1999 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY width
[x] Cancel search: widthPage 229 of 1529

ENGINE - V8
12-2-74 OVERHAUL
6.Reference mark main bearing caps to aid
assembly.
7.Remove 10 side bolts securing main bearing
caps to block.
8.Collect 'Dowty' washers from side bolts. Rear
side bolts have Allen heads.
9.Starting at the centre main bearing cap,
progressively loosen, then remove 2 bolts
securing each main bearing cap.
10.Release and remove main bearing caps.
CAUTION: Keep bearing caps, bearings and
bolts in their fitted order.
11.Remove and discard cruciform seals from rear
main bearing cap.
12.Remove crankshaft.
13.Remove main bearings from cylinder block and
main bearing caps.
14.Remove key from keyway.
15.Remove rear main sealing washers.
Inspect
1.Clean crankshaft journals and bearing
locations in cylinder block.
2.Inspect main bearings for wear and renew if
necessary. Main bearings are available in two
oversizes. If 2nd oversize bearing is being
fitted, it may be necessary to grind thrust
face of centre main bearing to achieve
correct end-float.
lMain bearing 1st oversize = 0.254 mm (0.01
in).
lMain bearing 2nd oversize = 0.508 mm
(0.02 in).3.Check main bearing journals for wear and
scoring. Measure for ovality; taking 3
measurements at 120° intervals at each end
and at centre of journals.
lJournal diameter - standard = 63.487 to
63.500 mm (2.499 to 2.520 in).
l1st undersize journal = 63.223 to 63.246
mm (2.511 to 2.512 in).
l2nd undersize journal = 62.979 to 62.992
mm (2.509 to 2.510 in).
lJournal width - standard = 26.975 to 27.026
mm (1.061 to 1.064 in).
lMaximum ovality = 0.040 mm (0.002 in)
Page 253 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
For NAS vehicles with positive pressure, EVAP system leak detection capability, the atmosphere vent line from the
EVAP canister connects to a port on the fuel leak detection pump via a short, large bore hose which is secured to the
component ports by crimped metal clips at each end. A large bore plastic hose from the top of the leak detection pump
is routed to the RH side of the engine bay where it connects to an air filter canister. Under normal operating conditions
(when the fuel leak detection solenoid valve is not energised), the EVAP canister is able to take in clean air via the
air filter, through the pipework and past the open solenoid valve to allow normal purge operation to take place and
release any build up of EVAP system pressure to atmosphere.
The EVAP system pipes are clipped at various points along the pipe runs and tied together with tie straps at suitable
points along the runs.
The NAS and ROW EVAP canisters are of similar appearance, but use charcoal of different consistency. The ROW
vehicles use granular charcoal of 11 bwc (butane working capacity) and NAS vehicles use pelletised charcoal with a
higher absorption capacity of 15 bwc. All canisters are of rectangular shape and have capacities of 1.8 litres (3 1/8
imp. pts) with purge foam retention.
Purge Valve
1Direction of flow indicator
2Inlet port – from EVAP canister3Outlet port – to inlet manifold
4Integral electrical connector
The EVAP canister purge valve is located in the engine bay at the LH side of the engine intake manifold. The valve
is held in position by a plastic clip which secures the inlet pipe of the purge valve to a bracket mounted at the rear of
the engine compartment. On vehicles with secondary air injection, the purge valve is fixed to a metal bracket together
with the SAI vacuum solenoid valve; the purge valve is fixed to the bracket by two plastic clips.
A nylon pipe connects the outlet of the purge valve to the stub pipe on the plenum chamber via a short rubber hose.
The connector to the plenum chamber is a quick-release type, plastic 90° female elbow; the connection is covered by
a rubber seal which is held in position on the port stub pipe.
A service port is connected in line between the EVAP canister and the inlet side of the purge valve and is rated at 1
psi maximum regulated pressure. The service port must be mounted horizontally and is located close to the bulkhead
at the rear of the engine bay. The service point is used by dealers for pressure testing using specialist nitrogen test
equipment for localising the source of small leaks.
The purge valve has a plastic housing, and a directional arrow is moulded onto the side of the casing to indicate the
direction of flow. The head of the arrow points to the outlet side of the valve which connects to the plenum chamber.
