2002 BMW 528I window
[x] Cancel search: windowPage 46 of 80

Power Window Motors: The window motors are mounted on the cable regulators. The
window motor control circuit consists of two wires for operating the motor in both direc-
tions.
The motors are activated by relays in the GM of door
modules (front doors). The relays provide either power
or ground depending on the direction of window travel.
The GM controls the polarity of the motor based on a
request to run the window (window switch,
Convenience Opening/ Closing).
The windows are run to the limit stops which is detect-
ed by an amperage increase in the control circuit.
Additionally, the window run cycle is limited to a 6-8
second duration if in case the amperage increase is not
detected or there is a malfunction with the regulator.
Window Motor Limit Stop Function: If the windows are run up and down continuously
a limit stop function is activated to prevent the window motors from overheating. The GM
monitors the number of times the window motors are activated. Each cycle is counted and
stored in memory.
If the repetitive window activation (up/down) exceeds one minute, the GM deactivates the
internal relays and disregards any further input requests. The GM provides motor activation
after a short duration but not for the full one minute monitoring cycle. Over time, the GM
slowly reverses the stored count of activation until the stored number equals 0.
Convenience Opening/Closing: The GM provides the convenience open/close feature
providing control of the power windows (and sunroof) from outside the vehicle with the key
in the driver’s door lock cylinder. The FZV provides the same function for the opening only.
• The anti-trap feature is active during convenience closing from the driver’s door lock.
• The convenience open feature provides outside activation of the windows and sunroof
in the same manner.
• If the GM receives a request to operate convenience close or open for more than 110
seconds, the function is deactivated and a fault code is stored.
• The Car Memory Feature can activate and deactivate the Convenience Open Feature
from the FZV’s control.
46
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
FRONT DOOR
REGULATOR
615200114.eps
Page 58 of 80

Seat/Mirror/Steering Column Memory
Purpose of the System
The front seats, outside rearview mirrors and steering column (if equipped) positions are
electrically adjustable. The “customized” adjustment positions can be memorized and
stored for three diferent users and recalled back to the individual positions (with the excep-
tion of the passenger seat - not in memory).
The basic features of seat/mirror/steering column operation, as well as the memory posi-
tions is integrated into the ZKE III system.
• Seat/Steering Column Memory
Module (PM SM).
• Driver’s Door Switchblock Mod-
ule (PM FT/SB - early E38 was
separate).
• Passenger’s Door Module (PM
BT - E53 combined with window
switch).
• General Module (GM III).
• 3 Position Memory Switch.
• Seat Switch.
• Steering Column Switch.
• Seat/Steering Column/Mirror
Motors.
The Seat/Steering Column Memory Module communicates with the DISplus or MoDiC for
diagnosis and Vehicle Memory encoding.
58
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
System Components: Inputs - Processing - Outputs
E38/E39 Shown
Page 68 of 80

68
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Center Console Switch Center (SZM): From 1999 MY E38, E39 and E53 vehicles are
equipped with a SZM to control the front seat heating and provide a diagnostic interface
with the DISplus/MoDiC via the K BUS.
The SZM directly controls:
• Front Seat Heating
• Rear Window Roller Blind
SZM also provides a unitized switching center
for:
• Park Distance Control (PDC)
• Dynamic Stability Control (DSC III)
• Electronic Damper Control (EDC).
The switch signal output for these systems is a direct output signal. All diagnosis functions
are carried out through their respective control systems.
SZM Monitoring of Seat Heating
Battery Voltage:The SZM switches current supply to the heating elements off when bat-
tery voltage drops below 11.4 volts. However, the heating stage LEDs remain on.
Regulated output current resumes when battery voltage raises above 12.2 volts for more
than 5 seconds.
