1998 SSANGYONG MUSSO wiring
[x] Cancel search: wiringPage 1037 of 1463
5A-60 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
DIAGNOSIS
DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
Recommended Test Equipment and Procedure
The test equipment is designed to be used with the control modules in all vehicles. The components used in the
transmission application are:
lMulti Function Tester, and
lAppropriate vehicle for testing.
Multi Function Tester (MFT)
The MFT is programmed with the special vehicle diagnostic software that allows selection of the unit under test.
The program allows the proper communication to the Transmission Control Unit (TCU).
It then requests information from the user via a menu system to select the required set up.
Examples are viewing codes, clearing error codes, and real-time operation. Set up and operation instructions are
detailed in the user manual.
This equipment can be used by trained personnel such as technicians and mechanics to diagnose electronic and
wiring problems relating to the vehicle transmission. Information that is available includes engine and road (shaft)
speed, transmission oil temperature, throttle position, solenoid/gear status and gear lever position. Current and
stored faults detected by the electronics are also available.
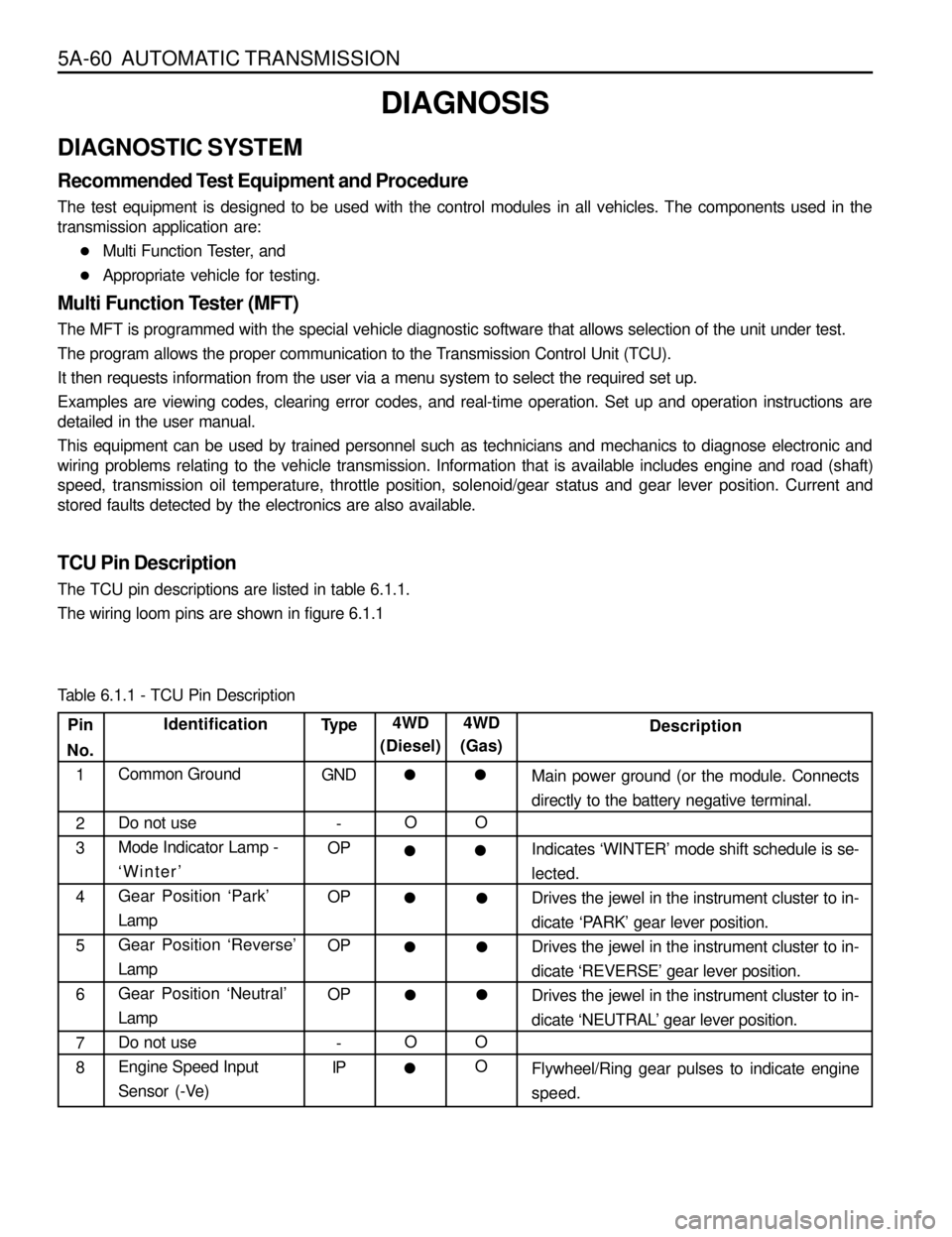
TCU Pin Description
The TCU pin descriptions are listed in table 6.1.1.
