2000 SUZUKI SWIFT harness
[x] Cancel search: harnessPage 361 of 698

5E-36 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
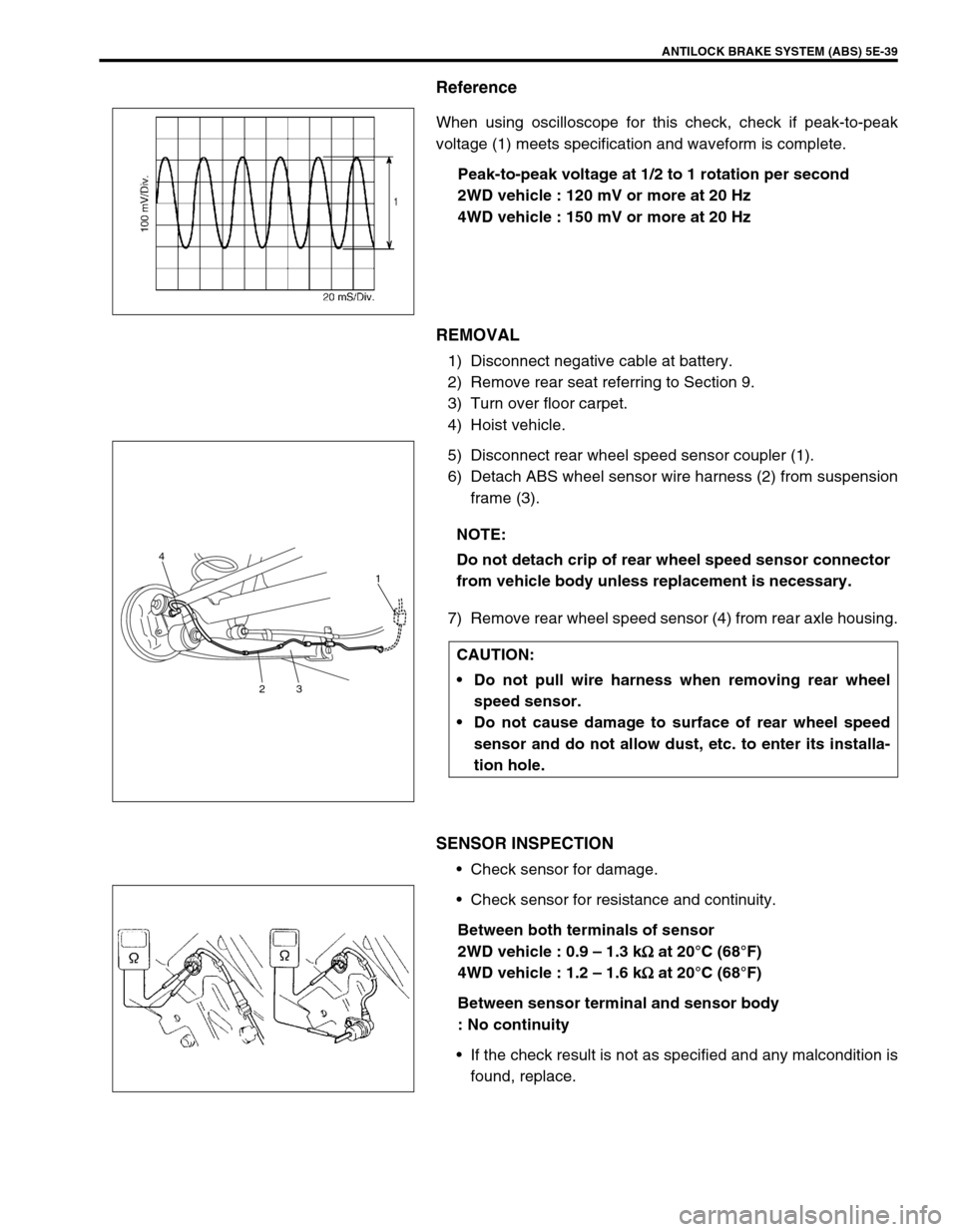
Reference
When using oscilloscope for this check, check if peak-to-peak
voltage (1) meets specification and waveform is complete.
