2001 SUZUKI GRAND VITARA Stop lamp
[x] Cancel search: Stop lampPage 128 of 656

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E2-3
General Description
Components/Parts Location
The ABS (Antilock Brake System) controls the fluid pressure applied to the wheel cylinder of each brake from
the master cylinder so that each wheel is not locked even when hard braking is applied.
This ABS has also the following function.
While braking is applied, but before ABS control becomes effective, braking force is distributed between the
front and rear so as to prevent the rear wheels from being locked too early for better stability of the vehicle.The
main component parts of this ABS include the following parts in addition to those of the conventional brake sys-
tem.
Wheel speed sensor which senses revolution speed of each wheel and outputs its signal.
ABS warning lamp which lights to inform abnormality when system fails to operate properly.
ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly is incorporated ABS control module, ABS hydraulic unit (actua-
tor assembly), fail-safe relay and pump motor relay.
–ABS control module which sends operation signal to ABS hydraulic unit to control fluid pressure applied to
each wheel cylinder based on signal from each wheel speed sensor so as to prevent wheel from locking.
–ABS hydraulic unit which operates according to signal from ABS control module to control fluid pressure
applied to wheel cylinder of each 4 wheels.
–Fail-safe relay (solenoid valve) relay which supplies power to solenoid valve in ABS hydraulic unit and
pump motor relay.
–Pump motor relay which supplies power to pump motor in ABS hydraulic unit.
G sensor which detects body deceleration speed. (For 4WD model only)
This ABS is equipped with Electronic Brake force Distribution (EBD) system that controls a fluid pressure of rear
wheels to best condition, which is the same function as that of proportioning valve, by the signal from wheel sen-
sor independently of change of load due to load capacity and so on. And if the EBD system fails to operate prop-
erly, the brake warning lamp lights to inform abnormality.
1. Wheel speed sensor (Right-front) 6. Wheel speed sensor (Left-rear) 11. G sensor (For 4WD model only)
2. Stop lamp switch 7. Ground 12. Wheel speed sensor rotor (ring)
3. Data link connector 8. Diagnosis connector (Black connector) 13. 4WD switch (For 4WD model only)
4.“ABS” warning lamp 9. Wheel speed sensor (Left-front) 14. EBD warning lamp (Brake warning lamp)
5. Wheel speed sensor (Right-rear) 10. ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly
(with ABS pump motor relay and fail-safe relay)
NOTE:
Above figure shows left-hand steering vehicle.
For right-hand steering vehicle, parts with (*) are installed at the side of symmetry.
Page 139 of 656

5E2-14 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
System Circuit
1. Battery 11. ABS fail-safe transistor (Solenoid valve transistor) 21. To ECM and SDM (if equipped)
2. Main fuses 12. ABS pump motor transistor 22. Stop lamp
3. Ignition switch 13. Pump motor 23. Stop lamp switch
4. Circuit fuses 14. Solenoid valves 24. G sensor (For 4WD vehicle only)
5. Combination meter 15. Diagnosis monitor coupler 25. 4WD lamp (For 4WD vehicle only)
6. ABS warning lamp 16. Right-rear wheel speed sensor 26. ECM (PCM) (For 4WD vehicle only)
7. Brake warning lamp (“EBD” warning lamp) 17. Left-rear wheel speed sensor 27. 4WD switch (For 4WD vehicle only)
8. Warning lamp driver module (for ABS) 18. Right-front wheel speed sensor 28. ECM (PCM)
9. ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly 19. Left-front wheel speed sensor
10. Terminal arrangement of connector E136 for
ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly20. Data link connector
TERMINAL CIRCUIT TERMINAL CIRCUIT
E1361 Idle up signal
E13614 ABS warning lamp
2 Stop lamp switch 15 Left-front wheel speed sensor (+)
3 Right-front wheel speed sensor (+) 16 Left-front wheel speed sensor (–)
4 Right-front wheel speed sensor (–) 17 4WD switch
5–18 Ignition switch
6 Right-rear wheel speed sensor (–) 19 Left-rear wheel speed sensor (+)
7 Right-rear wheel speed sensor (+) 20 Left-rear wheel speed sensor (–)
8–21 Data link connector
9–22 Ground (for ABS pump motor)
10 Brake warning lamp (EBD warning lamp) 23 ABS pump motor relay
11 G sensor (For 4WD vehicle only) 24 Ground (for ABS control module)
12 Diagnosis switch terminal 25 ABS fail-safe relay
13 Ground (For G sensor) (For 4WD vehicle only)
Page 145 of 656

5E2-20 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
DTC C1015 (DTC 15) – G Sensor Circuit and 4WD Lamp Circuit
DESCRIPTION
G sensor
While a vehicle is at stop or running, if the potential difference between the sensor signal terminal “E136-11” and
the sensor ground terminal “E136-13” is not within the specified voltage value, or if the signal voltage while at a
stop does not vary from that while running, this DTC is set.