The wiring loom pins are shown in figure 6.1.1
Pin
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8Identification
Common Ground
Do not use
Mode Indicator Lamp -
‘Winter’
Gear Position ‘Park’
Lamp
Gear Position ‘Reverse’
Lamp
Gear Position ‘Neutral’
Lamp
Do not use
Engine Speed Input
Sensor (-Ve)Type
GND
-
OP
OP
OP
OP
-
IPDescription
Main power ground (or the module. Connects
directly to the battery negative terminal.
Indicates ‘WINTER’ mode shift schedule is se-
lected.
Drives the jewel in the instrument cluster to in-
dicate ‘PARK’ gear lever position.
Drives the jewel in the instrument cluster to in-
dicate ‘REVERSE’ gear lever position.
Drives the jewel in the instrument cluster to in-
dicate ‘NEUTRAL’ gear lever position.
Flywheel/Ring gear pulses to indicate engine
speed. 4WD
(Diesel)
O
O
l
l l l
l
4WD
(Gas)
O
O
O
l
l l l
l
l
Table 6.1.1 - TCU Pin Description
Page 1040 of 1463
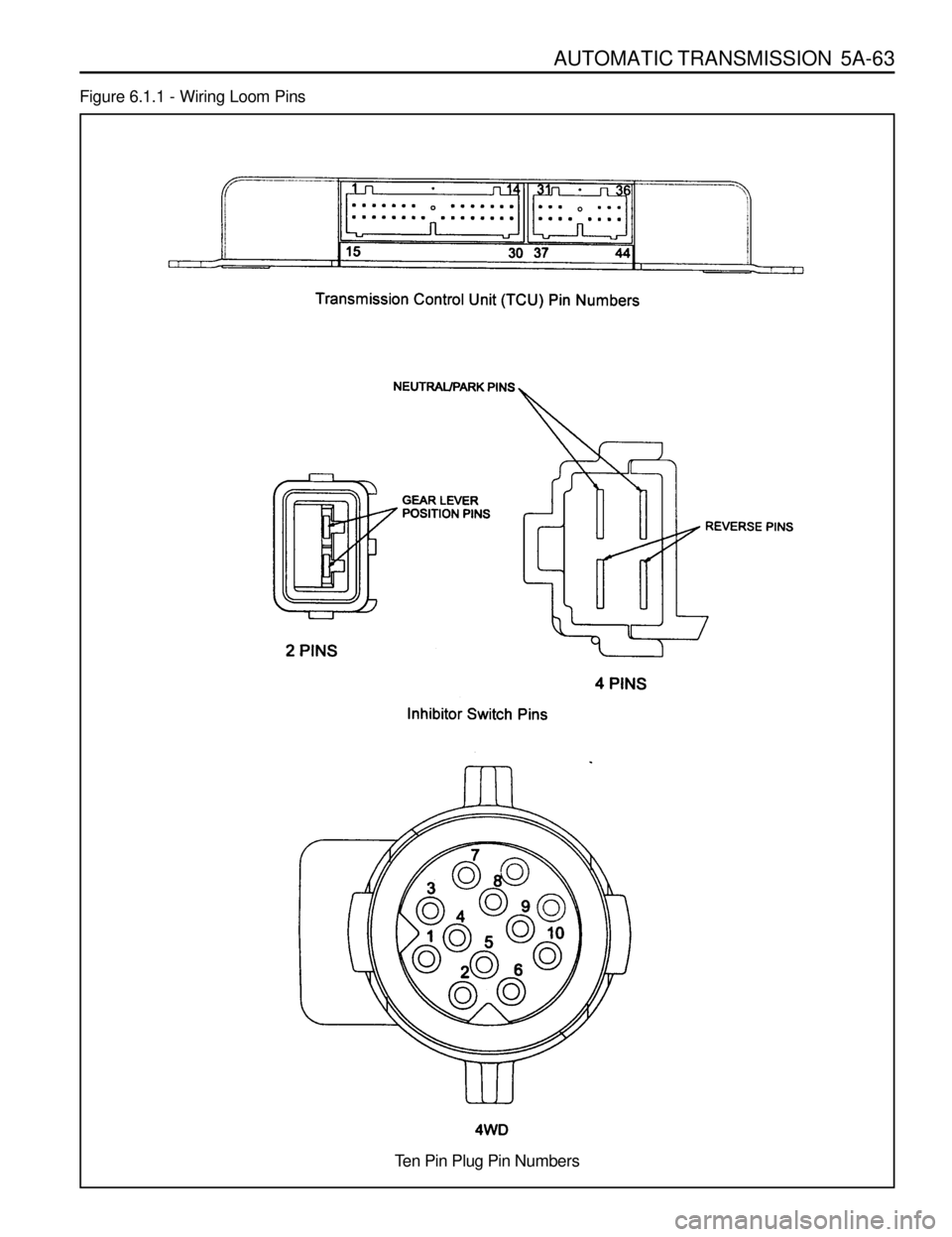
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-63
Ten Pin Plug Pin Numbers
Figure 6.1.1 - Wiring Loom Pins
Page 1044 of 1463

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-67
Table 6.1.3 - Diagnostic Trouble Messages
Description / Cause
There have been no faults recorded since the TCU was last cleared. If
the fault history has never been cleared, then there have been no
faults recorded since the TCU was originally powered up.
