1999 LAND ROVER DEFENDER engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 250 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
27
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION The turbocharger is exposed to extremely high operating temperatures (up to 1000°C, 1832°F) because of the
hot exhaust gases and the high speed revolution of the turbine (up to 15,000 rev/min). In order to resist wear of
the turbine bearings a flow of lubrication oil is supplied from the engine lubrication system to keep the bearings
cool. Oil is supplied from a tapping at the front of the full-flow filter adaptor housing via a metal pipe with banjo
connections. Oil is returned to the sump via a metal pipe which connects to the cylinder block at a port below the
turbocharger assembly.
A heatshield is attached to the LH side of the engine to protect adjacent components from the heat generated at
the turbocharger. The heatshield is attached to the engine by 2 bolts. An additional bolt attaches the heatshield to
the turbocharger casting.
The ECM controls the amount of boost pressure the engine receives by way of the turbocharger. When full boost
is reached a control signal is sent to the wastegate modulator, and a vacuum is applied to the wastegate valve.
The wastegate valve opens, bypassing some of the exhaust gases away from the turbine to be output to the
exhaust system.
The engine should be allowed to idle for 15 seconds following engine start up and before the engine is switched
off to protect the turbocharger by maintaining oil supply to the turbine bearings.
INTERCOOLER
The intercooler is an air-to-air heat exchanger which lowers the intake air temperature to obtain a higher air
density for better combustion efficiency. The intercooler receives compressed air from the turbocharger via a
metal pipe. It cools the intake air via the intercooler matrix and delivers it to the intake manifold by means of a
rubber hose which connects between the intercooler outlet and the intake manifold. The rubber hose is connected
to ports at each end by metal clips.
The intercooler is located at the front of the engine bay, forward of the radiator.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 259 of 667

19FUEL SYSTEM
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Fuel Pump
The fuel pump assembly comprises a top cover which locates the electrical connector, and four fuel pipe
couplings. The top cover is attached to a plastic cup shaped housing and retained on three sliding clips. Two coil
springs are located between the cover and the housing and ensure that the fuel pump remains seated positively at
the bottom of the tank when installed.
The housing locates the two stage fuel pump and also the fuel gauge sender unit. The lower part of the housing is
the swirl pot which maintains a constant level of fuel at the fuel pick-up. A coarse filter is located in the base of the
housing and prevents the ingress of contaminants into the pump and the fuel system from the fuel being drawn
into the pump. A fine filter is located in the intake to the low pressure stage to protect the pump from
contaminants. Flexible pipes connect the couplings on the top cover to the pump.
A non-return valve is located in the base of the housing. When the fuel tank is full, fuel pressure keeps the valve
lifted from its seat, allowing fuel to flow into the swirl pot. As the tank level reduces, the fuel pressure in the tank
reduces causing the valve to close. When the valve is closed, fuel is retained in the swirl pot, ensuring that the
swirl pot remains full and maintains a constant supply to the fuel pump.
The two stage pump comprises a high and low pressure stage. The low pressure stage draws fuel from the swirl
pot through a filter. The low pressure stage pumps fluid at a pressure of 0.75 bar (10.9 lbf.in) and a flow of 30
litres/hour (8 US Gallons/hour) to the fuel filter. A proportion of the fuel from the low pressure stage also passes,
via a restrictor, through a jet pump which keeps fuel circulating in the swirl pot. The high pressure stage draws the
low pressure fuel from the fuel filter and pressurises it to a pressure of 4.0 bar (58 lbf.in). The pressurised fuel is
then passed from the pump to the injectors at a flow of 180 litres/hour (47.6 US Gallons/hour). A fuel pressure
regulator is located at the rear of the engine and ensures that the delivery pressure remains at 4.0 bar (58 lbf.in)
by controlling the amount of fuel returning to the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a maximum current draw of 15 Amps at 12 Volts and is supplied a feed (C0114-1) from the fuel
pump relay (C0730-2) on a white/purple wire.
Fuel Gauge Sender
The fuel gauge sender unit comprises a rotary potentiometer operated by a float. The float rises and falls with the
fuel level in the tank and moves the potentiometer accordingly.
