1999 LAND ROVER DEFENDER coolant
[x] Cancel search: coolantPage 154 of 667
ENGINE
29
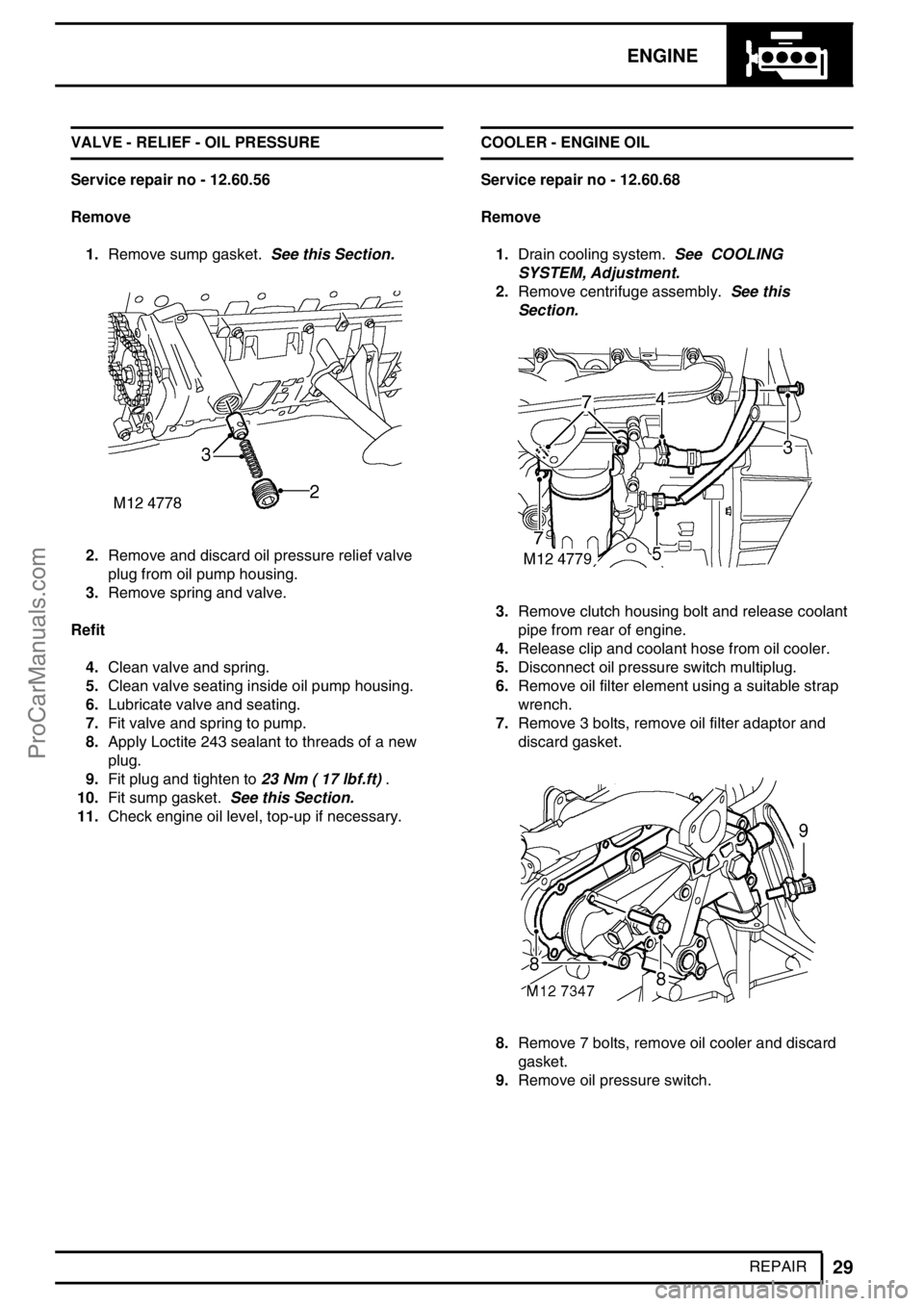
REPAIR VALVE - RELIEF - OIL PRESSURE
Service repair no - 12.60.56
Remove
1.Remove sump gasket.See this Section.
2.Remove and discard oil pressure relief valve
plug from oil pump housing.
3.Remove spring and valve.
Refit
4.Clean valve and spring.
5.Clean valve seating inside oil pump housing.