SZM Internal Temperature: The power output stages for the seat heating elements gen-
erate a considerable amount of heat when in stage 1 operation. The SZM monitors it’s own
internal temperatures and reduces the heating output when internal temperatures rise to a
temperature of 185
OF or switches it off completely above 203OF. As with battery voltage
monitoring, the heating stage LEDs remain on when these temperatures are exceeded.
Fault Monitoring:The SZM monitors the temperature sensors and heating mats for faults.
Detected faults are stored in the SZM. Fault Symptom Troubleshooting in conjunction with
stored faults will initiate the diagnostic paths using the DISplus/MoDiC. The following faults
can be recognized:
• Shorts or opens in the wiring circuits.
• Shorts or opens in the temperature sensors.
• Open in heating element.
If a short is detected in the temperature sensor, the seat heating is switched off to prevent
overheating. The Stage LEDs are also switched off with this fault present.
Page 69 of 80
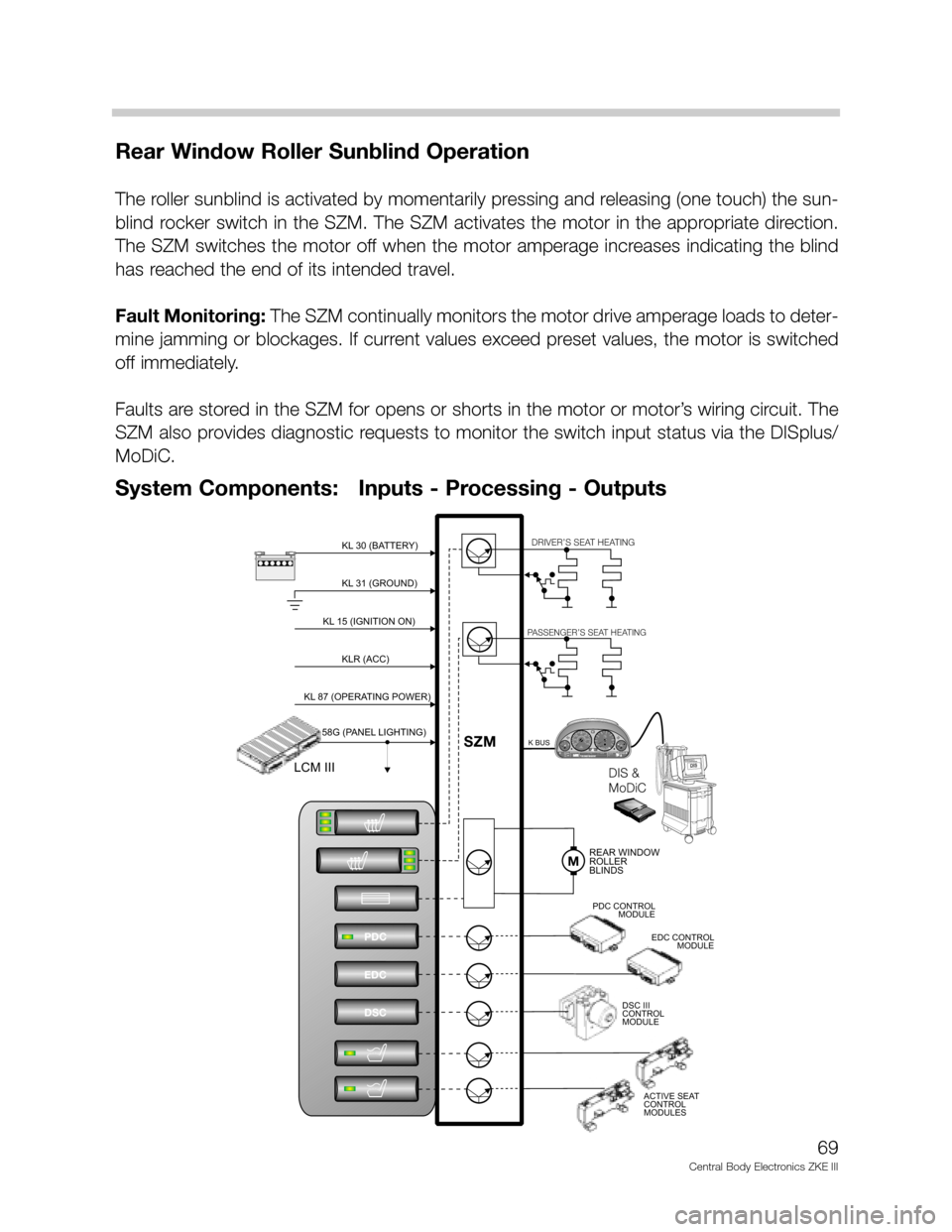
Rear Window Roller Sunblind Operation
The roller sunblind is activated by momentarily pressing and releasing (one touch) the sun-
blind rocker switch in the SZM. The SZM activates the motor in the appropriate direction.
