1999 DODGE NEON engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 220 of 1200

NOTE: BLACK OR DARK=0to75%state-of-charge
The battery is INADEQUATELY charged and must
be charged until green dot is visible, (12.4 volts or
greater) before the battery is tested or returned to
use. Refer to Causes of Battery Discharging in this
Group for more information.
NOTE: CLEAR COLOR = Replace Battery
WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE, ASSIST BOOST,
LOAD TEST, OR ADD WATER TO THE BATTERY
WHEN CLEAR COLOR DOT IS VISIBLE. PERSONAL
INJURY MAY OCCUR.
A clear color dot shows electrolyte level in battery
is below the test indicator (Fig. 1). Water cannot be
added to a maintenance free battery. The battery
must be replaced. A low electrolyte level may be
caused by an over charging condition. Refer to Gen-
erator Test Procedures on Vehicle.
CAUSES OF BATTERY DISCHARGING
It is normal to have a small 5 to 25 milliamperes
continuous electrical draw from the battery. This
draw will take place with the ignition in the OFF
position, and the courtesy, dome, storage compart-
ments, and engine compartment lights OFF. The con-
tinuous draw is due to various electronic features or
accessories that require electrical current with the
ignition OFF to function properly. When a vehicle is
not used over an extended period of approximately 20
days the IOD fuse should be pulled. The fuse is
located in the power distribution center. removal of
this fuse will reduce the level of battery discharge.
Refer to the Battery Diagnosis and Testing Table for
proper diagnosis.
ABNORMAL BATTERY DISCHARGING
²Corroded battery posts, cables or terminals.
²Loose or worn generator drive belt.
²Electrical loads that exceed the output of the
charging system due to equipment or accessories
installed after delivery.
²Slow driving speeds in heavy traffic conditions
or prolonged idling with high-amperage electrical
systems in use.
²Defective electrical circuit or component causing
excess Ignition Off Draw (IOD). Refer to Battery
Ignition Off Draw (IOD).
²Defective charging system.
²Defective battery.
BATTERY IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD)
High current draw on the battery with the ignition
OFF will discharge a battery. After a dead battery is
recharged, the vehicle ignition off draw (IOD) shouldbe checked. To determine if a high current draw con-
dition exists first check the vehicle with a test lamp.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF.
²Remove key from ignition switch
²Turn off all lights
²Trunk lid is closed
²Engine compartment hood lamp is disconnected
or lamp removed
²Glove box door is closed
²Sun visor vanity lights are OFF
²All doors are closed
²Allow the ignition key lamp system to time out
in approximately 30 seconds, if equipped.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable (Fig. 4).
(3) Connect a 12 Volt test lamp, with a cold resis-
tance of 5-7 ohms, between the battery negative cable
clamp and the negative post (Fig. 5). If test lamp
goes out system is OK. If test lamp lights and stays
ON, go to Test Lamp Stays ON procedure.
TEST LAMP STAYS ON
There is either a short circuit or a fault in an elec-
tronic module. Two fuses in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) feed the modules with ignition off
draw.
²Interior lamps fuse (10 Amp) (IOD) PDC.
²Fuel pump fuse (20 Amp) in PDC
(1) Remove interior lamp and fuel pump fuses. By
removing these fuses all ignition off draw from the
vehicle electronics will be disconnected. The test
lamp should go out. If test lamp goes out go to Step
2. If test lamp does not go out there is a current
draw or short circuit. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Dia-
grams.
(2) Install the fuel pump fuse. If test lamp lights,
there is a current draw or short circuit in the A14
wiring circuit feed.
(a) Disconnect Powertrain Control Module.
(b) If test lamp goes out, replace Powertrain
Control Module.
(c) If test lamp does not go out, there is a cur-
rent draw or short circuit in the A14 circuit feed.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(3) Install the interior lamp fuse. If test lamp
lights, there is a current draw or short circuit in the
M01 circuit. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. If
test lamp stays out, go to Step 4
(4) Use a multi-meter that has at least a range of
200 milliamperes. Install meter between the battery
negative cable and battery negative post (Fig. 6).