There is an internal fault within the TCU.
The voltage measured by the TCU corresponding to the battery sup-
ply voltage has been outside the range of the maximum operating
voltage of 16.5 volts.
The minimum operating voltage depends on the transmission tem-
perature but is typically between 8-9 V for a warm transmission.
The voltage measured by the TCU from the throttle potentiometer has
been outside acceptable levels.
This would typically indicate a loose connection in the wiring to, or
within, the throttle sensor which has caused the signal at the TCU to
read 0V or 5V.
The voltage measured by the TCU across the temperature Input ter-
minals has been outside acceptable levels.
This would typically be caused by a loose connection or short to ground
in the wiring to, or within, the temperature sensor which has caused
the signal at the TCU to read 0V or 5V.
The voltage measured by the TCU across the shift lever input termi-
nals has been outside acceptable levels for a significant length of
time. This would typically be caused by a loose connection or short to
ground in the wiring to, or within, the inhibitor switch which has caused
the signal at the TCU to read 0V or 5V.
The signal from the ignition, of ignition pulses, has either been non-
existent or has been unreliable.
There are two reasons this fault could occur. The first is due to a lack
of ignition pulses when other TCU inputs would indicate that the en-
gine is running, that is the gear lever is in a driving position, the throttle
is applied and vehicle speed increasing.
The second cause of this (aunt is the frequency of the pulses of the
ignition pulse input to the TCU indicate an unachievable engine speed.
The pulses from the shaft speed sensor have either been non-exis-
tent or have been unreliable.
There are three reasons this fault could occur. The first is due to a
sudden loss of speedometer pulses at a time when they were fre quent,
thus indicating an unachievable degree of deceleration of the drive
line. The second cause of this fault is that the frequency of the pulses
on the shaft speed sensor input to the TCU indicate an unachievable
propeller shaft speed. The third is the presence of a high engine speed
in a driving gear with no speedometer pulses. Condition
Test Pass
Transmission Control
Module Fault
Battery Voltage Input
Fault
Throttle Input Fault
Temperature Input Fault
Shift Lever Position
Input Fault
(Inhibitor/PRNDL Switch)
Engine Speed Sensor
Fault
Shaft Speed Sensor
Fault
(Speedo Sensor)Solenoid
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Page 1045 of 1463
5A-68 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Description / Cause
The signal from the mode switch is unreliable.
This fault is caused by too many changes in the mode input signal
over a period of time. Typical causes would be an intermittent connec
tion in the switch or wiring or an intermittent short to ground in the
wiring.
The data link between the TCU and the engine management module
is found to be unreliable because the checksum, or the data received,
did not match the correct checksum.
This could be caused by an open circuit, short circuit to ground or a
loose connection in the link wire itself.
Each solenoid in turn is switched off if it was energised, or switched on
if it was not energised by a very small 100 ms pulse. This pulse is too
short for the solenoid to react so transmission operation is not af
fected.
The solenoid feedback voltage is measured before the 100 ms pulse
and again during the pulse. If the difference is outside the acceptable
limits the relevant fault messages are set.
Typical causes would be an open circuit in the wiring to or within the
solenoid, or a short circuit to ground in the wiring to, from or within the
solenoid in question.