The SZM switches the motor off when the motor amperage increases indicating the blind
has reached the end of its intended travel.
Fault Monitoring: The SZM continually monitors the motor drive amperage loads to deter-
mine jamming or blockages. If current values exceed preset values, the motor is switched
off immediately.
Faults are stored in the SZM for opens or shorts in the motor or motor’s wiring circuit. The
SZM also provides diagnostic requests to monitor the switch input status via the DISplus/
MoDiC.
69
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
KL 31 (GROUND)KL 31 (GROUND)
DIS
DIS
BMWDIS
B
M
WD
I
S
BMWDIS
BMW
DIS
D
ia
g
n
o
s
e
-
a
n
d
In
fo
r
m
a
ti
o
n
S
y
s
t
e
mDIS &
MoDiCDIS &
MoDiC
M
o
Di
C
0½
CHECK
ENGINE
CHECK
ENGINEOIL SERVICEOIL SERVICEINSPECTIONINSPECTIONP
1/min
x1000km/hELECTRONICMPH1
2020404060608080100180160140 1201002001202201402400234
5
6
7!!ABS20 DIGIT READOUT20 DIGIT READOUT
123456
prnd432
m
prnd432
m
122.4 +72.0 fo
+72.0 fomiles0
10
15 20 40
KL 30 (BATTERY)KL 30 (BATTERY)-+
KL 15 (IGNITION ON)KL 15 (IGNITION ON)
KLR (ACC)KLR (ACC)
KL 87 (OPERATING POWER)KL 87 (OPERATING POWER)
58G (PANEL LIGHTING)58G (PANEL LIGHTING)
LCM IIILCM III
PDC
EDC
DSC
MREAR WINDOW
ROLLER
BLINDSREAR WINDOW
ROLLER
BLINDS
DRIVER’S SEAT HEATINGDRIVER’S SEAT HEATING
PASSENGER’S SEAT HEATINGPASSENGER’S SEAT HEATING
K BUSK BUS
PDC CONTROL
MODULEPDC CONTROL
MODULE
EDC CONTROL
MODULEEDC CONTROL
MODULE
SZMSZM
DSC III
CONTROL
MODULEDSC III
CONTROL
MODULE
ACTIVE SEAT
CONTROL
MODULESACTIVE SEAT
CONTROL
MODULES
System Components: Inputs - Processing - Outputs
Page 79 of 80

Review Questions
1. List the functions directly controlled by the GM III._______________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
2. How does the GM III communicate with other control modules?__________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
3. What effect does road speed have on the wiper system? What effect does it have on
an AIC equipped vehicle? Where does the road speed come from?_______________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
4. How does the GM III recognize the key position from the drivers door?____________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
5. Describe the procedure used by the GM III to recognize an FZV key. Can the GM
differentiate between different keys? How many can it recognize?________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
6. What “convenience” features are available from the FZV key?____________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
7. Describe what happens when the GM receives the crash signal from the MRS.
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
8. Why does the SHD (sunroof) module require initialization but the windows do not?
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
79
Central Body Electronics ZKE III