Peak-to-peak voltage at 1/2 to 1 rotation per second
: 150 mV or more at 20 Hz
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Disconnect front wheel speed sensor coupler (1).
3) Hoist vehicle and remove wheel.
4) Remove harness clamp bolts (2) and grommet (3).
5) Remove front wheel speed sensor (4) from knuckle.
SENSOR INSPECTION
Check sensor for damage.
Check sensor for resistance and continuity.
Between both terminals (1) sensor
: 1.2 – 1.6 k
Ω
ΩΩ Ω at 20°C (68°F)
Between sensor terminal and sensor body (2)
: No continuity
If the check result is not as specified and any malcondition is
found, replace.
CAUTION:
Do not pull wire harness when removing front wheel
speed sensor.
Do not cause damage to surface of front wheel speed
sensor and do not allow dust, etc. to enter its installa-
tion hole.
Page 362 of 698

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-37
SENSOR ROTER INSPECTION
Check rotor for being missing, damaged or deformed.
Turn drive shaft and check if rotor rotation is free from
eccentricity and looseness.
Check that no foreign material is attached.
If any faulty is found, repair or replace. Refer to “WHEEL
HUB” in Section 3D.
INSTALLATION
1) Check that no foreign material is attached to sensor (1) and
sensor ring (2).
2) Install it by reversing removal procedure.
Tightening torque
Front wheel speed sensor bolt (a) :
10 N·m (1.0 kg-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
3) Check that there is no clearance between sensor and
knuckle.
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR RING
For removal and installation of wheel side joint assembly of drive
shaft, refer to “FRONT DRIVE SHAFT” section.
CAUTION:
Do not pull or twist wire harness more than necessary
when installing front wheel speed sensor.
NOTE:
The front wheel sensor ring can not be removed or
replaced alone. If front wheel sensor ring needs to be
replaced, replace it as a wheel side joint assembly of
drive shaft.
Page 364 of 698
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-39
Reference
When using oscilloscope for this check, check if peak-to-peak
voltage (1) meets specification and waveform is complete.
Peak-to-peak voltage at 1/2 to 1 rotation per second
2WD vehicle : 120 mV or more at 20 Hz
4WD vehicle : 150 mV or more at 20 Hz
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Remove rear seat referring to Section 9.
3) Turn over floor carpet.
4) Hoist vehicle.
5) Disconnect rear wheel speed sensor coupler (1).
6) Detach ABS wheel sensor wire harness (2) from suspension
frame (3).
7) Remove rear wheel speed sensor (4) from rear axle housing.
SENSOR INSPECTION
Check sensor for damage.
Check sensor for resistance and continuity.
Between both terminals of sensor
2WD vehicle : 0.9 – 1.3 k
Ω
ΩΩ Ω at 20°C (68°F)
4WD vehicle : 1.2 – 1.6 k
Ω
ΩΩ Ω at 20°C (68°F)
Between sensor terminal and sensor body
: No continuity
If the check result is not as specified and any malcondition is
found, replace.
NOTE:
Do not detach crip of rear wheel speed sensor connector
from vehicle body unless replacement is necessary.
CAUTION:
Do not pull wire harness when removing rear wheel
speed sensor.
Do not cause damage to surface of rear wheel speed
sensor and do not allow dust, etc. to enter its installa-
tion hole.
4
231
Page 365 of 698

5E-40 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
SENSOR ROTOR INSPECTION
Check rotor serration (teeth) for being missing, damaged or
deformed.
Turn wheel and check if rotor rotation is free from eccentric-
ity and looseness.
Check that no foreign material is attached.
If any faulty is found, repair or replace.
INSTALLATION
Reverse removal procedure for installation noting the following.
Check that no foreign material is attached to sensor (1) and
ring.
Be sure to install wheel speed sensor and its bolt at the cor-
rect (upper) position as shown in figure.
Tighten sensor bolt to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Sensor bolt (a) : 10 N·m (1.0 kg-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
Check that there is no clearance between sensor and rear
axle shaft.