6.Lubricate valve and seating.
7.Fit valve and spring to pump.
8.Apply Loctite 243 sealant to threads of a new
plug.
9.Fit plug and tighten to23 Nm ( 17 lbf.ft).
10.Fit sump gasket.See this Section.
11.Check engine oil level, top-up if necessary.COOLER - ENGINE OIL
Service repair no - 12.60.68
Remove
1.Drain cooling system.See COOLING
SYSTEM, Adjustment.
2.Remove centrifuge assembly.See this
Section.
3.Remove clutch housing bolt and release coolant
pipe from rear of engine.
4.Release clip and coolant hose from oil cooler.
5.Disconnect oil pressure switch multiplug.
6.Remove oil filter element using a suitable strap
wrench.
7.Remove 3 bolts, remove oil filter adaptor and
discard gasket.
8.Remove 7 bolts, remove oil cooler and discard
gasket.
9.Remove oil pressure switch.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 155 of 667

12ENGINE
30
REPAIR Refit
10.Clean oil cooler and mating faces.
11.Fit oil pressure switch and tighten to9Nm(7
lbf.ft).
12.Position oil cooler using a new gasket and
tighten bolts to25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
13.Position oil filter adaptor, fit new gasket and
tighten bolts to25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
14.Position oil filter element hand tight then a
further half turn.
15.Position coolant hose to oil cooler and secure
clip.
16.Position coolant pipe and tighten clutch housing
bolt to50 Nm (37 lbf.ft).
17.Connect oil pressure switch multiplug.
18.Fit centrifuge assembly.See this Section.
19.Refill cooling system.See COOLING SYSTEM,
Adjustment.
20.Top up engine oil.CENTRIFUGE ASSEMBLY
Service repair no - 12.60.90
Remove
1.Remove fixings and remove underbelly panel.
See CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair.
