittings or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is nec-
essary, replace the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To release fuel system component from quick-
connect fitting, firmly push fitting towards compo-
nent being serviced while firmly pushing plastic
retainer ring into fitting (Fig. 25). With plastic ring
depressed, pull fitting from component.The plastic
retainer ring must be pressed squarely into fit-
ting body. If this retainer is cocked during
removal, it may be difficult to disconnect fit-
ting. Use an open-end wrench on shoulder of
plastic retainer ring to aid in disconnection.
(5) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(6) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage. Replace
as necessary.
(7) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(8) Insert quick-connect fitting into component
being serviced until a click is felt.
(9) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery or
auxiliary jumper terminal.
(11) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
Fig. 25 Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting
1 - FUEL TUBE
2 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
3 - PUSH
4 - PLASTIC RETAINER
5 - PUSH
6 - PUSH
7 - PUSH
8 - PUSH
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-15
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1469 of 2399

1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. If the vehicle is in
park or neutral (automatic transaxles) or the clutch
pedal is depressed (manual transaxles) the ignition
switch energizes the starter relay. The following
actions occur when the starter motor is engaged.
²If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay.
If the PCM does not receive both signals within
approximately one second, it will not energize the
ASD relay and fuel pump relay. The ASD and fuel
pump relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump,
fuel injectors, ignition coil, (EGR solenoid and PCV
heater if equipped) and heated oxygen sensors.
²The PCM energizes the injectors (on the 69É
degree falling edge) for a calculated pulse width until
it determines crankshaft position from the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position sensor sig-
nals. The PCM determines crankshaft position within
1 engine revolution.
²After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. It adjusts
injector pulse width and controls injector synchroni-
zation by turning the individual ground paths to the
injectors On and Off.
²When the engine idles within 64 RPM of its
target RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode.
Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM determines injector pulse width
based on the following:
²MAP
²Engine RPM
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature
²Inlet/Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Throttle position
²The number of engine revolutions since cranking
was initiated
During Start-up the PCM maintains ignition tim-
ing at 9É BTDC.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Engine coolant temperature
²Inlet/Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Camshaft position²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²A/C switch
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
²Speed control
²O2 sensors
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising or idle
the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²A/C control positions
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas (measured
by the upstream and downstream heated oxygen sen-
sor).
The PCM monitors for engine misfire. During
active misfire and depending on the severity, the
PCM either continuously illuminates or flashes the
malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine light on
instrument panel). Also, the PCM stores an engine
misfire DTC in memory, if 2nd trip with fault.
The PCM performs several diagnostic routines.
They include:
²Oxygen sensor monitor
²Downstream heated oxygen sensor diagnostics
during open loop operation (except for shorted)
²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor (if equipped)
²Purge system monitor
²Catalyst efficiency monitor
²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range,
rationality.
²All monitored components (refer to the Emission
section for On-Board Diagnostics).
14 - 18 FUEL INJECTIONRS
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com