Page 299 of 557
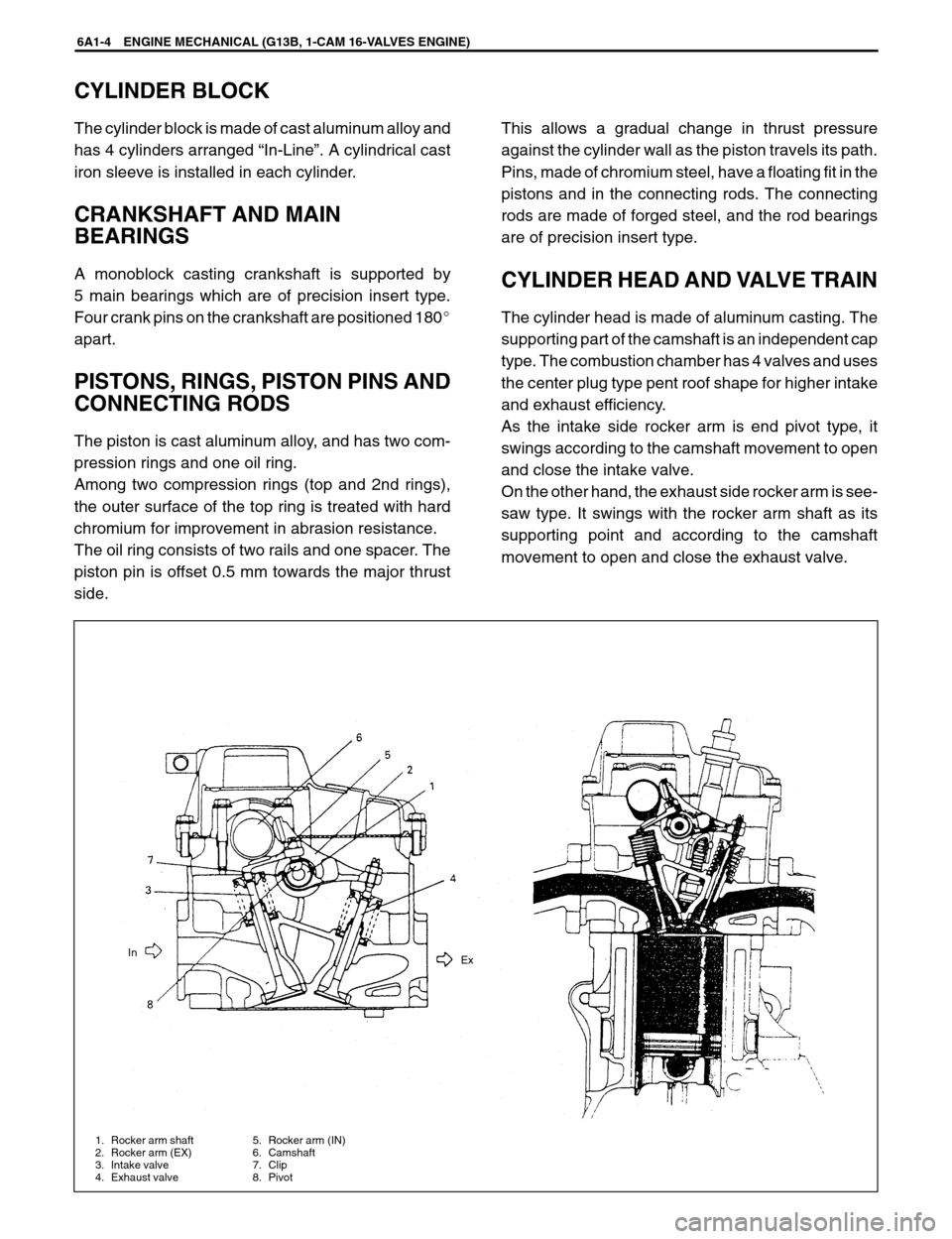
1. Rocker arm shaft
2. Rocker arm (EX)
3. Intake valve
4. Exhaust valve5. Rocker arm (IN)
6. Camshaft
7. Clip
8. PivotEx In
CYLINDER BLOCK
The cylinder block is made of cast aluminum alloy and
has 4 cylinders arranged “In-Line”. A cylindrical cast
iron sleeve is installed in each cylinder.
CRANKSHAFT AND MAIN
BEARINGS
A monoblock casting crankshaft is supported by
5 main bearings which are of precision insert type.