[A] : For 2WD
[B] : For 4WD
[B] [A]
1
CAUTION:
Do not pull or twist wire harness more than necessary
when installing rear wheel speed sensor.
Page 373 of 698
6-4 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
GENERAL INFORMATION
STATEMENT ON CLEANLINESS AND CARE
An automobile engine is a combination of many machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with tolerances
that are measured in the thousands of an millimeter (ten thousands of an inch).
Accordingly, when any internal engine parts are serviced, care and cleanliness are important.
Throughout this section, it should be understood that proper cleaning and protection of machined surfaces and
friction areas is part of the repair procedure. This is considered standard shop practice even if not specifically
stated.
A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to friction areas during assembly to protect and lubricate the
surfaces on initial operation.
Whenever valve train components, pistons, piston rings, connecting rods, rod bearings, and crankshaft jour-
nal bearings are removed for service, they should be retained in order.
At the time of installation, they should be installed in the same locations and with the same mating surfaces
as when removed.
Battery cables should be disconnected before any major work is performed on the engine.
Failure to disconnect cables may result in damage to wire harness or other electrical parts.
Throughout this manual, the four cylinders of the engine are
identified by numbers; No.1 (1), No.2 (2), No.3 (3) and No.4
(4) counted from crankshaft pulley side to flywheel side.
GENERAL INFORMATION ON ENGINE SERVICE
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION ON ENGINE SERVICE SHOULD BE NOTED CAREFULLY, AS IT IS
IMPORTANT IN PREVENTING DAMAGE, AND IN CONTRIBUTING TO RELIABLE ENGINE PERFOR-
MANCE.
When raising or supporting engine for any reason, do not use a jack under oil pan. Due to small clearance
between oil pan and oil pump strainer, jacking against oil pan may cause it to be bent against strainer result-
ing in damaged oil pick-up unit.
It should be kept in mind, while working on engine, that 12-volt electrical system is capable of violent and
damaging short circuits.
When performing any work where electrical terminals can be grounded, ground cable of the battery should
be disconnected at battery.
Any time the air cleaner, throttle body or intake manifold is removed, the intake opening should be covered.
This will protect against accidental entrance of foreign material which could follow intake passage into cylin-
der and cause extensive damage when engine is started.
1
2
3
4
Page 380 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-11
DATA LINK CONNECTOR (DLC)
ELC (1) is in compliance with SAEJ1962 in its installation posi-
tion, the shape of connector and pin assignment.
Serial data line (K line of ISO 9141) is used for SUZUKI scan tool
(Tech-1) to communicate with ECM, TCM, ABS control module
and Air bag SDM.
SUZUKI serial data line is used for SUZUKI scan tool (Tech -1) to
communicate with immobilizer control module.
PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE
Do not disconnect couplers from ECM, battery cable from battery, ECM ground wire harness from engine or
main fuse before confirming diagnostic information (DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in ECM memory.
Such disconnection will erase memorized information in ECM memory.
Diagnostic information stored in ECM memory can be cleared as well as checked by using SUZUKI scan
tool (Tech-1) or generic scan tool (Vehicle with immobilizer indicator lamp). Before using scan tool, read its
Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have good understanding as to what functions are available and
how to use it.
Priorities for diagnosing troubles (Vehicle with immobilizer indicator lamp).
If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the flow table of the DTC which has detected earliest in the order
(it can be identified by referring to freeze frame data) and follow the instruction in that table.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot diagnostic trouble codes according to the following priorities.
–Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) other than DTC P0171/P0172 (Fuel system too lean/too rich), DTC
P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304 (Misfire detected) and DTC P0400 (EGR flow malfunction)
–DTC P0171/P0172 (Fuel system too lean/too rich) and DTC P0400 (EGR flow malfunction)
–DTC P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304 (Misfire detected)
Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service” in Section 0A before inspection and observe what
is written there.
ECM Replacement
When substituting a known-good ECM, check for following conditions. Neglecting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
–Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as specified respectively.
