1999 HONDA CIVIC cover
[x] Cancel search: coverPage 707 of 2189

I
3. 3rd Gear
As the soeed of the vehicle reaches the prescribed value, shift control solenoid valve B is turned OFF by means ol the
pCM. Shift control solenoid valve A remains ON. The modulator pressure (6) flows to the right end of the 1-2 shift
valve and the left end oJ the 2-3 shift valve. The 2-3 shift valve is moved to the right side by the modulator pressure
(68). The 2-3 shift valve covers the port to stop line pressure (5) to the 2nd clutch and uncovers to the 3-4 shift valve
as the 2-3 shift valve is moved to the right side. The line pressure (5) becomes the 3rd clutch pressure (30) at the 3-4
shift valve. The 3rd clutch pressure (30) is applied to the 3rd clutch, and the 3rd clutch is engaged'
Fluid flows by way of:- Line Dressure (4) * CPB Valve - Line Pressure (5) * 1-2 Shift Valve - Line Pressure (5) * 2-3 Shift Valve
- Line Pressure (5) * 3-4 Shift Valve - 3rd Clutch Pressure (30) - 3rd Clutch
The hvdraulic pressure also flows to the 1st clutch. However, no power is transmitted because of the one-way clutch
as in 2nd gear.
NOTE: When used, "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
14-29
Page 708 of 2189
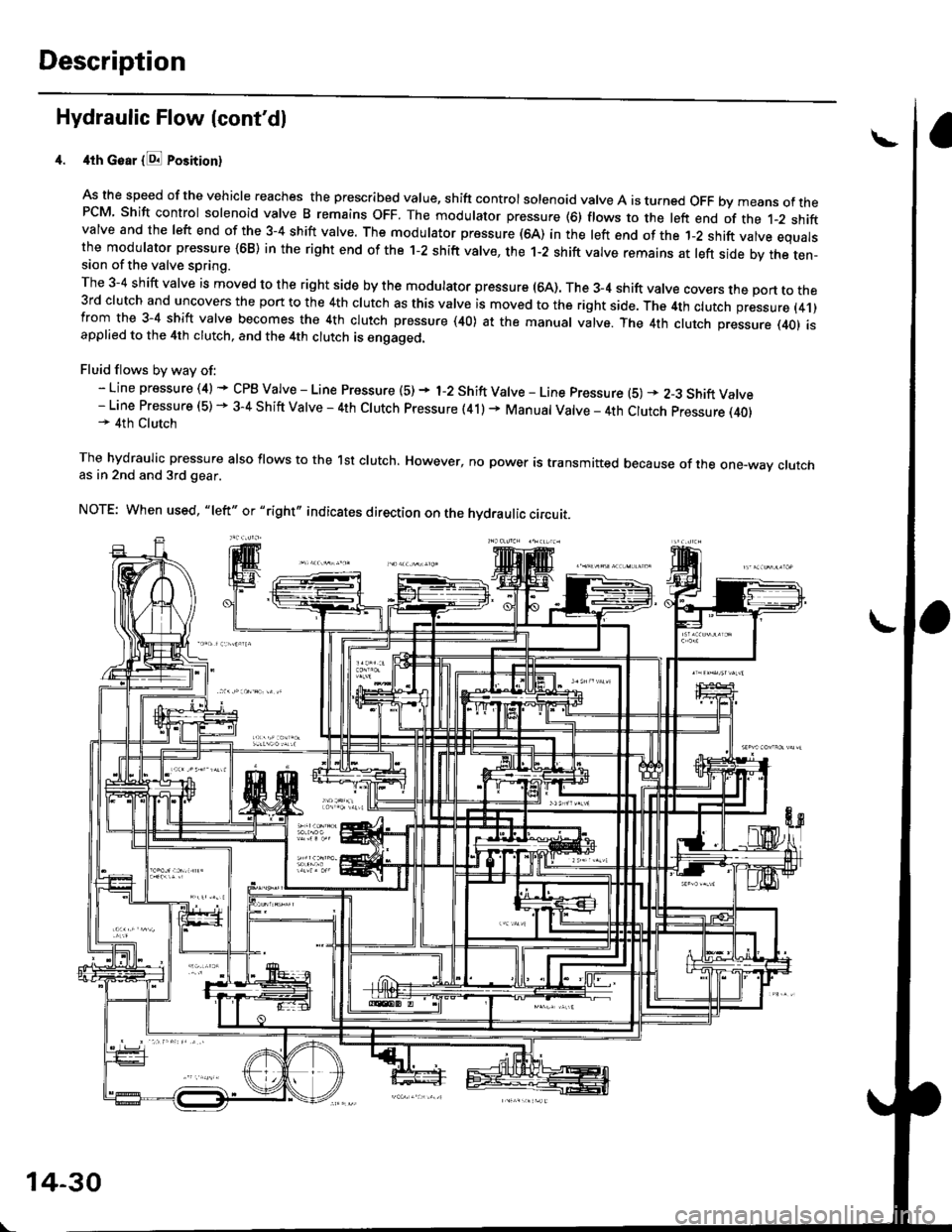
Description
Hydraulic Flow lcont'dl
4th Goar {E Position}