A feed is supplied to the fuel gauge sender (C0114-1) by the fuel pump relay (C0730-2) on a purple/white then
white/purple wire. The sender is earthed (C0114-3) on a slate/black wire via header 287. The output voltage
(C0114-2) from the sender to the instrument pack (C1061-3) varies in relation to the fuel level. This output voltage
is connected to the fuel gauge C1054-2). The fuel gauge receives a battery voltage input (C1054-3) on a
white/green wire. This is compared with the output voltage from the potentiometer. The difference between the two
voltages determines the deflection of the fuel gauge pointer.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 274 of 667
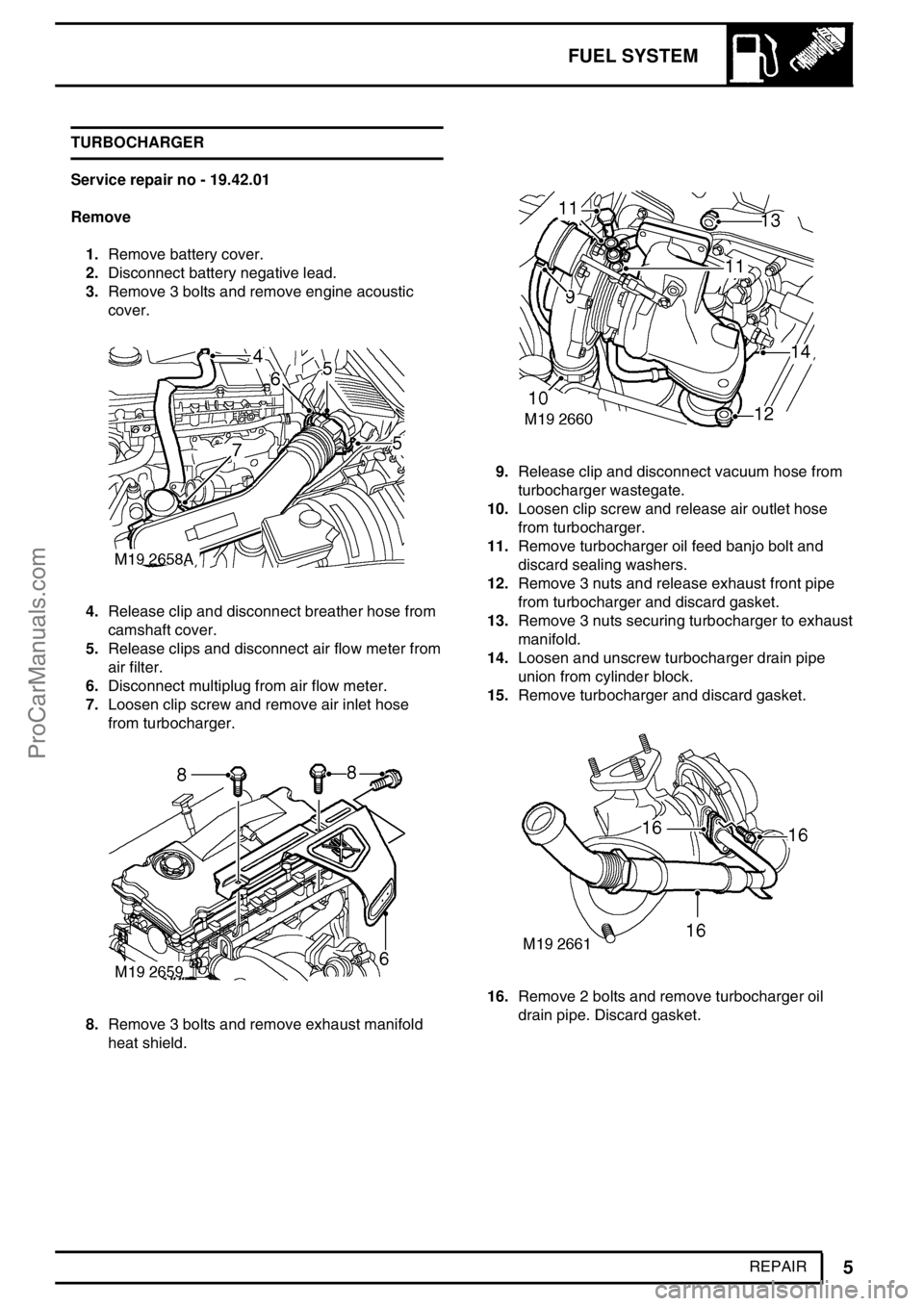
FUEL SYSTEM
5
REPAIR TURBOCHARGER
Service repair no - 19.42.01
Remove
1.Remove battery cover.
2.Disconnect battery negative lead.
3.Remove 3 bolts and remove engine acoustic
cover.
4.Release clip and disconnect breather hose from
camshaft cover.
5.Release clips and disconnect air flow meter from
air filter.
6.Disconnect multiplug from air flow meter.
7.Loosen clip screw and remove air inlet hose
from turbocharger.
8.Remove 3 bolts and remove exhaust manifold
heat shield.
