Page 1913 of 2189
PGM-FI (D1685) (cont'd)
EGRvdvo Fuer ia ( tEGR In pres$uro \valvs s€mor nd*6nc6 lP i.snsor h.tsl lank tenF, Icont ol inDut volt|ce s8fi8of inDul inbut ssnsof ifix, I: control inDln voltac€ s€{tlor input inout sonsol ingJl ;I G.€GF} GGf,q N@a fiPg' .(PFoJ fiFO) ,L------- ------J
j
c2887
c150PHOTO 112
C'ro1PHO|O sl
c575
vtEw 7i
(FUELTA}IKTEMPEB.ATURESENSOR
H1Y
FUEL TANKPRESSURESENSOnPHOTO 116
THROTTLEPOSrT|0NCIP)SENSOR
EXHAUSTGAS RECIR.CULATION(EGR) VALVEand LIFTSENSORPHOfO 36
"""r":x
o
GRI{/BLK
4
GNN/BLK
GNN/gLK
c575
c401PHOfO 57vtEw 40
2
GRN/BL(
cls0
a
POWERTBAINCONTROLMOOULE(PCM)PHOfO 86
I
I
IJ
n"*r"a^[
'rcai/BLX llcre Ar--?
lsJiH,
I ground
I
25-6
Page 1914 of 2189
-.t POWERTRAIN
lcoNTRoL
Fuel I MODULE
\. . -,.^-- p{sssure
I llglllTP-. . sansor sensor .s€nsor i;ir*,o; sensor_rnpul input input input :I nFa (PF2) GcD i|An IrL------ --------Jc13 I' c14Y c26
FUELTEMPERATURESENSOR
Fromfacingpage.
v
!
_l
Fromnenpage.
vi
GFN/BLK lI
i
EG-f
flltur'ffi
,{J
ENGINECOOLANTTEMPERATURE(Ecr)SENSOR
INTAKEAIRTEMPERATURE(rAr)SENSOR
c't 15(ferminals &14)
vtEw 38
(cont'd)
25-7
Page 1946 of 2189
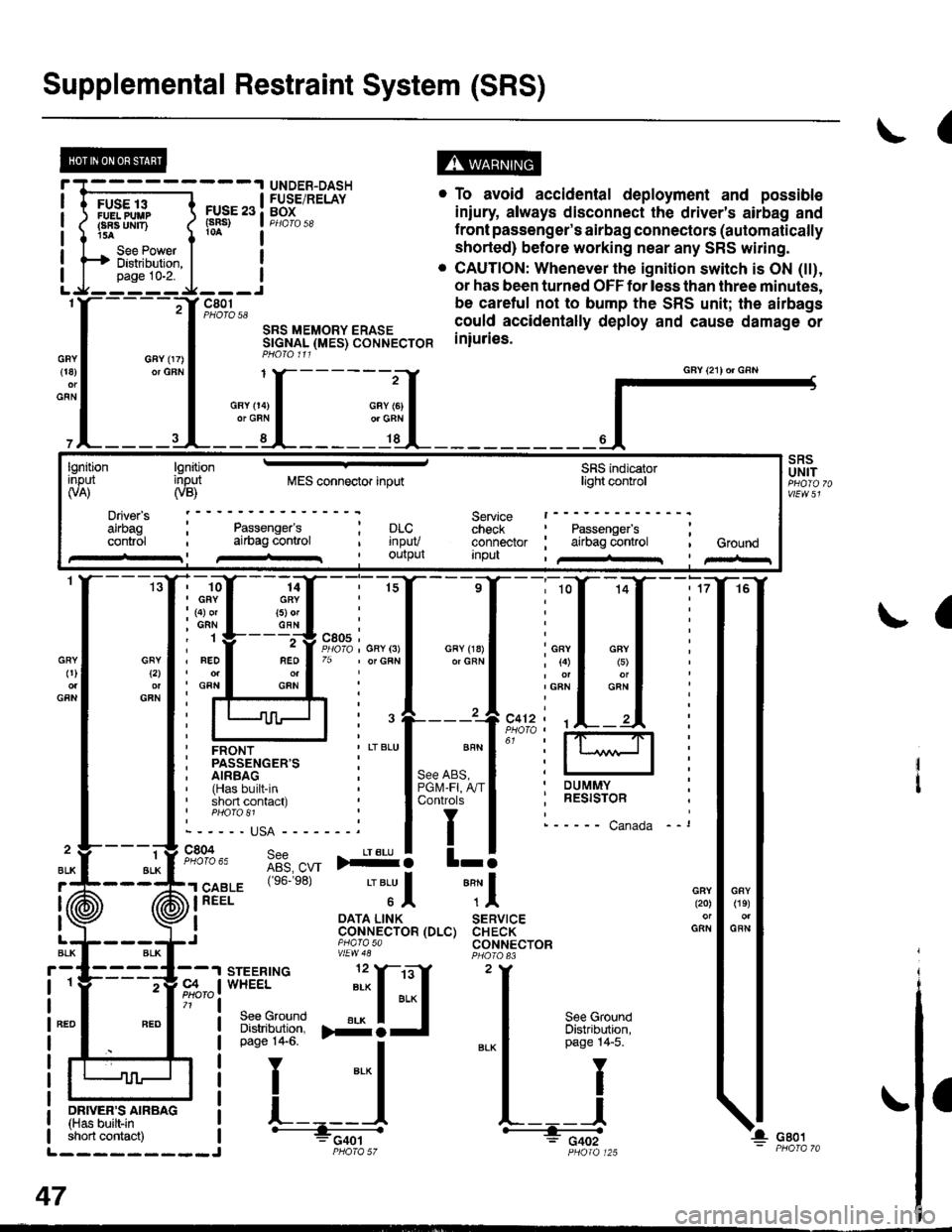
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)
(
FUSE 13FUELPUUPFBA UMT)15A
See PowerDistibution,page 10-2.
