Page 14 of 557
0A-10 GENERAL INFORMATION
�When disconnecting connectors, never pull the wiring har-
ness. Unlock the connector lock first and then pull them
apart by holding connectors themselves.
�When connecting connectors, also hold connectors and put
them together until they lock securely (a click is heard).
�When installing the wiring harness, fix it with clamps so that
no slack is left.
�When installing vehicle parts, be careful so that the wiring
harness is not interfered with or caught by any other part.
Page 19 of 557
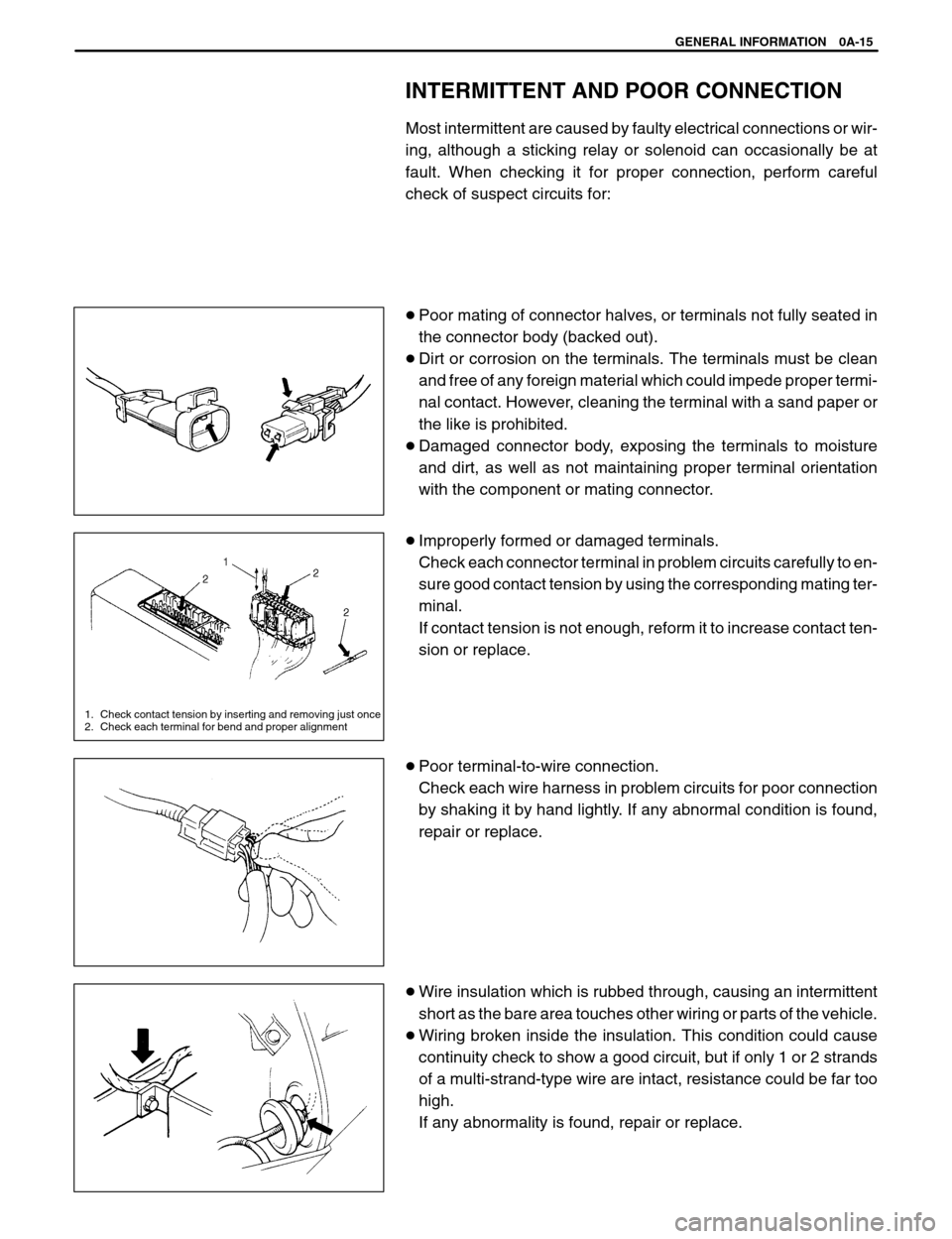
1. Check contact tension by inserting and removing just once
2. Check each terminal for bend and proper alignment
GENERAL INFORMATION 0A-15
INTERMITTENT AND POOR CONNECTION
Most intermittent are caused by faulty electrical connections or wir-
ing, although a sticking relay or solenoid can occasionally be at
fault. When checking it for proper connection, perform careful
check of suspect circuits for:
�Poor mating of connector halves, or terminals not fully seated in
the connector body (backed out).
