2001 DODGE RAM light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 2703 of 2889

Scratch Filler/Primer, Touch-Up Paints and Clear Top
Coat. Refer to Introduction group of this manual for
Body Code Plate information.
WARNING: USE A OSHA APPROVED BREATHING
FILTER WHEN SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN
A CONFINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
OPERATION
(1) Scrape loose paint and corrosion from inside
scratch or chip.
(2) Clean affected area with Moparž Tar/Road Oil
Remover, and allow to dry.
(3) Fill the inside of the scratch or chip with a coat
of filler/primer. Do not overlap primer onto good sur-
face finish. The applicator brush should be wet
enough to puddle-fill the defect without running. Do
not stroke brush applicator on body surface. Allow
the filler/primer to dry hard.
(4) Cover the filler/primer with color touch-up
paint. Do not overlap touch-up color onto the original
color coat around the scratch or chip. Butt the new
color to the original color, if possible. Do not stroke
applicator brush on body surface. Allow touch-up
paint to dry hard.
(5) On vehicles without clear coat, the touch-up
color can be lightly finesse sanded (1500 grit) and
polished with rubbing compound.(6) On vehicles with clear coat, apply clear top coat
to touch-up paint with the same technique as
described in Step 4. Allow clear top coat to dry hard.
If desired, Step 5 can be performed on clear top coat.
WARNING: AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT
WITH PETROLEUM OR ALCOHOL ± BASED CLEAN-
ING SOLVENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH PETRO-
LEUM OR ALCOHOL ± BASED CLEANING SOL-
VENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
WET SANDING/BUFFING &
POLISHING
DESCRIPTION
Minor acid etching, orange peel, or smudging in