Purge valve operation is controlled by the engine control module (ECM). The purge valve has a two-pin electrical
connector which links to the ECM via the engine harness. Pin-1 of the connector is the power supply source from fuse
2 in the engine compartment fusebox, and pin-2 of the connector is the switched earth from the ECM (pulse width
modulated (PWM) signal) which is used to control the purge valve operation time. Note that the harness connector
for the purge valve is black, and must not be confused with the connector for the Secondary Air Injection
vacuum solenoid valve which is grey.
When the purge valve is earthed by the ECM, the valve opens to allow hydrocarbons stored in the EVAP canister to
be purged to the engine inlet manifold for combustion.
Page 268 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-35
Exhaust Emission Control Operation
The oxygen content of the exhaust gas is monitored by heated oxygen sensors using either a four sensor (NAS only)
or two sensor setup, dependent on market destination and legislative requirements. Signals from the heated oxygen
sensors are input to the engine management ECM which correspond to the level of oxygen detected in the exhaust
gas. From ECM analysis of the data, necessary changes to the air:fuel mixture and ignition timing can be made to
bring the emission levels back within acceptable limits under all operating conditions.
Changes to the air:fuel ratio are needed when the engine is operating under particular conditions such as cold starting,
idle, cruise, full throttle or altitude. In order to maintain an optimum air:fuel ratio for differing conditions, the engine
management control system uses sensors to determine data which enable it to select the ideal ratio by increasing or
decreasing the air to fuel ratio. Improved fuel economy can be arranged by increasing the quantity of air to fuel to
create a lean mixture during part-throttle conditions, however lean running conditions are not employed on closed loop
systems where the maximum is λ = 1. Improved performance can be established by supplying a higher proportion of
fuel to create a rich mixture during idle and full-throttle operation. Rich running at wide open throttle (WOT) for
performance and at high load conditions helps to keep the exhaust temperature down to protect the catalyst and
exhaust valves.
The voltage of the heated oxygen sensors at λ = 1 is between 450 and 500 mV. The voltage decreases to 100 to 500
mV if there is an increase in oxygen content (λ > 1) indicating a lean mixture. The voltage increases to 500 to 1000
mV if there is a decrease in oxygen content (λ < 1), signifying a rich mixture.
The heated oxygen sensor needs to operate at high temperatures in order to function correctly (≥ 350° C). To achieve
this the sensors are fitted with heater elements which are controlled by a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal from
the engine management ECM. The heater element warms the sensor's ceramic layer from the inside so that the
sensor is hot enough for operation. The heater elements are supplied with current immediately following engine start
and are ready for closed loop control within about 20 to 30 seconds (longer at cold ambient temperatures less than
0°C (32°F)). Heating is also necessary during low load conditions when the temperature of the exhaust gases is
insufficient to maintain the required sensor temperatures. The maximum tip temperature is 930° C.
A non-functioning heater element will delay the sensor's readiness for closed loop control and influences emissions.
A diagnostic routine is utilised to measure both sensor heater current and the heater supply voltage so its resistance
can be calculated. The function is active once per drive cycle, as long as the heater has been switched on for a pre-
defined period and the current has stabilised. The PWM duty cycle is carefully controlled to prevent thermal shock to
cold sensors.
The heated oxygen sensors age with mileage, causing an increase in the response time to switch from rich to lean
and lean to rich. This increase in response time influences the closed loop control and leads to progressively
increased emissions. The response time of the pre-catalytic converter sensors are monitored by measuring the period
of rich to lean and lean to rich switching. The ECM monitors the switching time, and if the threshold period is exceeded
(200 milliseconds), the fault will be detected and stored in the ECM as a fault code (the MIL light will be illuminated
on NAS vehicles). NAS vehicle engine calibration uses downstream sensors to compensate for aged upstream
sensors, thereby maintaining low emissions.
Diagnosis of electrical faults is continuously monitored for both the pre-catalytic converter sensors and the post-
catalytic converter sensors (NAS only). This is achieved by checking the signal against maximum and minimum
threshold for open and short circuit conditions. For NAS vehicles, should the pre- and post-catalytic converters be
inadvertently transposed, the lambda signals will go to maximum but opposite extremes and the system will
automatically revert to open loop fuelling. The additional sensors for NAS vehicles provide mandatory monitoring of
the catalyst conversion efficiency and long term fuelling adaptations.
