2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 1426 of 2321
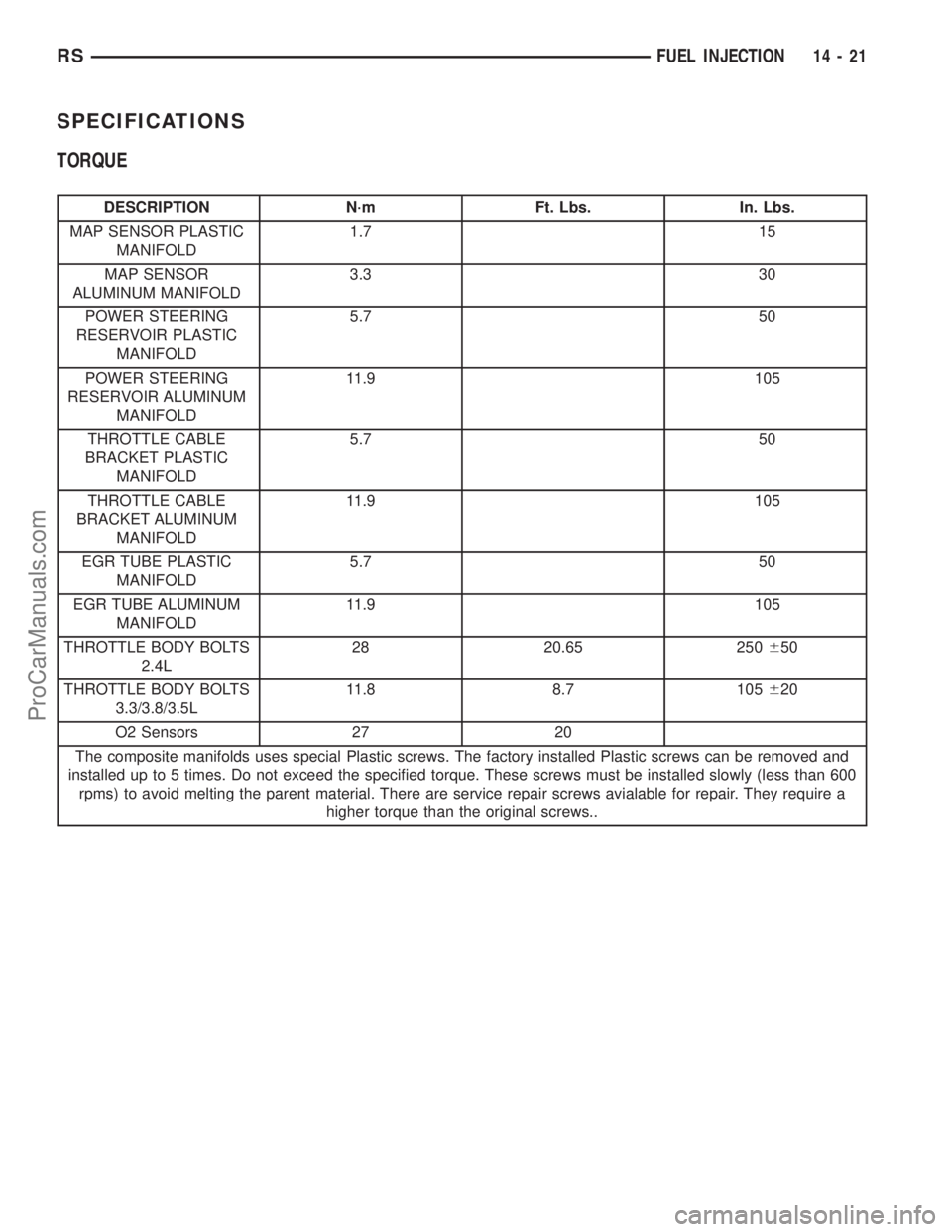
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
MAP SENSOR PLASTIC
MANIFOLD1.7 15
MAP SENSOR
ALUMINUM MANIFOLD3.3 30
POWER STEERING
RESERVOIR PLASTIC
MANIFOLD5.7 50
POWER STEERING
RESERVOIR ALUMINUM
MANIFOLD11.9 105
THROTTLE CABLE
BRACKET PLASTIC
MANIFOLD5.7 50
THROTTLE CABLE
BRACKET ALUMINUM
MANIFOLD11.9 105
EGR TUBE PLASTIC
MANIFOLD5.7 50
EGR TUBE ALUMINUM
MANIFOLD11.9 105
THROTTLE BODY BOLTS
2.4L28 20.65 250650
THROTTLE BODY BOLTS
3.3/3.8/3.5L11.8 8.7 105620
O2 Sensors 27 20
The composite manifolds uses special Plastic screws. The factory installed Plastic screws can be removed and
installed up to 5 times. Do not exceed the specified torque. These screws must be installed slowly (less than 600
rpms) to avoid melting the parent material. There are service repair screws avialable for repair. They require a
higher torque than the original screws..