2.Remove 2 bolts securing centrifuge drain pipe to
engine sump and discard gasket.
3.Remove turbocharger.See FUEL SYSTEM,
Repair.
Models with air conditioning only
4.Remove auxiliary drive belt.See
ELECTRICAL, Repair.
5.Remove 4 bolts securing compressor and move
to one side.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 164 of 667
ENGINE
5
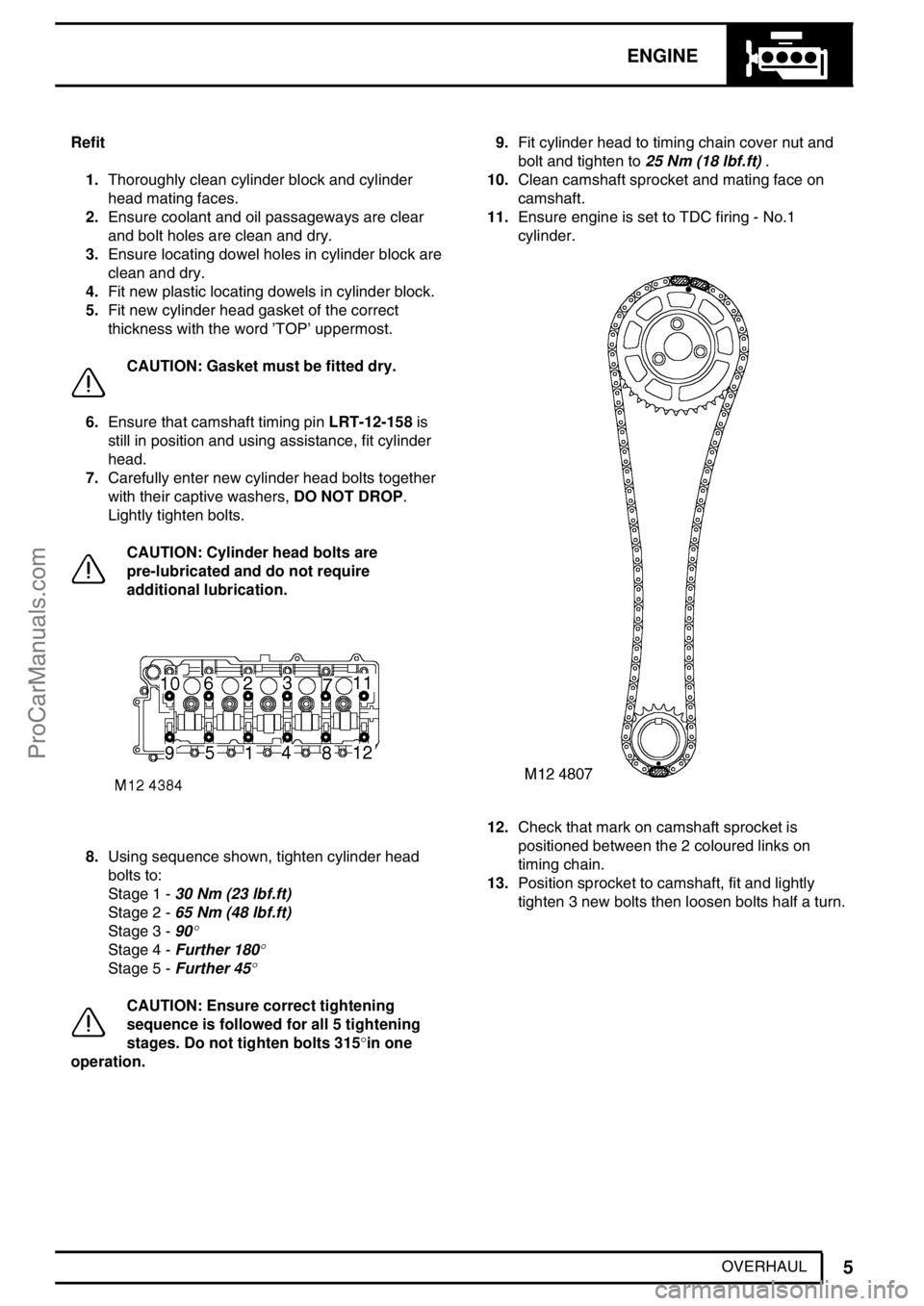
OVERHAUL Refit
1.Thoroughly clean cylinder block and cylinder
head mating faces.
2.Ensure coolant and oil passageways are clear
and bolt holes are clean and dry.
3.Ensure locating dowel holes in cylinder block are
clean and dry.
4.Fit new plastic locating dowels in cylinder block.
5.Fit new cylinder head gasket of the correct
thickness with the word’TOP’uppermost.
CAUTION: Gasket must be fitted dry.
6.Ensure that camshaft timing pinLRT-12-158is
still in position and using assistance, fit cylinder
head.
7.Carefully enter new cylinder head bolts together
with their captive washers,DO NOT DROP.
Lightly tighten bolts.
CAUTION: Cylinder head bolts are
pre-lubricated and do not require
additional lubrication.
8.Using sequence shown, tighten cylinder head
bolts to:
Stage 1 -30 Nm (23 lbf.ft)
Stage 2 -65 Nm (48 lbf.ft)
Stage 3 -90
°
Stage 4 -Further 180°
Stage 5 -Further 45°
CAUTION: Ensure correct tightening
sequence is followed for all 5 tightening
stages. Do not tighten bolts 315°in one
operation.9.Fit cylinder head to timing chain cover nut and
bolt and tighten to25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
10.Clean camshaft sprocket and mating face on
camshaft.
11.Ensure engine is set to TDC firing - No.1
cylinder.
12.Check that mark on camshaft sprocket is
positioned between the 2 coloured links on
timing chain.