9.Release clip and disconnect vacuum hose from
turbocharger wastegate.
10.Loosen clip screw and release air outlet hose
from turbocharger.
11.Remove turbocharger oil feed banjo bolt and
discard sealing washers.
12.Remove 3 nuts and release exhaust front pipe
from turbocharger and discard gasket.
13.Remove 3 nuts securing turbocharger to exhaust
manifold.
14.Loosen and unscrew turbocharger drain pipe
union from cylinder block.
15.Remove turbocharger and discard gasket.
16.Remove 2 bolts and remove turbocharger oil
drain pipe. Discard gasket.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 275 of 667
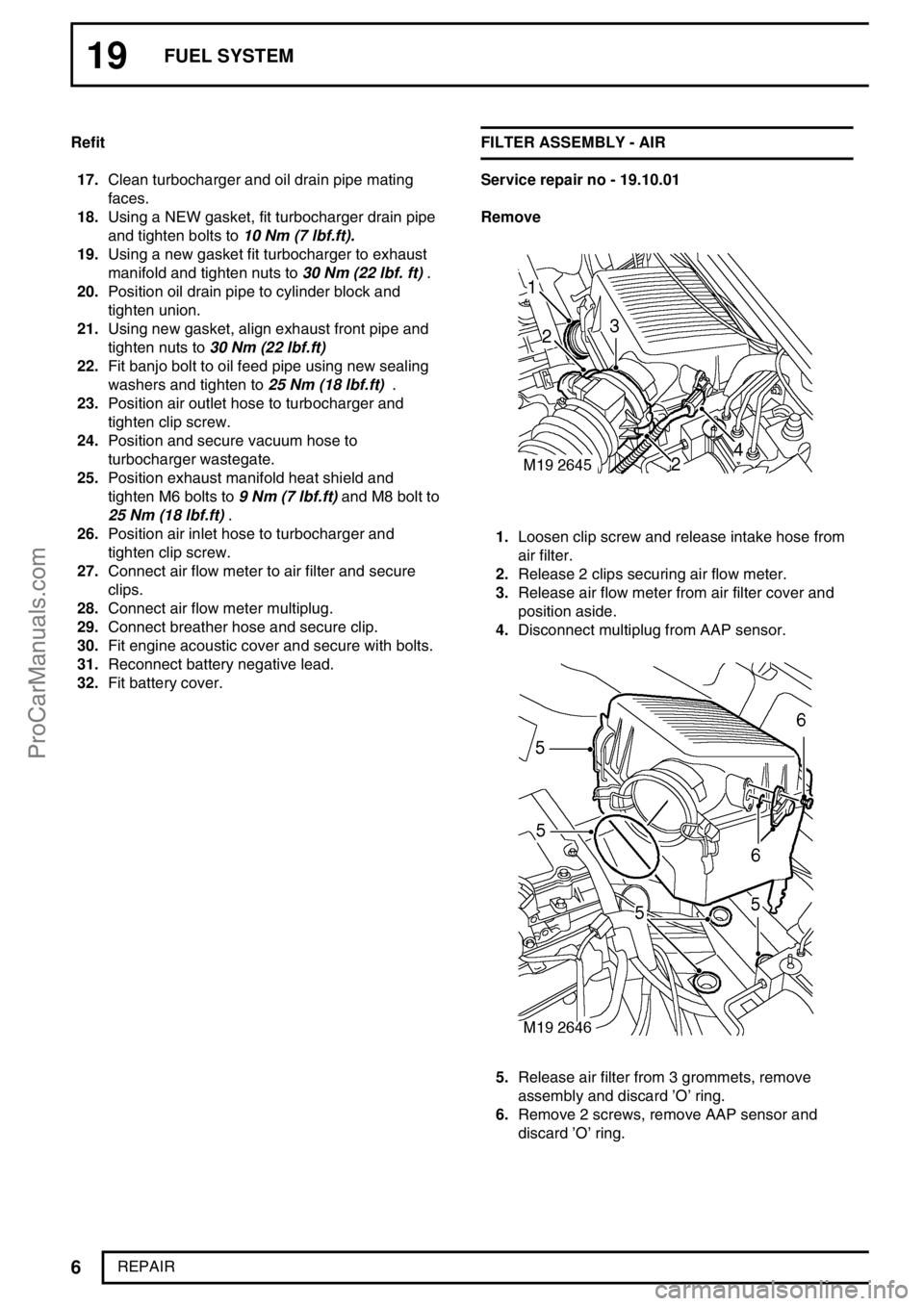
19FUEL SYSTEM
6
REPAIR Refit
17.Clean turbocharger and oil drain pipe mating
faces.
