2000 SUZUKI SWIFT check engine light
[x] Cancel search: check engine lightPage 491 of 698
![SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Workshop Manual 6-122 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-4 IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
INSPECTION
1. IAC valve 2. Main relay 3. To TCM
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Workshop Manual 6-122 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-4 IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
INSPECTION
1. IAC valve 2. Main relay 3. To TCM
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is](/manual-img/20/7606/w960_7606-490.png)
6-122 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-4 IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
INSPECTION
1. IAC valve 2. Main relay 3. To TCM
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
GRN/RED
BLK/YEL
BRN/WHT
BLK/RED
BLK/RED
ECM
C41-10
C41-6
C41-5
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
3
1
2
C42-6 C41-14 [A]
G02-6 [B]
LT BLU [A]
GRN RED [B]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
Step Action Yes No
1 Check engine idle speed and IAC duty referring
to “Idle Speed/IAC Duty Inspection” in Section
6E1.
Is idle speed within specification?Go to Step 2. Go to Step 4.
2 Is IAC duty within specification in Step 1? Go to Step 3. Check for followings :
Vacuum leak
EVAP canister purge con-
trol system
Clog of IAC air passage
Accessory engine load
Closed throttle position
(TP sensor)
Stuck of PCV valve
3 Is engine idle speed kept specified speed even
with headlight ON?System is in good condi-
tion.Check IAC system for
operation referring to Step
2 of DTC P0505 Diag.
Flow Table.
4 Was idle speed higher than specification in
Step 1?Go to Step 5. Go to Step 8.
Page 506 of 698
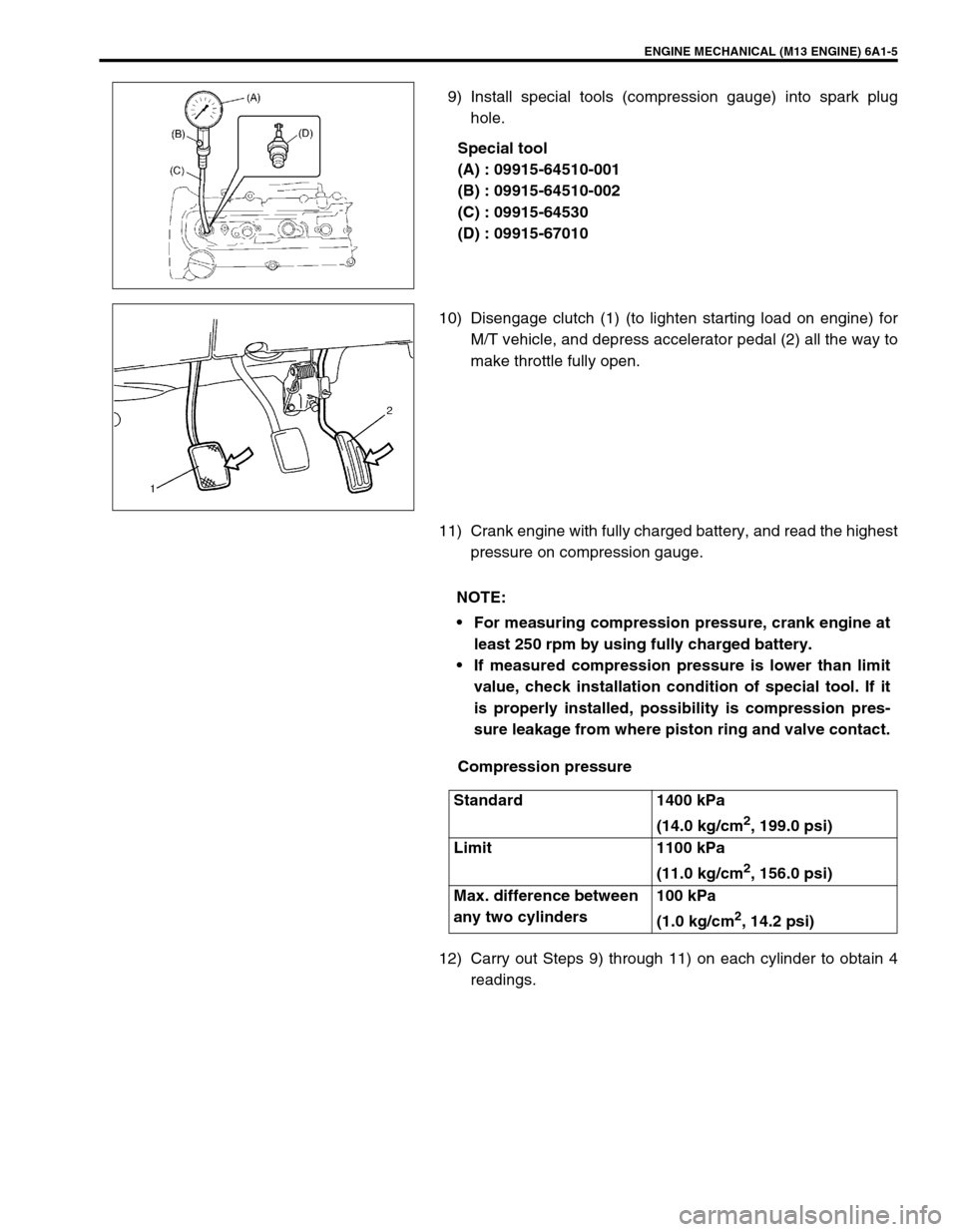
ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE) 6A1-5
9) Install special tools (compression gauge) into spark plug
hole.
Special tool
(A) : 09915-64510-001
(B) : 09915-64510-002
(C) : 09915-64530
(D) : 09915-67010
10) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for
M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator pedal (2) all the way to
make throttle fully open.
11) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest
pressure on compression gauge.
Compression pressure
12) Carry out Steps 9) through 11) on each cylinder to obtain 4
readings.
NOTE:
For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at
least 250 rpm by using fully charged battery.
If measured compression pressure is lower than limit
value, check installation condition of special tool. If it
is properly installed, possibility is compression pres-
sure leakage from where piston ring and valve contact.
Standard 1400 kPa
(14.0 kg/cm
2, 199.0 psi)
Limit 1100 kPa
(11.0 kg/cm
2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between
any two cylinders100 kPa
(1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi)
Page 636 of 698