RSFUEL INJECTION14-21
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1447 of 2321

FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The fuel transfer pump (fuel lift pump) is located
under the vehicle in front of the rear axle assembly
(Fig. 5). The 12±volt electric vane-type pump is oper-
ated and controlled by the Engine Control Module
(ECM) .
OPERATION
The purpose of the fuel transfer pump is to supply
(transfer) a low-pressure fuel source:fromthe fuel
tank,throughthe fuel filter/water separator andto
the fuel injection pump. Here, the low-pressure is
raised to a high-pressure by the fuel injection pump
for operation of the high-pressure fuel injectors.The fuel transfer pump is controlled by the Engine
Control Module(ECM). The ECM turns the fuel
transfer pump on for 30 seconds when the ignition
ket is turned ªONº.
With the ignition ªONº and fuel tranfer pump run-
ning, the low-pressure fuel pressure should be 13-17 psi.
FUEL INJECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
A radial-piston pump is used as the high pressure
pump for fuel pressure generation (Fig. 6).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL)
(3) Remove air cleaner housing assembly.
(4) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(5) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(6) Support engine and remove right engine mount
assembly.
(7) Remove outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Using special tool VM.1055, remove injection
pump sprocket retaining nut (Fig. 7).
Fig. 5 FUEL TRANSFER(LIFT) PUMP LOCATION
1 - LIFT PUMP RETAINING BOLTS
2 - LIFT PUMP
3 - FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR HOUSING
4 - FUEL HEATER
5 - CHECK BALL
6 - O-RING
7 - FLOW DIVERTER
8 - FUEL FILTER
9 - O-RING
10 - FUEL FILTER BOWL ASSEMBLY
Fig. 6 FUEL INJECTION PUMP
1 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
2 - INJECTION PUMP PRESSURE SOLENOID
14a - 6 FUEL DELIVERYRG
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1450 of 2321

(12) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(13) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(14) Install air cleaner housing assembly.
(15) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
INSTALLATION).
(16) Connect negative battery cable.
WATER IN FUEL SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The WIF sensor is located in the bowl assembly of
the fuel filter/water separator.
OPERATION
The sensor sends an input to the Engine Control
Module (ECM) when it senses water in the fuel filter/
water separator. As the water level in the filter/sep-
arator increases, the resistance across the WIF
sensor decreases. This decrease in resistance is sent
as a signal to the ECM and compared to a high
water standard value. Once the value reaches 30 to
40 kilohms, the ECM will activate the water-in-fuel
warning lamp through CCD bus circuits. This all
takes place when the ignition key is initially put in
the ON position. The ECM continues to monitor the
input at the end of the intake manifold air heater
post-heat cycle.
