1999 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY power steering
[x] Cancel search: power steeringPage 17 of 1529

CONTENTS
14 CONTENTS
STEERING ................................................................................................ 57-1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Steering system component layout................................................................................................. 57-1
Steering column assembly and intermediate shaft ......................................................................... 57-2
Steering box.................................................................................................................................... 57-4
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 57-5
Operation ........................................................................................................................................ 57-16
ADJUSTMENTS
Steering box - check and adjust ..................................................................................................... 57-17
Hydraulic system - bleed ................................................................................................................ 57-18
Steering linkage - centralise ......................................................................................................... 57-18
Wheel alignment - front ................................................................................................................. 57-19
Power steering pressure check - diesel models ............................................................................. 57-20
Power steering pressure check - V8 LHD models .......................................................................... 57-22
Power steering pressure check - V8 RHD models ......................................................................... 57-24
REPAIRS
Power steering box - V8 ................................................................................................................. 57-27
Power steering box - LHD - diesel .................................................................................................. 57-30
Steering box - RHD - diesel ............................................................................................................ 57-34
Seal - input shaft - steering box ..................................................................................................... 57-37
Seal - output shaft - steering box ................................................................................................... 57-38
Pump - power steering - V8 ............................................................................................................ 57-39
Pump - power steering - diesel ....................................................................................................... 57-42
Steering column assembly and lock ............................................................................................... 57-43
Shaft - intermediate and universal joint - steering column ............................................................ 57-45
Nacelle - steering column ............................................................................................................... 57-47
Drop arm - steering box ................................................................................................................ 57-47
Ball joint - track rod ....................................................................................................................... 57-48
Ball joint - drag link ....................................................................................................................... 57-49
Drag link ........................................................................................................................................ 57-50
Damper - steering ......................................................................................................................... 57-51
Steering wheel ............................................................................................................................... 57-52
Page 35 of 1529

INTRODUCTION
01-4
λLambda
lc Low compression
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
LH Left-Hand
LHD Left-Hand Drive
LVS Liquid Vapour Separator
mMetre
µMicro
MAF Mass Air Flow
MAP Manifold Absolute Pressure
MFU Multi-Function Unit
MFL Multi-Function Logic
max. Maximum
MEMS Modular Engine Management
System
MIL Malfunction Indicator Lamp
min. Minimum
MPa MegaPascal
- Minus (tolerance)
' Minute (angle)
mm Millimetre
mph Miles per hour
MPi Multi-Point injection
MY Model Year
NAS North American Specification
(-) Negative (electrical)
Nm Newton metre
No. Number
NO
2Nitrogen Dioxide
NO
xOxides of Nitrogen
NTC Negative Temperature
Coefficient
OBD On Board Diagnostics
o.dia. Outside diameter
ORM Off-road Mode
ΩOhm
PAS Power Assisted Steering
PCV Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PDC Parking Distance Control
% Percentage
+ Plus (tolerance) or Positive
(electrical)
±Plus or minus (tolerance)
PTC Positive Temperature Coefficient
PTFE Polytetrafluorethylene
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
rRadius
:Ratio
ref Reference
RES Rover Engineering Standards
rev/min Revolutions per minute
RF Radio Frequency
RH Right-Hand
RHD Right-Hand Drive
ROM Read Only Memory
RON Research Octane Number
ROV Roll Over ValveROW Rest Of World
SAE Society of Automotive Engineers
" Second (angle)
SLABS Self Levelling and Anti-Lock
Brake System
SLS Self Levelling Suspension
SOHC Single Overhead Camshaft
sp.gr Specific gravity
SRS Supplementary Restraint System
std. Standard
synchro Synchronizer or synchromesh
TDC Top Dead Centre
TMAP Temperature, Manifold Absolute
Pressure
TP Throttle Position
TPS Throttle Position Sensor
TV Torsional Vibration
TXV Thermostatic Expansion Valve
UK United Kingdom
US United States
V Volt
Var. Variable
VIN Vehicle Identification Number
VIS Variable Intake System
VRS Variable Reluctance Sensor
VSS Vehicle Speed Signal
WWatt
Page 48 of 1529