18.Using a NEW gasket, fit turbocharger drain pipe
and tighten bolts to10 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
19.Using a new gasket fit turbocharger to exhaust
manifold and tighten nuts to30 Nm (22 lbf. ft).
20.Position oil drain pipe to cylinder block and
tighten union.
21.Using new gasket, align exhaust front pipe and
tighten nuts to30 Nm (22 lbf.ft)
22.Fit banjo bolt to oil feed pipe using new sealing
washers and tighten to25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
23.Position air outlet hose to turbocharger and
tighten clip screw.
24.Position and secure vacuum hose to
turbocharger wastegate.
25.Position exhaust manifold heat shield and
tighten M6 bolts to9 Nm (7 lbf.ft)and M8 bolt to
25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
26.Position air inlet hose to turbocharger and
tighten clip screw.
27.Connect air flow meter to air filter and secure
clips.
28.Connect air flow meter multiplug.
29.Connect breather hose and secure clip.
30.Fit engine acoustic cover and secure with bolts.
31.Reconnect battery negative lead.
32.Fit battery cover.FILTER ASSEMBLY - AIR
Service repair no - 19.10.01
Remove
1.Loosen clip screw and release intake hose from
air filter.
2.Release 2 clips securing air flow meter.
3.Release air flow meter from air filter cover and
position aside.
4.Disconnect multiplug from AAP sensor.
5.Release air filter from 3 grommets, remove
assembly and discard’O’ring.
6.Remove 2 screws, remove AAP sensor and
discard’O’ring.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 290 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
NOTE: Inset A shows differences for Pre
EU3 models
1.Pressure cap
2.Overflow pipe
3.Heater return hose
4.Heater matrix
5.Heater inlet hose
6.Oil cooler return pipe - EU3 models
7.Connecting hose
8.Oil cooler housing assembly
9.Heater inlet pipe
10.Connecting hose
11.Outlet housing
12.Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
13.Bleed screw
14.Radiator top hose
15.Radiator - upper
16.Intercooler
17.Gearbox oil cooler
18.Radiator - lower
19.Viscous fan
20.Drain plug
21.Connecting hose
22.Fuel cooler feed hose
23.Radiator bottom hose
24.Thermostat housing
25.Connecting hose
26.Coolant pump feed pipe
27.Coolant by-pass pipe
28.Radiator bleed pipe
29.Connecting hose
30.Coolant pump
31.Fuel cooler
32.Heater/expansion tank return hose
33.Expansion tank
34.EGR Cooler - EU3 models
35.Connecting hose - EU3 models
36.Connecting hose - EU3 models
37.Hose - EGR Cooler to oil cooler return pipe -
EU3 models
38.Radiator lower feed hose - Pre EU3 models
39.Oil cooler return pipe - Pre EU3 models
ProCarManuals.com
Page 292 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION A - EU 3 Models
B- Pre EU3 Models
GENERAL
The cooling system used on the Diesel engine is a pressure relief by-pass type system which allows coolant to
circulate around the engine block and heater circuit when the thermostat is closed. With coolant not passing
through the by-pass or the radiator promotes faster heater warm-up which in turn improves passenger comfort.
A coolant pump is mounted on a casting behind the PAS pump and is driven from the PAS pump at crankshaft
speed by the auxiliary drive belt. The pump mounting casting connects with passages in the cylinder block and
pumps coolant from the radiator through the cylinder block.
A viscous fan is attached to an idler pulley at the front of the engine. The fan is attached to a threaded spigot on
the pulley with a right hand threaded nut. The fan draws air through the radiator to assist in cooling when the
vehicle is stationary. The fan rotational speed is controlled relative to the running temperature of the engine by a
thermostatic valve regulated by a bi-metallic coil.
The cooling system uses a 50/50 mix of anti-freeze and water.
Thermostat Housing
A plastic thermostat housing is located behind the radiator. The housing has three connections which locate the
radiator bottom hose, top hose and coolant pump feed pipe. The housing contains a wax element thermostat and
a spring loaded by-pass flow valve.
Thermostat - Main valve
The thermostat is used to maintain the coolant at the optimum temperature for efficient combustion and to aid
engine warm-up. The thermostat is closed at temperatures below approximately 82°C (179°F). When the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 82°C the thermostat starts to open and is fully open at approximately 96°C
(204°F). In this condition the full flow of coolant is directed through the radiator.
The thermostat is exposed to 90% hot coolant from the engine on one side and 10% cold coolant returning from
the radiator bottom hose on the other side.