If several of these fault codes are presents check the wiring or
connectors that are common to the selected solenoids, especially the
earth connections.
The state of the solenoid feedback voltage is outside acceptable
limits but the faulty solenoid could not be isolated.
The current to solenoid 5 was outside acceptable limits.
This fault results from a mismatch between the current set point for
solenoid 5 and the current measured by the feedback within the TCU.
Typical causes would be an open circuit or short circuit to ground in
the wiring to, from or within the solenoid. It is also possible that there
has been a fault in the solenoid output circuit. If this is the case
however, the fault should be continually present.
The closed throttle position has not been learnt. This fault
may be caused by the transmission not having reached normal
operating temperature or the engine idle speed being incorrect.
The TCU will learn the closed throttle position automatically
when the transmission is brought to normal operating
temperature and the engine is allowed to idle in Drive with the
‘base idle’ correctly set and the air conditioner (if fitted)
switched off. Condition
Mode Switch Input Fault
(Power/Economy Mode)
Data Output Link Fault
On/off Solenoid Fault
(Solenoid 1,2,3,4,6,7)
Solenoid 5 Fault
(Variable Pressure
Solenoid)
Throttle Not LearntSolenoid
9
10
11
12
13
Page 1047 of 1463

5A-70 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Action
Inspect S1. Repair or replace as necessary.
Check for 12 Volts applied to S1 at all times or
for wiring fault.
Inspect S1. Repair or replace as necessary.
Check for 12 Volts applied to S1 at all times or
for wiring fault.
Inspect S2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Check for open circuit or wiring fault.
Inspect S2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Check for open circuit or wiring fault.
Inspect and adjust as necessary.
Inspect and repair as necessary.
Inspect and replace or refit as necessary.
Inspect ‘O’ ring. Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect the 2-3 shift valve. Repair or replace
as necessary.
Inspect C1 clutch. Repair or replace as neces-
sary.
Inspect ball. Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect C4. Repair C4 or replace C4 wave plate
as necessary.
Inspect rear band adjustment. Adjust as nec-
essary.
Inspect ball- Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect’0’ring. Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect C4 and C4 wave plate. Repair or re-
place as necessary.
Inspect inhibitor switch.
Repair or replace as necessary.
Inspect the 1-2 shift valve.
Repair or replace as necessary
Inspect inhibitor switch.
Repair or replace as necessary.
Inspect the 2-3 shift valve.
Repair or replace as necessary. Possible Cause
S1 always OFF.
S1 always ON.
S2 always OFF.
S2 always ON.
B1 failed.
Loose band adjustment.
Front servo piston or seal failed.
S1/S2 ball misplaced,
Smaller’0’ring on front servo piston failed
or missing.
2-3 shift valve jammed.
C1 clutch failed or slipping in 3rd and 4th.
(Gives 1st in 3rd and 2nd in 4th.)
Over-run clutch (OC)/low ball misplaced.
C4 failed or C4 wave plate broken.
Rear band slipping when hot.
Reverse/Low-1st ball misplaced.
Rear servo inner ‘O’ ring missing.
C4 failed or C4 wave plate broken.
Inhibitor switch faulty.
1-2 shift valve jammed.
Inhibitor switch fault, 1-2 only.