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-13
Self-locking nuts
Self-locking nuts, i.e. nylon insert or deferred thread
nuts can be re-used providing resistance can be felt
when the locking portion of the nut passes over the
thread of the bolt or stud.
Where self-locking nuts have been removed, it is
advisable to replace them with new ones of the same
type.
Flexible Pipes and Hoses
General
When removing and installing flexible hydraulic pipes
and hoses, ensure that the following practices are
observed to ensure component serviceability.
lBefore removing any brake or power steering
hose, clean end fittings and area surrounding
them as thoroughly as possible.
lObtain appropriate plugs or caps before
detaching hose end fittings, so that the ports can
be immediately covered to prevent the ingress
of dirt.
lClean hose externally and blow through with
airline. Examine carefully for cracks, separation
of plies, security of end fittings and external
damage. Reject any faulty hoses.
lWhen refitting a hose, ensure that no
unnecessary bends are introduced, and that
hose is not twisted before or during tightening of
union nuts.
lFit a cap to seal a hydraulic union and a plug to
its socket after removal to prevent ingress of
dirt.
lAbsolute cleanliness must be observed with
hydraulic components at all times.
lAfter any work on hydraulic systems, carefully
inspect for leaks underneath the vehicle while a
second operator applies maximum brake
pressure to the brakes (engine running) and
operates the steering.
Page 115 of 1529

LIFTING AND TOWING
08-2
Before commencing work on underside of vehicle re-
check security of vehicle on stands.
WARNING: Always chock the wheels when
jacking. The hand brake acts on the the
transmission, not the rear wheels, and may be
ineffective when the wheels are off the ground.
Reverse procedure when removing vehicle from
stands.
Hydraulic ramps
Use only a 'drive on' type ramp which supports a
vehicle by it's own road wheels. If a 'wheel free'
condition is required, use a 'drive on' ramp
incorporating a 'wheel free' system that supports
under axle casings. Alternatively, place vehicle on a
firm, flat floor and support on axle stands.
TOWING
Towing
The vehicle has permanent four wheel drive. The
following towing instructions must be adhered
to:
Towing on 4 wheels with driver
Turn ignition key to position '1' to release steering
lock.
Select neutral in main gearbox and transfer gearbox.
Secure tow rope, chain or cable to towing eye.
Release the handbrake.
The brake servo and power assisted steering
system will not be functional without the engine
running. Greater pedal pressure will be required
to apply the brakes, the steering system will
require greater effort to turn the front road
wheels. The vehicle tow connection should be
used only in normal road conditions, 'snatch'
recovery should be avoided.
Suspended tow
To prevent vehicle damage, front or rear
propeller shaft MUST BE removed, dependent
upon which axle is being trailed.
Mark propeller shaft drive flanges at transfer box and
axles with identification lines to enable the propeller
shaft to be refitted in its original position.
Page 119 of 1529

