2000 SUZUKI SWIFT Air Condition
[x] Cancel search: Air ConditionPage 341 of 698
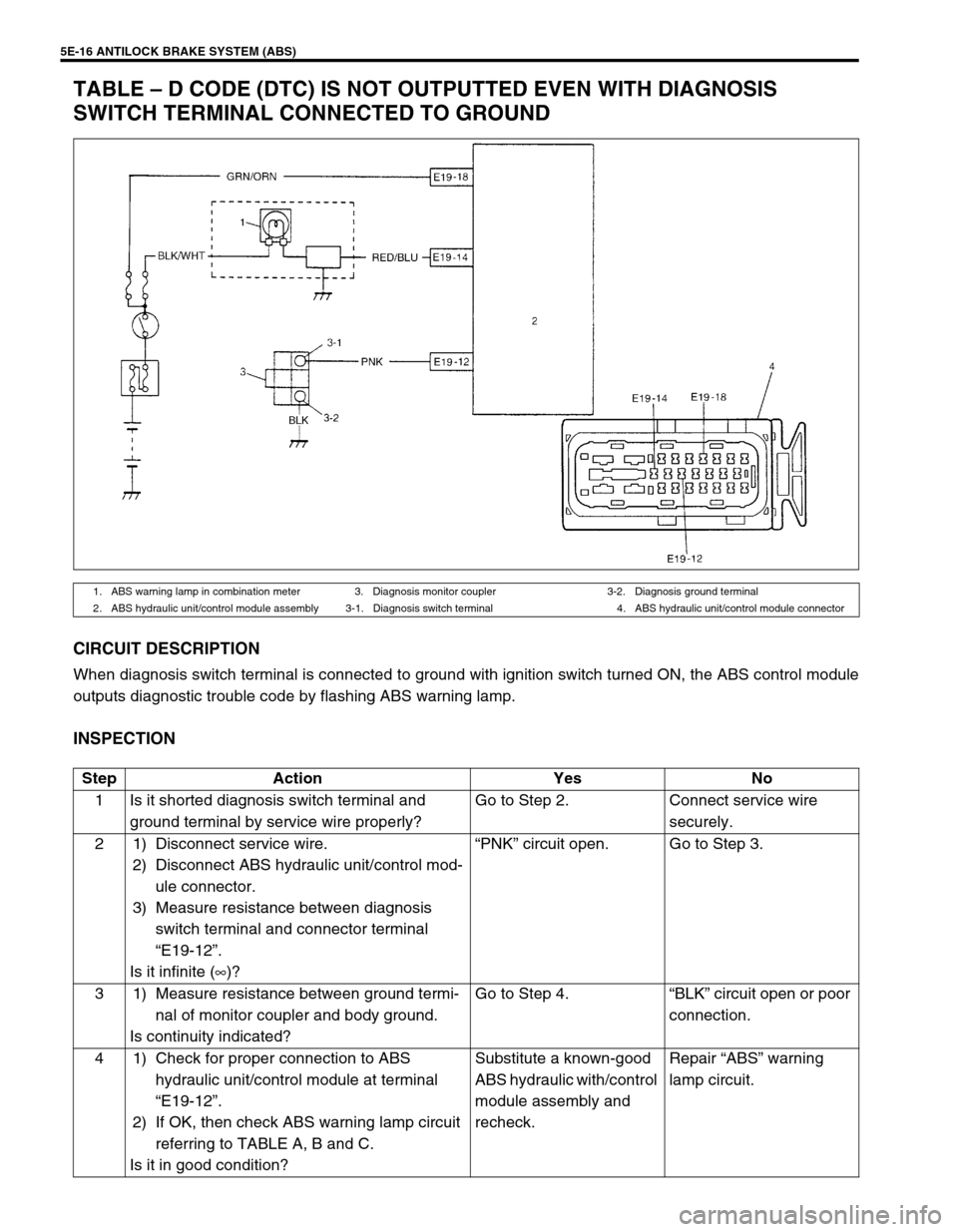
5E-16 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
TABLE – D CODE (DTC) IS NOT OUTPUTTED EVEN WITH DIAGNOSIS
SWITCH TERMINAL CONNECTED TO GROUND
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When diagnosis switch terminal is connected to ground with ignition switch turned ON, the ABS control module
outputs diagnostic trouble code by flashing ABS warning lamp.