�Dirt or corrosion on the terminals. The terminals must be clean
and free of any foreign material which could impede proper termi-
nal contact. However, cleaning the terminal with a sand paper or
the like is prohibited.
�Damaged connector body, exposing the terminals to moisture
and dirt, as well as not maintaining proper terminal orientation
with the component or mating connector.
�Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Check each connector terminal in problem circuits carefully to en-
sure good contact tension by using the corresponding mating ter-
minal.
If contact tension is not enough, reform it to increase contact ten-
sion or replace.
�Poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Check each wire harness in problem circuits for poor connection
by shaking it by hand lightly. If any abnormal condition is found,
repair or replace.
�Wire insulation which is rubbed through, causing an intermittent
short as the bare area touches other wiring or parts of the vehicle.
�Wiring broken inside the insulation. This condition could cause
continuity check to show a good circuit, but if only 1 or 2 strands
of a multi-strand-type wire are intact, resistance could be far too
high.
If any abnormality is found, repair or replace.
Page 85 of 557
6-34 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (TBI FOR G10)
1. ECM (PCM)
2. ECM (PCM) couplers
(Viewed from harness side)
1. ECM (PCM)
2. Couplers
3. Body ground
4. Service wire
16
C03 C02 C01
1
2
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 1 2
3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
12
13 14 15
16 17 18 19
20 21 22 9 10
11 12 13 14 15 14 15
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
25 26
INSPECTION OF ECM (PCM) AND ITS
CIRCUITS
ECM (PCM) and its circuits can be checked at ECM (PCM) wiring
couplers by measuring voltage and resistance.
CAUTION:
ECM (PCM) cannot be checked by itself. It is strictly prohib-
ited to connect voltmeter or ohmmeter to ECM (PCM) with
coupler disconnected from it.
Voltage Check
1) Remove ECM (PCM) (1) from body referring to Section 6E.
2) Check voltage at each terminal of couplers (2) connected.
NOTE:
As each terminal voltage is affected by the battery voltage,
confirm that it is 11 V or more when ignition switch is ON.
Page 189 of 557
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-33
1. ECM (PCM)
2. ECM (PCM) couplers
(Viewed from harness side)
INSPECTION OF ECM (PCM) AND ITS
CIRCUITS
ECM (PCM) and its circuits can be checked at ECM (PCM) wiring
couplers by measuring voltage and resistance.
CAUTION:
ECM (PCM) cannot be checked by itself. It is strictly prohib-
ited to connect voltmeter or ohmmeter to ECM (PCM) with
coupler disconnected from it.
Voltage Check
1) Remove ECM (PCM) (1) from body referring to Section 6E2.
2) Check voltage at each terminal of couplers (2) connected.
NOTE:
As each terminal voltage is affected by the battery voltage,
confirm that it is 11 V or more when ignition switch is ON.
Page 406 of 557
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (TBI FOR G10) 6E1-15
1. Injector coupler
2. TP sensor
3. Water hose
4. Vacuum hose
5. ISC actuator
6. Fuel return hose
7. Fuel feed hose
1. Injector coupler
Good No good
2) Install throttle body to EFE heater and tighten bolts to specified
torque.
Tightening Torque
(a): 23 N
.m (2.3 kg-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
3) Install accelerator cable to throttle valve lever and cable brack-
et.
4) Connect fuel, cooling water and vacuum hoses to throttle body,
and clamp securely.
5) Connect TP sensor and injector couplers securely.
6) Refill cooling system referring to Section 6B.
7) Connect negative cable at battery.
8) With engine “OFF” and ignition switch “ON”, check for fuel
leaks around fuel line connection.
9) Install air cleaner assembly referring to Section 6A.
10) Upon completion of installation, start engine and check for fuel
leaks and engine coolant leaks.
Adjust cable play to specification according to procedure de-
scribed in ACCELERATOR CABLE ADJUSTMENT.
FUEL INJECTOR
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
1) With battery negative cable disconnected, disconnect injector
coupler.
2) Connect ohmmeter to each injector terminal and measure resis-
tance.
Resistance of injector: 0.5 – 1.5 Ω at 20�C (68�F)
If resistance is out of specification, replace fuel injector.
3) Connect injector coupler.
4) Remove air cleaner assembly without disconnecting IAT sensor
coupler.
5) Check that fuel is injected out in conical shape from fuel injector
when cranking or running engine.
If no fuel is injected, check wiring harness for continuity and cou-
plers for proper connection referring to “DIAGNOSTIC FLOW
TABLE B-1”.
If fuel is not injected out in conical shape, replace injector.
6) Check injector for fuel leakage after injection is stopped (i.e., af-
ter cranking or engine stop).
Replace if leakage exists.
Fuel leakage: Less than 1 drop/min.
7) Install air cleaner assembly.