13.Position sprocket to camshaft, fit and lightly
tighten 3 new bolts then loosen bolts half a turn.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 170 of 667
ENGINE
11
OVERHAUL
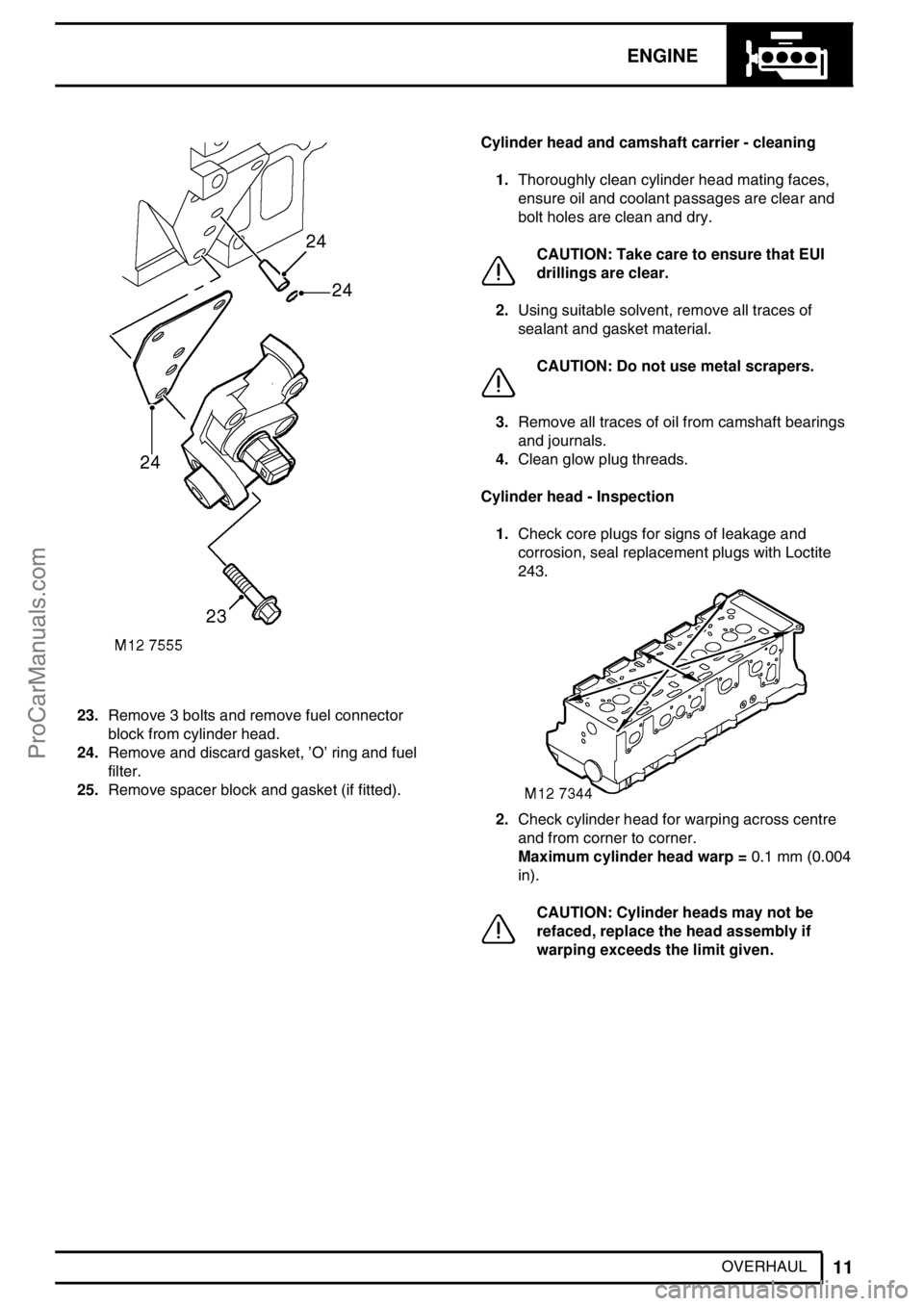
23.Remove 3 bolts and remove fuel connector
block from cylinder head.
24.Remove and discard gasket,’O’ring and fuel
filter.
25.Remove spacer block and gasket (if fitted).Cylinder head and camshaft carrier - cleaning
1.Thoroughly clean cylinder head mating faces,
ensure oil and coolant passages are clear and
bolt holes are clean and dry.
CAUTION: Take care to ensure that EUI
drillings are clear.
2.Using suitable solvent, remove all traces of
sealant and gasket material.
CAUTION: Do not use metal scrapers.
3.Remove all traces of oil from camshaft bearings
and journals.
4.Clean glow plug threads.
Cylinder head - Inspection
1.Check core plugs for signs of leakage and
corrosion, seal replacement plugs with Loctite
243.
2.Check cylinder head for warping across centre
and from corner to corner.
Maximum cylinder head warp =0.1 mm (0.004
in).
CAUTION: Cylinder heads may not be
refaced, replace the head assembly if
warping exceeds the limit given.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 209 of 667

17EMISSION CONTROL
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve permits a controlled amount of exhaust gas to combine with the fresh
air entering the engine. The exhaust gas reduces the combustion temperature by delaying the fuel burning rate,
which assists in reducing the quantity of oxides of nitrogen.
On EU3 models, an EGR cooler is employed to further reduce the combustion temperature. By passing the
exhaust gas through a bundle of pipes flooded by coolant, the density of the exhaust gas going into the engine is
increased. This process further reduces the amount of NO
2in the exhaust.