Four crank pins on the crankshaft are positioned 180�
apart.
PISTONS, RINGS, PISTON PINS AND
CONNECTING RODS
The piston is cast aluminum alloy, and has two com-
pression rings and one oil ring.
Among two compression rings (top and 2nd rings),
the outer surface of the top ring is treated with hard
chromium for improvement in abrasion resistance.
The oil ring consists of two rails and one spacer. The
piston pin is offset 0.5 mm towards the major thrust
side.This allows a gradual change in thrust pressure
against the cylinder wall as the piston travels its path.
Pins, made of chromium steel, have a floating fit in the
pistons and in the connecting rods. The connecting
rods are made of forged steel, and the rod bearings
are of precision insert type.
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVE TRAIN
The cylinder head is made of aluminum casting. The
supporting part of the camshaft is an independent cap
type. The combustion chamber has 4 valves and uses
the center plug type pent roof shape for higher intake
and exhaust efficiency.
As the intake side rocker arm is end pivot type, it
swings according to the camshaft movement to open
and close the intake valve.
On the other hand, the exhaust side rocker arm is see-
saw type. It swings with the rocker arm shaft as its
supporting point and according to the camshaft
movement to open and close the exhaust valve.
6A1-4 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
Page 302 of 557

ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-7
OIL PRESSURE CHECK
NOTE:
Prior to checking oil pressure, check the following items.
�Oil level in oil pan.
If oil level is low, add oil up to Full level mark on oil level
gauge.
�Oil quality.
If oil is discolored, or deteriorated, change it.
For particular oil to be used, refer to the table in Section 0B.
�Oil leaks.
If leak is found, repair it.
1) Remove oil pressure switch (1) from cylinder block.
2) Install special tool (Oil pressure gauge) to vacated threaded
hole.
Special Tool
(A): 09915-77311
3) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature.
NOTE:
Be sure to place transmission gear shift lever in “Neutral”
(shift selector lever to “P” range for A / T model), and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
4) After warming up, raise engine speed to 4,000 r / min and mea-
sure oil pressure.
Oil pressure specification:
360 – 440 kPa (3.6 – 4.4 kg / cm
2, 51.2 – 62.6 psi) at 4,000 r / min
(rpm)
5) Stop engine and remove oil pressure gauge.