RGFUEL DELIVERY14a-9
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1458 of 2321

STEERING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STEERING
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................1
POWER STEERING SYSTEM FLOW AND
PRESSURE TEST........................1STEERING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHARTS....3
SPECIFICATIONS.........................9
SPECIAL TOOLS..........................9
COLUMN...............................10
GEAR.................................17
PUMP.................................24
STEERING
DESCRIPTION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
This vehicle comes with power steering as stan-
dard equipment and it is the only steering system
available. The power steering system consists of
these major components:
²POWER STEERING PUMP
²POWER STEERING GEAR
²POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR
²POWER STEERING FLUID SUPPLY HOSE
²POWER STEERING FLUID PRESSURE HOSE
²POWER STEERING FLUID RETURN HOSE
²POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
For information on the first two components, refer
to their respective sections within this service man-
ual group. Information on all other components can
be found in POWER STEERING PUMP.
OPERATION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into linear
(side-to-side) travel through the meshing of the helical
pinion teeth with the rack teeth within the steering
gear. The lateral travel pushes and pulls the tie rods to
change the direction of the vehicle's front wheels.
Power assist steering is provided by a belt driven
rotary type pump. It directs fluid through power
steering fluid hoses to the power steering gear where
it is used to assist the driver's turning effort.
Manual steering control of the vehicle can be main-
tained if power steering assist is lost. However, under
this condition, steering effort is significantly increased.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING
SYSTEM FLOW AND PRESSURE TEST
ALL ENGINES
The following procedure is to be used to test the
operation of the power steering system on this vehi-
cle. This test will provide the flow rate of the power
steering pump along with the maximum relief pres-sure. This test is to be performed any time a power
steering system problem is present to determine if
the power steering pump or power steering gear is
not functioning properly. The following flow and pres-
sure test is performed using the Power Steering Ana-
lyzer Kit, Special Tool 6815 (Fig. 1), hoses, Special
Tools 6905 and 6959, and fittings from adapter kit,
Special Tool 6893.
Assemble hoses on Power Steering Analyzer, Spe-
cial Tool 6815, as shown. Install Pressure Hose, Spe-
cial Tool 6905 (in 6893 kit), in the inlet fitting on
Power Steering Analyzer. Install Pressure Hose, Spe-
cial Tool 6713 (in 6815 kit) on Pressure Hose, Special
Tool 6905. Install Pressure Hose, Special Tool 6959,
in the outlet fitting on Power Steering Analyzer.
Install the following adapters from Adapter Set,
Special Tool 6893 (Fig. 2), on the analyzer hose ends:
Install Adapter Fitting, Special Tool 6844, on Pres-
sure Hose, Special Tool 6713. Install Adapter Fitting,
Special Tool 6826, on Pressure Hose, Special Tool
6959.
Fig. 1 Power Steering Analyzer With Hoses Installed
1 - OUTLET
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6815
3 - INLET
RSSTEERING19-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1459 of 2321

CAUTION: To prevent personal injury, safety gog-
gles should be worn at all times when performing
any test procedures on the power steering pump or
power steering gear.
The following procedure is to be used to test the
operation of the power steering system on the vehi-
cle.
(1) Check belt tension and adjust as necessary.
(2) Disconnect the power steering fluid pressure
hose from the power steering pump (Fig. 3) (Fig. 4).
(3) Connect Adapter Fitting, Special Tool 6844,
attached to pressure hose from inlet (gauge end) ofPower Steering Analyzer to the pressure fitting on
the power steering pump.
(4) Connect vehicle power steering fluid pressure
hose to Adapter Fitting, Special Tool 6826, which
should be already installed in the outlet hose (valve
end) of Power Steering Analyzer.
(5) Completely open valve on Power Steering Ana-
lyzer.
(6) Start engine and let idle long enough to circu-
late power steering fluid through the analyzer and
hoses, until the air is out of the fluid. Shut off
engine.
(7) Check power steering fluid level and add fluid
as necessary. Start engine again and let idle.
(8) Gauge should read below 862 kPa (125 psi). If
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure should be in the range
of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi). The flow meter should
read between 1.3 and 1.9 GPM.