clear coat or single-stage finishes can be reduced
with light finesse sanding, hand buffing, and polish-
ing.If the finish has been finesse sanded in the
past, it cannot be repeated. Finesse sanding
operation should be performed by a trained
automotive paint technician.
CAUTION: Do not remove clear coat finish, if
equipped. Base coat paint must retain clear coat for
durability.
23 - 130 PAINTBR/BE
PAINT TOUCH-UP (Continued)
Page 2723 of 2889
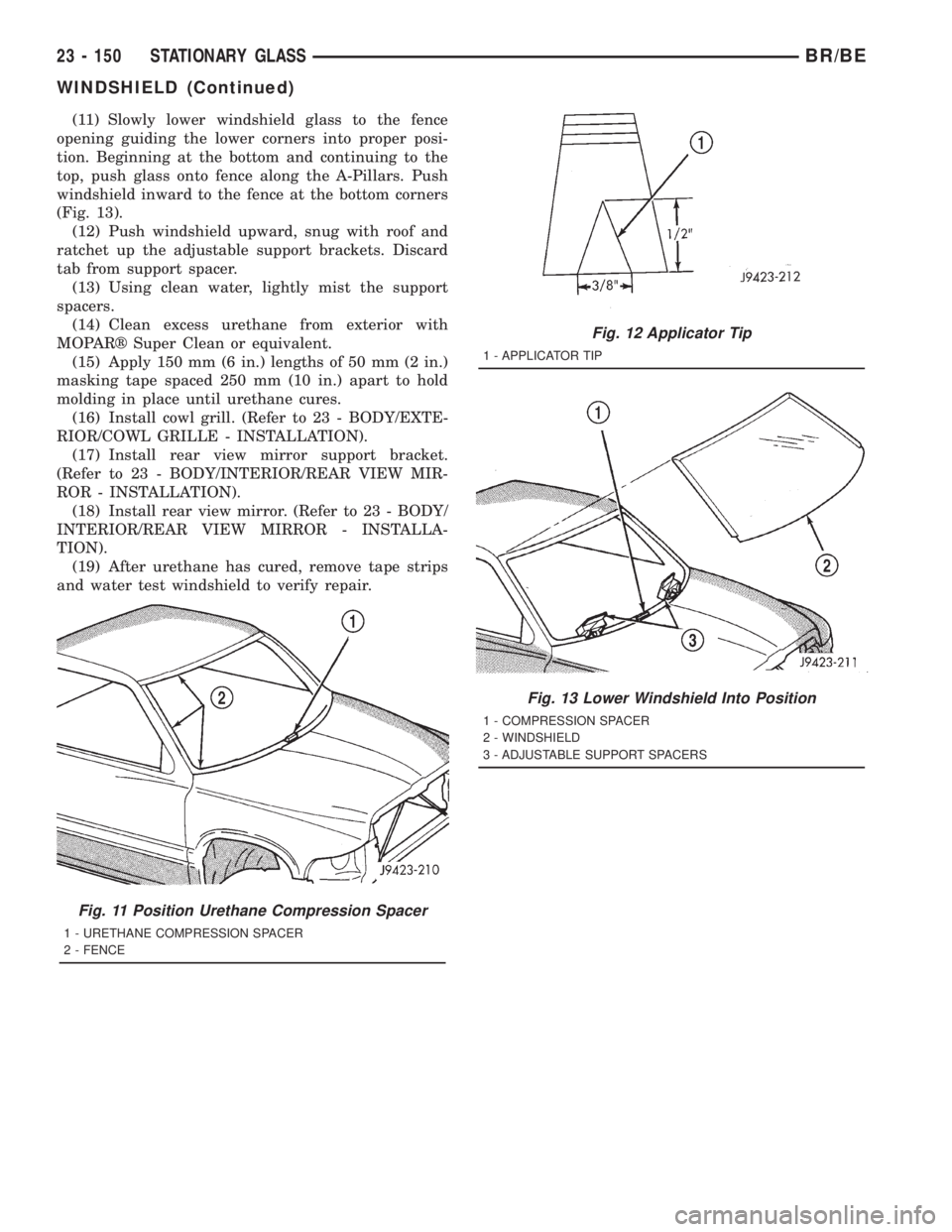
(11) Slowly lower windshield glass to the fence
opening guiding the lower corners into proper posi-
tion. Beginning at the bottom and continuing to the
top, push glass onto fence along the A-Pillars. Push
windshield inward to the fence at the bottom corners
(Fig. 13).
(12) Push windshield upward, snug with roof and
ratchet up the adjustable support brackets. Discard
tab from support spacer.
(13) Using clean water, lightly mist the support
spacers.
(14) Clean excess urethane from exterior with
MOPARž Super Clean or equivalent.
(15) Apply 150 mm (6 in.) lengths of 50 mm (2 in.)
masking tape spaced 250 mm (10 in.) apart to hold
molding in place until urethane cures.
(16) Install cowl grill. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTE-
RIOR/COWL GRILLE - INSTALLATION).
(17) Install rear view mirror support bracket.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/REAR VIEW MIR-
ROR - INSTALLATION).
(18) Install rear view mirror. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/REAR VIEW MIRROR - INSTALLA-
TION).
(19) After urethane has cured, remove tape strips
and water test windshield to verify repair.
Fig. 11 Position Urethane Compression Spacer
1 - URETHANE COMPRESSION SPACER
2 - FENCE
Fig. 12 Applicator Tip
1 - APPLICATOR TIP
Fig. 13 Lower Windshield Into Position
1 - COMPRESSION SPACER
2 - WINDSHIELD
