Page 269 of 557
1. Stay
2. Throttle body
3. Gasket
4. EFE heater
5. Intake manifold
6. Gasket : Tightening Torque
: Do not reuse
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G10, 1-CAM 6-VALVES ENGINE) 6A-5
THROTTLE BODY AND INTAKE MANIFOLD
REMOVAL
1) Relieve fuel pressure according to procedure described in
“FUEL PRESSURE RELIEF PROCEDURE” of Section 6.
2) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
3) Drain cooling system.
WARNING:
To help avoid danger of being burned, do not remove
drain plug (2) and radiator cap while engine and radiator
(1) are still hot. Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out
under pressure if plug and cap are taken off too soon.
Page 299 of 557
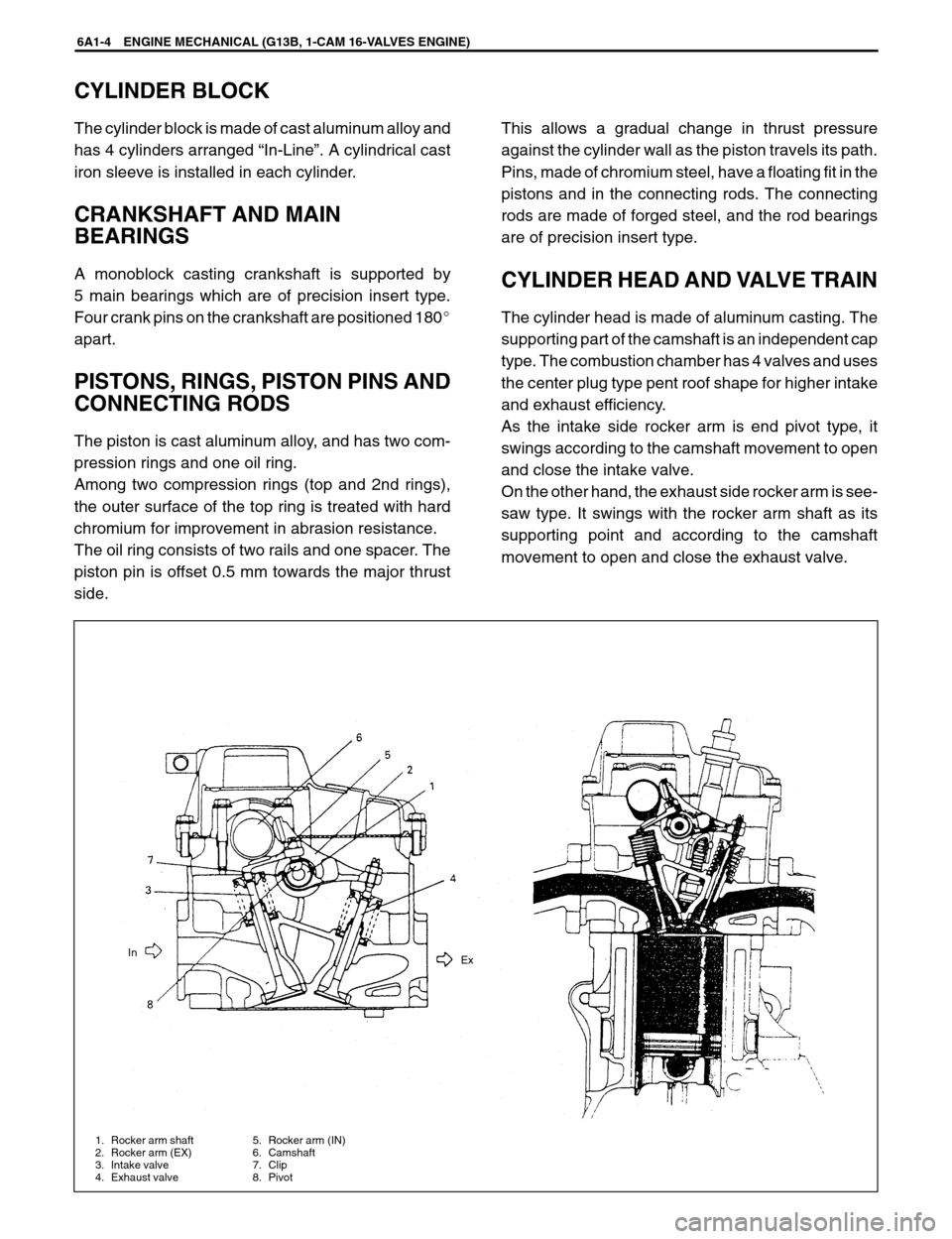
1. Rocker arm shaft
2. Rocker arm (EX)
3. Intake valve
4. Exhaust valve5. Rocker arm (IN)
6. Camshaft
7. Clip
8. PivotEx In
CYLINDER BLOCK
The cylinder block is made of cast aluminum alloy and
has 4 cylinders arranged “In-Line”. A cylindrical cast
iron sleeve is installed in each cylinder.
