2001 SUZUKI GRAND VITARA engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 166 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-5
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
After making sure that engine is cold, relief fuel pressure as fol-
lows.
1) Place transmission gear shift lever in “Neutral” (shift selector
lever to “P” range for A/T vehicle), set parking brake, and
block drive wheels.
2) Remove fuel pump relay (1) from its connector.
3) Remove fuel filler cap to release fuel vapor pressure in fuel
tank and then reinstall it.
4) Start engine and run it till it stops for lack of fuel. Repeat
cranking engine 2 – 3 times of about 3 seconds each time to
dissipate fuel pressure in lines. Fuel connections are now
safe for servicing.
5) Upon completion of servicing, install fuel pump relay to relay
box.
Fuel Leakage Check Procedure
After performing any service on fuel system, check to make sure
that there are no fuel leakages as follows.
1) Turn ON ignition switch for 3 seconds (to operate fuel pump)
and then turn it OFF.
Repeat this (ON and OFF) 3 or 4 times and apply fuel pres-
sure to fuel line (till fuel pressure is felt by hand placed on
fuel return hose).
2) In this state, check to see that there are no fuel leakages
from any part of fuel system. CAUTION:
This work must not be done when engine is hot. If done
so, it may cause adverse effect to catalyst.
[A] : Left hand steering vehicle
[B] : Right hand steering vehicle
2. Fuse box
Page 167 of 656
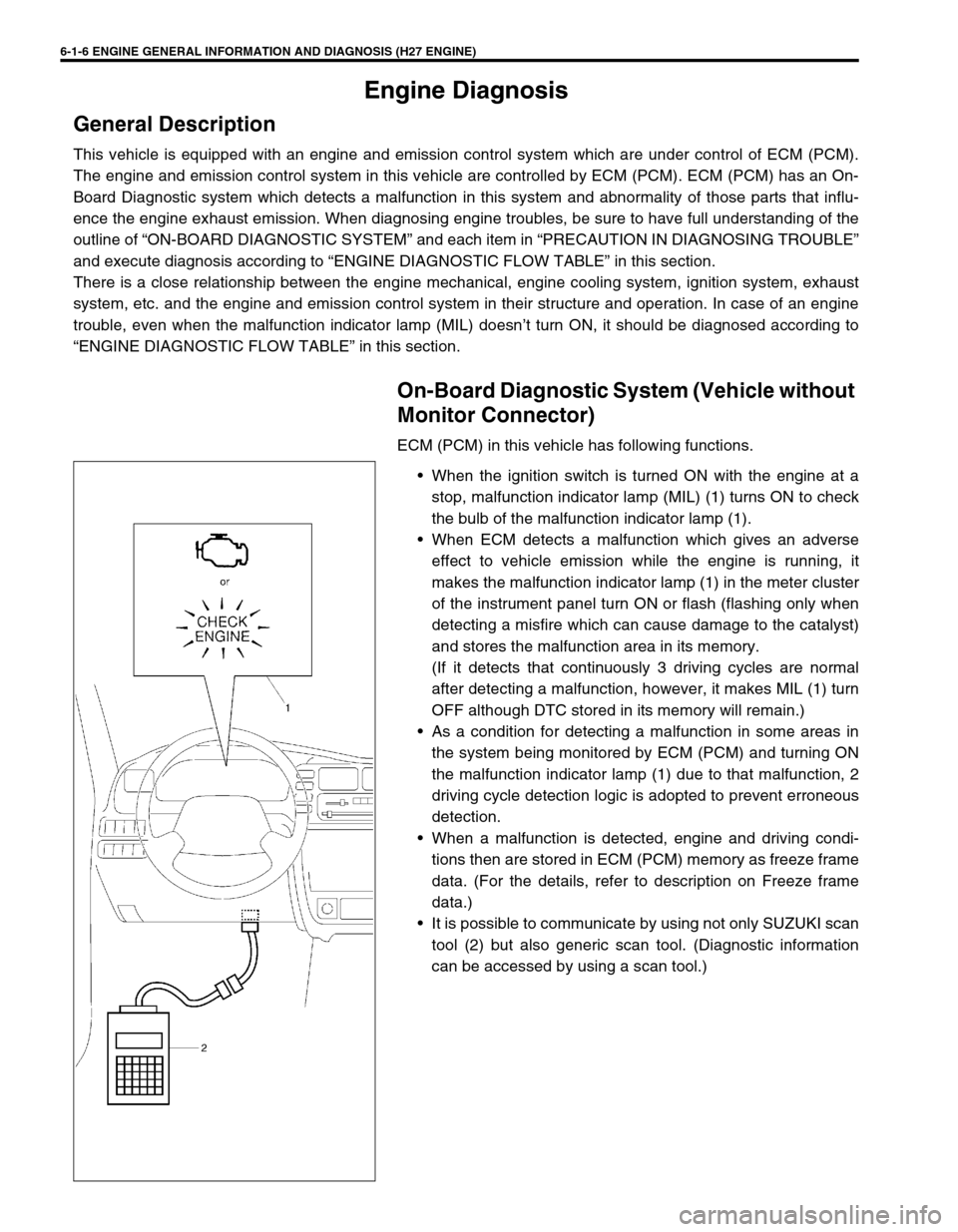
6-1-6 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Engine Diagnosis
General Description
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ECM (PCM).