3 - ADJUSTABLE SUPPORT SPACERS
23 - 150 STATIONARY GLASSBR/BE
WINDSHIELD (Continued)
Page 2733 of 2889
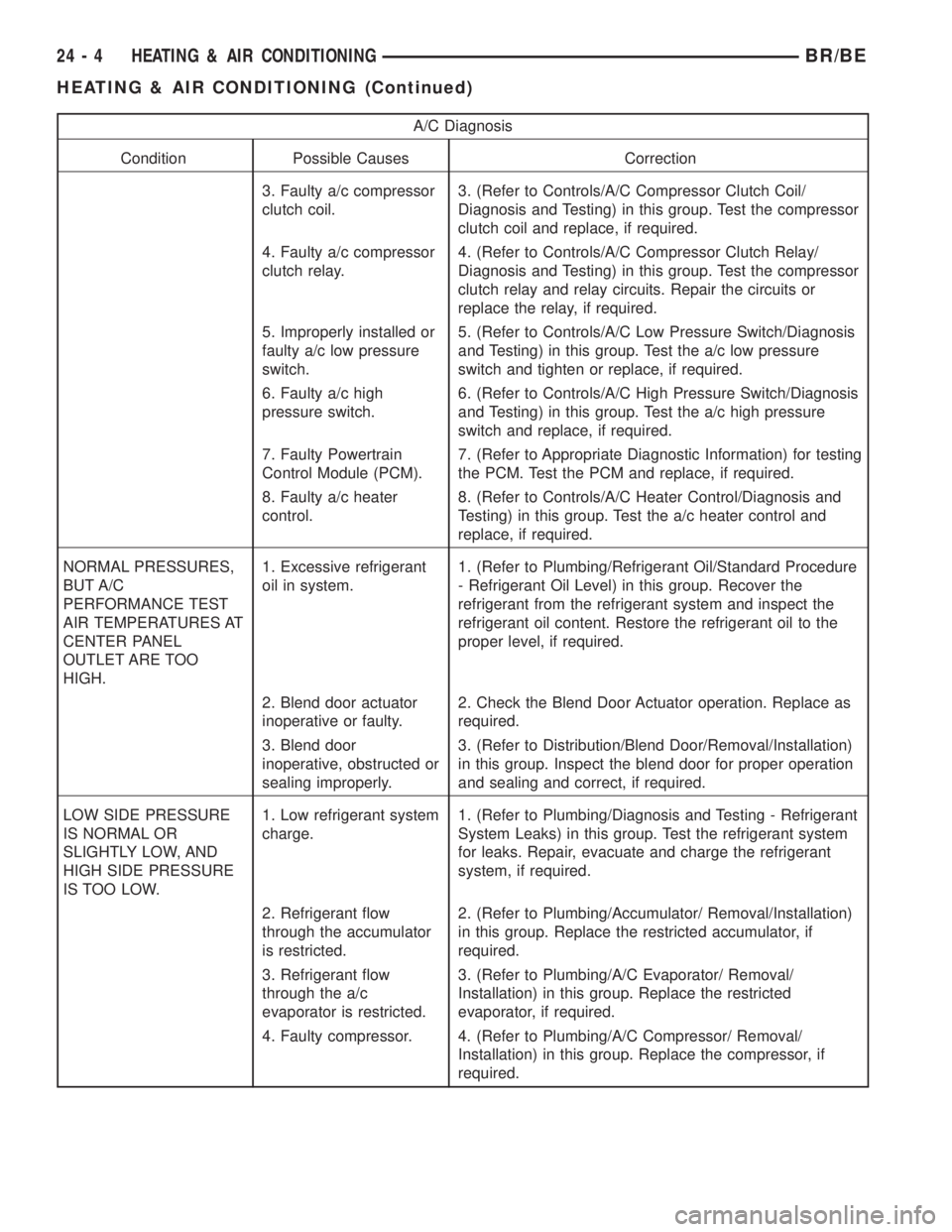
A/C Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
3. Faulty a/c compressor
clutch coil.3. (Refer to Controls/A/C Compressor Clutch Coil/
Diagnosis and Testing) in this group. Test the compressor
clutch coil and replace, if required.
4. Faulty a/c compressor
clutch relay.4. (Refer to Controls/A/C Compressor Clutch Relay/
Diagnosis and Testing) in this group. Test the compressor
clutch relay and relay circuits. Repair the circuits or
replace the relay, if required.
5. Improperly installed or
faulty a/c low pressure
switch.5. (Refer to Controls/A/C Low Pressure Switch/Diagnosis
and Testing) in this group. Test the a/c low pressure
switch and tighten or replace, if required.
6. Faulty a/c high
pressure switch.6. (Refer to Controls/A/C High Pressure Switch/Diagnosis
and Testing) in this group. Test the a/c high pressure
switch and replace, if required.
7. Faulty Powertrain
Control Module (PCM).7. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information) for testing
the PCM. Test the PCM and replace, if required.
8. Faulty a/c heater
control.8. (Refer to Controls/A/C Heater Control/Diagnosis and
Testing) in this group. Test the a/c heater control and
replace, if required.
NORMAL PRESSURES,
BUT A/C
PERFORMANCE TEST
AIR TEMPERATURES AT
CENTER PANEL
OUTLET ARE TOO
HIGH.1. Excessive refrigerant
oil in system.1. (Refer to Plumbing/Refrigerant Oil/Standard Procedure
- Refrigerant Oil Level) in this group. Recover the
refrigerant from the refrigerant system and inspect the
refrigerant oil content. Restore the refrigerant oil to the
proper level, if required.
2. Blend door actuator
inoperative or faulty.2. Check the Blend Door Actuator operation. Replace as
required.