Hot coolant from the engine passes from the by-pass pipe through four sensing holes in the flow valve into a tube
surrounding 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant returning from the radiator, cooled by the ambient
air, conducts through 10% of the thermostat sensitive area.
In cold ambient temperatures, the engine temperature is raised approximately 10°C (50°F) to compensate for the
heat loss of 10% exposure to the cold coolant returning from the radiator bottom hose.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 294 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Radiator
The 44 row radiator is located at the front of the vehicle in the engine compartment. The cross flow type radiator is
manufactured from aluminium with moulded plastic end tanks interconnected with tubes. The bottom four rows are
separate from the upper radiator and form the lower radiator for the fuel cooler. Aluminium fins are located
between the tubes and conduct heat from the hot coolant flowing through the tubes, reducing the coolant
temperature as it flows through the radiator. Air intake from the front of the vehicle when moving carries the heat
away from the fins. When the vehicle is stationary, the viscous fan draws air through the radiator fins to prevent
the engine from overheating.
Two connections at the top of the radiator provide for the attachment of the top hose from the outlet housing and
bleed pipe to the expansion tank. Three connections at the bottom of the radiator allow for the attachment of the
bottom hose to the thermostat housing and the return hose from the oil cooler and the feed hose to the fuel cooler.
The bottom four rows of the lower radiator are dedicated to the fuel cooler. The upper of the two connections at
the bottom of the radiator receives coolant from the oil cooler. This is fed through the four rows of the lower
radiator in a dual pass and emerges at the lower connection. The dual pass lowers the coolant temperature by up
to 24°C before being passed to the fuel cooler. Two smaller radiators are located in front of the cooling radiator.
The upper radiator is the intercooler for the air intake system and the lower radiator provides cooling of the
gearbox oil.
Pipes and Hoses
The coolant circuit comprises flexible hoses and metal formed pipes which direct the coolant into and out of the
engine, radiator and heater matrix. Plastic pipes are used for the bleed and overflow pipes to the expansion tank.
A bleed screw is installed in the radiator top hose and is used to bleed air during system filling. A drain plug to
drain the heater and cylinder block circuit of coolant is located on the underside of the coolant pump feed pipe.
Oil Cooler
The oil cooler is located on the left hand side of the engine block behind the oil centrifuge and oil filter. Oil from the
oil pump is passed through a heat exchanger which is surrounded by coolant in a housing on the side of the
engine.
Full water pump flow is directed along the cooler housing which also distributes the flow evenly along the block
into three core holes for cylinder cooling. This cools the engine oil before it is passed into the engine. A small
percentage of the coolant from the oil cooler passes into a metal pipe behind the engine. It then flows into the
lower radiator via a hose.
Fuel Cooler
The fuel cooler is located on the right hand side of the engine and is attached to the inlet manifold. The cooler is
cylindrical in design and has a coolant feed connection at its forward end. A’T’connection at the rear of the cooler
provides a connection for the coolant return from the heater matrix and coolant return from the fuel cooler.
The’T’connection houses a thermostat which opens at approximately 82°C. This prevents the cooler operating in
cold climates. Two quick release couplings on the cooler allow for the connection of the fuel feed from the
pressure regulator and return to the fuel tank. A counter flow system is used within the cooler.
Fuel flows around a coolant jacket within the cooler and flows from the back to the front of the cooler. As the hot
fuel cools travelling slowly forwards it meets progressively colder coolant travelling in the opposite direction
maintaining a differential cooling effect.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 295 of 667

26COOLING SYSTEM
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Coolant Pump
1.Drive lugs (hidden)
2.Housing
3.’O’rings4.Cover
5.Feed hose connection
6.Impeller
The coolant pump is attached on the left hand side of the engine, behind the PAS pump. A cast housing, bolted to
the cylinder block provides a common attachment point for both pumps. The housing has galleries which connect
the coolant pump to the cylinder block and the oil cooler housing. The coolant pump comprises a shaft, a housing
and a cover.
The shaft, which passes through the alloy housing, is supported at each end by bearings. Seals at each end of the
shaft protect the bearings from the coolant. The forward end of the shaft has two lugs which engage with the PAS
pump shaft. The opposite end of the shaft is fitted with an impeller which draws coolant from the feed pipe and
circulates it through galleries in the cylinder block. The shaft is driven by the auxiliary drive belt at the same
rotational speed as the crankshaft by a pulley attached to the PAS pump.
The pump is sealed in the cast housing with two’O’rings. An outer cover is positioned over the pump and secured
with six bolts and sealed to the pump with an’O’ring. The cover provides the attachment for the feed pipe
connecting hose.
ProCarManuals.com