Carefully remove the test lamp without disconnecting
the meter. After all modules time-out the total vehi-
cle IOD should be less than 10 milliamperes. If igni-
tion off draw is more than 10 milliamperes go to Step
5.
(5) Remove both fuses from the Power Distribution
Center:
PLBATTERY 8A - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 222 of 1200
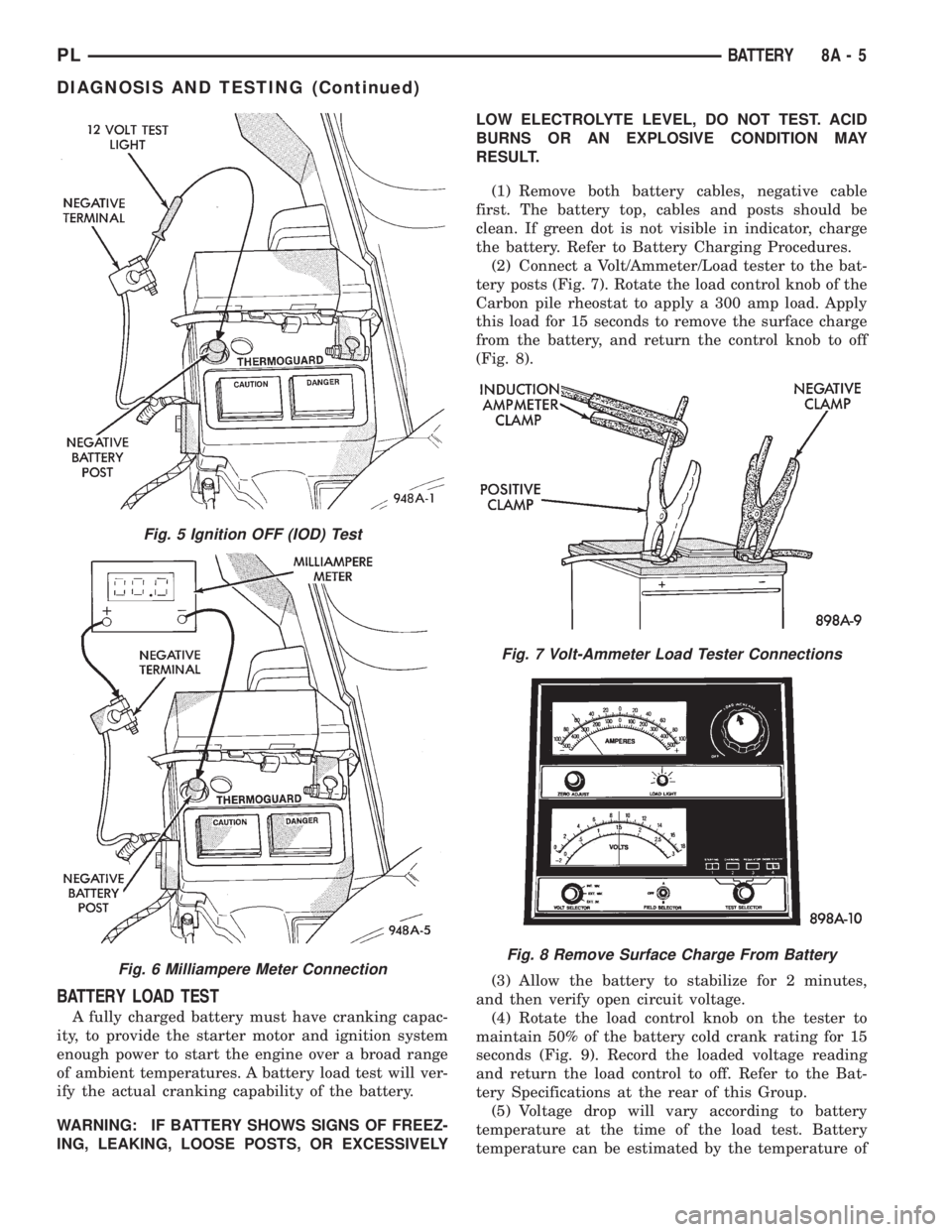
BATTERY LOAD TEST
A fully charged battery must have cranking capac-
ity, to provide the starter motor and ignition system
enough power to start the engine over a broad range
of ambient temperatures. A battery load test will ver-
ify the actual cranking capability of the battery.