3. Blend door
inoperative, obstructed or
sealing improperly.3. (Refer to Distribution/Blend Door/Removal/Installation)
in this group. Inspect the blend door for proper operation
and sealing and correct, if required.
LOW SIDE PRESSURE
IS NORMAL OR
SLIGHTLY LOW, AND
HIGH SIDE PRESSURE
IS TOO LOW.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. (Refer to Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing - Refrigerant
System Leaks) in this group. Test the refrigerant system
for leaks. Repair, evacuate and charge the refrigerant
system, if required.
2. Refrigerant flow
through the accumulator
is restricted.2. (Refer to Plumbing/Accumulator/ Removal/Installation)
in this group. Replace the restricted accumulator, if
required.
3. Refrigerant flow
through the a/c
evaporator is restricted.3. (Refer to Plumbing/A/C Evaporator/ Removal/
Installation) in this group. Replace the restricted
evaporator, if required.
4. Faulty compressor. 4. (Refer to Plumbing/A/C Compressor/ Removal/
Installation) in this group. Replace the compressor, if
required.
24 - 4 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGBR/BE
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2734 of 2889
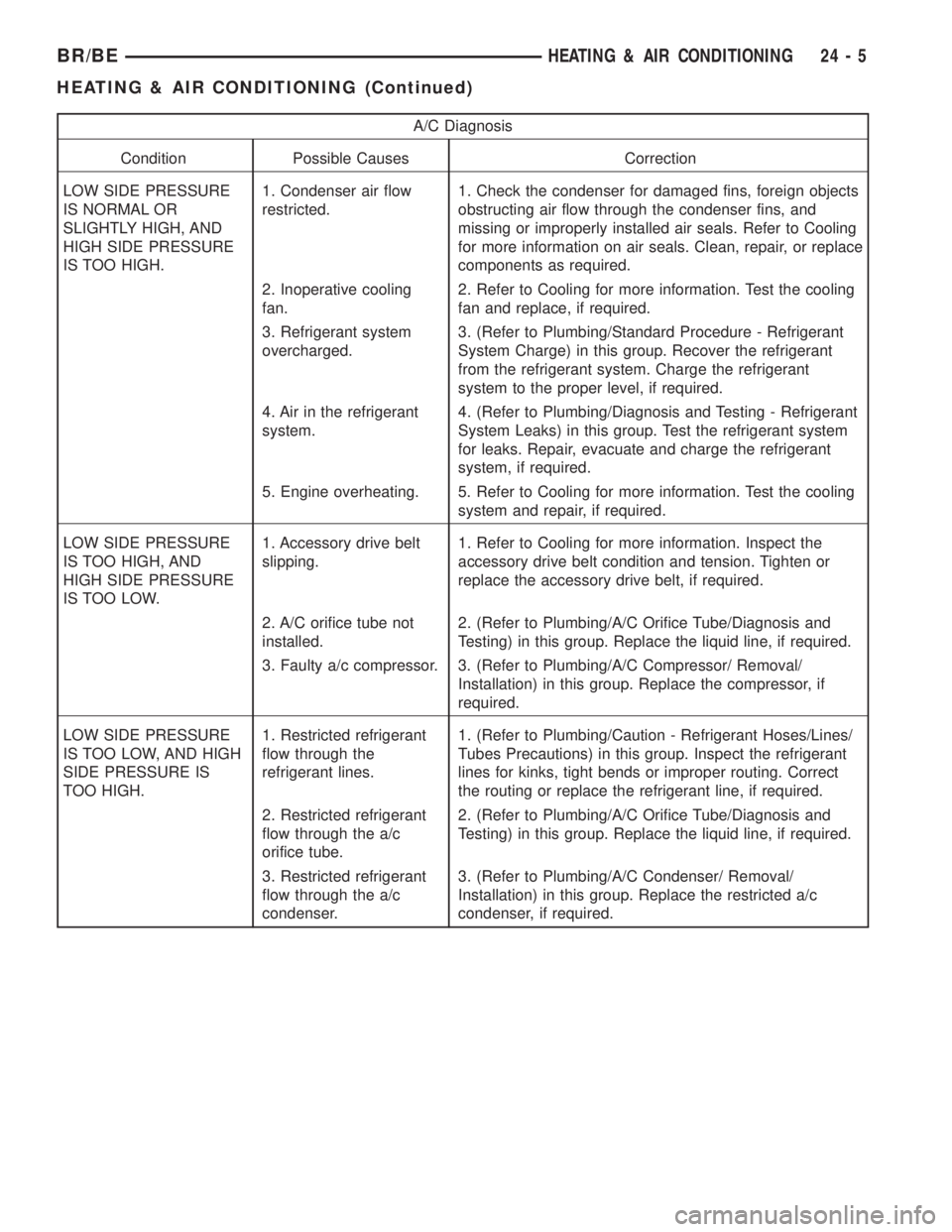
A/C Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
LOW SIDE PRESSURE
IS NORMAL OR
SLIGHTLY HIGH, AND
HIGH SIDE PRESSURE
IS TOO HIGH.1. Condenser air flow
restricted.1. Check the condenser for damaged fins, foreign objects
obstructing air flow through the condenser fins, and
missing or improperly installed air seals. Refer to Cooling
for more information on air seals. Clean, repair, or replace
components as required.