FUSE 23(sRs)
c801PHOTO 58
SRS MEMORY ERASESTGNAL (MES) CONNECTORPHO|O 111
. To avoid accidental deployment and possible
iniury always disconnect the driver's airbag and
f ront passenger's airbag connectors (automatically
shorted) before working near any SRS wiring.
. CAUTION: Whenever the ignition switch is ON (tt),
or has been turned OFF for less than three minutes,
be caretul not to bump the SRS unit; the airbags
could accidentally deploy and cause damage or
iniuries.
UNDER-DASHFUSE/RELAYBOX
GFY 07)or GFN{18)
GFN
GFYt2l
GFN
GRY0)
GFN
2
ALK
J (ii
t\
GFY O4)or GRN
SRSUNIT
a
-ffiffi,*l-{
H!=";=_J
iffii'r:fi:*" i tH-
PHOIO 125short contact) | - FCqOtL_________J PHO|A 57
47
GAY (21) or GRN
lgnitionInput(VA)
Driver's
cont.ol
lgnitioninput(VB)MES connector inputSRS indicatorlighl control
Service t------check : Passengefs ;connector ; airbag control , GroundInpu , /+rr I pir-r
Passenger'sai|bag conlrol; prc..t rnpuv, Ourpul
14GRY(5) orGFN
rffi{{_ilil
i ffi i""'"1*"o,"'.1'' i lffil
ffirtu!-T:l
ir:r*::"."
ilstEl'{s6.e8'�
'"'Jl "Tl
, I oATA L|NK SERVTCE: CoNNECTOR (DLC) CHECK,J piarasa CONNECTORvtEw48
Page 1972 of 2189
Low Fuel Indicator Light
l
't
I
I
I
IJ
pag6 106.
,
-ls,T,*-*:lligff*,
l',;l:'l?,'
A3A
!'-{ilril}-1 PowERTRAtNI Lowtuel I CONTROL
I i$grtor I MoD]LE (pcM)
i
S' i18l7"*
UNDER.DASHFUSE/RELAYBOXPHOTO 58
!ra
or*+* i
TFI i
--l------i"I
I
A oxc€pt GX
c503PHO|O 61
AFN/GFI{
9FN/GBN
15
BLU/FEO
c410
vlEw 3s
c'131PHO|O A5vtEw 59
I TANK: UNITThan|tlrlor
So€qauges
L-----J- ----J
Sae GroundDistribution,pa$ 14-9.
74
Page 1973 of 2189

How the Gircuit Works
All Except GX
Do not smoke while working on the fuel system.
Keep open flame away trom the work area. Drain
fuel only into an approved container.
A thermistor is mounted in the fuel tank unit. When
the thermistor is cool, its resistance is very high.
When the thermistor's temperature increases, its
resistance decreases. Fuel in the fuel tank transters
heat away lrom the thermistor fast enough to keep it
cool so the thermistor's resistance stays high and
lhe low fuel indicator light does not come on. When
the fuel level drops below the thermistor, the
thermistor's temoerature increases. Without the fuel
to cool it, the thermistor's resislance decreases,
allowing current to llow through the low fuel
indicator light and the thermistor to ground, and the
low fuel indicator light comes on.
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
GX
The PCM turns on the low fuel indicator light when
the fuel level is low. The PCM will also blink the
indicator light when a problem is detected by the
fuel tank pressure sensor or the fuel tank
temperature sensor.
Refer to the Service Manual GX Supplement
(Section 11 , Fuel and Emissions) for specific tests
or troubleshooting procedures.