INSPECTION
1. ABS warning lamp in combination meter 3. Diagnosis monitor coupler 3-2. Diagnosis ground terminal
2. ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly 3-1. Diagnosis switch terminal 4. ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector
Step Action Yes No
1 Is it shorted diagnosis switch terminal and
ground terminal by service wire properly?Go to Step 2. Connect service wire
securely.
2 1) Disconnect service wire.
2) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit/control mod-
ule connector.
3) Measure resistance between diagnosis
switch terminal and connector terminal
“E19-12”.
Is it infinite (∞)?“PNK” circuit open. Go to Step 3.
3 1) Measure resistance between ground termi-
nal of monitor coupler and body ground.
Is continuity indicated?Go to Step 4.“BLK” circuit open or poor
connection.
4 1) Check for proper connection to ABS
hydraulic unit/control module at terminal
“E19-12”.
2) If OK, then check ABS warning lamp circuit
referring to TABLE A, B and C.
Is it in good condition?Substitute a known-good
ABS hydraulic with/control
module assembly and
recheck.Repair “ABS” warning
lamp circuit.
Page 349 of 698

5E-24 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
DTC C1021 (DTC 21), DTC C1022 (DTC 22) – RIGHT-FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR CIRCUIT OR SENSOR RING
DTC C1025 (DTC 25), DTC C1026 (DTC 26) – LEFT-FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR CIRCUIT OR SENSOR RING
DTC C1031 (DTC 31), DTC C1032 (DTC 32) – RIGHT-REAR WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR CIRCUIT OR SENSOR RING
DTC C1035 (DTC 35), DTC C1036 (DTC 36) – LEFT-REAR WHEEL SPEED SEN-
SOR CIRCUIT OR SENSOR RING
DESCRIPTION
The ABS control module monitors the voltage at the terminal of each sensor while the ignition switch is ON.
When the voltage is not within the specified range, an applicable DTC will be set. Also, when no sensor signal is
inputted at starting or while running, an applicable DTC will be set.
1. Ignition switch 4. Right-front wheel speed sensor 7. ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector
2. ABS control module/hydraulic unit assembly 5. Left-rear wheel speed sensor
3. Left-front wheel speed sensor 6. Right-rear wheel speed sensor
NOTE:
When the vehicle was operated in any of the following ways, one of these DTCs may be set even when
the sensor is in good condition. If such possibility is suspected, repair the trouble (dragging of brake,
etc.) of the vehicle, clear DTC once and then after performing the driving test as described in Step 2 of
“ABS DIAGNOSIS FLOW TABLE”, check whether or not any abnormality exists.
The vehicle was driven with parking brake pulled.
The vehicle was driven with brake dragging.
Wheel spin occurred while driving.
Wheel(s) was turned while the vehicle was jacked up.
The vehicle was stuck.
Page 350 of 698

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-25
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1 1) Disconnect applicable ABS wheel speed sensor coupler
with ignition switch OFF.
2) Measure resistance between terminals of ABS wheel
speed sensor. Refer to “FRONT WHEEL SPEED SEN-
SOR” and/or “REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR” in this
section.
Is measured resistance value as specified?Go to Step 2. Replace ABS wheel
speed sensor
assembly.
2 1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit/control module connec-
tor.
3) Check for proper connection to ABS control module at
each sensor terminal.
4) If OK, then turn ignition switch ON and measure voltage
between sensor terminal of module connector and body
ground.
Is it 0V?Go to Step 3. ABS wheel speed
sensor circuit
shorted to power.
3 1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Connect ABS wheel speed sensor coupler.
3) Measure resistance between the following points.
Both ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector termi-
nals of the corresponding sensor.
This check result should be the same as above Step 1.
Either terminal of wheel speed sensor coupler and body
ground.
This check result should be no continuity.
Are both check results OK?Go to Step 4. Circuit open or
shorted to ground.
4 1) Remove applicable ABS wheel speed sensor.
2) Check sensor for damage or foreign material attached.
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 5. Clean, repair or
replace.
5 Check front and/or rear sensor ring for the following
(remove rear drum as necessary) :
Rotor serration (teeth) neither missing nor damaged.
No foreign material being attached.
Rotor not being eccentric.