Page 322 of 557
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-27
3) Install new gasket and drain plug to oil pan.
Tighten drain plug to specified torque.
Tightening Torque
(a): 50 N
.m (5.0 kg-m, 36 lb-ft)
4) Install clutch (torque converter) housing lower plate.
5) Install CKP sensor (1) and connect its coupler, then clamp its
harness.
Tightening Torque
(a): 10 N
.m (1.0 kg-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
6) Install right side of engine under cover.
7) Refill engine with engine oil referring to “ENGINE OIL CHANGE”
in Section 0B.
Page 327 of 557
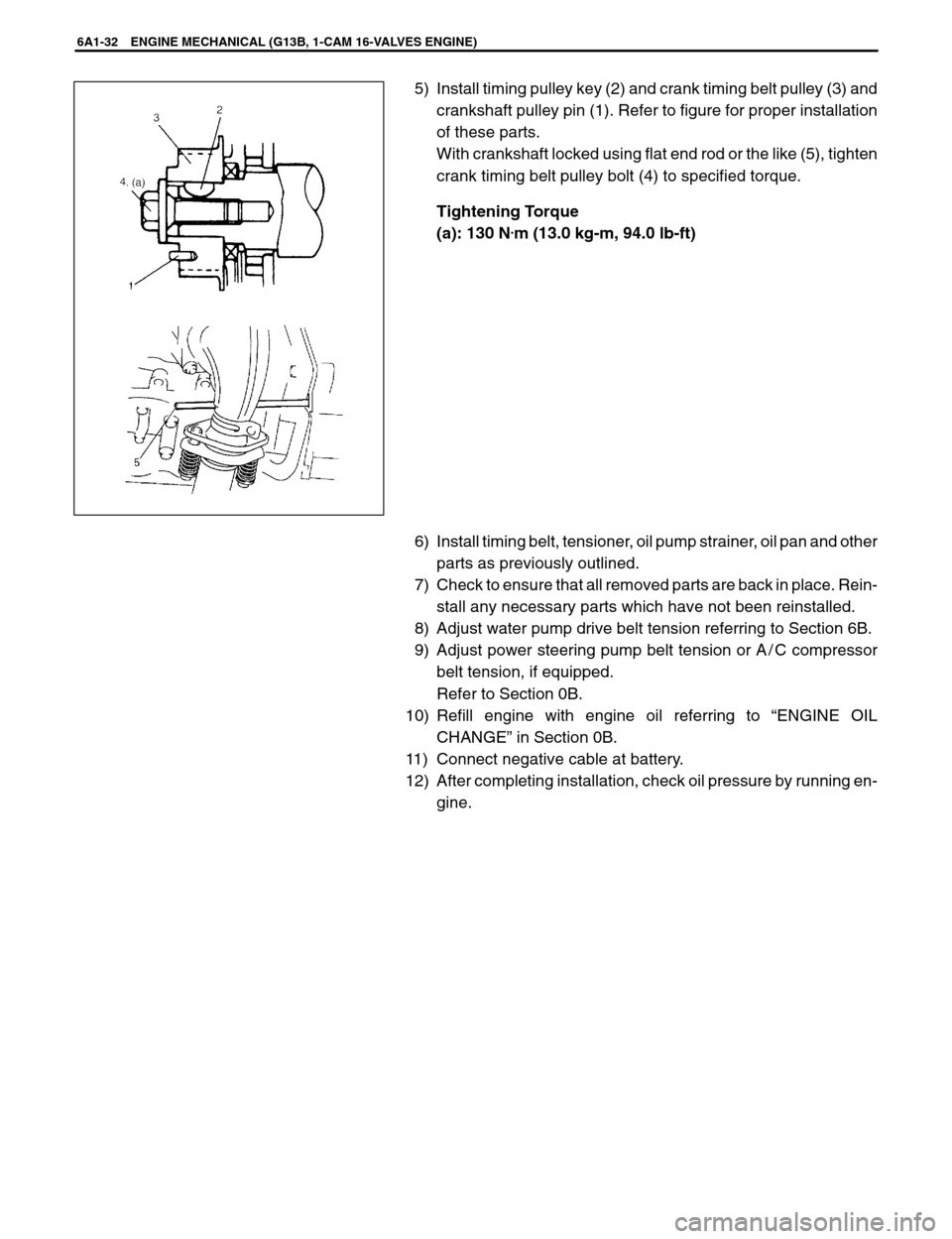
6A1-32 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
5) Install timing pulley key (2) and crank timing belt pulley (3) and
crankshaft pulley pin (1). Refer to figure for proper installation
of these parts.
With crankshaft locked using flat end rod or the like (5), tighten
crank timing belt pulley bolt (4) to specified torque.
Tightening Torque
(a): 130 N
.m (13.0 kg-m, 94.0 lb-ft)
6) Install timing belt, tensioner, oil pump strainer, oil pan and other
parts as previously outlined.
7) Check to ensure that all removed parts are back in place. Rein-
stall any necessary parts which have not been reinstalled.
8) Adjust water pump drive belt tension referring to Section 6B.
9) Adjust power steering pump belt tension or A / C compressor
belt tension, if equipped.
Refer to Section 0B.
10) Refill engine with engine oil referring to “ENGINE OIL
CHANGE” in Section 0B.
11) Connect negative cable at battery.
12) After completing installation, check oil pressure by running en-
gine.
Page 358 of 557
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-63
6) Reverse removal procedure for installation, as previously out-
lined.
7) Adjust water pump drive belt tension referring to Section 6B.
8) Adjust power steering pump belt tension or A / C compressor
belt tension, if equipped.
Refer to Section 0B.
9) Adjust accelerator cable play.
Refer to Section 6E.
10) Check to ensure that all removed parts are back in place. Rein-
stall any necessary parts which have not been reinstalled.
11) Refill engine with engine oil by referring to item “ENGINE OIL
CHANGE” in Section 0B.
12) Refill cooling system referring to Section 6B.
13) Connect negative cable at battery.
14) Check ignition timing referring to Section 6F.
15) Verify that there is no fuel leakage, coolant leakage, oil leakage
and exhaust gas leakage at each connection.