–MAP sensor and TP sensor are in good condition and none of power circuits of these sensors is shorted
to ground.AMBIENT
TEMPERATURETIME TO CUT POWER TO ECM
Over 0°C (32°F) 60 sec. or longer
Under 0°C (32°F) Not specifiable. Select a place with
temperature higher than 0°C (32°F).
2. B+
3. Serial data line (K line of ISO 9141)
4. ECM ground
5. Body ground
6. SUZUKI serial data line
2
3456
1
Page 382 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-13
1. CUSTOMER COMPLAINT ANALYSIS
Record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this
purpose, use of such an inspection form will facilitate collecting information to the point required for proper anal-
ysis and diagnosis.
2. DTC/FREEZE FRAME DATA CHECK, RECORD AND CLEARANCE
First, check DTC (including pending DTC), referring to “DTC check” section. If DTC is indicated, print it and
freeze frame data or write them down and then clear them by referring to “DTC clearance” section. DTC indi-
cates malfunction that occurred in the system but does not indicate whether it exists now or it occurred in the
past and the normal condition has been restored now. To check which case applies, check the symptom in
question according to Step 4 and recheck DTC according to Step 5.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit or difficulty in troubleshooting.
3. and 4. VISUAL INSPECTION
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of the items that support proper function of the engine
referring to “Visual Inspection” section.
5. TROUBLE SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION
Based on information obtained in Step 1 Customer complaint analysis and Step 2 DTC/freeze frame data check,
confirm trouble symptoms. Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC Confirmation Procedure” described in each
DTC Diagnosis section.
6. and 7. RECHECKING AND RECORD OF DTC/FREEZE FRAME DATA
Refer to “DTC check” section for checking procedure.
8. ENGINE BASIC INSPECTION AND ENGINE DIAGNOSIS TABLE
Perform basic engine check according to the “Engine Basic Inspection Flow Table” first. When the end of the
flow table has been reached, check the parts of the system suspected as a possible cause referring to ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS TABLE and based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle (symptoms obtained through steps of
customer complaint analysis, trouble symptom confirmation and/or basic engine check) and repair or replace
faulty parts, if any.
9. TROUBLESHOOTING FOR DTC (See each DTC Diag. Flow Table)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 5 and referring to the applicable DTC diag. flow table in this section, locate
the cause of the trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness, connector, actuator, ECM or other part and
repair or replace faulty parts.
10. CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEM
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“INTERMITTENT AND POOR CONNECTION” in Section 0A and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2.
11. FINAL CONFIRMATION TEST
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the engine is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has
been repaired is related to the DTC, clear the DTC once, perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm that
no DTC is indicated.NOTE:
If only Automatic transmission DTCs (P0702-P1709) or Immobilizer DTCs (P1620-P1623) are indicated
in this step, perform trouble diagnosis according to “Diagnosis” in Section 7B or Section 8G.
Page 391 of 698
6-22 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
VISUAL INSPECTION
Visually check following parts and systems.
INSPECTION ITEM REFERRING SECTION
Engine oil – level, leakage Section 0B
Engine coolant – level, leakage Section 0B
Fuel – level, leakage Section 0B
A/T fluid – level, leakage Section 0B
Air cleaner element – dirt, clogging Section 0B
Battery – fluid level, corrosion of terminal
Water pump belt – tension, damage Section 0B
Throttle cable – play, installation
Section 6E1 Vacuum hoses of air intake system – disconnection, looseness,
deterioration, bend
Connectors of electric wire harness – disconnection, friction
Fuses – burning Section 8
Parts – installation, bolt – looseness
Parts – deformation
Other parts that can be checked visually
Check following items at engine start, if possible
–Malfunction indicator lamp – Operation Section 6
–Charge warning lamp – Operation Section 6H
–Engine oil pressure warning lamp – Operation Section 8 (Section 6 for pressure check)
–Engine coolant temp. meter – Operation Section 8
–Fuel level meter – Operation Section 8
–Tachometer, if equipped – Operation
–Abnormal air being inhaled from air intake system
–Exhaust system – leakage of exhaust gas, noise