2001 DODGE RAM bolt pattern
[x] Cancel search: bolt patternPage 186 of 2889

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other gears
and bearings for possible damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure ring
gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion contact
pattern. Adjust backlash or pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched ring
gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out. Replace
components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap bolts. 8. Inspect differential components and
replace as necessary. Ensure that the
bearing caps are torqued tot he proper
specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a suitable lifting device under the
axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove the wheels and tires.
(5) Secure brake drums to the axle shaft.
(6) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing, if necessary. Refer to 5 Brakes for proce-
dures.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block. Do not disconnect the brake hydraulic lines at
the wheel cylinders. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.(8) Disconnect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the vent hose from the axle shaft
tube.
(10) Mark propeller shaft and yoke for installation
alignment reference.
(11) Remove propeller shaft.
(12) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle.
(13) Remove spring clamps and spring brackets.
Refer to 2 Suspension for procedures.
(14) Separate axle from the vehicle.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 113
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 187 of 2889

INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle with lifting device and align to the
leaf spring centering bolts.
(2) Install spring clamps and spring brackets.
Refer to 2 Suspension for procedures.
(3) Install shock absorbers and tighten nuts to 82
N´m (60 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install RWAL sensor to the differential hous-
ing, if necessary. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(5) Install parking brake cables, cable brackets
and brake drums. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(6) Connect brake hose to axle junction block.
Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(7) Install axle vent hose.
(8) Align propeller shaft and pinion yoke reference
marks. Install universal joint straps and bolts.
Tighten to 19 N´m (14 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the wheels and tires.
(10) Add gear lubricant, if necessary. Refer to
Lubricant Specifications for lubricant requirements.
(11) Remove lifting device from axle and lower the
vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig.
4). A plus (+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
ter line of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 127 mm (5.00 in.). The standard depth provides
the best gear tooth contact pattern. Refer to Back-
lash and Contact Pattern in this section for addi-
tional information.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim/oil baffle. The shims are
placed between the rear pinion bearing and the pin-
ion gear head (Fig. 5).
If a new gear set is being installed, note the depth
variance etched into both the original and replace-
ment pinion. Add or subtract this number from the
thickness of the original depth shim/oil slinger to
compensate for the difference in the depth variances.
Refer to the Depth Variance chart.
Note where Old and New Pinion Marking columns
intersect. Intersecting figure represents plus or