Page 494 of 557

1. Final gear
2. Differential gear assembly
3. Counter shaft
4. 1st and reverse brake
5. Counter driven gear11. Forward clutch
12. Direct clutch
13. Input shaft
14. Torque converter
15. Oil pump 6. Output shaft
7. Rear planetary gear
8. Front planetary gear
9. Valve body assembly
10. Oil strainer
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (3 A / T) (VEHICLE WITH WU-TWC) 7B-3
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The automatic transmission consists of the hydraulic torque converter, electronically controlled 3-speed automatic
transmission, countershaft and differential.
The transmission consists of 2 planetary gears, 2 disk clutches, 1 band brake, 1 disk brake and 1 one-way clutch.
Its operation is controlled by selecting a position from 6 positions (P, R, N, D, 2 and L ranges) manually by means
of the selector lever installed on the compartment floor.
In the D or 2 range, the gear ratio is changed for the 1st, 2nd or 3rd speed (D range only) automatically by engine
control module (electronic control).
For the automatic transmission fluid, DEXRON
-��E, DEXRON-��� or its equivalent must be used. Lubrication
in the automatic transmission is provided by the oil pump which is operated by the engine revolution. Therefore,
the engine should not be stopped even during coasting to obtain proper lubrication.
When it becomes necessary to be towed, front wheels must be raised so as not to roll them.
Page 499 of 557
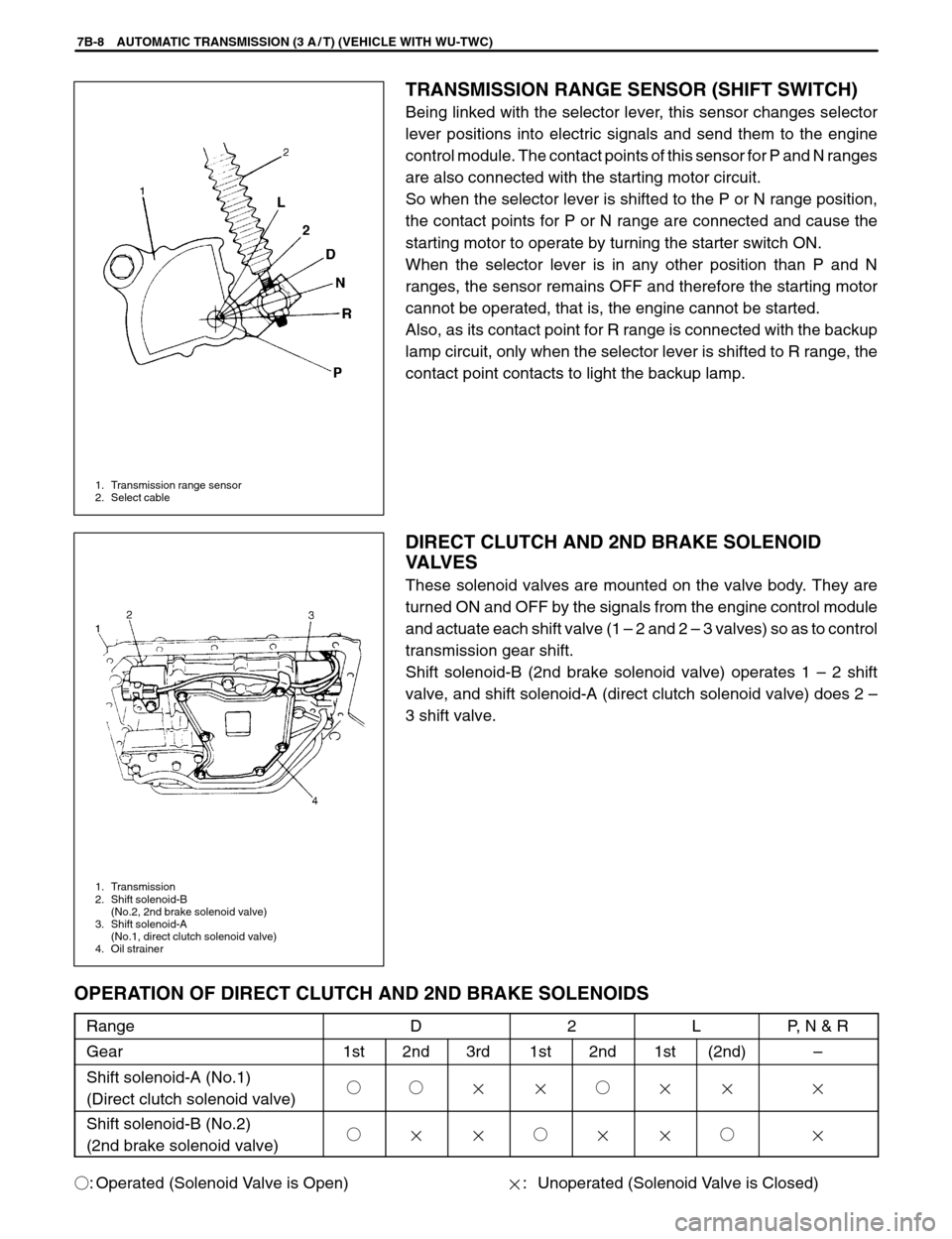
1. Transmission range sensor
2. Select cable
1. Transmission
2. Shift solenoid-B
(No.2, 2nd brake solenoid valve)
3. Shift solenoid-A
(No.1, direct clutch solenoid valve)
4. Oil strainer
7B-8 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (3 A / T) (VEHICLE WITH WU-TWC)
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (SHIFT SWITCH)
Being linked with the selector lever, this sensor changes selector
lever positions into electric signals and send them to the engine
control module. The contact points of this sensor for P and N ranges
are also connected with the starting motor circuit.