74-1
Page 1976 of 2189
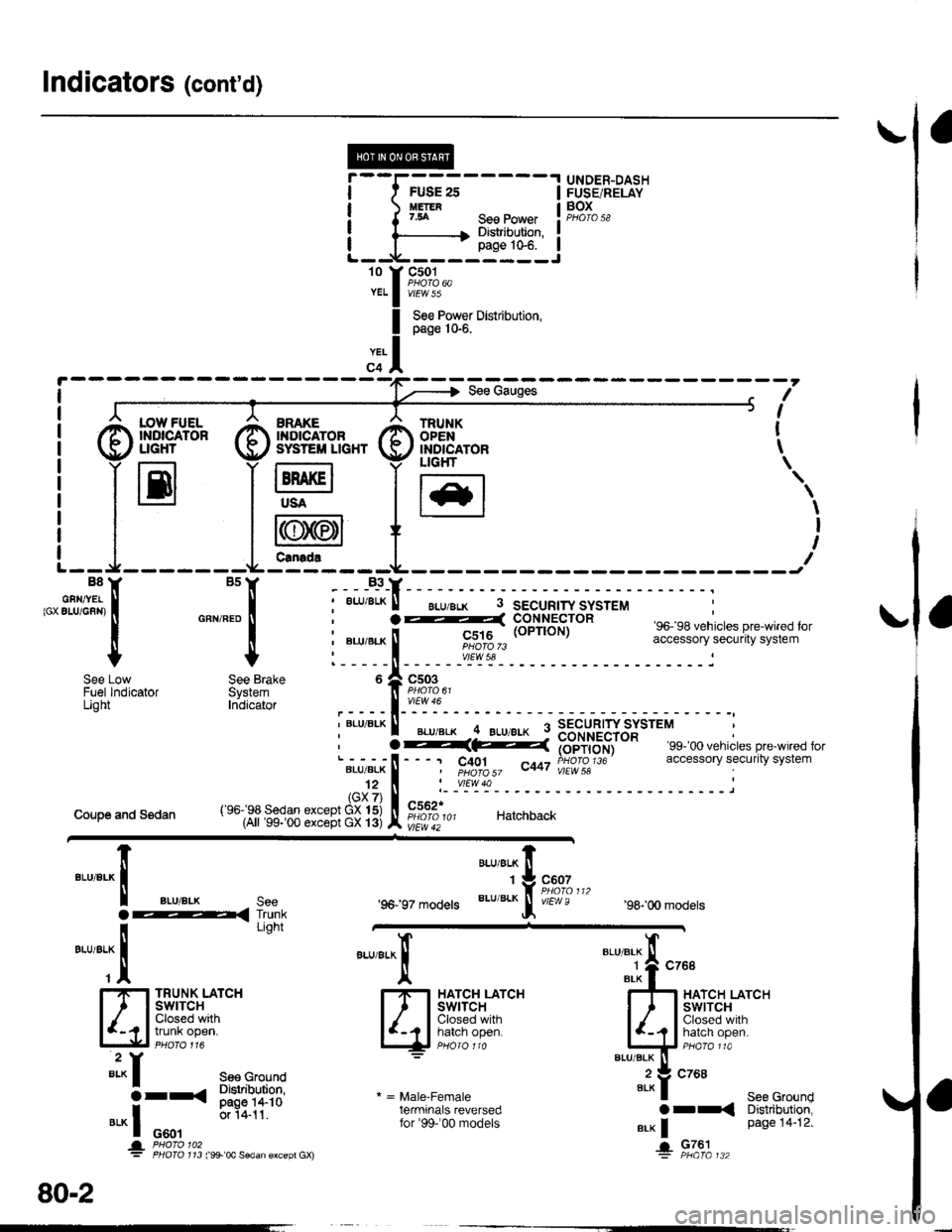
Indicators (cont'd)
I
I
I
I
't0 t
YEL
YEL
FUSE 2sUETER7.54
.I UNDER-DASH
IFUSE/RELAY
! F,gI".,I
IJ
See PowerDistribution,page 10€.
@f,*+* @sv#ftn* G)ffig^,", t
I
S€e Pow€r Distribution,page 10-6.