As the speed of the vehicle reaches the prescribed value, shift controlsolenoid valve A is turned OFF bymeans ofthePCM Shift control solenoid valve B remains oFF. The modulator pressure (6) flows to the left end of the t-2 shiftvalve and the left end of the 3-4 shift valve. The modulator pressure (64) in the left end of the 1-2 shift valve equalsthe modulator pressure {68) in the right end of the 1-2 shift valve, the 1-2 shift valve remains at left side by the ten-sion of the valve spring.
The 3-4 shift valve is moved to the right side by the modulator pressure (64). The 3_4 shift valve covers the port to the3rd clutch and uncovers the port to the 4th clutch as this valve is moved to the right side. The 4th clutch pressure (4.1)from the 3-4 shift valve becomes the 4th clutch pressure (40) at the manual valve. The 4th clutch pressure (401 isapplied to the 4th clutch, and the 4th clutch is engaged.
Fluid flows by way of:- Line pressure (4) * CPB Valve - Line Pressure (5) + 1-2 Shift Valve - Line pressure (5) * 2-3 Shift Valve- Line Pressure (5) - 3-4 Shift Valve - 4th Clutch pressure (41) + Manual Valve _ 4th Clutch pressure (40)* 4th Clutch
The hydraulic pressure also flows to the lst clutch. However, no power is transmitted because of the one-way crutchas in 2nd and 3rd gear.
NOTE: When used, "|eft" or "right,, indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
\
14-30
Page 709 of 2189