Note that some markets do not legislate for closed loop fuelling control and in this instance no heated oxygen
sensors will be fitted to the exhaust system.
Page 272 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-39
Evaporative Emission Control Operation
Fuel vapour is stored in the activated charcoal (EVAP) canister for retention when the vehicle is not operating. When
the vehicle is operating, fuel vapour is drawn from the canister into the engine via a purge control valve. The vapour
is then delivered to the intake plenum chamber to be supplied to the engine cylinders where it is burned in the
combustion process.
During fuel filling the fuel vapour displaced from the fuel tank is allowed to escape to atmosphere, valves within the
fuel filler prevent any vapour escaping through to the EVAP canister as this can adversely affect the fuel cut-off height.
Only fuel vapour generated whilst driving is prevented from escaping to atmosphere by absorption into the charcoal
canister. The fuel filler shuts off to leave the tank approximately 10% empty to ensure the ROVs are always above
the fuel level and so vapour can escape to the EVAP canister and the tank can breathe. The back pressures normally
generated during fuel filling are too low to open the pressure relief valve, but vapour pressures accumulated during
driving are higher and can open the pressure relief valve. Should the vehicle be overturned, the ROVs shut off to
prevent any fuel spillage.
Fuel vapour generated from within the fuel tank as the fuel heats up is stored in the tank until the pressure exceeds
the operating pressure of the two-way valve. When the two-way valve opens, the fuel vapour passes along the vent
line from the fuel tank (via the fuel tank vapour separator) to the evaporation inlet port of the EVAP canister. The fuel
tank vents between 5.17 and 6.9 kPa.
Fuel vapour evaporating from the fuel tank is routed to the EVAP canister through the fuel vapour separator and vent
line. Liquid fuel must not be allowed to contaminate the charcoal in the EVAP canister. To prevent this, the fuel vapour
separator fitted to the fuel neck allows fuel to drain back into the tank. As the fuel vapour cools, it condenses and is
allowed to flow back into the fuel tank from the vent line by way of the two-way valve.
The EVAP canister contains charcoal which absorbs and stores fuel vapour from the fuel tank while the engine is not
running. When the canister is not being purged, the fuel vapour remains in the canister and clean air exits the canister
via the air inlet port.
The engine management ECM controls the electrical output signal to the purge valve. The system will not work
properly if there is leakage or clogging within the system or if the purge valve cannot be controlled.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
When the engine is running, the ECM decides when conditions are correct for vapour to be purged from the EVAP
canister and opens the canister purge valve. This connects a manifold vacuum line to the canister and fuel vapour
containing the hydrocarbons is drawn from the canister's charcoal element to be burned in the engine. Clean air is
drawn into the canister through the atmosphere vent port to fill the displaced volume of vapour.
The purge valve remains closed below preset coolant and engine speed values to protect the engine tune and
catalytic converter performance. If the EVAP canister was purged during cold running or at idling speed, the additional
enrichment in the fuel mixture would delay the catalytic converter light off time and cause erratic idle. When the purge
valve is opened, fuel vapour from the EVAP canister is drawn into the plenum chamber downside of the throttle
housing, to be delivered to the combustion chambers for burning.
The purge valve is opened and closed in accordance with a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal supplied from the
engine management ECM. The system will not work properly if the purge valve cannot be controlled. Possible failure
modes associated with the purge valve are listed below:
lValve drive open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply or ground.
lPurge valve or pipework blocked or restricted.
lPurge valve stuck open.
lPipework joints leaking or disconnected.
Possible symptoms associated with a purge valve or associated pipework failure is listed below:
lEngine may stall on return to idle if purge valve is stuck open.
lPoor idling quality if the purge valve is stuck open
lFuelling adaptions forced excessively lean if the EVAP canister is clear and the purge valve is stuck open.
lFuelling adaptions forced excessively rich if the EVAP canister is saturated and the purge valve is stuck open.
lSaturation of the EVAP canister if the purge valve is stuck closed.