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6E1-15
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
ACCELERATOR CABLE ADJUSTMENT
With accelerator pedal depressed fully (1), check clearance
between throttle lever (2) and lever stopper (3) (throttle body)
which should be within following specification.
If measured value is out of specification, adjust it to specification
with cable adjusting nut (4).
Accelerator cable adjustment clearance (with pedal
depressed fully)
“a” : 0.5 – 2.0 mm (0.02 – 0.07 in.)
IDLE SPEED/IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) DUTY
INSPECTION
Before idle speed/IAC duty check, make sure of the following.
Lead wires and hoses of Electronic Fuel Injection and engine
emission control systems are connected securely.
Accelerator cable has some play, that is, it is not tight.
Valve lash is checked and adjusted according to mainte-
nance schedule.
Ignition timing is within specification.
All accessories (wipers, heater, lights, A/C, etc.) are out of
service.
Air cleaner has been properly installed and is in good condi-
tion.
No abnormal air inhaling from air intake system.
After above items are all confirmed, check idle speed and IAC
duty as follows.
NOTE:
Before starting engine, place transmission gear shift
lever in “Neutral” (shift selector lever to “P” range for A/T
vehicle), and set parking brake and block drive wheels.
Page 670 of 698

6F1-8 IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM)
IGNITION TIMING
INSPECTION
1) When using SUZUKI scan tool, connect SUZUKI scan tool to
DLC with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A) : 09931-76011 (SUZUKI scan tool)
(B) : Mass storage cartridge
(C) : 09931-76030 (16/14 pin DLC cable)
2) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating tempera-
ture.
3) Make sure that all of electrical loads except ignition are
switched off.
4) Check to be sure that idle speed is within specification.
(Refer to Section 6E1)
5) Fix ignition timing to initial one as follows.
Select “MISC” mode on SUZUKI scan tool and fix ignition
timing to initial one.
If scan tool is not available (vehicle without immobilizer indi-
cator lamp), connect D and E terminals of monitor connector
(1) by using service wire so that ignition timing is fixed on ini-
tial one.
6) Using timing light (1), check that ignition timing is within
specification.
Initial ignition timing (test switch terminal grounded or
fixed with SUZUKI scan tool)
: 5
± 3° BTDC at idle speed
Ignition order
: 1-3-4-2 NOTE:
Ignition timing is not adjustable. If ignition timing is
out of specification, check system related parts.
Before starting engine, place transmission gear shift
lever in “Neutral” (shift selector lever to “P” range for
A/T model), and set parking brake.
(C)
(A)
(B)
D
E1
Page 682 of 698

6H-2 CHARGING SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
BATTERY
The battery has three major functions in the electrical system.
It is a source of electrical energy for cranking the engine.
It acts as a voltage stabilizer for the electrical system.
It can, for a limited time, provide energy when the electrical load exceeds the output of the generator.
CARRIER AND HOLD-DOWN
The battery carrier should be in good condition so that it will support the battery securely and keep it level.
Before installing the battery, the battery carrier and hold-down clamp should be clean and free from corrosion
and make certain there are no parts in carrier.
To prevent the battery from shaking in its carrier, the hold-down bolts should be tight enough but not over-tight-
ened.
ELECTROLYTE FREEZING
The freezing point of electrolyte depends on its specific gravity. Since freezing may ruin a battery, it should be
protected against freezing by keeping it in a fully charged condition. If a battery is frozen accidentally, it should
not be charged until it is warmed.
SULFATION
If the battery is allowed to stand for a long period in discharged condition, the lead sulfate becomes converted
into a hard, crystalline substance, which will not easily turn back to the active material again during the subse-
quent recharging. “Sulfation” means the result as well as the process of that reaction. Such a battery can be
revived by very slow charging and may be restored to usable condition but its capacity is lower than before.
BUILT-IN INDICATOR (IF EQUIPPED)
The battery has a built-in temperature compensated indicator in the top of the battery. This indicator is to be
used with the following diagnostic procedure. When checking the indicator, make sure that the battery has a
clean top. A light may be needed in some poorly-lit areas.
Three types of indication available under normal operation are as
follows.
Green Dot
Battery is sufficiently charged for testing.
Dark
Battery must be charged before testing.
If there is a cranking complaint, battery should be tested as
described in Diagnosis section. Charging and electrical sys-
tems should also be checked at this time.
Clear or Light Yellow
This means that fluid level is below the bottom of hydrome-
ter. Its possible cause is excessive or prolonged charging, a
broken case, excessive tipping or normal battery deteriora-
tion. When the battery is found in such condition, it is possi-
ble that high charging voltage is caused by the faulty
charging system and therefore, charging and electrical sys-
tems need to be checked. If there is a trouble in cranking
and its cause lies in the battery, it should be replaced.
Page 686 of 698