?-(: i#i',du), c401 ^t,a PHOfO 1J6I pHOfO 57 v"r vlEW 58
'99- 00 vehicles pre-wired foraccessory security system
I :7 r----r -7 ucHr \
i llEl lH lt*l
'.,
| | i r{rN/,6n1I I I l\y
//l I t
t--J-------Lfe---t---- ---JB8Y BsY B3YB8Y BsY -___B_3_Y_
,"' sfilJi:, i "*,*" i ;
""'"'*
! - "*-i
F"EIi,6HiJttr" so. sa venricres pre_w reo ror
I | : ".u,"r" ! ii|ot$,, accessory securrtv svstem
+ + l-----il------"rl';r'- ------------i
i "Lu,"r" ! rc;1rg (oPrroN) """"";:"J; !H;fi;"";Jt"'
l_____ll_ ____-v'_E\s!- __________-_i
o A csoeI PsOrO 6t
,----l-'':y:-
i """'^ I ".u"." -4 ELueLx 9 3B"rU"?'JYSJtttt :
See Low See Brake 6 Zl C503Fuel lndicator System ]l Paoro o'Light Inbicator ,____l_'':Y":-, BLU BLK ll _... _.._ q SECURTW SYSTEM, I BLU'BLK .. BLU/8!K : nourpcrrip
Coupe and Sedan
'96197 models
"ar,"a^ fi
'tg::1",,,
BLU/BLK
Jf v/Er,! e'98-'00 models
TRUNK LATCHSWITCHClosed withtrunk open.
"arr"a*l
qF*til'-""
* = Male-Femaleterminals reversedfor'99-'00 models
"'"'"i{ "^'
4r*liT;--'""""'-it:':
Bi?fi,,ri"li
".* | Page 14"12'
+ Fla'|",.
""'"'-lt
aLU/aLK see
i-< I'dli
-*TT
"'*f see cround
3rr< Sl"JliT:?s
".* I o*.,
0.1411'
* '&3i311'" ,:*'* ""dan €xcep, Gx)
80-2
Page 1979 of 2189
GAUGEASSEMBLYf
l-*
,'
I
t
\
\
I
I
,
,:
ENGlrlECOOLANTTEiTPERATNEGAI'GE
FUELGAUGE
--------J
GX modelBl2
tr' Alt€xcsp't Gx mod€t B1o
IYEUGFN I
,r, A "oll "., ","11"
fi;rt"r4." ,1,"g[ s;g,,YEUGFN I 2lvtuea
r-----.|FUEL
- A ^.^. I |fl Fuer lll,l5
-*"L[
F*H4''
L
t#4iorn-i'**
-
t '-;5-
OFN/BLU
OFN/BLU
OFN
A4
c410
vlEw 35
c131
vtEw 59
r --= .I POWERTRAIN
!r+i-'' !fi8tsllP.
331ffi !i;E-i/'i
#."o,". t f
14
ii11"t:'f""'
*!--*
il?:+:ifll--JvtEwzo
81-1
Page 1980 of 2189

Gauges (cont'd)
- How the Gircuit Works
When the ignition switch is in ON (ll) or START (lll),
battery voltage is supplied through fuse 25 to the
gauges in the gauge assembly.
Speedometer and Odometer
The odometer and soeedometer drive circuits
receive pulses from the vehicle speed sensor
(VSS). The pulse rate increases as the car
accelerates. The frequency and duration of these
input pulses are measured and displayed by the
speedometer, odometer and tripmeter.
Tachometer
The tachometer drive circuit receives pulses from
the ignition control module (lCM) in the distributor
assembly or the ECM/PCM. The solid-state
lachometer then displays these pulses as engine
speed. For each 200 pulses per minute from the
ignition control modul€ (lCM) or the ECM/PCM, the
tachometer displays 100 RPM.
Engine Coolant Temperature Gauge
The engine coolant temperature gauge has two
intersecting coils wound around a permanent
magnet rotor. Voltage applied to the coils, through
fuse 25, generates a magnetic lield. The magnetic
field, controlled by the coolant temperature sending
unit, causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge
needle to move. As the resistance in the sending
unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The 6ngine coolant temperature sending unit's
resistance varies from about 137 ohms at low
engine temperature to between 3H6 ohms at high
temperature (radiator fan running).
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
81-2
(
Fuel Gauge (All except cX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through tuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the fuel
gauge sending unit, causes the rotor to rotate and
the gauge needle to move. As the resislance in the
sending unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The fuel gauge sending unit's resistance varies
from about 2-5 ohms at full, to about 110 ohms at
empty. When you turn the ignition switch off, the
gauge remains at the last reading until you turn the
ignition switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again,
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
Fuel Gauge (GX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through fuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the PCM,
causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge needle to
move. The PCM calculates the gas quantity in the
fuel tank by using the fuel pressure value detected
by the tuel tank pressure sensor and the fuel
temperature value detected by the fuel tank
temperalure sensor, and outputs the signal to the
gauge assembly. The gauge needle moves toward
the coil with the strongest magnetic field.
When you turn the ignition switch off , the gauge
remains at the last reading until you turn the ignition
switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again. When the
PCM detects a malfunction with the fuel pressure or
temperature, or detects a gas leak, the PCM
reduces the fuel meter to 0.
Refer to the Service Manual GX Supplement
(Section 11 , Fuel and Emissions) for specific tests
or troubleshooting procedures.
a
a