Wheel bearing free from excessive play.
Are they in good condition?Go to Step 6. Clean, repair or
replace.
6 1) Install ABS wheel speed sensor to knuckle.
2) Tighten sensor bolt to specified torque and check that
there is no clearance between sensor and knuckle.
Is it OK?Go to Step 7. Replace ABS wheel
speed sensor.
7 Referring to “Reference” of “FRONT WHEEL SPEED SEN-
SOR” and/or “Reference” of “REAR WHEEL SPEED SEN-
SOR” in this section, check output voltage or waveform.
Is specified voltage and/or waveform obtained?Substitute a known-
good ABS hydrau-
lic unit/control mod-
ule assembly and
recheck.Replace sensor and
recheck.
Page 354 of 698

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-29
DTC C1063 (DTC 63) – ABS FAIL-SAFE RELAY CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTION
ABS control module monitors the voltage at the terminal of solenoid circuit constantly with ignition switch turned
ON. Also, immediately after ignition switch is turned ON, perform initial check as follows.
Switch fail-safe relay in the order of OFF → ON and check if voltage changes to Low → High. If anything faulty
is found in the initial check and when the voltage is low with ignition switch turned ON, this DTC will be set.
INSPECTION
1. Ignition switch 3. ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector 5. To pump motor relay
2. ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly 4. To solenoid valves 6. Fail-safe relay
Step Action Yes No
1 Check battery voltage. Is it about 11 V or
higher?Go to Step 2. Check charging system
referring to “CHARGING
SYSTEM” section.
2 Check ABS main fuse and connection.
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 3. Repair and/or replace
fuse.
3 1) Ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit/control mod-
ule connector.
3) Check proper connection to ABS hydraulic
unit/control module at terminal “E19-25”.
4) If OK, then measure voltage between con-
nector terminal “E19-25” and body ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V?Substitute a known-good
ABS hydraulic unit/con-
trol module assembly and
recheck.“WHT/BLU” circuit open
or short to ground.
Page 357 of 698

5E-32 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
7) With diagnosis switch terminal (1) of monitor coupler (2) con-
nected to ground terminal (3) using service wire (4), turn
ignition switch ON and check if ABS warning lamp indicates
DTC 12.
If malfunction DTC is indicated, repair it first.
8) Turn ignition switch OFF.
9) Perform the following checks with help of another person.
Brake pedal (1) should be depressed and then ignition
switch (2) turned ON by one person and wheel (3) should be
turned by another person’s hand. At this time, check that :
Operation sound of solenoid is heard and wheel turns only
about 0.5 sec. (Brake force is depressurized).
Operation sound of pump motor is heard and pulsation is felt
at brake pedal.
10) If all 4-wheels cannot be checked during one ignition cycle
(OFF → ON), repeat Steps 8) and 9) till all 4 wheels are
checked.
If a faulty condition is found in Steps 9) and 10), replace
hydraulic unit/control module assembly.
11) Turn ignition switch OFF and remove service wire from mon-
itor coupler.
3 22
1
4
Page 370 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-1
6
6F2
6G
6H
6K
7A
7A1
7B1
7C1
7D
7E
7F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
9
10A
10B
SECTION 6
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND
DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND ENGINE DIAGNOSIS................................................. Section 6
ENGINE MECHANICAL ................................................................................................................. Section 6A1
ENGINE COOLING......................................................................................................................... Section 6B
ENGINE FUEL ................................................................................................................................ Section 6C
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM ............................................................................ Section 6E1
IGNITION SYSTEM ........................................................................................................................ Section 6F1
CRANKING SYSTEM ..................................................................................................................... Section 6G
CHARGING SYSTEM ..................................................................................................................... Section 6H
EXHAUST SYSTEM ....................................................................................................................... Secton 6K
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION ................................ 6-4
STATEMENT ON CLEANLINESS AND
CARE .............................................................. 6-4
GENERAL INFORMATION ON ENGINE
SERVICE ........................................................ 6-4PRECAUTION ON FUEL SYSTEM
SERVICE .................................................... 6-5
FUEL PRESSURE RELIEF
PROCEDURE ............................................. 6-6
FUEL LEAKAGE CHECK PROCEDURE.... 6-6 WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System :
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
NOTE:
Whether the following systems (parts) are used in the particular vehicle or not depends on vehicle
specifications. Be sure to bear this in mind when performing service work.