Therefore, this DTC may be set when a vehicle is lifted up and its wheel(s) is turned. In such case, clear the
DTC and check again.
When G sensor is installed to 2WD vehicle, this DTC is set.
4WD lamp
When 4WD lamp circuit open or shorted, this DTC is set.
1. Ignition switch 3. ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly 5. 4WD lamp 7. 4WD switch
2. G sensor 4. ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector 6. ECM (PCM)
Page 157 of 656

5E2-32 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
3) Using special tool, loosen flare nuts (1) and disconnect brake
pipes (2) from ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly
(3).
Special tool
09950-78220
4) Remove three bolts and take out ABS hydraulic unit/control
module assembly (1) from bracket using flat end rod or the
like (2).
INSTALLATION
1) Install hydraulic unit/control module assembly by reversing
removal procedure.
Tightening torque
Brake pipe flare nut (a) :
16 N·m (1.6 kg-m, 11.5 lb-ft)
ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly bolt (b) :
9 N·m (0.9 kg-m, 6.5 lb-ft)
Bracket bolt (c) : 10 N·m (1.0 kg-m, 6.5 lb-ft)
2) Bleed air from brake system referring to “BRAKES” section.
3) Check each installed part for fluid leakage and perform “ABS
HYDRAULIC UNIT OPERATION CHECK” in this section. NOTE:
Put bleeder plug cap onto pipe to prevent fluid from spill-
ing. Do not allow brake fluid to get on painted surfaces.
2
1
3
CAUTION:
Do not give an impact to hydraulic unit.
Use care not to allow dust to enter hydraulic unit.
Do not place hydraulic unit on its side or upside down.
Handling it in inappropriate way will affect its original
performance.
NOTE:
For new ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly, if
“ABS HYDRAULIC UNIT OPERATION CHECK” procedure
has not been performed, “ABS” warning lamp may flash
when ignition switch is turned ON position.
Accordingly preform “ABS HYDRAULIC UNIT OPERA-
TION CHECK” to stop flashing of ABS warning lamp.
(b) (b) (a)
(c) (c)
Page 162 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-1
6-1
SECTION 6-1
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND
DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
CONTENTS
General Information ...................................... 6-1-3
Statement of Cleanliness and Care ............ 6-1-3
General Information on Engine Service ...... 6-1-3
Precaution on Fuel System Service ............ 6-1-4
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure .................. 6-1-5
Fuel Leakage Check Procedure .................. 6-1-5
Engine Diagnosis .......................................... 6-1-6
General Description .................................... 6-1-6
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle
without Monitor Connector) ......................... 6-1-6
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle with
Monitor Connector) ..................................... 6-1-9
Precaution in Diagnosing Trouble ............. 6-1-10
Engine Diagnostic Flow Table ................... 6-1-11
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check... 6-1-16
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check ..... 6-1-16
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Clearance 6-1-17
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Table ...... 6-1-18For A/T system (Refer to Section 7B1
for diagnosis)......................................... 6-1-21
For immobilizer control system (Refer to
Section 8G for diagnosis) ...................... 6-1-22
Fail-Safe Table.......................................... 6-1-23
Scan Tool Data ......................................... 6-1-24
Scan tool data definitions ...................... 6-1-27
Engine Diagnosis Table ............................ 6-1-31
Inspection of PCM (ECM) and its Circuits. 6-1-36
Table A-1 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Circuit Check – Lamp Does Not Come
“ON” or Dims at Ignition Switch ON
(But Engine at Stop).................................. 6-1-43
Table A-2 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Circuit Check – Lamp Remains “ON” after
Engine Starts ............................................ 6-1-44
Table A-3 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Check – MIL Flashes at Ignition Switch
ON (Vehicle with Monitor Connector) ....... 6-1-45 WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
NOTE:
Whether following systems (parts) are used in the particular vehicle or not depends on specifications.
Be sure to bear this in mind when performing service work.
Monitor connector
CKP sensor
MAP sensor
EGR valve
Heated oxygen sensor or CO adjusting resistor
Three way catalytic converter, Warm-up three way catalytic converter
Page 165 of 656

6-1-4 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
When disconnecting couplers, don’t pull wire harness but
make sure to hold coupler itself. With lock type coupler, be
sure to unlock before disconnection. Attempt to disconnect
coupler without unlocking may result in damage to coupler.
When connecting lock type coupler, insert it till clicking
sound is heard and connect it securely.