2. Inoperative cooling
fan.2. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the cooling
fan and replace, if required.
3. Refrigerant system
overcharged.3. (Refer to Plumbing/Standard Procedure - Refrigerant
System Charge) in this group. Recover the refrigerant
from the refrigerant system. Charge the refrigerant
system to the proper level, if required.
4. Air in the refrigerant
system.4. (Refer to Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing - Refrigerant
System Leaks) in this group. Test the refrigerant system
for leaks. Repair, evacuate and charge the refrigerant
system, if required.
5. Engine overheating. 5. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the cooling
system and repair, if required.
LOW SIDE PRESSURE
IS TOO HIGH, AND
HIGH SIDE PRESSURE
IS TOO LOW.1. Accessory drive belt
slipping.1. Refer to Cooling for more information. Inspect the
accessory drive belt condition and tension. Tighten or
replace the accessory drive belt, if required.
2. A/C orifice tube not
installed.2. (Refer to Plumbing/A/C Orifice Tube/Diagnosis and
Testing) in this group. Replace the liquid line, if required.
3. Faulty a/c compressor. 3. (Refer to Plumbing/A/C Compressor/ Removal/
Installation) in this group. Replace the compressor, if
required.
LOW SIDE PRESSURE
IS TOO LOW, AND HIGH
SIDE PRESSURE IS
TOO HIGH.1. Restricted refrigerant
flow through the
refrigerant lines.1. (Refer to Plumbing/Caution - Refrigerant Hoses/Lines/
Tubes Precautions) in this group. Inspect the refrigerant
lines for kinks, tight bends or improper routing. Correct
the routing or replace the refrigerant line, if required.
2. Restricted refrigerant
flow through the a/c
orifice tube.2. (Refer to Plumbing/A/C Orifice Tube/Diagnosis and
Testing) in this group. Replace the liquid line, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant
flow through the a/c
condenser.3. (Refer to Plumbing/A/C Condenser/ Removal/
Installation) in this group. Replace the restricted a/c
condenser, if required.
BR/BEHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 5
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2735 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE
Before performing the following tests, refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures to check the engine coolant
level and flow, engine coolant reserve/recovery sys-
tem operation, accessory drive belt condition and ten-
sion, radiator air flow and the fan drive operation.
Also be certain that the accessory vacuum supply
line is connected at the engine vacuum source.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT
Engine coolant is delivered to the heater core
through two heater hoses. With the engine idling atnormal operating temperature, set the temperature
control knob in the full hot position, the mode control
switch knob in the floor position, and the blower
motor switch knob in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged at the HVAC housing floor
outlets. Compare the test thermometer reading to the
Temperature Reference chart.
Temperature Reference
Ambient Air Temperature15.5É C
(60É F)21.1É C
(70É F)26.6É C
(80É F)32.2É C
(90É F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet62.2É C
(144É F)63.8É C
(147É F)65.5É C
(150É F)67.2É C
(153É F)
If the floor outlet air temperature is too low, refer
to Cooling to check the engine coolant temperature
specifications. Both of the heater hoses should be hot
to the touch. The coolant return heater hose should
be slightly cooler than the coolant supply heater
hose. If the return hose is much cooler than the sup-
ply hose, locate and repair the engine coolant flow
obstruction in the cooling system. Refer to Cooling
for the procedures.