CRANKSHAFT AND MAIN
BEARINGS
A monoblock casting crankshaft is supported by
5 main bearings which are of precision insert type.
Four crank pins on the crankshaft are positioned 180�
apart.
PISTONS, RINGS, PISTON PINS AND
CONNECTING RODS
The piston is cast aluminum alloy, and has two com-
pression rings and one oil ring.
Among two compression rings (top and 2nd rings),
the outer surface of the top ring is treated with hard
chromium for improvement in abrasion resistance.
The oil ring consists of two rails and one spacer. The
piston pin is offset 0.5 mm towards the major thrust
side.This allows a gradual change in thrust pressure
against the cylinder wall as the piston travels its path.
Pins, made of chromium steel, have a floating fit in the
pistons and in the connecting rods. The connecting
rods are made of forged steel, and the rod bearings
are of precision insert type.
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVE TRAIN
The cylinder head is made of aluminum casting. The
supporting part of the camshaft is an independent cap
type. The combustion chamber has 4 valves and uses
the center plug type pent roof shape for higher intake
and exhaust efficiency.
As the intake side rocker arm is end pivot type, it
swings according to the camshaft movement to open
and close the intake valve.
On the other hand, the exhaust side rocker arm is see-
saw type. It swings with the rocker arm shaft as its
supporting point and according to the camshaft
movement to open and close the exhaust valve.
6A1-4 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