Precaution on Fuel System Service
Work must be done with no smoking, in a well-ventilated area and away from any open flames.
As fuel feed line (between fuel pump and fuel pressure regulator) is still under high fuel pressure even after
engine was stopped, loosening or disconnecting fuel feed line directly may cause dangerous spout of fuel to
occur where loosened or disconnected. Before loosening or disconnecting fuel feed line, make sure to
release fuel pressure according to “FUEL PRESSURE RELIEF PROCEDURE” in this section.
A small amount of fuel may be released after the fuel line is disconnected.
In order to reduce the chance of personal injury, cover the fitting to be disconnected with a shop cloth. Put
that cloth in an approved container when disconnection is completed.
Never run engine with fuel pump relay disconnected when engine and exhaust system are hot.
Fuel or fuel vapor hose connection varies with each type of
pipe. When reconnecting fuel or fuel vapor hose, be sure to
connect and clamp each hose correctly referring to left fig-
ure.
After connecting, make sure that the hose has no twist or
kink.
When installing fuel union bolt gasket, always use new gas-
ket and tighten union bolt to specified torque according to
“TIGHTENING TORQUE SPECIFICATION” in Section 6C.
When installing injector, fuel feed pipe or fuel pressure regu-
lator, lubricate its O-ring with gasoline.
When connecting fuel pipe flare nut, first tighten flare nut by
hand and then tighten it to specified torque.
[A] : With short pipe, fit hose as far as it reaches pipe joint as shown.
[B] : With following type pipe, fit hose as far as its peripheral projection as shown.
[C] : With bent pipe, fit hose as far as its bent part as shown or till pipe is about 20
to 30 mm (0.79 – 1.18 in.) into the hose.
[D] : With straight pipe, fit hose till pipe is about 20 to 30 mm (0.79 – 1.18 in.) into
the hose.
1. Hose
2. Pipe
3. Clamp
“a” : Clamp securely at a position 3 to 7 mm (0.12 – 0.27 in.) from hose end.
“b” : 20 to 30 mm (0.79 – 1.18 in.)
Page 167 of 656
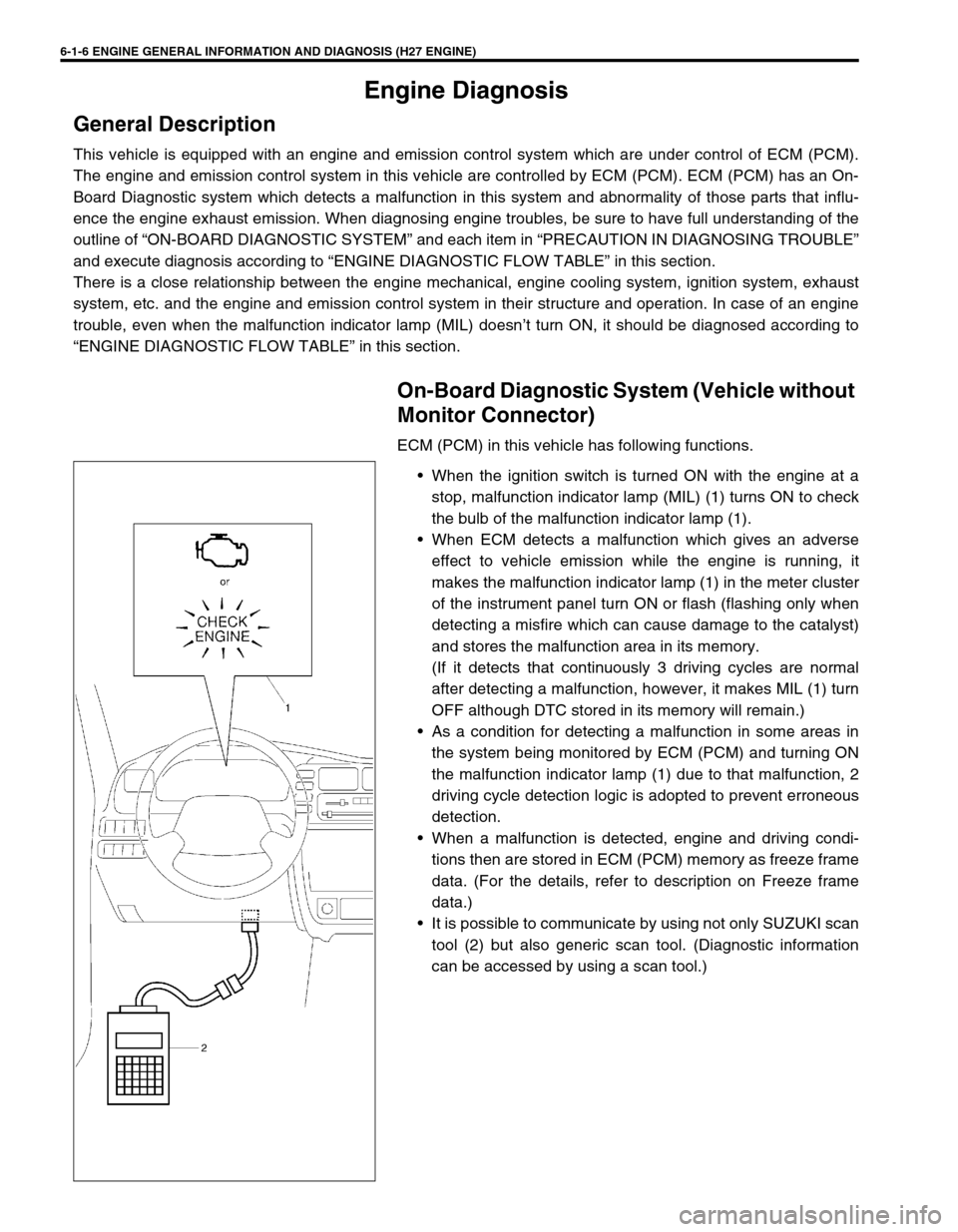
6-1-6 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Engine Diagnosis
General Description
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ECM (PCM).