An alternate method of checking heater perfor-
mance is to use a DRBIIItscan tool to monitor the
engine coolant temperature. The floor outlet air tem-
perature reading should be no more than 4.5É C (40É
F) lower than the engine coolant temperature read-
ing.
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW Possible loca-
tions or causes of obstructed coolant flow:
²Faulty water pump.
²Faulty thermostat.
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²A plugged heater core.If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is still
low, a mechanical problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS Possible locations or
causes of insufficient heat:
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²A faulty, obstructed or improperly installed
blend door.
²A faulty blower system.
²A faulty a/c heater control.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be
adjusted with the temperature control knob on the
a/c heater control panel, the following could require
service:
²A faulty a/c heater control.
²A faulty blend door actuator.
²A faulty, obstructed or improperly installed
blend door.
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²The engine cooling system.
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGBR/BE
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2745 of 2889

INSPECTION
Examine the friction surfaces of the clutch pulley
and the front plate for wear. The pulley and front
plate should be replaced if there is excessive wear or
scoring.
If the friction surfaces are oily, inspect the shaft
and nose area of the compressor for oil. Remove the
felt from the front cover. If the felt is saturated with
oil, the shaft seal is leaking and the compressor must
be replaced.
Check the clutch pulley bearing for roughness or
excessive leakage of grease. Replace the bearing, if
required.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the clutch field coil and snap ring.
(2) Install the clutch coil lead wire harness retain-
ing clip on the compressor front housing and tighten
the retaining screw.
(3) Align the rotor assembly squarely on the front
compressor housing hub.
(4) Thread the handle (Special Tool 6464 in Kit
6460) into the driver (Special Tool 6143 in Kit 6460)
(Fig. 12).
(5) Place the driver tool assembly into the bearing
cavity on the rotor. Make certain the outer edge of
the tool rests firmly on the rotor bearing inner race
(Fig. 13).
(6) Tap the end of the driver while guiding the
rotor to prevent binding. Tap until the rotor bottoms
against the compressor front housing hub. Listen for
a distinct change of sound during the tapping pro-
cess, to indicate the bottoming of the rotor.(7) Install the external front rotor snap ring with
snap ring pliers. The bevel side of the snap ring must
be facing outward. Press the snap ring to make sure
it is properly seated in the groove.
CAUTION: If the snap ring is not fully seated in the
groove it will vibrate out, resulting in a clutch fail-
ure and severe damage to the front housing of the
compressor.
(8) Install the original clutch shims on the com-
pressor shaft.
(9) Install the clutch plate. On models with the
diesel engine option, install the shaft key. Use the
shaft protector (Special Tool 6141-2 in Kit 6460) to
install the clutch plate on the compressor shaft (Fig.
14). Tap the clutch plate over the compressor shaft
until it has bottomed against the clutch shims. Lis-
ten for a distinct change of sound during the tapping
process, to indicate the bottoming of the clutch plate.
(10) Install the compressor shaft hex nut. Tighten
the nut to 14.4 N´m (10.5 ft. lbs.).
(11) Check the clutch air gap with a feeler gauge
(Fig. 15). If the air gap does not meet the specifica-
tion, add or subtract shims as required. The air gap
specification is 0.41 to 0.79 millimeter (0.016 to 0.031
inch). If the air gap is not consistent around the cir-
cumference of the clutch, lightly pry up at the mini-
mum variations. Lightly tap down at the points of
maximum variation.
Fig. 12 ROTOR INSTALLER SET
Fig. 13 ROTOR INSTALL
24 - 16 CONTROLSBR/BE
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 2769 of 2889

PLUMBING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION...........................40
OPERATION.............................41
WARNING..............................41
CAUTION...............................41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................43
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAKS...........43
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................43
A/C LINE COUPLERS....................43
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
EQUIPMENT...........................44
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY...............45
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE........45
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE.........46
SPECIFICATIONS........................46
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................46
OPERATION.............................46
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................46
A/C COMPRESSOR.....................46
REMOVAL..............................47
INSTALLATION...........................47
A/C CONDENSER
DESCRIPTION...........................48
OPERATION.............................48
REMOVAL..............................49
INSTALLATION...........................49
SUCTION AND DISCHARGE LINE
REMOVAL..............................50
INSTALLATION...........................51
LIQUID LINE
REMOVAL..............................52INSTALLATION...........................52
A/C EVAPORATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................52
OPERATION.............................53
REMOVAL..............................53
INSTALLATION...........................53
A/C ORIFICE TUBE
DESCRIPTION...........................53
OPERATION.............................53
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................54
FIXED ORIFICE TUBE...................54
REMOVAL..............................54
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................54
OPERATION.............................54
REMOVAL..............................54
INSTALLATION...........................55
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION...........................55
OPERATION.............................55
REMOVAL..............................56
INSTALLATION...........................56
REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION...........................56
OPERATION.............................56
REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION...........................56
OPERATION.............................56
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................57
REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL................57
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION - A/C LINE COUPLERS
Spring-lock type refrigerant line couplers are used
to connect many of the refrigerant lines and other
components to the refrigerant system. These couplers
require a special tool for disengaging the two coupler
halves.