CAPACITIES, FLUIDS, LUBRICANTS AND SEALANTS
09-2
Fluids
Anti-freeze
Use Havoline Extended Life Coolant (XLC), or any
ethylene glycol based anti-freeze (containing no
methanol) with only Organic Acid Technology (OAT)
corrosion inhibitors, to protect the cooling system
CAUTION: No other anti-freeze should be used
with Havoline Extended Life Coolant.
The cooling system should be drained, flushed and
refilled with the correct amount of anti-freeze solution
at the intervals given on the Service Maintenance
Check Sheet.
After filling with anti-freeze solution, attach a warning
label to a prominent position on the vehicle stating
the type of anti-freeze contained in the cooling
system to ensure that the correct type is used for
topping-up.
Brake/Clutch fluid
Use only DOT 4 brake fluid.
PAS fluid
Use Texaco cold climate power assisted steering
fluid PSF 14315.
ACE fluid
Where ambient temperature falls below -20° C (-4°
F), use only Texaco cold climate power assisted
steering fluid PSF 14315. Where ambient
temperature remains above -20° C (-4° F), use either
Texaco cold climate power assisted steering fluid ,
Dexron 11 or Dexron 111 non-synthetic fluid.
Air conditioning
Use only refrigerant R134a.
Refrigerant oil
Use only Nippon Denso ND-oil 8.
Refrigerant oil absorbs water and must not be stored
for long periods. Do not pour unused oil back into the
container.
NOTE: The total quantity of refrigerant oil in the
system is 180 ml.
CAUTION: Do not use any other type of
refrigerant oil.
Anti-Freeze Concentration
The overall anti-freeze concentration should not fall,
by volume, below 50% to ensure that the anti-
corrosion properties of the coolant are maintained.
Anti-freeze concentrations greater than 60% are not
recommended as cooling efficiency will be impaired.
The following recommended quantities of anti-freeze
will provide frost protection to -48°C (-53°F):
Engine - TD5
Engine - V8
Concentration 50%
Amount of Anti-freeze 4 litres
Concentration 50%
Amount of Anti-freeze 6.5 litres
13.5 pts (US)
Page 147 of 1529
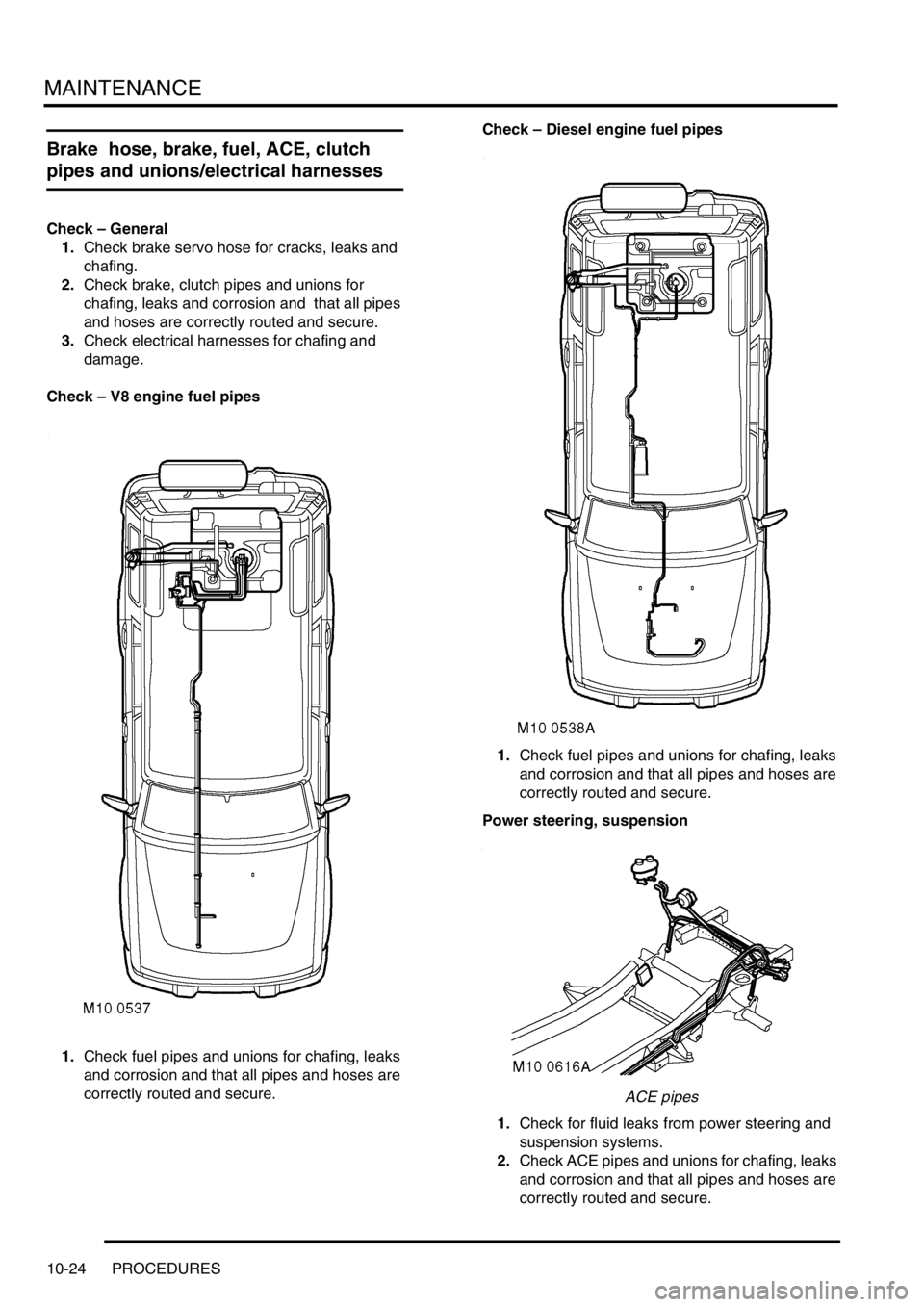
MAINTENANCE
10-24 PROCEDURES
Brake hose, brake, fuel, ACE, clutch
pipes and unions/electrical harnesses
Check – General
1.Check brake servo hose for cracks, leaks and
chafing.
2.Check brake, clutch pipes and unions for
chafing, leaks and corrosion and that all pipes
and hoses are correctly routed and secure.
3.Check electrical harnesses for chafing and
damage.
Check – V8 engine fuel pipes
1.Check fuel pipes and unions for chafing, leaks
and corrosion and that all pipes and hoses are
correctly routed and secure. Check – Diesel engine fuel pipes
1.Check fuel pipes and unions for chafing, leaks
and corrosion and that all pipes and hoses are
correctly routed and secure.
Power steering, suspension
ACE pipes
1.Check for fluid leaks from power steering and
suspension systems.
2.Check ACE pipes and unions for chafing, leaks
and corrosion and that all pipes and hoses are
correctly routed and secure.
Page 154 of 1529