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ECM (PCM). ECM (PCM) has an On-
Board Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this system and abnormality of those parts that influ-
ence the engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the
outline of “ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM” and each item in “PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE”
and execute diagnosis according to “ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
There is a close relationship between the engine mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system, exhaust
system, etc. and the engine and emission control system in their structure and operation. In case of an engine
trouble, even when the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed according to
“ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle without
Monitor Connector)
ECM (PCM) in this vehicle has following functions.
When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a
stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns ON to check
the bulb of the malfunction indicator lamp (1).
When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an adverse
effect to vehicle emission while the engine is running, it
makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in the meter cluster
of the instrument panel turn ON or flash (flashing only when
detecting a misfire which can cause damage to the catalyst)
and stores the malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that continuously 3 driving cycles are normal
after detecting a malfunction, however, it makes MIL (1) turn
OFF although DTC stored in its memory will remain.)
As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in
the system being monitored by ECM (PCM) and turning ON
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to that malfunction, 2
driving cycle detection logic is adopted to prevent erroneous
detection.
When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving condi-
tions then are stored in ECM (PCM) memory as freeze frame
data. (For the details, refer to description on Freeze frame
data.)
It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan
tool (2) but also generic scan tool. (Diagnostic information
can be accessed by using a scan tool.)
Page 168 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-7
WARM-UP CYCLE
A warm-up cycle means sufficient vehicle operation such that the
coolant temperature has risen by at least 22°C (40°F) from
engine starting and reaches a minimum temperature of 70 °C
(160 °F).
DRIVING CYCLE
A “Driving Cycle” consists of engine startup, driving mode where
a malfunction would be detected if present and engine shutoff.
2 DRIVING CYCLE DETECTION LOGIC
The malfunction detected in the first driving cycle is stored in
ECM (PCM) memory (in the form of pending DTC) but the mal-
function indicator lamp does not light at this time. It lights up at the
second detection of same malfunction also in the next driving
cycle.
PENDING DTC
Pending DTC means a DTC detected and stored temporarily at 1
driving cycle of the DTC which is detected in the 2 driving cycle
detection logic.
FREEZE FRAME DATA
ECM (PCM) stores the engine and driving conditions (in the form
of data as shown in the figure) at the moment of the detection of a
malfunction in its memory. This data is called “Freeze frame data”.
Therefore, it is possible to know engine and driving conditions
(e.g., whether the engine was warm or not, where the vehicle was
running or stopped, where air/fuel mixture was lean or rich) when
a malfunction was detected by checking the freeze frame data.
Also, ECM (PCM) has a function to store each freeze frame data
for three different malfunctions in the order as the malfunction is
detected. Utilizing this function, it is possible to know the order of
malfunctions that have been detected. Its use is helpful when
rechecking or diagnosing a trouble.
1. 1st, 2nd or 3rd in parentheses here represents which position in the
order the malfunction is detected.