WARNING: IF BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF FREEZ-
ING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, OR EXCESSIVELYLOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL, DO NOT TEST. ACID
BURNS OR AN EXPLOSIVE CONDITION MAY
RESULT.
(1) Remove both battery cables, negative cable
first. The battery top, cables and posts should be
clean. If green dot is not visible in indicator, charge
the battery. Refer to Battery Charging Procedures.
(2) Connect a Volt/Ammeter/Load tester to the bat-
tery posts (Fig. 7). Rotate the load control knob of the
Carbon pile rheostat to apply a 300 amp load. Apply
this load for 15 seconds to remove the surface charge
from the battery, and return the control knob to off
(Fig. 8).
(3) Allow the battery to stabilize for 2 minutes,
and then verify open circuit voltage.
(4) Rotate the load control knob on the tester to
maintain 50% of the battery cold crank rating for 15
seconds (Fig. 9). Record the loaded voltage reading
and return the load control to off. Refer to the Bat-
tery Specifications at the rear of this Group.
(5) Voltage drop will vary according to battery
temperature at the time of the load test. Battery
temperature can be estimated by the temperature of
Fig. 5 Ignition OFF (IOD) Test
Fig. 6 Milliampere Meter Connection
Fig. 7 Volt-Ammeter Load Tester Connections
Fig. 8 Remove Surface Charge From Battery
PLBATTERY 8A - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 229 of 1200

To disable the ignition and fuel systems, disconnect
the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The ASD relay
is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay location.
FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST
Before proceeding with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter,
accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition system also must be disabled
to prevent engine start while performing the follow-
ing tests.
(1) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(2) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following:
(a) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative post, and positive lead to the
battery negative cable clamp (Fig. 2). Rotate and
hold the ignition switch in the START position.
Observe the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, cor-
rect poor contact between cable clamp and post.
(b) Connect positive lead of the voltmeter to the
battery positive post, and negative lead to the bat-
tery positive cable clamp (Fig. 2). Rotate and hold
the ignition switch key in the START position.
Observe the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, cor-
rect poor contact between the cable clamp and
post.
(c) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to battery
negative terminal, and positive lead to engine
block near the battery cable attaching point (Fig.
3). Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt,
correct poor contact at ground cable attaching
point. If voltage reading is still above 0.2 volt after
correcting poor contacts, replace ground cable.
(3) Connect positive voltmeter lead to the starter
motor housing and the negative lead to the battery
negative terminal (Fig. 4). Hold the ignition switch
key in the START position. If voltage reads above 0.2
volt, correct poor starter to engine ground.
(a) Connect the positive voltmeter lead to the
battery positive terminal, and negative lead to bat-
tery cable terminal on starter solenoid (Fig. 5).
Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct
poor contact at battery cable to solenoid connec-
tion. If reading is still above 0.2 volt after correct-
ing poor contacts, replace battery positive cable.(b) If resistance tests do not detect feed circuit
failures, replace the starter motor.
FEED CIRCUIT TEST
The following procedure will require a suitable
volt-ampere tester (Fig. 6).
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
Fig. 2 Test Battery Connection Resistance
Fig. 3 Test Ground Circuit Resistance
8B - 2 STARTINGPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 230 of 1200

(1) Connect a volt-ampere tester to the battery ter-
minals (Fig. 7). Refer to the operating instructions
provided with the tester being used.
(2) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location. The 2.5L Diesel Engine, to disable the
engine from starting, disconnect wire connector from
the Fuel Solenoid.
(3) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in the PARKposition or with the clutch pedal depressed and SET
parking brake.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(4) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
6).
²If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 280 amps or the Diesel engine
above 450 amps, check for engine seizing or faulty
starter.