minus the amount needed.
Note the etched number on the face of the pinion
gear head (±1, ±2, 0, +1, +2, etc.). The numbers rep-
resent thousands of an inch deviation from the stan-dard. If the number is negative, add that value to the
required thickness of the depth shims. If the number
is positive, subtract that value from the thickness of
the depth shim. If the number is 0 no change is nec-
essary.
Fig. 4 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
Fig. 5 Adjustment Shim Loactions
1 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM/OIL BAFFLE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
3 - 114 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 189 of 2889
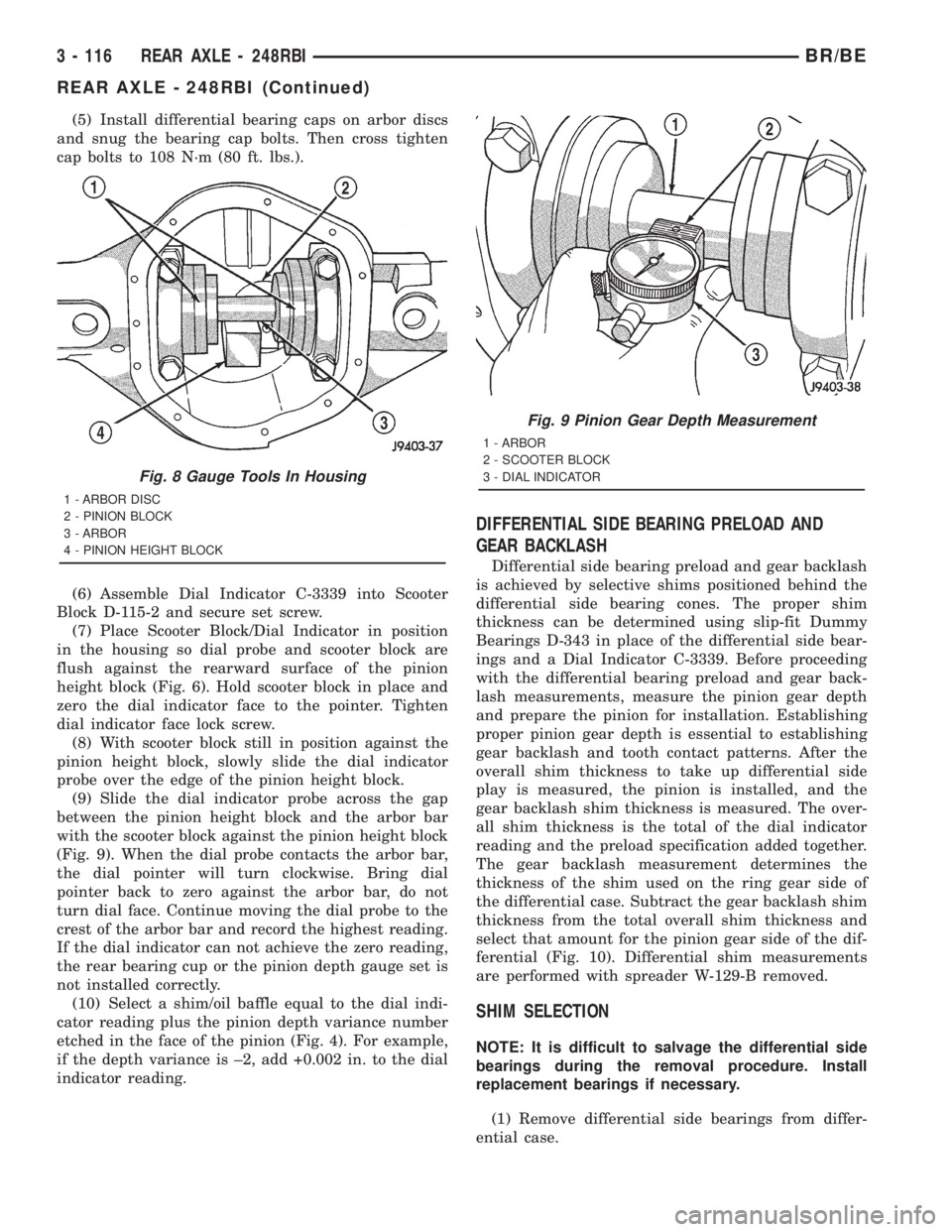
(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(7) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in the housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the rearward surface of the pinion
height block (Fig. 6). Hold scooter block in place and
zero the dial indicator face to the pointer. Tighten
dial indicator face lock screw.
(8) With scooter block still in position against the
pinion height block, slowly slide the dial indicator
probe over the edge of the pinion height block.
(9) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 9). When the dial probe contacts the arbor bar,
the dial pointer will turn clockwise. Bring dial
pointer back to zero against the arbor bar, do not
turn dial face. Continue moving the dial probe to the
crest of the arbor bar and record the highest reading.
If the dial indicator can not achieve the zero reading,
the rear bearing cup or the pinion depth gauge set is
not installed correctly.
(10) Select a shim/oil baffle equal to the dial indi-
cator reading plus the pinion depth variance number
etched in the face of the pinion (Fig. 4). For example,
if the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
DIFFERENTIAL SIDE BEARING PRELOAD AND
GEAR BACKLASH
Differential side bearing preload and gear backlash
is achieved by selective shims positioned behind the
differential side bearing cones. The proper shim
thickness can be determined using slip-fit Dummy
Bearings D-343 in place of the differential side bear-
ings and a Dial Indicator C-3339. Before proceeding
with the differential bearing preload and gear back-
lash measurements, measure the pinion gear depth
and prepare the pinion for installation. Establishing
proper pinion gear depth is essential to establishing
gear backlash and tooth contact patterns. After the
overall shim thickness to take up differential side
play is measured, the pinion is installed, and the
gear backlash shim thickness is measured. The over-
all shim thickness is the total of the dial indicator
reading and the preload specification added together.
The gear backlash measurement determines the
thickness of the shim used on the ring gear side of
the differential case. Subtract the gear backlash shim
thickness from the total overall shim thickness and
select that amount for the pinion gear side of the dif-
ferential (Fig. 10). Differential shim measurements
are performed with spreader W-129-B removed.
SHIM SELECTION
NOTE: It is difficult to salvage the differential side
bearings during the removal procedure. Install
replacement bearings if necessary.
(1) Remove differential side bearings from differ-
ential case.
Fig. 8 Gauge Tools In Housing
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 9 Pinion Gear Depth Measurement
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
3 - 116 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 193 of 2889