1. TROUBLE CODE
2. COOLANT TEMP.
3. ENGINE SPEED
4. SHORT FT B1
5. SHORT FT B2
6. LONG FT B1
7. LONG FT B2
8. CALC LOAD
9. FUEL SYSTEM B1
10. FUEL SYSTEM B2
11. MAP
12. VEHICLE SPEEDP0100
80 C
750 RPM
– 0.8
– 0.1
– 1.3
– 1.5
20.5
CLOSED
CLOSED
30.6 kPa
0 km/h(1st)
1
Page 169 of 656

6-1-8 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Priority of Freeze Frame Data
ECM (PCM) has 4 frames where the freeze frame data can be stored. The first frame stores the freeze frame
data of the malfunction which was detected first. However, the freeze frame data stored in this frame is updated
according to the priority described below. (If malfunction as described in the upper square “1” below is detected
while the freeze frame data in the lower square “2” has been stored, the freeze frame data “2” will be updated by
the freeze frame data “1”.)
In the 2nd through the 4th frames, the freeze frame data of each malfunction is stored in the order as the mal-
function is detected. These data are not updated regardless of the priority.
Shown in the table below are examples of how freeze frame data are stored when two or more malfunctions are
detected.
Freeze Frame Data Clearance
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as clearance of DTC.
DATA LINK CONNECTOR (DLC)
DLC (1) is in compliance with SAEJ1962 in its installation posi-
tion, the shape of connector and pin assignment.
K line of ISO 9141 is used for SUZUKI scan tool or generic scan
tool to communicate with ECM (PCM), ABS control module and
Air bag SDM. SUZUKI serial data line is used for SUZUKI scan
tool to communicate with Immobilizer control module. PRIORITY FREEZE FRAME DATA IN FRAME 1
1Freeze frame data at initial detection of malfunction among misfire detected (P0300-P0306), fuel
system too lean (P0171, P0174) and fuel system too rich (P0172, P0175)
2 Freeze frame data when a malfunction other than those in “1” above is detected
FRAME 1 FRAME 2 FRAME 3 FRAME 4
FREEZE FRAME
DATA to be updated1st FREEZE
FRAME DATA2nd FREEZE
FRAME DATA3rd FREEZE
FRAME DATA
No malfunction No freeze frame dataNo freeze frame
dataNo freeze frame
dataNo freeze frame
data
MALFUNCTION
DETECTED ORDER
1P0110 (IAT)
detectedData at P0110
detectionData at P0110
detectionNo freeze frame
dataNo freeze frame
data
2P0171 (Fuel sys-
tem) detectedData at P0171
detectionData at P0110
detectionData at P0171
detectionNo freeze frame
data
3P0300 (Misfire)
detectedData at P0171
detectionData at P0110
detectionData at P0171
detectionData at P0300
detection
4P0301 (Misfire)
detectedData at P0171
detectionData at P0110
detectionData at P0171
detectionData at P0300
detection
2. B+
3. SUZUKI Serial data line
4. K line of ISO 9141
5. Body ground
6. ECM ground
Page 170 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-9
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle with
Monitor Connector)
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area including the
following parts when the ignition switch is ON and the engine is
running, and indicates the result by turning on of flashing mal-
function indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor (if equipped)
•ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• IAT sensor
• CMP sensor
•MAF sensor
• Knock sensor
• EGR (if equipped)
•VSS
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) light when the ignition switch
is turned ON (but the engine at stop) with the diagnosis
switch terminal ungrounded regardless of the condition of
Engine and Emission control system. This is only to check
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) bulb and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is
free from any trouble after the engine start (while engine is
running), malfunction indicator lamp (1) turns OFF.
• When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in the
above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp (1) turn ON
while the engine is running to warn the driver of such occur-
rence of trouble and at the same time it stores the trouble
area in ECM back-up memory. (The memory is kept as it is
even if the trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to ECM is
shut off for specified time.)
ECM also indicates trouble area in memory by means of
flashing of malfunction indicator lamp (1) at the time of
inspection. (i.e. when diagnosis switch terminal (2) is con-
nected to ground terminal (3) with a service wire and ignition
switch is turned ON.)
NOTE:
When a trouble occurs in the above areas and disappears
soon while the diagnosis switch terminal is ungrounded
and the engine is running, malfunction indicator lamp (1)
lights and remains ON as the trouble exists but it turns
OFF when the normal condition is restored.
Page 171 of 656

6-1-10 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
DATA LINK CONNECTOR (DLC)
DLC (1) is in compliance with SAEJ1962 in its installation posi-
tion, the shape of connector and pin assignment.
