2000 FORD WINDSTAR lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 131 of 280
Always transport children 12 years old and under in the back
seat and always properly use appropriate child restraints.
Combination lap and shoulder belts
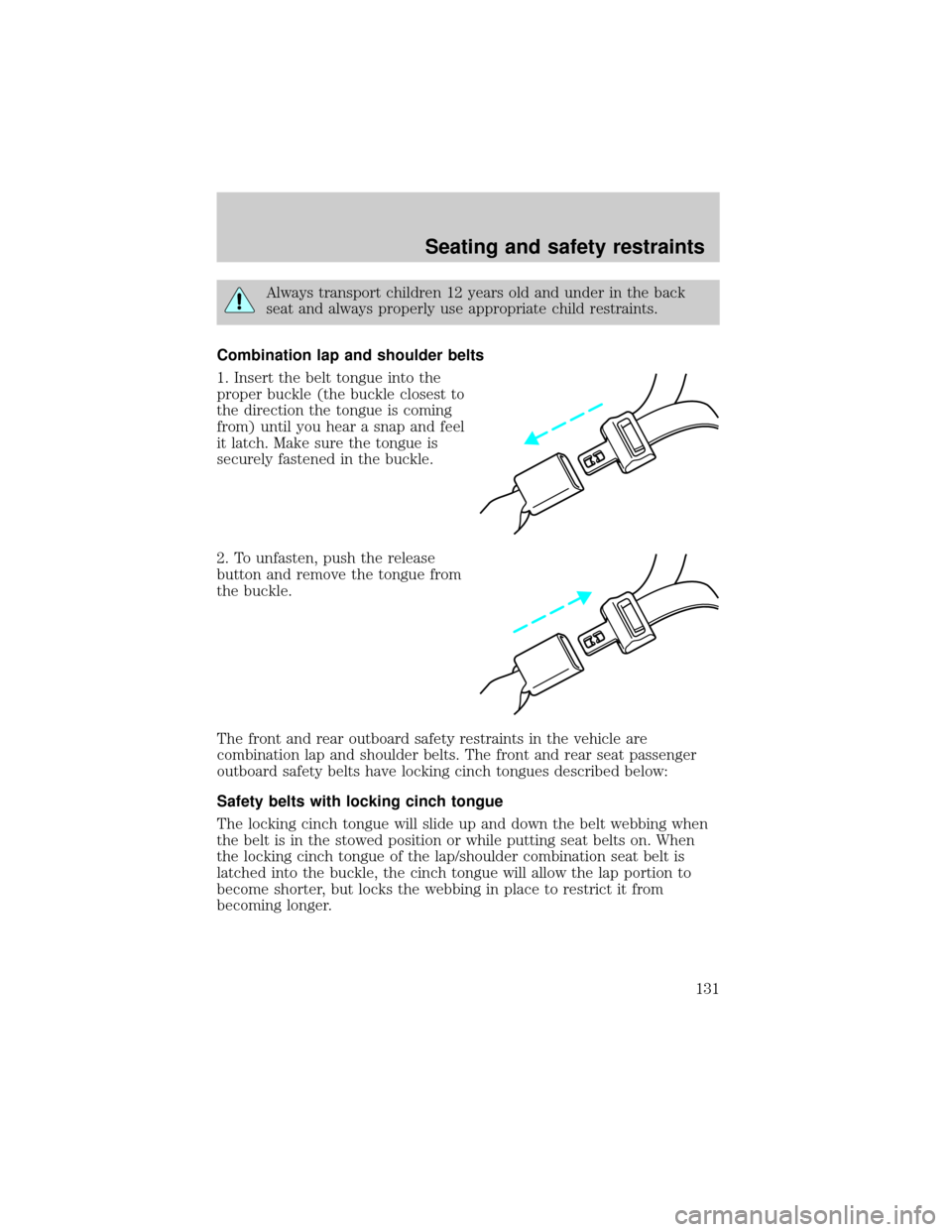
1. Insert the belt tongue into the
proper buckle (the buckle closest to
the direction the tongue is coming
from) until you hear a snap and feel
it latch. Make sure the tongue is
securely fastened in the buckle.
2. To unfasten, push the release
button and remove the tongue from
the buckle.
The front and rear outboard safety restraints in the vehicle are
combination lap and shoulder belts. The front and rear seat passenger
outboard safety belts have locking cinch tongues described below:
Safety belts with locking cinch tongue
The locking cinch tongue will slide up and down the belt webbing when
the belt is in the stowed position or while putting seat belts on. When
the locking cinch tongue of the lap/shoulder combination seat belt is
latched into the buckle, the cinch tongue will allow the lap portion to
become shorter, but locks the webbing in place to restrict it from
becoming longer.