GEAR CONTACT PATTERN
The ring and pinion gear contact patterns will
show if the pinion depth is correct. It will also show
if the ring gear backlash has been adjusted correctly.
The backlash can be adjusted within specifications to
achieve desired tooth contact patterns.
(1) Apply a thin coat of hydrated ferric oxide or
equivalent to the drive and coast side of the ring gear
teeth.
(2) Wrap, twist and hold a shop towel around the
pinion yoke to increase the turning resistance of the
pinion. This will provide a more distinct contact pat-
tern.
(3) With a boxed end wrench on the ring gear bolt,
rotate the differential case one complete revolution in
both directions while a load is being applied from
shop towel.
The areas on the ring gear teeth with the greatest
degree of contact against the pinion teeth will squee-
gee the compound to the areas with the least amount
of contact. Note and compare patterns on the ring
gear teeth to Gear Tooth Contact Patterns chart (Fig.
21)and adjust pinion depth and gear backlash as nec-
essary.
Fig. 20 Backlash Shim
3 - 120 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 203 of 2889

(10) Apply a bead of Mopar Silicone Rubber Seal-
ant or equivalent to the housing cover (Fig. 34).
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes
after applying the sealant.
(11) Install the cover and any identification tag.
Tighten the cover bolts in a criss-cross pattern to 47
N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
(12) Refill the differential with Mopar Hypoid
Gear Lubricant or equivalent to bottom of the fill
plug hole. Refer to the Lubricant Specifications for
correct quantity and type.
(13) Install the fill hole plug and tighten to 34 N´m
(25 ft. lbs.).
(14) Remove support and lower vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRAC-LOKY
The most common problem is a chatter noise when
turning corners. Before removing a Trac-lokyunit
for repair, drain, flush and refill the axle with the
specified lubricant. A container of Mopar Trac-loky
Lubricant (friction modifier) should be added after
repair service or during a lubricant change.
After changing the lubricant, drive the vehicle and
make 10 to 12 slow, figure-eight turns. This maneu-
ver will pump lubricant through the clutches. Thiswill correct the condition in most instances. If the
chatter persists, clutch damage could have occurred.
DIFFERENTIAL TEST
The differential can be tested without removing the
differential case by measuring rotating torque. Make
sure brakes are not dragging during this measure-
ment.
(1) Place blocks in front and rear of both front
wheels.
(2) Raise one rear wheel until it is completely off
the ground.
(3) Engine off, transmission in neutral, and park-
ing brake off.
(4) Remove wheel and bolt Special Tool 6790 or
equivalent tool to studs.
(5) Use torque wrench on special tool to rotate
wheel and read rotating torque (Fig. 35).
(6) If rotating torque is less than 22 N´m (30 ft.
lbs.) or more than 271 N´m (200 ft. lbs.) on either
wheel the unit should be serviced.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Clamp side gear Holding Fixture 6965 in a vise
and position the differential case on the Holding Fix-
ture (Fig. 36).
(2) Remove ring gear if the ring gear is to be
replaced. The Trac-lokydifferential can be serviced
with the ring gear installed.
(3) Remove pinion shaft roll pin.
(4) Remove pinion shaft with a drift and hammer
(Fig. 37).
(5) Install and lubricate Step Plate C-6960-3 (Fig.
38).
Fig. 34 Differential Cover
1 - SEALANT SURFACE
2 - SEALANT
3 - SEALANT THICKNESS
Fig. 35 Trac-lokYTest -Typical
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6790 WITH BOLT IN CENTER HOLE
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
3 - 130 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
DIFFERENTIAL (Continued)
Page 212 of 2889