CAUTION: The following test procedure involves
testing maximum pump pressure output and flow
control valve operation. Do not leave valve closed
for more than five seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
Fig. 2 Power Steering Analyzer Adapters 6893
Fig. 3 Pressure Hose Connection To Power Steering
Pump - 2.4L
1 - POWER STEERING FLUID RETURN HOSE
2 - POWER STEERING PUMP
3 - POWER STEERING FLUID PRESSURE HOSE
Fig. 4 SUPPLY & PRESSURE HOSES AT PUMP -
3.3L/3.8L
1 - PRESSURE HOSE AND FITTING
2 - SUPPLY HOSE AND CLAMP
3 - POWER STEERING PUMP
19 - 2 STEERINGRS
STEERING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1460 of 2321

NOTE: Power steering pump maximum relief pres-
sure is 9,653 to 10,342 kPa (1,400 to 1,500 psi.).
(9) Close analyzer valve fully three times and
record highest pressure indicated each time. All three
readings must be above specifications and within 345
kPa (50 psi) of each other.
²If power steering pump pressures are above
specifications, but not within 345 kPa (50 psi) of each
other, replace pump.
²If power steering pump pressures are within 345
kPa (50 psi) of each other, but are below specifica-
tions, replace pump.
CAUTION: Do not force the pump to operate against
the stops for more than 2 to 4 seconds at a time
because, pump damage will result.
(10) Completely open the valve on the Power
Steering Analyzer. Turn the steering wheel to theextreme left until the stop in the steering gear is
met, then turn the steering wheel to the right until
the right stop is met. Record the highest indicated
pressure at each position. Compare the recorded
readings to the specifications. If the highest output
pressures are not the same against either stop, the
steering gear is leaking internally and must be
replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
NOTE: There are three diagnosis charts following
that cover POWER STEERING NOISE, STEERING
WHEEL FEEL, and POWER STEERING FLUID.
POWER STEERING NOISE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONABLE HISS
OR WHISTLE*1. Damaged or mispositioned
steering column shaft/coupling dash
panel seal.1. Reposition or replace steering
column shaft/coupling dash panel seal.
2. Noisy valve in power steering
gear.2. Replace power steering gear.
3. Mis-routed power steering hose. 3. Check routing of power steering
hoses. Ensure hoses do not come in
unwanted contact with other
components and objects.
RATTLE OR CLUNK 1. Power steering gear loose on front
suspension crossmember.1. Inspect power steering gear
mounting bolts. Replace as necessary.
Tighten to the specified torque.
2. Front suspension crossmember
mounting fasteners loose at frame.2. Tighten the front suspension
crossmember mounting fasteners to the
specified torque.
3. Loose tie rod (outer or inner). 3. Check tie rod pivot points for wear.
Replace worn/loose parts as required.
4. Loose lower control arm mounting
bolts at front suspension
crossmember.4. Tighten control arm mounting bolts to
the specified torques.
5. Lower control arm pivot bushing
worn.5. Replace lower control arm pivot
bushing.
6. Loose strut assembly mounting
fasteners at tower.6. Tighten strut assembly fasteners to
the specified torque.
7. Power steering fluid pressure
hose touching the body of the
vehicle.7. Adjust hose to proper position by
loosening, repositioning, and tightening
fitting to specified torque. Do not bend
tubing.