L
E Position
The flow of fluid through the torque convefter circuit is the same as in E position The line pressure (1) changes to the
line pressure (3) and flows to the l-2 shift valve. The iine pressure (3) changes to the line pressure (3') at the 'l-2 shift valve
and flows to the servo valve. The servo valve is moved to the right side (Reverse range position) and uncovers the port to
allow line pressure {3") to the manual valve, The line pressure {3') from the 1-2 shift valve flows through the servo valve to
the manual valve and changes the 4th clutch pressure (40). The 4th clutch pressure (40) is applied to the 4th clutch, and
the 4th clutch is engaged,
Reverse Inhibitor Control
When the E position is selected while the vehicle is moving forward at spe€ds over 6 mph (10 km/h)' the PCM outputs the
1st speed signal to shift control solenoid valves A and B; shift control solenoid valve A is turned oFF, shift control solenoid
valve B is turned ON. The 1-2 shift valve is moved to the right side and covers the port to stop line pressure (3') to the
servo valve. The line pressure (3'�) is not applied to the servo valve, and the 4th clutch pressure (40) is not applied to the
4th clutch, as a result, power is not transmitted to the reverse direction'
When used. 'left" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit'
14-31
Page 710 of 2189

Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'd)
lll Position
The flow of fluid through the torque converter circuit is the same as in E position. The line pressure (1) changes to theline pressure (3) and flows to the l-2 shift valve. The line pressure (3) changes to the line pressure (3,) at the 1-2 shift valveand flows to the servo valve. The servo valve is moved to the right side (Reverse range position) and uncovers the port toallow line pressure (3") to the manual valve as in @ position. The line pressure (3") from the servo valve is Intercepted bythe manual valve. However, hydraulic pressure is not supplied to the clutches, and the power is not transmitted.
NOTE: When used, "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
14-32
Page 711 of 2189

\
Lock-up System
Lock-up Clutch
1. Ooeration (clutch onl
with the lock-up clutch on, the fluid in the chamber between the torque converter cover and the lock-up piston is drained
off, and the converter fluid exerts pressure through the piston against the torque converter cover, As a result, the conven-
er turbine is locked to the convefter cover. The effect is to bypass the converter, thereby placing the vehicle in direct drive
LOCK.UP PISTONDAMPER SPRING
The power flows by way ot:
Engine
{
Drive plate
i
Torque converter cover
I
Lock-up piston
Damper spring
I
Turbine
Mainshaft
ODeration {clutch off}
With the lock-up clutch off, the fluid flows in the reverse of "clutch on." As a result, the lock-up piston moves away from
the converter cover, and the torque converter lock-up is releassd.
Engine
t
Drive plate
I
Torque convener cover
{
Pump
I
Turbine
Mainshaft
TOROUECOVER
(cont'd)
COI{VERTER
\
TURBNE
MAINSHAFT
14-33
Page 712 of 2189

Description
Lock-up System (cont'd)
TOROUE CONVERTER
In B.rl position, in 3rd and 4th, and lDl_- position in 3rd.pressurized fluid is drajned from the back of the torqueconverter through a fluid passage. causing the lock-uppiston to be held against the torque convener cover. Asthis takes place, the mainshaft rotates at the same speedas the engine crankshaft, Together with the hydrauliccontrol, the PCM optimized the timing of the lock_upsystem. Under certain conditions, the lock_up clutch isapplied during deceleration, in 3rd and 4th gear.
The lock-up system controls the range of lock_up accord_ing to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B. and thelinear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves Aand B activate, modulator pressure changes. Lock_upcontrol solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoidare mounted on the outside of the torque converterhousing. and are controlled by the pclvl.
Lock-up Conditions/Lock-up Control Solenoid Valves/Linear Solenoid Pressure
MODULATOR PRESSURE
.-- LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
LOCK.UP CONTROL. VALVE
LOCK.UP CONTROLSOLENOID VALVELock-up
Conditions
Lock-up Control
Solenoid ValveLineal
Solenoid
PressureAB
Lock-up OFFOFFOFFHig h
Lock-up. HalfONDuty operation
OFF - ON
Lock-up. FullONONHigh
Lock-up
during
decelerationONDuty operation
OFF * ONLowTOROUE CONVERTERCHECI( VALVE
RELIEF VAI-VE
LOCK.UP TIMINGVALVE
^ r______rr r cooLER RELTEF VALVE
t'-
14-34
ATF PUMP
Page 786 of 2189

Mai nshaft/Cou ntershaft
Linear Solenoid AssemblySpeed Sensors
Replacement
1. Remove the mounting bolts and the linear solenoid
assemory.
Clean the mounting surfaceand flu id passages.
6x1.0mm12 N.m 11.2 kgl m,8.7 tbf.ftl
@
@
GASKET
Clean the mounting surface and fluid passage of the
linear solenoid assembly and transmission housing.
Install a new linear solenoid assembly with a new
gasl(et.
NOTE; Do not pinch the gasket when installing the
linear solenoid; make sure that the gasket is installedproperly in the mounting groove of the linear sole-
noid.
Check the linear solenoid connector for rust, dirt or
oil, and connect it securely,
LINEARSOLENOIDASSEMELY
I
14-108
Replacement
't.
6x128.7
Remove the 6 mm bolt and the countershaft speed
sensor from the right side cover.
COUNTERSI{AFTSPEED SENSOR
O.RINGReplace.
MAINSHAFTSPEEDSENSOR
MAINSHAFT SPEEDSENSOB WAS}IER(D16Y7 enginel
6x1.0mm12 N.m (1.2 kgf m,8.7 tbf.ft)
1.0 mmN.m (1.2 kgf.m,rbf ft)
\\
/,
%/E:)
Remove the 6 mm bolt and the mainshaft sDeed
sensor from the transmission housino.
Replace the O-ring with a new one before installing
the countershaft speed sensor or th€ mainshaft speed
sensor.
NOTE: Installthe mainshaft speed sensor washer on
the mainshaft speed sensor. The mainshaft speed
sensor washer is used on models with the D'|6Y7
engine.
Page 790 of 2189