Seating and safety restraints
131
Page 133 of 280

Each seating position in your vehicle has a specific safety belt
assembly which is made up of one buckle and one tongue that
are designed to be used as a pair. 1) Use the shoulder belt on the
outside shoulder only. Never wear the shoulder belt under the arm.
2) Never swing the safety belt around your neck over the inside
shoulder. 3) Never use a single belt for more than one person.
While you are fastened in the seat belt, the combination lap/shoulder belt
with a cinch tongue adjusts to your movement. However, if you brake
hard, turn hard, or if your vehicle receives an impact of 8 km/h (5 mph)
or more, the safety belt will become locked and help reduce your
forward movement.
Energy Management Feature
²This vehicle has a seat belt system with an energy management
feature at the driver seating position and second row bench seat belt
assemblies adjacent to a sliding door to help further reduce the risk of
injury in the event of a head-on collision.
²This seat belt system has a retractor assembly that is designed to pay
out webbing in a controlled manner. This feature is designed to help
reduce the belt force acting on the occupant's chest.
Failure to replace the Belt and Retractor assembly could
increase the risk of injury in collisions.
Seating and safety restraints
133
Page 135 of 280

Safety belt height adjustment
Your vehicle has safety belt height
adjustments for the driver, front
passenger and second row
passengers. Adjust the height of the
shoulder belt so the belt rests
across the middle of your shoulder.
To lower the shoulder belt height,
push the button and slide the height
adjuster down. To raise the height
of the shoulder belt, slide the height
adjuster up. Pull down on the height
adjuster to make sure it is locked in place.
Position the shoulder belt height adjusters so that the belt rests
across the middle of your shoulder. Failure to adjust the safety
belt properly could reduce the effectiveness of the seat belt and
increase the risk of injury in a collision.
Safety belt extension assembly
If the safety belt assembly is too short, even when fully extended, 20 cm
(8 inches) can be added to the safety belt assembly by adding a safety
belt extension assembly (part number 611C22). Safety belt extension
assemblies can be obtained from your dealer at no cost.
Use only extensions manufactured by the same supplier as the safety
belt. Manufacturer identification is located at the end of the webbing on
the label. Also, use the safety belt extension only if the safety belt is too
short for you when fully extended. Do not use extensions to change the
fit of the shoulder belt across the torso.
Safety belt warning light and indicator chime
The seat belt warning light illuminates in the instrument cluster and a
chime sounds to remind the occupants to fasten their safety belts.
Seating and safety restraints
135
Page 163 of 280

STARTING THE ENGINE
1. Turn the key to 5 (START)
without pressing the accelerator
pedal and release as soon as the
engine starts. The key will return to
4 (ON).
2. If the temperature is above ±12ÉC
(10ÉF) and the engine does not
start within five seconds on the first
try, turn the key to OFF, wait 10
seconds and try again.
3. If the temperature is below -12É C (10É F) and the engine does not
start in 15 seconds on the first try, turn the key OFF and wait 10
seconds and try again. If the engine does not start in two attempts, Press
the accelerator pedal all the way to floor and hold. Turn the key to
START position.
4. When the engine starts, release the key, then release the accelerator
pedal gradually as the engine speeds up.
5. After idling for a few seconds, apply the brake and release the parking
brake.
Using the engine block heater (if equipped)
An engine block heater warms the engine coolant, which improves
starting, warms up the engine faster and allows the heater-defroster
system to respond quickly. Use of an engine block heater is strongly
recommended if you live in a region where temperatures reach -23ÉC
(-10ÉF) or below.
For best results, plug the heater in at least three hours before starting
the vehicle. Using the heater for longer than three hours will not harm
the engine, so the heater can be plugged in the night before starting the
vehicle.
To prevent electrical shock, do not use your heater with
ungrounded electrical systems or two-pronged (cheater)
adapters.
3
2
1
5
4
Starting
163
Page 165 of 280
BRAKES
Your service brakes are self-adjusting. Refer to the scheduled
maintenance guide for scheduled maintenance.
Occasional brake noise is normal and often does not indicate a
performance concern with the vehicle's brake system. In normal
operation, automotive brake systems may emit occasional or intermittent
squeal or groan noises when the brakes are applied. Such noises are
usually heard during the first few brake applications in the morning;
however, they may be heard at any time while braking and can be
aggravated by environmental conditions such as cold, heat, moisture,
road dust, salt or mud. If a ªmetal-to-metal,º ªcontinuous grindingº or
ªcontinuous squealº sound is present while braking, the brake linings
may be worn-out and should be inspected by a qualified service
technician.
Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
On vehicles equipped with an anti-lock braking system (ABS), a noise
from the hydraulic pump motor and pulsation in the pedal may be
observed during ABS braking events. Pedal pulsation coupled with noise
while braking under panic conditions or on loose gravel, bumps, wet or
snowy roads is normal and indicates proper functioning of the vehicle's
anti-lock brake system. The ABS performs a self-check after you start
the engine and begin to drive away. A brief mechanical noise may be
heard during this test. This is normal. If a malfunction is found, the ABS
warning light will come on. If the vehicle has continuous vibration or
shudder in the steering wheel while braking, the vehicle should be
inspected by a qualified service technician.
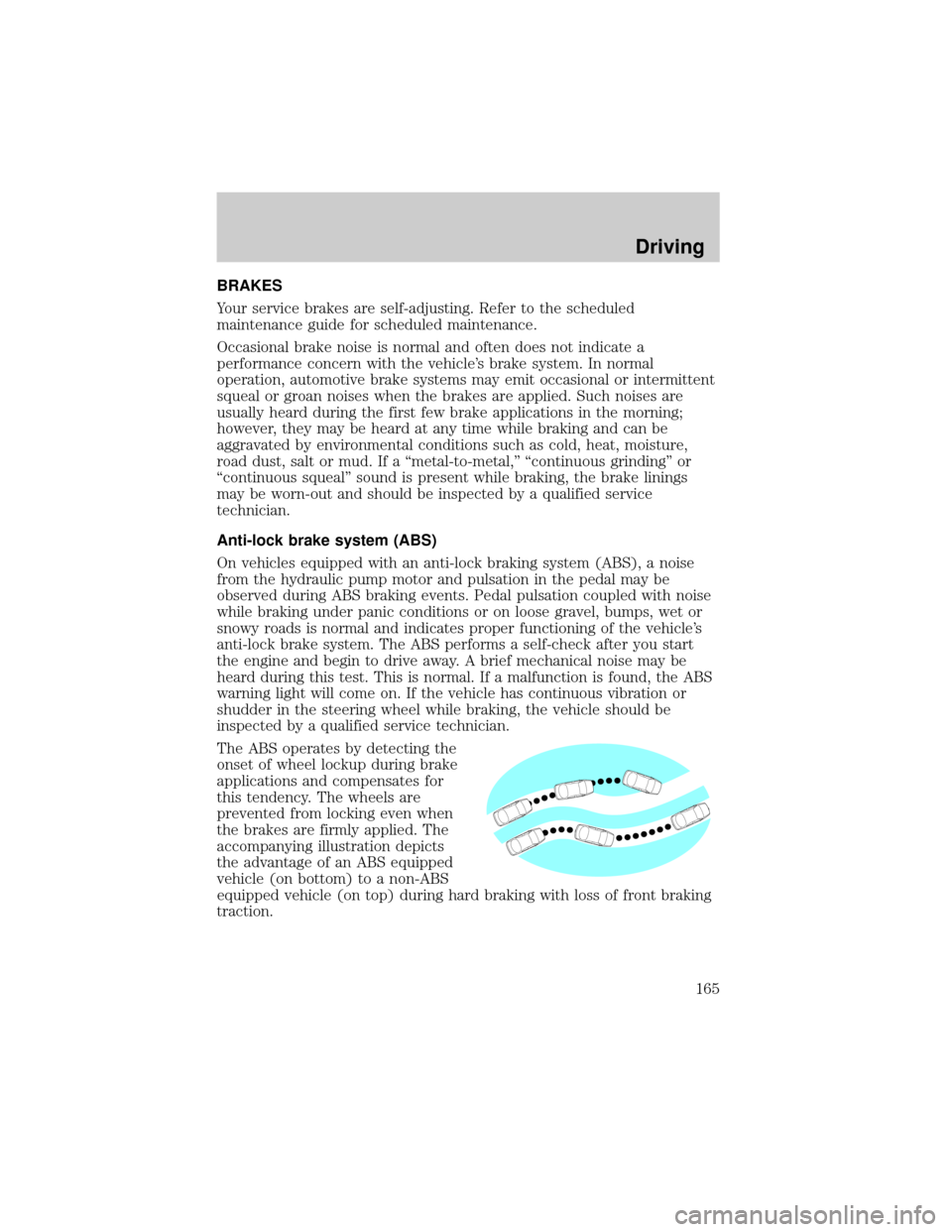
The ABS operates by detecting the
onset of wheel lockup during brake
applications and compensates for
this tendency. The wheels are
prevented from locking even when
the brakes are firmly applied. The
accompanying illustration depicts
the advantage of an ABS equipped
vehicle (on bottom) to a non-ABS
equipped vehicle (on top) during hard braking with loss of front braking
traction.