6H-6 CHARGING SYSTEM
GENERATOR
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the fol-
lowing conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or
indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by excessive spewing
of electrolyte from vents.
Noise from generator may be caused by loose drive pulley, loose
mounting bolts, worn or dirty bearings, defective diode, or defec-
tive stator.
CHARGING INDICATOR LAMP OPERATION
CAUTION:
Do not mistake polarities of IG terminal and L terminal.
Do not create short circuit between IG and L terminals.
Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
Do not connect any load between L and E.
When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle
battery, refer to this section describing battery charg-
ing.
B: Generator output (Battery terminal)
D: Dummy terminal
E: Ground
F: Field coil terminal
IG: Ignition terminal
L: Lamp terminal
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON
and engine offFuse blown Check fuse.
Light burned out Replace light.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Check generator.
Poor contact between brush and slip ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires fre-
quent recharging)Drive belt loose or worn Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Check charging system.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.
Page 688 of 698

6H-8 CHARGING SYSTEM
3) Ground F terminal and start engine, then measure voltage at
B terminal as shown in left figure.
Voltage is higher than standard value
It is considered that generator itself is good but IC regulator
has been damaged, replace IC regulator.
Voltage is lower than standard value
Generator itself has problem, check the generator.
LOAD CHECK
1) Run engine at 2,000 rpm and turn on head light and heater
motor.
2) Measure current and if it is less than 20 A repair or replace
generator.
OVERCHARGED BATTERY
1) To determine battery condition, refer to Battery section.
2) If obvious overcharge condition exists as evidenced by
excessive spewing of electrolyte, measure generator B ter-
minal voltage at engine 2000 rpm.
3) If measured voltage is higher than upper limit value, disas-
semble generator.
4) Check ground of brushes. If brushes are not grounded,
replace IC regulator. Then check field coil for grounds and
shorts.
A: Regulated voltage (V)
B: Heatsink temperature (°C)
16.0
15.5
14.2 15.3
14.8
14.2
13.314.8
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
13.0
-30 0 25 135
[A]
[B]
Page 689 of 698
CHARGING SYSTEM 6H-9
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BATTERY
JUMP STARTING IN CASE OF EMERGENCY
WITH AUXILIARY (BOOSTER) BATTERY
Both booster and discharged battery should be treated carefully when using jumper cables. Follow procedure
outlined below, being careful not to cause sparks.
1) Set parking brake and place automatic transmission in PARK (NEUTRAL on manual transmission). Turn off
ignition, turn off lights and all other electrical loads.
2) Check electrolyte level. If it is below low level line, add distilled water.
3) Attach end of one jumper cable to positive terminal of booster battery and the other end of the same cable to
positive terminal of discharged battery. (Use 12-volt battery only to jump start engine).
4) Attach one end of the remaining negative cable to negative terminal of booster battery, and the other end to
a solid engine ground (such as exhaust manifold) at least 45 cm (18 in.) away from battery of vehicle being
started.
5) Start engine of vehicle with booster battery and turn off electrical accessories. Then Start engine of the vehi-
cle with discharged battery.
6) Disconnect jumper cables in the exact reverse order.
WITH CHARGING EQUIPMENT
CAUTION:
If vehicle is manual transmission model and has a catalytic converter, do not push or tow it to start.
Damage to its emission system and/or to other parts may result.
WARNING:
Departure from these conditions or procedure described below could result in:
–Serious personal injury (particularly to eyes) or property damage from such causes as battery
explosion, battery acid, or electrical burns.
–Damage to electronic components of either vehicle.
Remove rings, watches, and other jewelry. Wear approved eye protection.
Be careful so that metal tools or jumper cables do not contact positive battery terminal (or metal in
contact with it) and any other metal on vehicle, because a short circuit could occur.
WARNING:
Do not connect negative cable directly to negative terminal of dead battery.
CAUTION:
When jump starting engine with charging equipment, be sure equipment used is 12-volt and negative
ground. Do not use 24-volt charging equipment. Using such equipment can cause serious damage to
electrical system or electronic parts.