K line of ISO 9141 is used for SUZUKI scan tool to communicate
with ECM (PCM), ABS control module and air bag SDM. SUZUKI
serial data line is used for SUZUKI scan tool to communicate with
Immobilizer control module.
Precaution in Diagnosing Trouble
• Don’t disconnect couplers from ECM (PCM), battery cable from battery, ECM (PCM) ground wire harness
from engine or main fuse before confirming diagnostic information (DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in
ECM (PCM) memory. Such disconnection will erase memorized information in ECM (PCM) memory.
• Diagnostic information stored in ECM (PCM) memory can be cleared as well as checked by using SUZUKI
scan tool or generic scan tool. Before using scan tool, read its Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to
have good understanding as to what functions are available and how to use it.
• Priorities for diagnosing troubles (Vehicle without monitor connector)
If two or more diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are stored, proceed to the flow table of the DTC which was
detected earliest in the order and follow the instruction in that table.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot diagnostic trouble codes according to the following priorities.
– Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) other than DTC P0171/P0172/P0174/P0175 (Fuel system too lean/too
rich), DTC P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304/P0305/P0306 (Misfire detected) and DTC P0400 (EGR
flow malfunction)
– DTC P0171/P0172/P0174/P0175 (Fuel system too lean/too rich) and DTC P0400 (EGR flow malfunction)
– DTC P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304/P0305/P0306 (Misfire detected)
• Be sure to read “PRECAUTIONS FOR ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT SERVICE” in Section 0A before inspection
and observe what is written there.
• ECM (PCM) Replacement
When substituting a known-good ECM (PCM), check for following conditions. Neglecting this check may
cause damage to a known-good ECM (PCM).
– Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as specified respectively.
– MAF sensor, MAP sensor and TP sensor are in good condition and none of power circuits of these sen-
sors is shorted to ground.
2. B+
3. SUZUKI Serial data line
4. K line of ISO 9141
5. Body ground
6. ECM ground
Page 172 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-11
Engine Diagnostic Flow Table
Refer to following pages for the detail of each step.
Step Action Yes No
1 Customer Complaint Analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis.
Was customer complaint analysis performed?Go to Step 2. Perform customer com-
plaint analysis.
2 DTC(s)/Freeze Frame Data Check
1) Check DTC(s)/Freeze frame data.
Is there any malfunction DTC(s)?Record DTC(s)/Freeze
frame data.
Clear DTC(s).
Go to Step 3.Go to Step 4.
3 Visual Inspection
1) Perform visual inspection.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part.
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 5.
4 Visual Inspection
1) Perform visual inspection.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part.
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 8.
5 Trouble Symptom Confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom based on cus-
tomer complaint analysis, DTC(s)/freeze
frame data in Step 1.
Is trouble symptom identified?Go to Step 6. Go to Step 7.
6 DTC/Freeze Frame Data Recheck
1) Recheck DTC/freeze frame data.
Is there any malfunction DTC(s)?Go to Step 9. Go to Step 8.
7 DTC/Freeze Frame Data Recheck
1) Recheck DTC/freeze frame data.
Is there any malfunction DTC(s)?Go to Step 9. Go to Step 10.
8 Engine Basic Inspection
1) Check and repair according to “ENGINE
BASIC INSPECTION FLOW TABLE” and
“ENGINE DIAGNOSIS TABLE” in this sec-
tion.
Are check and repair complete?Go to Step 11. Check and repair mal-
function part(s).
Go to Step 11.
9 DTC Trouble Shooting
1) Check and repair according to applicable
“DTC Diag. flow table” in this section.
Are check and repair complete?Go to Step 11. Check and repair mal-
function part(s).
Go to Step 11.
10 Intermittent Problems Check
1) Check for intermittent problems referring to
“Check for Intermittent Problem” in “GEN-
ERAL INFORMATION” section.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part.
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 11.
11 Final Confirmation Test
1) Clear DTC if any.
2) Perform final confirmation test referring to
“DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE” in
this section.
Is there any problem symptom, malfunction
DTC or abnormal condition?Go to Step 6. END.
Page 173 of 656

6-1-12 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
STEP 1. CUSTOMER COMPLAINT ANALYSIS
Record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this
purpose, use of such an inspection form will facilitate collecting information to the point required for proper anal-
ysis and diagnosis.
NOTE:
The above form is a standard sample. It should be modified according to conditions characteristic of
each market.