RSSTEERING19-3
STEERING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1461 of 2321
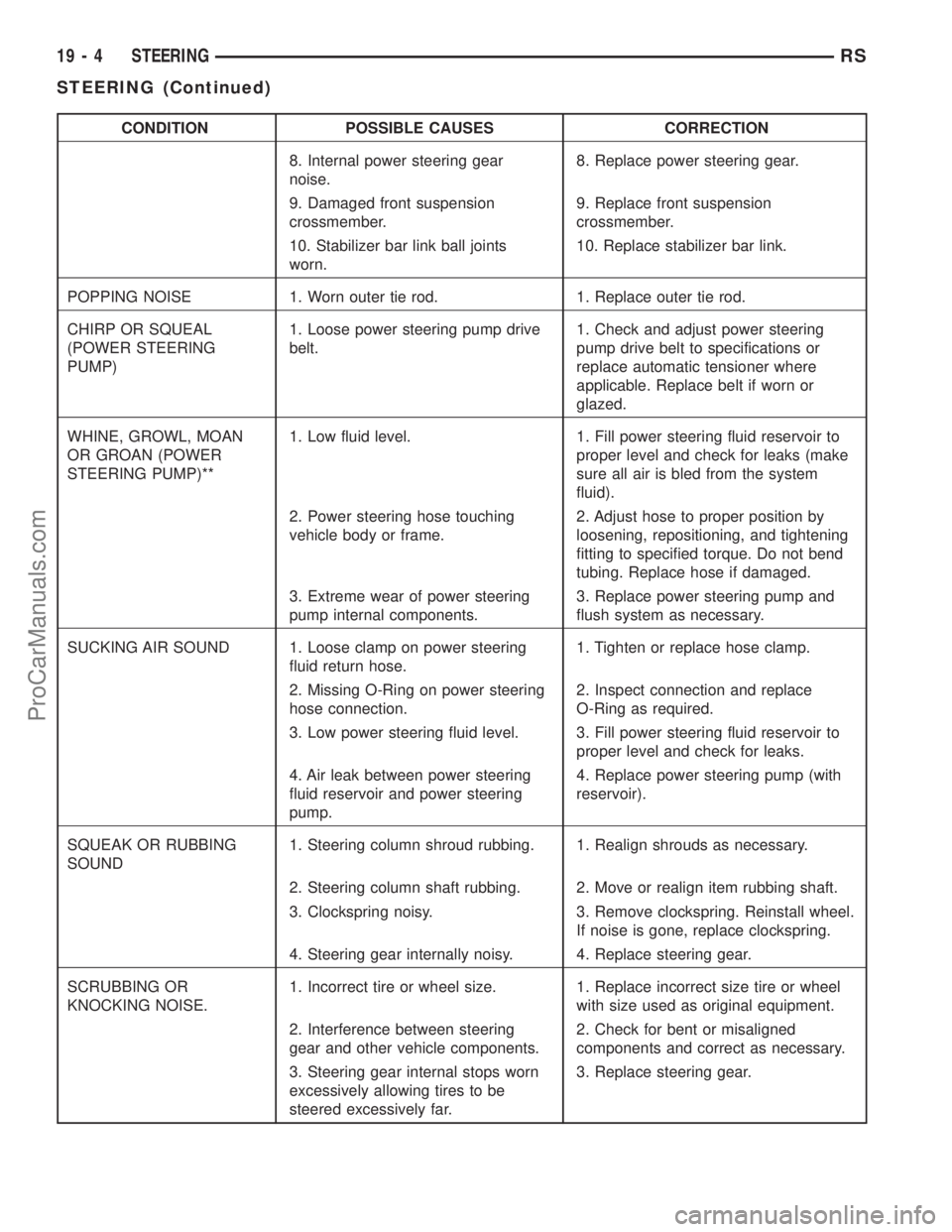
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
8. Internal power steering gear
noise.8. Replace power steering gear.
9. Damaged front suspension
crossmember.9. Replace front suspension
crossmember.
10. Stabilizer bar link ball joints
worn.10. Replace stabilizer bar link.
POPPING NOISE 1. Worn outer tie rod. 1. Replace outer tie rod.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL
(POWER STEERING
PUMP)1. Loose power steering pump drive
belt.1. Check and adjust power steering
pump drive belt to specifications or
replace automatic tensioner where
applicable. Replace belt if worn or
glazed.
WHINE, GROWL, MOAN
OR GROAN (POWER
STEERING PUMP)**1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level and check for leaks (make
sure all air is bled from the system
fluid).