Page 317 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-18 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor (C0196)
The ECT sensor is located at the front of the engine adjacent to the coolant outlet pipe. The ECT sensor forms a vital
part of the ECM operating strategy, and therefore the optimum control of the running of the engine. Richer air/ fuel
ratio is required at lower coolant temperatures such as cold starting. Coolant temperature information from the ECT
sensor is also vital to enable the ECM to weaken the air/ fuel mixture as temperature rises to maintain low emissions
and optimum performance.
For NAS vehicles with secondary air injection, the signal from the ECT sensor is monitored at engine start, to
determine whether the conditions are cold enough to warrant secondary air injection to be employed. The ECT sensor
is then monitored to switch off the secondary air injection when the required engine coolant temperature has been
attained.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Secondary Air Injection System.
The ECT works as a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) sensor. As temperature rises, the resistance in the
sensor decreases, as temperature decreases, the resistance in the sensor increases. The ECT sensor forms part of
a voltage divider chain with a pull up resistor within the ECM. Consequently as the ECT sensor resistance changes,
the analogue voltage at the input signal from the ECT sensor to the ECM will be adjusted which corresponds to the
temperature of the engine coolant. With this information, the ECM can implement the correct strategies for cold start,
warm up etc. The ECM supplies the instrument cluster with a pulse width modulated (PWM) coolant temperature
signal to drive the temperature gauge.
Page 332 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-33
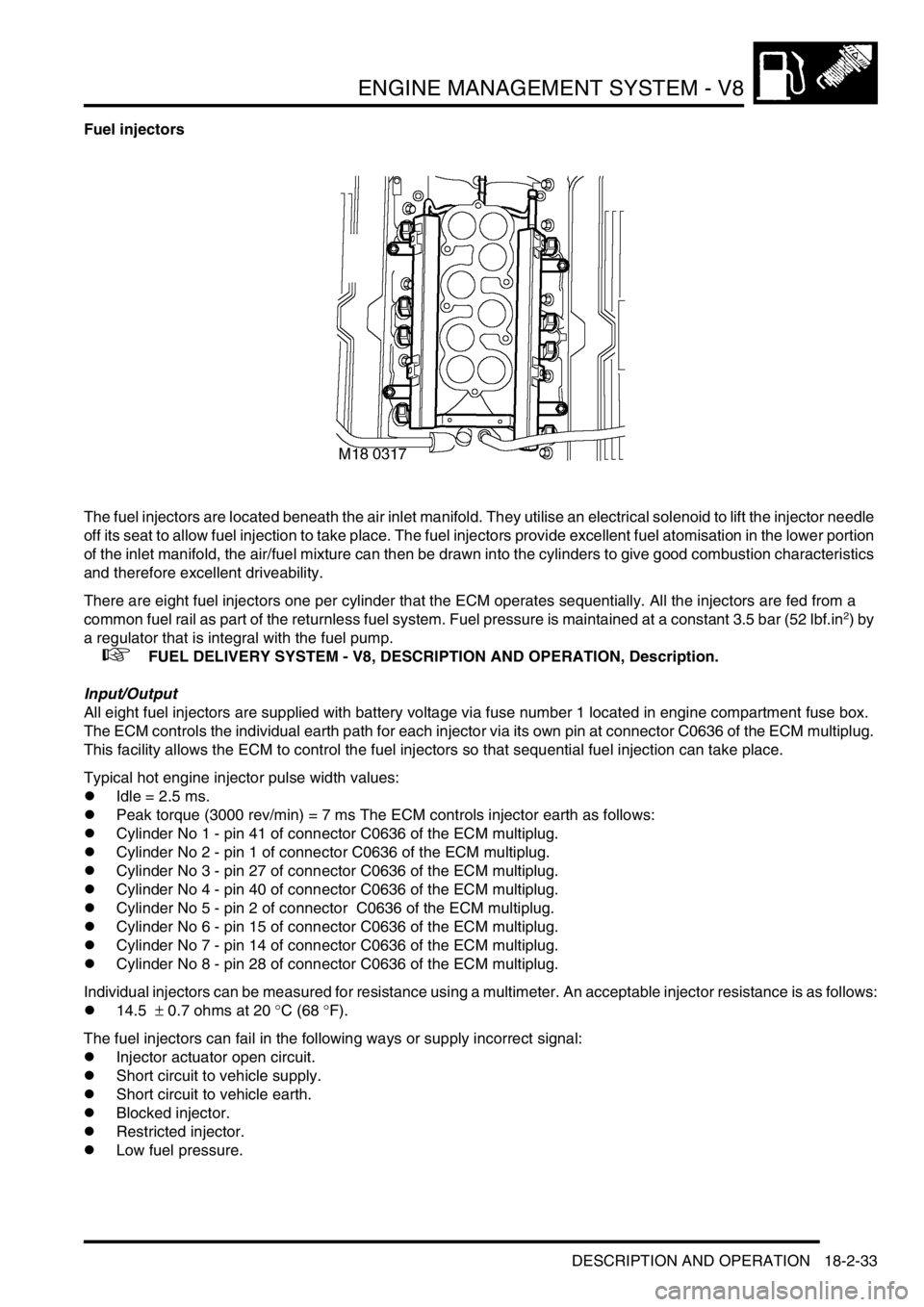
Fuel injectors
The fuel injectors are located beneath the air inlet manifold. They utilise an electrical solenoid to lift the injector needle
off its seat to allow fuel injection to take place. The fuel injectors provide excellent fuel atomisation in the lower portion
of the inlet manifold, the air/fuel mixture can then be drawn into the cylinders to give good combustion characteristics
and therefore excellent driveability.
There are eight fuel injectors one per cylinder that the ECM operates sequentially. All the injectors are fed from a
common fuel rail as part of the returnless fuel system. Fuel pressure is maintained at a constant 3.5 bar (52 lbf.in
2) by
a regulator that is integral with the fuel pump.
+ FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Input/Output
All eight fuel injectors are supplied with battery voltage via fuse number 1 located in engine compartment fuse box.
The ECM controls the individual earth path for each injector via its own pin at connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