Page 300 of 557
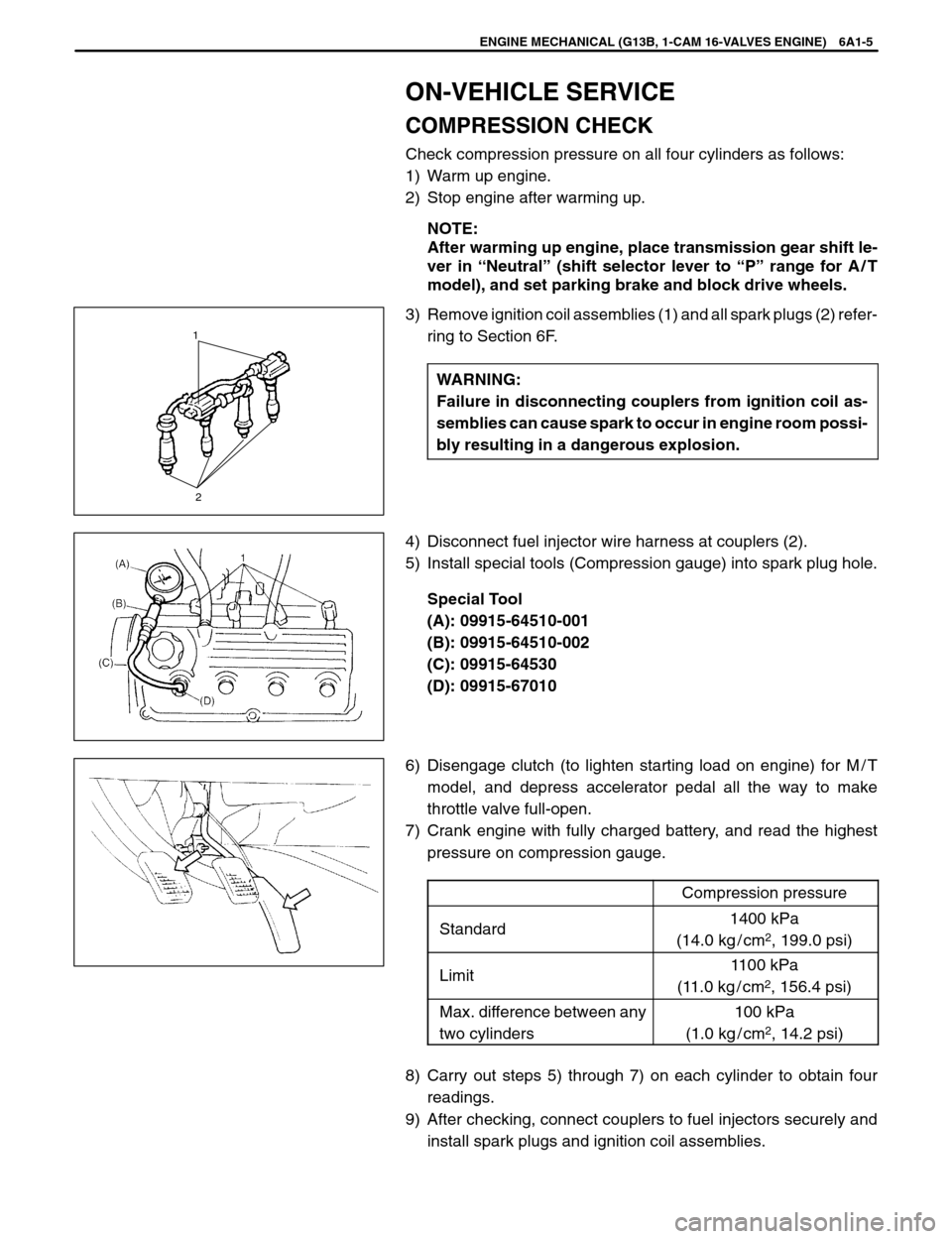
1
2
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-5
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
COMPRESSION CHECK
Check compression pressure on all four cylinders as follows:
1) Warm up engine.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE:
After warming up engine, place transmission gear shift le-
ver in “Neutral” (shift selector lever to “P” range for A / T
model), and set parking brake and block drive wheels.
3) Remove ignition coil assemblies (1) and all spark plugs (2) refer-
ring to Section 6F.
WARNING:
Failure in disconnecting couplers from ignition coil as-
semblies can cause spark to occur in engine room possi-
bly resulting in a dangerous explosion.
4) Disconnect fuel injector wire harness at couplers (2).
5) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special Tool
(A): 09915-64510-001
(B): 09915-64510-002
(C): 09915-64530
(D): 09915-67010
6) Disengage clutch (to lighten starting load on engine) for M / T
model, and depress accelerator pedal all the way to make
throttle valve full-open.
7) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest
pressure on compression gauge.
Compression pressure
Standard1400 kPa
(14.0 kg / cm
2, 199.0 psi)
Limit1100 kPa
(11.0 kg / cm
2, 156.4 psi)
Max. difference between any
two cylinders100 kPa
(1.0 kg / cm
2, 14.2 psi)
8) Carry out steps 5) through 7) on each cylinder to obtain four
readings.
9) After checking, connect couplers to fuel injectors securely and
install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies.