MAINTENANCE
PROCEDURES 10-31
Road/roller test
WARNING: Roller test must be restricted to 3
mph (5 km/h). If 2 wheel rolling road is to be used,
disconnect propeller shaft from the transfer box
output shaft driving the axle which is NOT on the
rolling road.
Testing
1. 2 wheel rolling road: Engage differential lock
using a 10 mm open ended spanner on flats
machined on differential lock selector
shaft.Switch on ignition and check that the
differential lock, electronic brake
distribution and hill descent warning lamps
are illuminated.
2.Check for correct operation of starter switch,
ensure engine starts correctly; leave the engine
running.
3.Check for correct operation of starter switch,
ensure engine starts correctly; leave the engine
running.
4.With vehicle stationary, turn steering from lock
to lock. Check for smooth operation and ensure
there is no undue noise from power steering
pump or drive belt.
5.Depress clutch and select all gears in turn,
check for smooth, notch free engagement.6. Check all vehicle systems for correct
operation.
7.Check for unusual engine, gearbox and
suspension noises.
8.Check braking system operation.
9.Check for smooth gear engagement.
10.Check engine performance.
11.Check operation of all instruments and warning
devices where practicable.
12.Where possible, check for correct operation of
hill descent control (HDC) mechanism. This
should not be carried out if excessive journey
time is required.
13.After road/roller test, carry out a final inspection
of vehicle, with vehicle on a ramp.
14.Check all fluid levels and top-up if necessary.
15. 2 wheel rolling road: Ensure differential lock is
disengaged and propeller shaft is connected on
completion of test. Switch on ignition and
check that differential lock, electronic brake
distribution and hill descent warning lamps
are extinguished.
Page 698 of 1529

STEERING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 57-5
Description
General
The major steering components comprise an impact absorbing telescopic steering column, a Power Assisted Steering
(PAS) box, a PAS pump, and fluid reservoir. Hydraulic fluid from the fluid reservoir is filtered and then supplied
through the suction line to the inlet on the PAS pump. The PAS pump supplies fluid to the steering box through a
pressure line routed above the front cross member. Fluid returns to the reservoir along the same route through a
return line. On LH drive vehicles the pipe route above the front cross member is still used, the length of pipe acting
as an oil cooler.
To minimise driver's injury in the event of an accident the steering system has a number of safety features including
a collapsible steering column. An additional safety feature is an air bag located in the steering wheel.
+ RESTRAINT SYSTEMS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - SRS.
Steering column assembly and intermediate shaft
The steering column central shaft comprises of two shafts, the upper shaft is splined to accept the steering wheel and
located in bearings in the column tube. A universal joint is located on the bottom of the upper shaft, the joint allows
for angular movement between the upper and lower shafts. The lower shaft is made in two parts, the top section of
the lower shaft is located outside of the lower section. The two sections of the lower shaft are connected by two nylon
injection moulded shear pins. The lower shaft goes through a lower bearing attached to the bulkhead, the lower shaft
is connected by a universal joint to the intermediate shaft in the engine compartment.
Steering column
An upper column tube provides for the location of the steering lock and ignition switch and also the steering switch
gear and a rotary coupler. The rotary coupler provides the electrical connection for the steering wheel mounted airbag,
switches and horn. The upper mounting bracket has two slots, a slotted metal bracket is held in each slot by four resin
shear pins.
The column is mounted on four captive studs which are located on a column mounting bracket. The captive studs
pass through the metal brackets, locknuts secure the steering column to the bulkhead. The two lower mountings are
fixed and cannot move when loads are applied to them. The upper mounting is designed to disengage or deform when
a load is applied, allowing the column to collapse in the event of an accident. The steering column must be replaced
as a complete assembly if necessary.
When an axial load is applied to the upper column tube, energy absorption is achieved by the following mechanism:
lthe mounting bracket deforms,
lthe resin shear pins holding the slotted metal brackets shear,
lthe top mounting bracket slides out of the slotted metal brackets.
The slotted metal brackets remain on the captive studs on the bulkhead. If the column mounting moves, injection
moulded shear pins retaining the two sections of the lower column shaft will shear. This allows the two sections of the
lower shaft to 'telescope' together.
In the event of a collision where the steering box itself moves, two universal joints in the column allow the intermediate
shaft to articulate, minimising movement of the column towards the driver. If movement continues energy absorption
is achieved by the following mechanism:
lthe decouple joint in the intermediate shaft will disengage,
lthe lower section of the steering column shaft will move through the lower bearing,
lthe injection moulded shear pins retaining the two sections of the lower column shaft will shear.
This allows the two sections of the lower shaft to 'telescope' together reducing further column intrusion. Protection to
the drivers face and upper torso is provided by an SRS airbag module located in the centre of the steering wheel.
+ RESTRAINT SYSTEMS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - SRS.