This facility allows the ECM to control the fuel injectors so that sequential fuel injection can take place.
Typical hot engine injector pulse width values:
lIdle = 2.5 ms.
lPeak torque (3000 rev/min) = 7 ms The ECM controls injector earth as follows:
lCylinder No 1 - pin 41 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 2 - pin 1 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 3 - pin 27 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 4 - pin 40 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 5 - pin 2 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 6 - pin 15 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 7 - pin 14 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 8 - pin 28 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
Individual injectors can be measured for resistance using a multimeter. An acceptable injector resistance is as follows:
l14.5 ± 0.7 ohms at 20 °C (68 °F).
The fuel injectors can fail in the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lInjector actuator open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lBlocked injector.
lRestricted injector.
lLow fuel pressure.
Page 349 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-50 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Conditions
To achieve closed loop fuelling, the ECM interacts with the following components:
lHO
2S.
lFuel injectors.
Closed loop fuelling is a rolling process controlled by the ECM. The ECM uses information gained from the CKP, ECT,
MAF/ IAT and the TP sensors, to operate under the following conditions:
lPart throttle.
lLight engine load.
lCruising.
lIdle.
Function
When the engine is operating in the above conditions, the ECM implements the closed loop fuelling strategy. The air/
fuel mixture is ignited by the high tension (ht) spark in the combustion chambers and the resulting gas is expelled into
the exhaust pipe. Upon entering the exhaust pipe the exhaust gas passes over the protruding tip of the HO
2S. The
HO
2S measures the oxygen content of the gas compared to that of ambient air and converts it into a voltage, which
is measured by the ECM.
The voltage signal read by the ECM is proportional to the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. This signal can then be
compared to stored values in the ECM's memory and an adaptive strategy can be implemented.
If the HO
2S informs the ECM of an excess of oxygen (lean mixture), the ECM extends the opening time of the fuel
injectors via the Injector Pulse Width (IPW) signal. Once this new air/ fuel ratio has been 'burnt' in the combustion
chambers the HO
2S can again inform the ECM of the exhaust gas oxygen content, this time there will be a lack of
oxygen or a rich mixture. The ECM reduces the opening time of the injectors via the IPW signal using the ECM's
adaptive fuel strategy. During closed loop fuelling the HO
2S will constantly switch from rich to lean and back again,
this indicates that the ECM and the HO
2S are operating correctly.