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ECM (PCM). ECM (PCM) has an On-
Board Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this system and abnormality of those parts that influ-
ence the engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the
outline of “ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM” and each item in “PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE”
and execute diagnosis according to “ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
There is a close relationship between the engine mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system, exhaust
system, etc. and the engine and emission control system in their structure and operation. In case of an engine
trouble, even when the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed according to
“ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle without
Monitor Connector)
ECM (PCM) in this vehicle has following functions.
When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a
stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns ON to check
the bulb of the malfunction indicator lamp (1).
When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an adverse
effect to vehicle emission while the engine is running, it
makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in the meter cluster
of the instrument panel turn ON or flash (flashing only when
detecting a misfire which can cause damage to the catalyst)
and stores the malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that continuously 3 driving cycles are normal
after detecting a malfunction, however, it makes MIL (1) turn
OFF although DTC stored in its memory will remain.)
As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in
the system being monitored by ECM (PCM) and turning ON
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to that malfunction, 2
driving cycle detection logic is adopted to prevent erroneous
detection.
When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving condi-
tions then are stored in ECM (PCM) memory as freeze frame
data. (For the details, refer to description on Freeze frame
data.)
It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan
tool (2) but also generic scan tool. (Diagnostic information
can be accessed by using a scan tool.)
Page 168 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-7
WARM-UP CYCLE
A warm-up cycle means sufficient vehicle operation such that the
coolant temperature has risen by at least 22°C (40°F) from
engine starting and reaches a minimum temperature of 70 °C
(160 °F).
DRIVING CYCLE
A “Driving Cycle” consists of engine startup, driving mode where
a malfunction would be detected if present and engine shutoff.
2 DRIVING CYCLE DETECTION LOGIC
The malfunction detected in the first driving cycle is stored in
ECM (PCM) memory (in the form of pending DTC) but the mal-
function indicator lamp does not light at this time. It lights up at the
second detection of same malfunction also in the next driving
cycle.
PENDING DTC
Pending DTC means a DTC detected and stored temporarily at 1
driving cycle of the DTC which is detected in the 2 driving cycle
detection logic.
FREEZE FRAME DATA
ECM (PCM) stores the engine and driving conditions (in the form
of data as shown in the figure) at the moment of the detection of a
malfunction in its memory. This data is called “Freeze frame data”.
Therefore, it is possible to know engine and driving conditions
(e.g., whether the engine was warm or not, where the vehicle was
running or stopped, where air/fuel mixture was lean or rich) when
a malfunction was detected by checking the freeze frame data.
Also, ECM (PCM) has a function to store each freeze frame data
for three different malfunctions in the order as the malfunction is
detected. Utilizing this function, it is possible to know the order of
malfunctions that have been detected. Its use is helpful when
rechecking or diagnosing a trouble.
1. 1st, 2nd or 3rd in parentheses here represents which position in the
order the malfunction is detected.
1. TROUBLE CODE
2. COOLANT TEMP.
3. ENGINE SPEED
4. SHORT FT B1
5. SHORT FT B2
6. LONG FT B1
7. LONG FT B2
8. CALC LOAD
9. FUEL SYSTEM B1
10. FUEL SYSTEM B2
11. MAP
12. VEHICLE SPEEDP0100
80 C
750 RPM
– 0.8
– 0.1
– 1.3
– 1.5
20.5
CLOSED
CLOSED
30.6 kPa
0 km/h(1st)
1