2. Power steering hose touching
vehicle body or frame.2. Adjust hose to proper position by
loosening, repositioning, and tightening
fitting to specified torque. Do not bend
tubing. Replace hose if damaged.
3. Extreme wear of power steering
pump internal components.3. Replace power steering pump and
flush system as necessary.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose clamp on power steering
fluid return hose.1. Tighten or replace hose clamp.
2. Missing O-Ring on power steering
hose connection.2. Inspect connection and replace
O-Ring as required.
3. Low power steering fluid level. 3. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level and check for leaks.
4. Air leak between power steering
fluid reservoir and power steering
pump.4. Replace power steering pump (with
reservoir).
SQUEAK OR RUBBING
SOUND1. Steering column shroud rubbing. 1. Realign shrouds as necessary.
2. Steering column shaft rubbing. 2. Move or realign item rubbing shaft.
3. Clockspring noisy. 3. Remove clockspring. Reinstall wheel.
If noise is gone, replace clockspring.
4. Steering gear internally noisy. 4. Replace steering gear.
SCRUBBING OR
KNOCKING NOISE.1. Incorrect tire or wheel size. 1. Replace incorrect size tire or wheel
with size used as original equipment.
2. Interference between steering
gear and other vehicle components.2. Check for bent or misaligned
components and correct as necessary.
3. Steering gear internal stops worn
excessively allowing tires to be
steered excessively far.3. Replace steering gear.
19 - 4 STEERINGRS
STEERING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1462 of 2321

NOTE: * There is some noise in all power steering
systems. One of the most common is a hissing
sound evident when turning the steering wheel
when at a standstill or when parking and the steer-
ing wheel is at the end of its travel. Hiss is a very
high frequency noise similar to that experienced
while slowly closing a water tap. The noise is
present in every valve and results when high veloc-ity fluid passes valve orifice edges. There is no
relationship between this noise and the perfor-
mance of the steering system.
NOTE: ** Power steering pump growl results from
the development of high pressure fluid flow. Nor-
mally this noise level should not be high enough to
be objectionable.
STEERING WHEEL FEEL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
STEERING WHEEL/
COLUMN CLICKING,
CLUNKING OR RATTLING.1. Loose steering coupling pinch
bolt.1. Replace pinch bolt and torque to
specifications.
2. Steering column bearings. 2. Replace steering column.
STEERING WHEEL HAS
FORE AND AFT
LOOSENESS.1. Steering wheel retaining nut not
properly tightened and torqued.1. Tighten the steering wheel retaining nut
to its specified torque.
2. Steering column lower bearing
spring retainer slipped on steering
column shaft.2. Replace steering column.
3. Loose steering column to
instrument panel fasteners.3. Tighten fasteners to specified torque.
STEERING WHEEL OR
DASH VIBRATES DURING
LOW SPEED OR
STANDSTILL STEERING
MANEUVERS.1. Air in the fluid of the power
steering system.1. Bleed air from system following the
power steering pump initial operation
service procedure.*
2. Tires not properly inflated. 2. Inflate tires to the specified pressure.
3. Excessive engine vibration. 3. Ensure that the engine is running
properly.
4. Loose tie rod end jam nut. 4. Tighten the inner to outer tie rod jam nut
to the specified torque.
5.Overcharged air conditioning
system.5.Check air conditioning pump head
pressure and correct as necessary.
STEERING CATCHES,
STICKS IN CERTAIN
POSITIONS OR IS
DIFFICULT TO TURN.1. Low power steering fluid level. 1. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
specified level and check for leaks.
2. Tires not inflated to specified
pressure.2. Inflate tires to the specified pressure.
3. Lack of lubrication in front lower
control arm ball joints.3. Lubricate ball joints if ball joints are not a
lubricated-for-life type ball joint. If ball joint
is a lubricated-for-life ball joint, replace ball
joint.
4. Worn or binding lower control arm
ball joint.4. Replace lower control arm ball joint.
RSSTEERING19-5
STEERING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com