Open loop fuelling
Open loop fuelling does not rely on information from the HO
2S, but the air/ fuel ratio is set directly by the ECM, which
uses information gained from the ECT, MAF/ IAT, the TP sensors and also the vehicle speed sensor (VSS). The ECM
uses open loop fuelling under the following conditions:
lCold start.
lHot start.
lWide open throttle.
lAcceleration.
The ECM uses open loop fuelling to control fuel quantity in all non adaptive strategy conditions. The ECM implements
fuelling information carried in the form of specific mapped data contained within its memory.
Because there is no sensor information (e.g. HO
2S), provided back to the ECM, the process is called an 'open loop'.
The ECM will also go into open loop fuelling if a HO
2S fails.
Ignition timing
The ignition timing is an important part of the ECM adaptive strategy. Ignition is controlled by a direct ignition system
using two four-ended coils operating on the wasted spark principle.
When the ECM triggers an ignition coil to spark, current from the coil travels to one spark plug, then jumps the gap at
the spark plug electrodes, igniting the mixture in the cylinder in the process. Current continues to travel along the earth
path (via the cylinder head) to the spark plug negative electrode at the cylinder that is on the exhaust stroke. The
current jumps across the spark plug electrodes and back to the coil completing the circuit. Since it has simultaneously
sparked in a cylinder that is on the exhaust stroke, it has not provided an ignition source there and is consequently
termed 'wasted'.
Page 350 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-51
Conditions
The ECM calculates ignition timing using input from the following:
lCKP sensor.
lKnock sensors (KS).
lMAF sensor.
lTP sensor (idle only).
lECT sensor.
Function
At engine start up, the ECM sets ignition timing dependent on ECT information and starting rev/min from the CKP. As
the running characteristics of the engine change, the ignition timing changes. The ECM compares the CKP signal to
stored values in its memory, and if necessary advances or retards the spark via the ignition coils.
Ignition timing is used by the ECM for knock control.
Knock control
The ECM uses active knock control to prevent possible engine damage due to pre-ignition. This is achieved by
converting engine block noise into a suitable electrical signal that can be processed by the ECM. A major contributing
factor to engine 'knock' is fuel quality, the ECM can function satisfactorily on 91 RON fuel as well as the 95 RON fuel
that it is calibrated for.
Conditions
The ECM knock control system operates as follows:
lHot running engine.
l91 or 95 RON fuel.
Function
The ECM knock control uses two sensors located one between the centre two cylinders of each bank. The knock
sensors consist of piezo ceramic crystals that oscillate to create a voltage signal. During pre-ignition, the frequency
of crystal oscillation increases which alters the signal output to the ECM.
If the knock sensors detect pre-ignition in any of the cylinders, the ECM retards the ignition timing by 3° for that
particular cylinder. If this action stops the engine knock, the ignition timing is restored to its previous figure in
increments of 0.75°. If this action does not stop engine knock then the ECM retards the ignition timing a further 3° up
to a maximum of -15° and then restores it by 0.75° and so on until the engine knock is eliminated.
The ECM also counteracts engine knock at high intake air temperatures by retarding the ignition as above. The ECM
uses the IAT signal to determine air temperature.
Idle speed control
The ECM regulates the engine speed at idling. The ECM uses the idle air control valve (IACV) to compensate for the
idle speed drop that occurs when the engine is placed under greater load than usual. When the throttle is in the rest
position i.e. it has not been pressed, the majority of intake air that the engine consumes comes from the idle air control
valve.
IACV control idle speed
Conditions in which the ECM operates the IACV control idle speed is as follows:
lIf any automatic transmission gears other than P or N are selected.
lIf air conditioning is switched on.
lIf cooling fans are switched on.
lAny electrical loads activated by the driver.
Function
The idle air control valve utilises two coils that use opposing pulse width modulated (PWM) signals to control the
position of a rotary valve. If one of the circuits that supplies the PWM signal fails, the ECM closes down the remaining
signal preventing the idle air control valve from working at its maximum/ minimum setting. If this should occur, the idle
air control valve assumes a default idle position at which the engine idle speed is raised to 1200 rev/min with no load
placed on the engine.