Symptom-to-Component Chart
Hydraulic System (cont'dl
G.
n,
set idle rpm in gear to specified idle speed. lf still no good, adjust motor mounts as outlined in enginesection of this manual.
lf the clutch pack is seized or is excessively worn. inspect the other clutches for wear, and check the orificecontrol valves, CPC valve and linear solenoid for free movement.
lf the linear solenoid is stuck, inspect the clutches for wear.
lmproper alignment or main valve body and torque converter housing may cause ATF pump seizure. Thesymptoms are mostly an rpm-related ticking noise or a high-pitched squeak.
lf the l st clutch feed pipe guide in the end cover is scored by the mainshaft, inspect the ball bearing forexcessive movement in the transmission housing. lf oK, replace the end cover as it is dented. The o-rinounder the guide is probably worn.
Replace the mainshaft if the bushing for the 4th feed pipe is loose or damaged. lf the 4th feed pipe is danFaged or out of round, replace the right side cover.
Replace the mainshaft if the bushing for the 1st feed pipe is loose or damaged. lf the 1st feed pipe is darn-aged or out of round, replace it.
A worn or damaged sprag clutch is mostly a result of shifting the transmission inthe wheels rotate in reverse, such as rocking the vehicle in snow.
or E position while
Inspect for damage and wear:
1. Reverse selector gear teeth chamfers.
2. Engagement teeth chamfers of countershaft 4th and reverse gear.
3. Shift fork for scuff marks in center.
4. Differential pinion shaft for wear u nder pin ion gears.
5. Bottom of 3rd clutch for swirl marks.
Replace items 1,2,3 and 4 if worn or damaged. lf transmission makes a clicking, grinding orwhirring noise,also replace mainshaft 4th gear, reverse idler gear. and countershaft 4th gear in addition to 1, 2, 3 or 4.lf differential pinion shaft is worn, overhaul differential assembly, and replace ATF strainer, and thoroughlyclean transmission, flush torque converter, cooler and lines.lf bottom of 3rd clutch is swirled and transmission makes gear noise, replace the countershaft and final drivengear.
Be very careful not to damage the torque converter housing when replacing the main ball bearing, you
may also damage the ATF pump when you torque down the main valve body. This will result in ATF pumpseizure if not detected. Use the oroper roors.
Install the main seal flush with the torque converter housing. lf you push it into the torque converterhousing until it bottoms out, it will block the fluid return passage and result in damage.
See flushing procedure, page 14-187 and 188.
lf the large clutch piston O-ring is broken, inspect the piston groove for rough machining.
lf the l-2 shift valve is stuck closed, the transmission will not upshift. lf stuck open, the transmission hasno 1st gear.
lf the znd orifice control valve is stuck. inspect the 2nd and 3rd clutch oacks for wear.
lf the 3-4 orifice control valve is stuck, inspect the 3rd and 4th clutch oacks for wear.
lf the clutch pressure control valve is stuck closed, the transmission will not shift out of 1st gear.
lf the ATF strainer is clogged with particles of steel or aluminum, inspect the ATF pump and differentialpinion shaft. lf both are OK and no cause for the contamination is found, replace the torque converter.
Inspect the frame for collision damage.
14-112