Driving
165
Page 166 of 280
ABS warning lampABS
TheABSwarning lamp in the instrument cluster momentarily illuminates
when the ignition is turned to the ON position. If the light does not
illuminate momentarily at start up or remains on the ABS needs to be
serviced.
With the ABS light on, the anti-lock
brake system is disabled and normal
braking is still effective unless the
brake warning light also remains
illuminated with parking brake released. (If your brake warning lamp
illuminates, have your vehicle serviced immediately.)
Using ABS
²In an emergency or when maximum efficiency from the ABS is
required, apply continuous force on the brake. The ABS will be
activated immediately, thus allowing you to retain full steering control
of your vehicle and, providing there is sufficient space, will enable you
to avoid obstacles and bring the vehicle to a controlled stop.
²The Anti-Lock system does not decrease the time necessary to apply
the brakes or always reduce stopping distance. Always leave enough
room between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you to stop.
²We recommend that you familiarize yourself with this braking
technique. However, avoid taking any unnecessary risks.
Parking brake
Apply the parking brake whenever
the vehicle is parked. To set the
parking brake, pull the handle up as
far as possible.
The BRAKE warning lamp in the
instrument cluster illuminates and
remains illuminated (when the
ignition is turned ON) until the
parking brake is released.
!
BRAKE
!
BRAKE
Driving
166
Page 167 of 280

The parking brake is not recommended to stop a moving vehicle.
However, if the normal brakes fail, the parking brake can be used to stop
your vehicle in an emergency. Since the parking brake applies only the
rear brakes, the vehicle's stopping distance will increase greatly and the
handling of your vehicle will be adversely affected.
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure that the
gearshift is securely latched in P (Park) (automatic transaxle).
Push the button on the end of the
parking brake and push the handle
down as far as possible to release
the brake. Driving with the parking
brake on will cause the brakes to
wear out quickly and reduce fuel
economy.
TRACTION CONTROLY(IF EQUIPPED)
Traction Controlyhelps the driver maintain the stability and steerability
of the vehicle. It is especially useful on slippery and/or hilly road
surfaces. The system operates by detecting and controlling wheel spin.
The system borrows many of the electronic and mechanical elements
already present in the anti-lock braking system (ABS).
Wheel-speed sensors allow excess front wheel spin to be detected by the
Traction Controlyportion of the ABS computer. The system limits front
wheel spin by automatically applying and releasing the front brakes in
conjunction with engine torque reductions. Engine torque reduction is
realized via the fully electronic spark and fuel injection systems. This
process is very sensitive to driving conditions and very fast acting. The
front wheels ªsearchº for optimum traction several times a second and
adjustments are made accordingly.
The Traction Controlysystem will assist you in making better use of
available traction on slippery surfaces. The system is a driver aid which
makes your vehicle easier to handle primarily on snow and ice covered
roads.
During Traction Controlyoperation, TRACTION CONTROL OK is
displayed on the message center (if equipped). You may hear an electric
Driving
167
Page 168 of 280

motor type of sound coming from the engine compartment and the
engine will not ªrev-upº when you push further on the accelerator. This
is normal system behavior.
If you should become stuck in snow or on a very slippery road surface,
try switching the Traction Controlysystem off with the traction control
switch located on the left hand side of the radio. This may allow excess
wheel spin to ªdigº the vehicle out or enable a successful ªrockingº
maneuver.
If the Traction Controlysystem is cycled excessively, the brake portion
of the system will shut down to prevent the front brakes from
overheating. A limited Traction Controlyfunction using only engine
torque reduction will still control wheels from over-spinning. When the
front brakes have cooled down, the system will again function normally.
Anti-lock braking is not affected by this condition and will function
normally during the cool down period.
If a system fault is detected, CHECK TRACTION CONTROL is displayed
on the message center, the ªTC OFFº warning indicator lamp is on and
your vehicle should be serviced.
STEERING
Your vehicle is equipped with power steering. Power steering uses energy
from the engine to help steer the vehicle.
To prevent damage to the power steering pump:
²Never hold the steering wheel to the extreme right or the extreme left
for more than a few seconds when the engine is running.
²Do not operate the vehicle with a low power steering pump fluid level.
If the power steering system breaks down (or if the engine is turned
off), you can steer the vehicle manually, but it takes more effort.
If the steering wanders or pulls, the condition could be caused by any of
the following:
²underinflated tire(s) on any wheel(s)
²high crown in center of road
²high crosswinds
²wheels out of alignment
²loose or worn components in steering linkage
Driving
168