Recirculation of too much exhaust gas can result in higher emissions of soot, HC and CO due to insufficient air.
The recirculated exhaust gas must be limited so that there is sufficient oxygen available for combustion of the
injected fuel in the combustion chamber. To do this the ECM is used to control the precise quantity of exhaust gas
to be recirculated in accordance with the prevailing operating conditions. Influencing factors include:
The mass of air flow detected by the MAF sensor.
The ambient air temperature detected by the AAP sensor. This is used to initiate adjustments to reduce the
amount of smoke produced at high altitudes.
The mass of air flow detected by the MAF sensor.
The ambient air temperature detected by the AAP sensor. This is used to initiate adjustments to reduce the
amount of smoke produced at high altitudes.
Other factors which are taken into consideration by the engine management system for determining the optimum
operating condition include:
Manifold inlet air temperature
Coolant temperature
Engine speed
Fuel delivered
The main components of the EGR system are as follows.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 222 of 667

18 - ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CONTENTS
Page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COMPONENT LOCATION 2...................................................................................
DESCRIPTION 5.....................................................................................................
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) 6.................................................................
SENSOR - MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) 7....................................................................
SENSOR - AMBIENT AIR PRESSURE AND 8.......................................................
SENSOR - MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE 9................................................
SENSOR - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE 11.............................................
SENSOR - CRANKSHAFT SPEED AND 12...........................................................
SENSOR - THROTTLE POSITION (TP) 14............................................................
SENSOR - THROTTLE POSITION (TP) 15............................................................
ELECTRONIC UNIT INJECTOR (EUI) 18...............................................................
SENSOR - FUEL TEMPERATURE (FT) 20............................................................
RELAY - FUEL PUMP 21........................................................................................
RELAY - MAIN 21...................................................................................................
SWITCH - BRAKE PEDAL 22.................................................................................
SWITCH - CLUTCH PEDAL 22...............................................................................
MODULATOR - EXHAUST GAS REGULATOR (EGR) 23.....................................
WARNING LAMP - GLOW PLUG 23......................................................................
GLOW PLUGS 24...................................................................................................
TURBOCHARGER 26.............................................................................................
INTERCOOLER 27.................................................................................................
OPERATION 28......................................................................................................
REPAIR
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) 1.................................................................
SENSOR - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) 1....................................
SENSOR - CRANKSHAFT SPEED AND POSITION (CKP) 2................................
ProCarManuals.com
Page 226 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1.Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
2.Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
3.Glow plugs.
4.Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) / Inlet Air Temperature (IAT) sensor.
5.Fuel pump relay.
6.Engine Control Module (ECM).
7.Air Conditioning (A/C) and cooling fan relay.
8.Fuel Temperature (FT) sensor.
9.Crankshaft Speed and Position (CKP) sensor.
10.Electronic Unit Injectors (EUI).
11.Ambient Air Pressure (AAP) sensor.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 228 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
General
An engine control module (ECM) controls the five cylinder direct injection diesel engine, and works on the drive by
wire principal. This means there is no throttle cable, the ECM controls the drivers needs via a signal from the
Throttle Position (TP) sensor on the throttle pedal.
The ECM is a full authoritative diesel specific microprocessor that also incorporates features for air conditioning. In
addition, the ECM supplies output control for the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) and turbocharger boost
pressure. The ECM has a self diagnostic function, which is able to provide backup strategies for most sensor
failures.
The ECM processes information from the following input sources:
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
Ambient Air Pressure (AAP) sensor.
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) / Inlet Air Temperature (IAT) sensor.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
Crankshaft Speed and Position (CKP) sensor.
Throttle Position (TP) sensor.
Fuel Temperature (FT) sensor.
Air conditioning request.
Air conditioning fan request.
Brake pedal switch.
Clutch pedal switch.
The input from the sensors constantly updates the ECM with the current operating condition of the engine. Once
the ECM has compared current information with stored information within its memory, it can make any adjustment
it requires to the operation of the engine via the following:
Air conditioning clutch relay.
Air conditioning cooling fan relay.
Electronic vacuum regulator solenoid.
Fuel pump relay.
Glow plug warning lamp.
Glow plugs.
Fuel injectors.
Main relay.
Turbocharger wastegate modulator.
Temperature gauge.
The ECM interfaces with the following:
Serial communication link.
Instrument pack.
ProCarManuals.com