DESCRIPTION
The refrigerant lines and hoses are used to carry
the refrigerant between the various air conditioning
system components. A barrier hose design with a
nylon tube, which is sandwiched between rubber lay-
ers, is used for the R-134a air conditioning system onthis vehicle. This nylon tube helps to further contain
the R-134a refrigerant, which has a smaller molecu-
lar structure than R-12 refrigerant. The ends of the
refrigerant hoses are made from lightweight alumi-
num or steel, and commonly use braze-less fittings.
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
24 - 40 PLUMBINGBR/BE
Page 2772 of 2889

The refrigerant system will remain chemically sta-
ble as long as pure, moisture-free R-134a refrigerant
and refrigerant oil is used. Dirt, moisture, or air can
upset this chemical stability. Operational troubles or
serious damage can occur if foreign material is
present in the refrigerant system.
When it is necessary to open the refrigerant sys-
tem, have everything needed to service the system
ready. The refrigerant system should not be left open
to the atmosphere any longer than necessary. Cap or
plug all lines and fittings as soon as they are opened
to prevent the entrance of dirt and moisture. All lines
and components in parts stock should be capped or
sealed until they are to be installed.
All tools, including the refrigerant recycling equip-
ment, the manifold gauge set, and test hoses should
be kept clean and dry. All tools and equipment must
be designed for R-134a refrigerant.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM LEAKS
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
If the air conditioning system is not cooling prop-
erly, determine if the refrigerant system is fully-
charged. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
A/C PERFORMANCE) If the refrigerant system is
low or empty; a leak at a refrigerant line, connector
fitting, component, or component seal is likely.
An electronic leak detector designed for R-134a
refrigerant, or a fluorescent R-134a leak detection
dye and a black light are recommended for locating
and confirming refrigerant system leaks. Refer to the
operating instructions supplied by the equipment
manufacturer for proper care and use of this equip-
ment.
An oily residue on or near refrigerant system lines,
connector fittings, components, or component seals
can indicate the general location of a possible refrig-
erant leak. However, the exact leak location should
be confirmed with an electronic leak detector prior to
component repair or replacement.
To detect a leak in the refrigerant system with an
electronic leak detector, perform one of the following
procedures:
SYSTEM EMPTY
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(2) Connect and dispense 0.283 kilograms (0.625
pounds or 10 ounces) of R-134a refrigerant into the
evacuated refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
CHARGE)
(3) Position the vehicle in a wind-free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(4) With the engine not running, use a electronic
R-134a leak detector and search for leaks. Because
R-134a refrigerant is heavier than air, the leak detec-
tor probe should be moved slowly along the bottom
side of all refrigerant lines, connector fittings and
components.
(5) To inspect the evaporator coil for leaks, insert
the electronic leak detector probe into the center
instrument panel outlet. Set the blower motor switch
to the lowest speed position, and the mode control
switch in the recirculation mode.
SYSTEM LOW
(1) Position the vehicle in a wind-free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(2) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run with the air conditioning system
turned on for five minutes.
(3) With the engine not running, use a electronic
R-134a leak detector and search for leaks. Because
R-134a refrigerant is heavier than air, the leak detec-
tor probe should be moved slowly along the bottom
side of all refrigerant lines, connector fittings and
components.
(4) To inspect the evaporator coil for leaks, insert
the electronic leak detector probe into the center
instrument panel outlet. Set the blower motor switch
to the lowest speed position, and the mode control
switch in the recirculation mode.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE
COUPLERS
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
REMOVAL
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
BR/BEPLUMBING 24 - 43
PLUMBING (Continued)