Page 309 of 557
1. Intake manifold
2. Throttle body
3. Gasket
4. EGR valve
5. Fuel delivery pipe
6. Fuel injector7. Fuel pressure regulator
8. EVAP canister purge valve
9. MAP sensor
10. O-ring
11. Gasket
12. Cushion : Tightening Torque
: Do not reuse
1
2
6A1-14 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
THROTTLE BODY AND INTAKE MANIFOLD
REMOVAL
1) Relieve fuel pressure according to procedure described in Sec-
tion 6.
2) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
3) Drain cooling system.
WARNING:
To help avoid danger of being burned, do not remove
drain plug (2) and radiator cap while engine and radiator
(1) are still hot. Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out
under pressure if plug and cap are taken off too soon.
4) Disconnect IAT sensor at coupler.
5) Remove air cleaner outlet hose (2) with resonator.
6) Disconnect accelerator cable (1) from throttle body.
Page 320 of 557
1. Oil pan:
Apply sealant 99000-31150 to
oil pan mating surface.
2. Oil pump strainer
3. Seal
4. Drain plug gasket
5. Drain plug
6. CKP sensor : Tightening Torque
: Do not reuse
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-25
OIL PAN AND OIL PUMP STRAINER
REMOVAL
1) Raise vehicle.
2) Drain engine oil by removing drain plug (1).
3) Remove right side of engine under cover.
4) Disconnect CKP sensor coupler and remove CKP sensor (1) by
removing its bolt. Then remove CKP sensor wire harness from
clamp.
5) Remove clutch housing (torque converter housing for A / T) low-
er plate.
Page 322 of 557
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-27
3) Install new gasket and drain plug to oil pan.
Tighten drain plug to specified torque.
Tightening Torque
(a): 50 N
.m (5.0 kg-m, 36 lb-ft)
4) Install clutch (torque converter) housing lower plate.
5) Install CKP sensor (1) and connect its coupler, then clamp its
harness.
Tightening Torque
(a): 10 N
.m (1.0 kg-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
6) Install right side of engine under cover.
7) Refill engine with engine oil referring to “ENGINE OIL CHANGE”
in Section 0B.
Page 329 of 557
1. Oil plug
6A1-34 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
4) Disconnect CMP sensor coupler from CMP sensor.
5) Remove CMP sensor case (1) from cylinder head.
Place a container or rag under CMP sensor case, for a small
amount of oil flows out during removal of case.
6) After loosening all valve adjusting screw lock nuts (2), turn ad-
justing screws (1) back all the way to allow all rocker arms (3) to
move freely.
7) Remove camshaft housing and camshaft.
NOTE:
To remove camshaft housing bolts, loosen them in such or-
der as indicated in figure, a little at a time.
8) Remove timing belt inside cover (2).
9) Remove intake rocker arm (1) with clip (2) from rocker arm shaft
(3).
NOTE:
Do not bend clip when removing intake rocker arm.
Page 336 of 557
: Do not reuse
1. Valve cotters
2. Valve spring retainer
3. Valve spring:
be sure to position
spring in place with its
bottom end (small-pitch
end) facing the bottom
(valve spring seat side).
4. Valve stem seal
5. Valve spring seat
6. Exhaust valve
7. Intake valve
8. Cylinder head bolt
9. Camshaft housing bolt10. Camshaft housing:
Apply sealant to mating surface of
No.1 and No.6 housings.
11. Valve guide
12. Oil venturi plug
13. Cylinder head gasket:
“TOP” mark provided on gasket comes to
crankshaft pulley side, facing up
(toward cylinder head side).
14. Dowel pin
: Tightening Torque
: Apply engine oil to sliding
: surfaces of each part.
3.5 N.m (0.35 kg-m)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-41
VALVES AND CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVAL
1) Relieve fuel pressure according to procedure described in Sec-
tion 6.
2) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
3) Drain cooling system.
4) Remove air cleaner outlet hose as previously outlined.