²If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amper-
age reads 0 to 10 amps, check for corroded cables
and/or bad connections.
²Voltage below 9.6 volts and amperage draw
above 300 amps or Diesel engine above 500 amps,
the problem is the starter. Replace the starter refer
to starter removal.
(5) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state-of-charge and
Fig. 6 Volt Ampere Tester
Fig. 7 Volt-Ampere Tester Connections
Fig. 4 Test Starter Motor Ground
Fig. 5 Test Battery Positive Cable Resistance
PLSTARTING 8B - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 232 of 1200
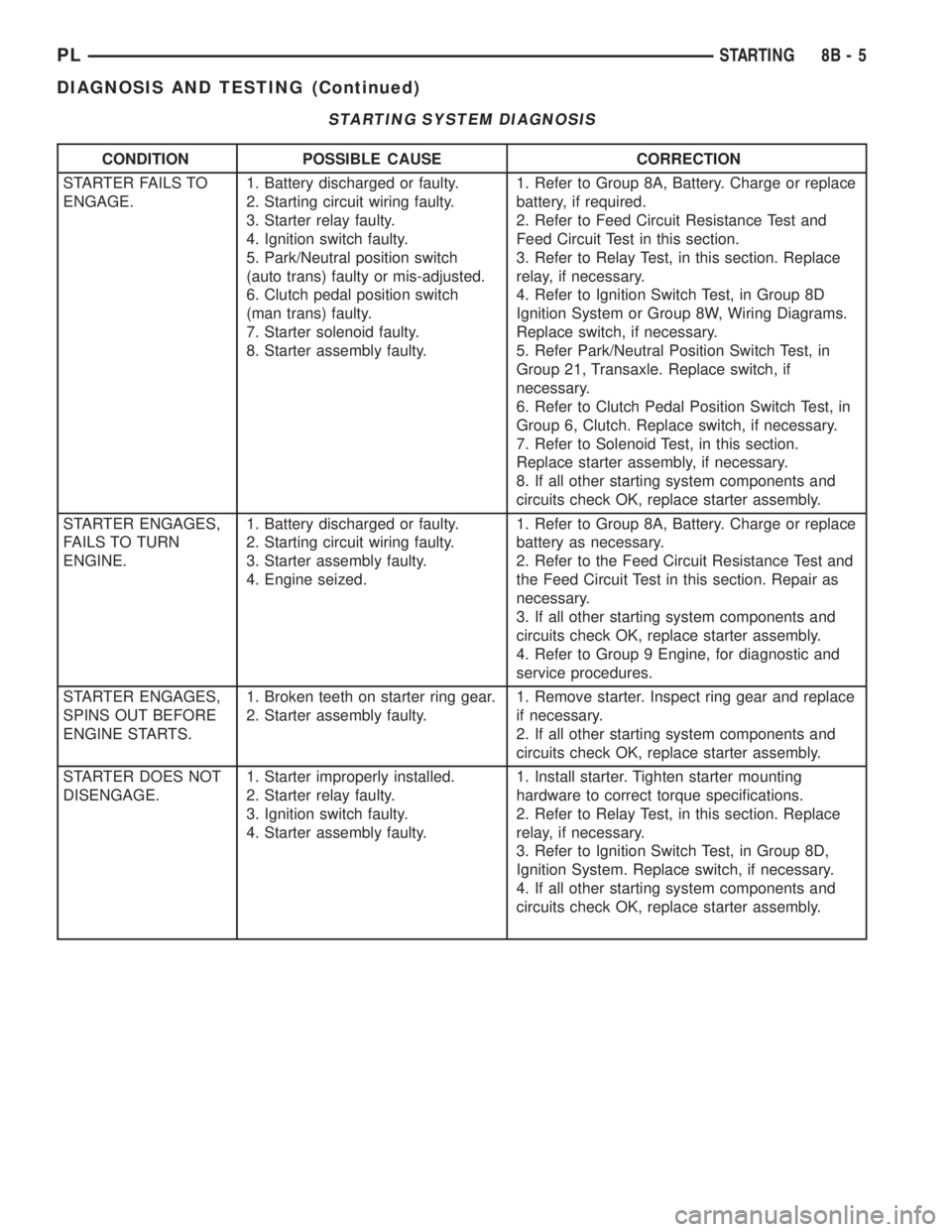
STARTING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER FAILS TO
ENGAGE.1. Battery discharged or faulty.