So when the selector lever is shifted to the P or N range position,
the contact points for P or N range are connected and cause the
starting motor to operate by turning the starter switch ON.
When the selector lever is in any other position than P and N
ranges, the sensor remains OFF and therefore the starting motor
cannot be operated, that is, the engine cannot be started.
Also, as its contact point for R range is connected with the backup
lamp circuit, only when the selector lever is shifted to R range, the
contact point contacts to light the backup lamp.
DIRECT CLUTCH AND 2ND BRAKE SOLENOID
VALVES
These solenoid valves are mounted on the valve body. They are
turned ON and OFF by the signals from the engine control module
and actuate each shift valve (1 – 2 and 2 – 3 valves) so as to control
transmission gear shift.
Shift solenoid-B (2nd brake solenoid valve) operates 1 – 2 shift
valve, and shift solenoid-A (direct clutch solenoid valve) does 2 –
3 shift valve.
OPERATION OF DIRECT CLUTCH AND 2ND BRAKE SOLENOIDS
RangeD2LP, N & R
Gear1st2nd3rd1st2nd1st(2nd)–
Shift solenoid-A (No.1)
(Direct clutch solenoid valve)��������
Shift solenoid-B (No.2)
(2nd brake solenoid valve)��������
�: Operated (Solenoid Valve is Open)�: Unoperated (Solenoid Valve is Closed)
Page 522 of 557

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (3 A / T) (VEHICLE WITH WU-TWC) 7B-31
TABLE A-2 GEAR CHANGE FAILURE
STEPACTIONYESNO
1Was “AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSTIC
FLOW TABLE” performed?Go to Step 2.Go to “AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
DIAGNOSTIC FLOW
TABLE”.
2Disconnect solenoid valve wire coupler and perform
manual road test.
Is upshift from 1st to 2nd possible?Go to Step 3.1-2 shift valve sticks
or Shift solenoid-B
(2nd brake solenoid)
valve sticks.
3Is upshift from 2nd to 3rd possible?Gear shift control
system defective.
Go to A / T Diagnostic
Flow Table B.2-3 shift valve sticks
or Shift solenoid-A
(Direct clutch
solenoid) valve
sticks.
TABLE A-3 EXCESSIVE SHOCK AT RANGE SELECTION OR GEAR CHANGE
STEPACTIONYESNO
1Was “AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSTIC
FLOW TABLE” performed?Go to Step 2.Go to “AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
DIAGNOSTIC FLOW
TABLE”.
2Is line pressure proper?Go to Step 3.Regulator valve
defective, Throttle
valve defective or
Accelerator cable
maladjusted.
3Does excessive shock occur when selecting “D” range
from “N” range?Forward clutch
accumulator
operation failure,
Forward clutch worn
or Forward clutch oil
circuit check ball
operation failure. Go to Step 4.
4Does excessive shock occur when selecting “R” range
from “N” range?1st-Reverse brake
worn, 1st-Reverse
brake oil circuit check
ball operation failure.Go to Step 5.
5Does excessive shock occur at 1st to 2nd gear
change?2nd brake
accumulator
defective, 2nd brake
worn, 2nd brake oil
circuit check ball
operation failure.In case of excessive
shock at 2nd to 3rd
gear change, Direct
clutch worn or Direct
clutch oil circuit check
ball operation failure.