Measure the rotating torque frequently to avoid over
crushing the collapsible spacer (Fig. 62).
(12) Check bearing rotating torque with an inch
pound torque wrench (Fig. 62). Pinion rotating torque
should be:
²Original Bearings-1to3N´m(10to20in.lbs.).
²New Bearings - 2.3 to 5.1 N´m (20 to 45 in. lbs.).
(13) Align previously made marks on yoke and
propeller shaft and install propeller shaft.
CAUTION: Do not reuse ring gear bolts, the bolts
can fracture causing extensive damage.
(14) Invert the differential case.
(15) Position exciter ring on differential case.
(16) Using a brass drift, slowly and evenly tap the
exciter ring into position.
(17) Invert the differential case and start two ring
gear bolts. This will provide case-to-ring gear bolt
hole alignment.
(18) Invert the differential case in the vise.
(19) Install new ring gear bolts and alternately
tighten to 176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 63).
(20) Install differential in axle housing and verify
gear mesh and contact pattern.
(21) Install differential into the housing.
Fig. 61 Pinion Yoke
1 - YOKE INSTALLER
2 - YOKE HOLDERFig. 62 Check Pinion Gear Rotation Torque
1 - PINION YOKE
2 - INCH POUND TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 63 Ring Gear Bolt
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - RING GEAR BOLT
3 - RING GEAR
4 - CASE
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 139
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR/TONE RING (Continued)
Page 217 of 2889

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other gears
and bearings for possible damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure ring
gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion contact
pattern. Adjust backlash or pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched ring
gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out. Replace
components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap bolts. 8. Inspect differential components and
replace as necessary. Ensure that the
bearing caps are torqued tot he proper
specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a suitable lifting device under the
axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove the wheels and tires.
(5) Secure brake drums to the axle shaft.
(6) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing, if necessary. Refer to 5 Brakes for proce-
dures.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block. Do not disconnect the brake hydraulic lines at
the wheel cylinders. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.(8) Disconnect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the vent hose from the axle shaft
tube.
(10) Mark propeller shaft and yoke for installation
alignment reference.
(11) Remove propeller shaft.
(12) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle.
(13) Remove spring clamps and spring brackets.
Refer to 2 Suspension for procedures.
(14) Separate axle from the vehicle.
3 - 144 REAR AXLE - 267RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)
Page 218 of 2889

INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle with lifting device and align to the
leaf spring centering bolts.
(2) Install spring clamps and spring brackets.
Refer to 2 Suspension for procedures.
(3) Install shock absorbers and tighten nuts to 82
N´m (60 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install RWAL sensor to the differential hous-
ing, if necessary. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(5) Install parking brake cables, cable brackets
and brake drums. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(6) Connect brake hose to axle junction block.
Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(7) Install axle vent hose.
(8) Align propeller shaft and pinion yoke reference
marks. Install universal joint straps and bolts.
Tighten to 19 N´m (14 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the wheels and tires.
(10) Add gear lubricant, if necessary. Refer to
Lubricant Specifications for lubricant requirements.
(11) Remove lifting device from axle and lower the
vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig.
4). A plus (+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
ter line of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 136.53 mm (5.375 in.). The standard depth pro-
vides the best gear tooth contact pattern. Refer to
Backlash and Contact Pattern in this section for
additional information.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim/oil baffle. The shims are
placed between the rear pinion bearing and the pin-
ion gear head (Fig. 5).
If a new gear set is being installed, note the depth
variance etched into both the original and replace-
ment pinion. Add or subtract this number from the
thickness of the original depth shim/oil slinger to
compensate for the difference in the depth variances.
Refer to the Depth Variance chart.
Note where Old and New Pinion Marking columns
intersect. Intersecting figure represents plus or
minus the amount needed.
Note the etched number on the face of the pinion
gear head (±1, ±2, 0, +1, +2, etc.). The numbers rep-
resent thousands of an inch deviation from the stan-dard. If the number is negative, add that value to the
required thickness of the depth shims. If the number
is positive, subtract that value from the thickness of
the depth shim. If the number is 0 no change is nec-
essary.
Fig. 4 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
Fig. 5 Adjustment Shim Loactions
1 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM/OIL BAFFLE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 267RBI 3 - 145
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)