EGR valve
Heated oxygen sensor(s) or CO adjusting resistor
Three way catalytic converter
Immobilizer indicator lamp (vehicle with immobilizer indicator lamp can be identified also by HO2S-
2)
Knock sensor
Page 377 of 698

6-8 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
FREEZE FRAME DATA
ECM stores the engine and driving conditions (in the from of data
as shown in the figure) at the moment of the detection of a mal-
function in its memory. This data is called “Freeze frame data”.
Therefore, it is possible to know engine and driving conditions
(e.g., whether the engine was warm or not, whether the vehicle
was running or stopped, whether air/fuel mixture was lean or rich)
when a malfunction was detected by checking the freeze frame
data. Also, ECM has a function to store each freeze frame data
for three different malfunctions in the order as the malfunction is
detected. Utilizing this function, it is possible to know the order of
malfunctions that have been detected. Its use is helpful when
rechecking or diagnosing a trouble.
Priority of freeze frame data :
ECM has 4 frames where the freeze frame data can be stored.
The first frame stores the freeze frame data of the malfunction
which was detected first. However, the freeze frame data stored
in this frame is updated according to the priority described below.
(If malfunction as described in the upper square “1” below is
detected while the freeze frame data in the lower square “2” has
been stored, the freeze frame data “2” will be updated by the
freeze frame data “1”.)
In the 2nd through the 4th frames, the freeze frame data of each
malfunction is stored in the order as the malfunction is detected.
These data are not updated.
Shown in the table below are examples of how freeze frame data
are stored when two or more malfunctions are detected.
[A] : An Example of Freeze Frame Data
[B] : 1st, 2nd or 3rd in parentheses here represents which position in the order
the malfunction is detected.
PRIORITY FREEZE FRAME DATA IN FRAME 1
1 Freeze frame data at initial detection of mal-
function among misfire detected (P0300-
P0304), fuel system too lean (P0171) and fuel
system too rich (P0172)
2 Freeze frame data when a malfunction other
than those in “1” above is detected
Page 380 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-11
DATA LINK CONNECTOR (DLC)
ELC (1) is in compliance with SAEJ1962 in its installation posi-
tion, the shape of connector and pin assignment.
Serial data line (K line of ISO 9141) is used for SUZUKI scan tool
(Tech-1) to communicate with ECM, TCM, ABS control module
and Air bag SDM.
SUZUKI serial data line is used for SUZUKI scan tool (Tech -1) to
communicate with immobilizer control module.
PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE
Do not disconnect couplers from ECM, battery cable from battery, ECM ground wire harness from engine or
main fuse before confirming diagnostic information (DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in ECM memory.
Such disconnection will erase memorized information in ECM memory.
Diagnostic information stored in ECM memory can be cleared as well as checked by using SUZUKI scan
tool (Tech-1) or generic scan tool (Vehicle with immobilizer indicator lamp). Before using scan tool, read its
Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have good understanding as to what functions are available and
how to use it.
Priorities for diagnosing troubles (Vehicle with immobilizer indicator lamp).
If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the flow table of the DTC which has detected earliest in the order
(it can be identified by referring to freeze frame data) and follow the instruction in that table.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot diagnostic trouble codes according to the following priorities.
–Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) other than DTC P0171/P0172 (Fuel system too lean/too rich), DTC
P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304 (Misfire detected) and DTC P0400 (EGR flow malfunction)
–DTC P0171/P0172 (Fuel system too lean/too rich) and DTC P0400 (EGR flow malfunction)
–DTC P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304 (Misfire detected)
Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service” in Section 0A before inspection and observe what
is written there.
ECM Replacement
When substituting a known-good ECM, check for following conditions. Neglecting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
–Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as specified respectively.
–MAP sensor and TP sensor are in good condition and none of power circuits of these sensors is shorted
to ground.AMBIENT
TEMPERATURETIME TO CUT POWER TO ECM
Over 0°C (32°F) 60 sec. or longer
Under 0°C (32°F) Not specifiable. Select a place with
temperature higher than 0°C (32°F).
2. B+
3. Serial data line (K line of ISO 9141)
4. ECM ground
5. Body ground
6. SUZUKI serial data line
2
3456
1