2. Starting circuit wiring faulty.
3. Starter relay faulty.
4. Ignition switch faulty.
5. Park/Neutral position switch
(auto trans) faulty or mis-adjusted.
6. Clutch pedal position switch
(man trans) faulty.
7. Starter solenoid faulty.
8. Starter assembly faulty.1. Refer to Group 8A, Battery. Charge or replace
battery, if required.
2. Refer to Feed Circuit Resistance Test and
Feed Circuit Test in this section.
3. Refer to Relay Test, in this section. Replace
relay, if necessary.
4. Refer to Ignition Switch Test, in Group 8D
Ignition System or Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
Replace switch, if necessary.
5. Refer Park/Neutral Position Switch Test, in
Group 21, Transaxle. Replace switch, if
necessary.
6. Refer to Clutch Pedal Position Switch Test, in
Group 6, Clutch. Replace switch, if necessary.
7. Refer to Solenoid Test, in this section.
Replace starter assembly, if necessary.
8. If all other starting system components and
circuits check OK, replace starter assembly.
STARTER ENGAGES,
FAILS TO TURN
ENGINE.1. Battery discharged or faulty.
2. Starting circuit wiring faulty.
3. Starter assembly faulty.
4. Engine seized.1. Refer to Group 8A, Battery. Charge or replace
battery as necessary.
2. Refer to the Feed Circuit Resistance Test and
the Feed Circuit Test in this section. Repair as
necessary.
3. If all other starting system components and
circuits check OK, replace starter assembly.
4. Refer to Group 9 Engine, for diagnostic and
service procedures.
STARTER ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT BEFORE
ENGINE STARTS.1. Broken teeth on starter ring gear.
2. Starter assembly faulty.1. Remove starter. Inspect ring gear and replace
if necessary.
2. If all other starting system components and
circuits check OK, replace starter assembly.
STARTER DOES NOT
DISENGAGE.1. Starter improperly installed.
2. Starter relay faulty.
3. Ignition switch faulty.
4. Starter assembly faulty.1. Install starter. Tighten starter mounting
hardware to correct torque specifications.
2. Refer to Relay Test, in this section. Replace
relay, if necessary.
3. Refer to Ignition Switch Test, in Group 8D,
Ignition System. Replace switch, if necessary.
4. If all other starting system components and
circuits check OK, replace starter assembly.
PLSTARTING 8B - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 233 of 1200

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SAFETY SWITCHES
For Removal and Installation of the:
²Clutch Position Switch, refer to Group 6, Clutch.
²Park/Neutral Switch, refer to Group 21, Tran-
saxle.
STARTER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable (Fig. 8).
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Vehicles equipped with A/C:
(a) Using a floor jack or jack stand, support the
engine and transmission assembly so they will not
rotate.
(b) Remove the front engine mount bolt from the
insulator and front crossmember mounting bracket
(Fig. 9).
(c) Lower the front of the engine, rotate the
engine forward, allowing easier removal of starter
motor.
(4) For easier servicing, do not remove the wiring
from starter at this time.
(5) Remove two bolts attaching starter to trans-
mission housing (Fig. 10).
(6) Remove starter/starter solenoid assembly from
transmission housing. Position the starter to gain
access to the wiring connectors.
(7) Remove the battery positive cable nut and
remove the battery positive and generator output
wire from the starter (Fig. 11).
(8) Disconnect push-on solenoid connector. Pull
back on slide and push down on rear tab to release
lock.
(9) Position the starter vertically such that the
pinion end faces downward.
(10) Remove the starter through the bottom of the
vehicle. Move aside A/C plumbing as necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean corrosion/dirt from the cable and wire
terminals before installing wiring to the solenoid.(2) Connect the battery positive and generator out-
put wire to the starter solenoid post (Fig. 11).
CAUTION: It is critical that the generator output ter-
minal be connected to the battery positive terminal
of the starter solenoid, for proper operation of the
charging and cranking systems.
(3) Connect the push-on until fully engaged.
(4) Position the starter face into transmission
housing. Support starter in pilot and start the top
bolt (Fig. 10).
(5) Attach ground cable to lower mounting bolt
and start bolt.
(6) Ensure the proper starter alignment before
tightening the starter mounting bolts to 54 N´m (40
ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 9 Front Engine Mount Bolt Removal
Fig. 10 Starter Removal
Fig. 8 Battery Cable Removal and Installation
8B - 6 STARTINGPL
Page 234 of 1200

(7) Vehicles equipped with A/C:
(a) Using a floor jack or jack stand, raise the
engine and transmission assembly to the original
position.
(b) Install the front engine mount bolt through
the insulator and front crossmember mounting
bracket (Fig. 9).
(c) Tighten bolt to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Lower vehicle and connect battery cables.
STARTER RELAY
The relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for relay location.
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTER
Engine should be up to operating temperature.
Extremely heavy oil or tight engine will increase
starter amperage draw.
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Starter Mounting Bolts.........54N´m(40ft.lbs.)
Starter Solenoid Battery Nut. . . .10 N´m (90 in. lbs.)
Fig. 11 Wire Connection
Manufacturer BOSCH
Engine Application 2.0L OHC - DOHC
Power rating 0 .95 Kw
Voltage 12 VOLTS
No. of Fields 6
No. of Poles 6
Brushes 4
Drive Planetary Gear Train
Cranking Amperage Draw
test150 - 280 Amps.
PLSTARTING 8B - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 236 of 1200

CHARGING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
OVERVIEW............................. 1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR.......... 2
CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION........... 1
ELECTRONIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR......... 2
GENERATOR............................ 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR.......... 8
CHARGING SYSTEM RESISTANCE TESTS..... 5CHARGING SYSTEM...................... 2
CURRENT OUTPUT TEST.................. 8
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM TEST..... 10
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR......... 11
GENERATOR........................... 10
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS................... 12
TORQUE.............................. 12
GENERAL INFORMATION
OVERVIEW
The battery, starting, and charging systems oper-
ate with one another, and must be tested as a com-
plete system. In order for the vehicle to start and
charge properly, all of the components involved in
these systems must perform within specifications.
Group 8A covers the battery, Group 8B covers the
starting system, and Group 8C covers the charging
system. Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams for
complete circuit descriptions and diagrams. We have
separated these systems to make it easier to locate
the information you are seeking within this Service
Manual. However, when attempting to diagnose any
of these systems, it is important that you keep their
interdependency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used in these groups
include the most basic conventional diagnostic meth-
ods to the more sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). Use of an induction ammeter, volt/ohmmeter,
battery charger, carbon pile rheostat (load tester),
and 12-volt test lamp may be required.
All OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the
PCM. Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in
electronic memory for any failure it detects. See the
On-Board Diagnostics Test in Group 8C - Charging
System for more information.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION
The charging system consists of:
²Generator
²Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry
within the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Ignition switch (refer to Group 8D, Ignition Sys-
tem for information)
²Battery (refer to Group 8A, Battery for informa-
tion)
²Battery temperature sensor
²Voltmeter (refer to Group 8E, Instrument Panel
and Gauges for information)
²Wiring harness and connections (refer to Group
8W, Wiring for information)
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. When the ignition switch is turned to
the ON position, battery voltage is applied to the
generator rotor through one of the two field termi-
nals to produce a magnetic field. The generator is
driven by the engine through a serpentine belt and
pulley arrangement.
The amount of DC current produced by the gener-
ator is controlled by the EVR (field control) circuitry,
contained within the PCM. This circuitry is con-
nected in series with the second rotor field terminal
and ground.
PLCHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1