2-3 shift valve jammed.Symptom
2-3 shift only
(no 4th or 1st)
1-4 shift only
1-3-4 (Delayed
1-2shift)
4-3 shift only
1-2-Neutral
(1st over run)
1-3 shift only
1-3-4 only
1-2-1 only
No manual 4-3,3-2
or 2-1
No manual 1st
1st gear only or
2nd,3rd, and 4th
only
1st and 2nd only
or 1st, 3rd and 4th
only
Page 1063 of 1463
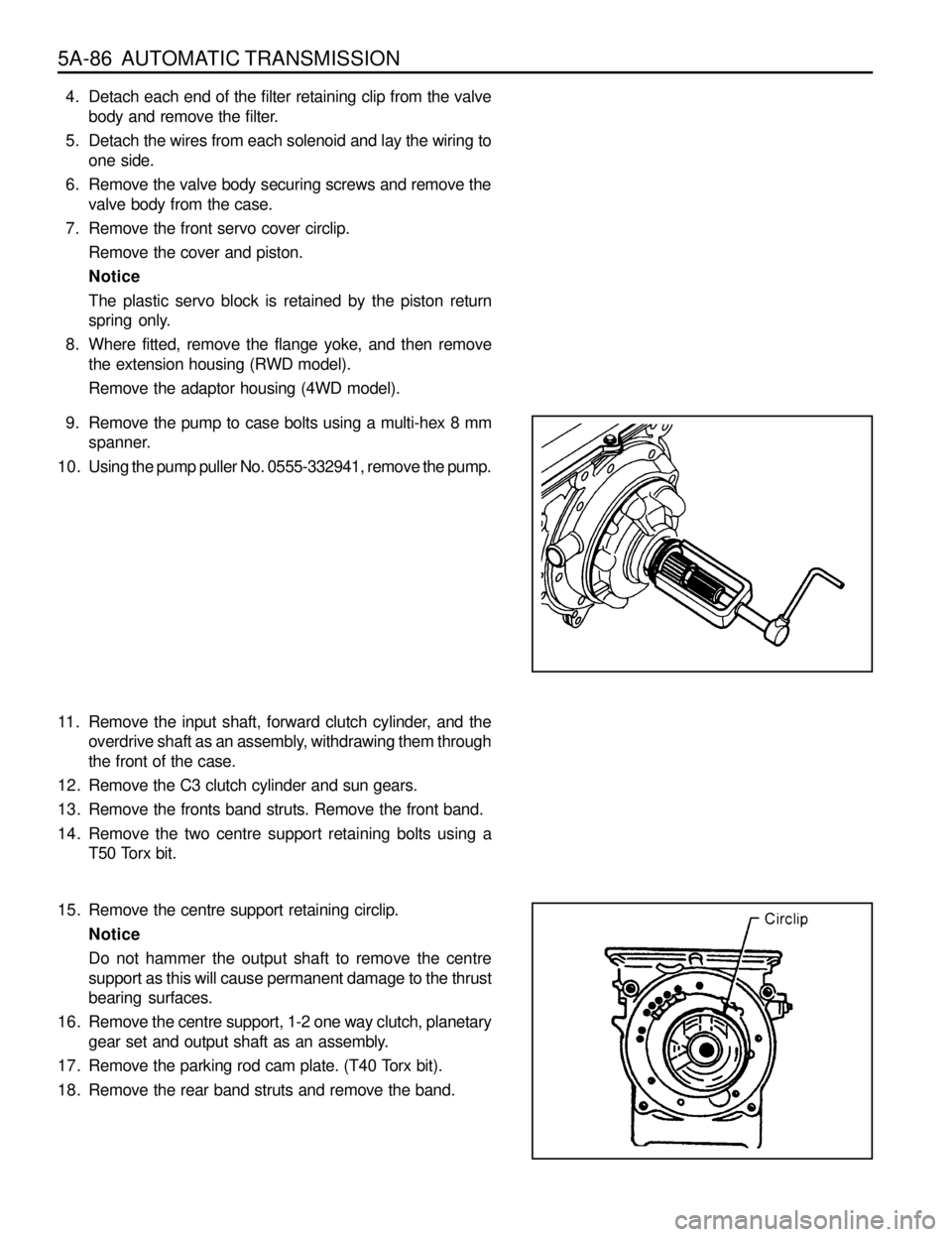
5A-86 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
9. Remove the pump to case bolts using a multi-hex 8 mm
spanner.
10. Using the pump puller No. 0555-332941, remove the pump.
11. Remove the input shaft, forward clutch cylinder, and the
overdrive shaft as an assembly, withdrawing them through
the front of the case.
12. Remove the C3 clutch cylinder and sun gears.
13. Remove the fronts band struts. Remove the front band.
14. Remove the two centre support retaining bolts using a
T50 Torx bit.
15. Remove the centre support retaining circlip.
Notice
Do not hammer the output shaft to remove the centre
support as this will cause permanent damage to the thrust
bearing surfaces.
16. Remove the centre support, 1-2 one way clutch, planetary
gear set and output shaft as an assembly.
17. Remove the parking rod cam plate. (T40 Torx bit).
18. Remove the rear band struts and remove the band.4. Detach each end of the filter retaining clip from the valve
body and remove the filter.
5. Detach the wires from each solenoid and lay the wiring to
one side.
6. Remove the valve body securing screws and remove the
valve body from the case.
7. Remove the front servo cover circlip.
Remove the cover and piston.
Notice
The plastic servo block is retained by the piston return
spring only.
8. Where fitted, remove the flange yoke, and then remove
the extension housing (RWD model).
Remove the adaptor housing (4WD model).
Page 1064 of 1463
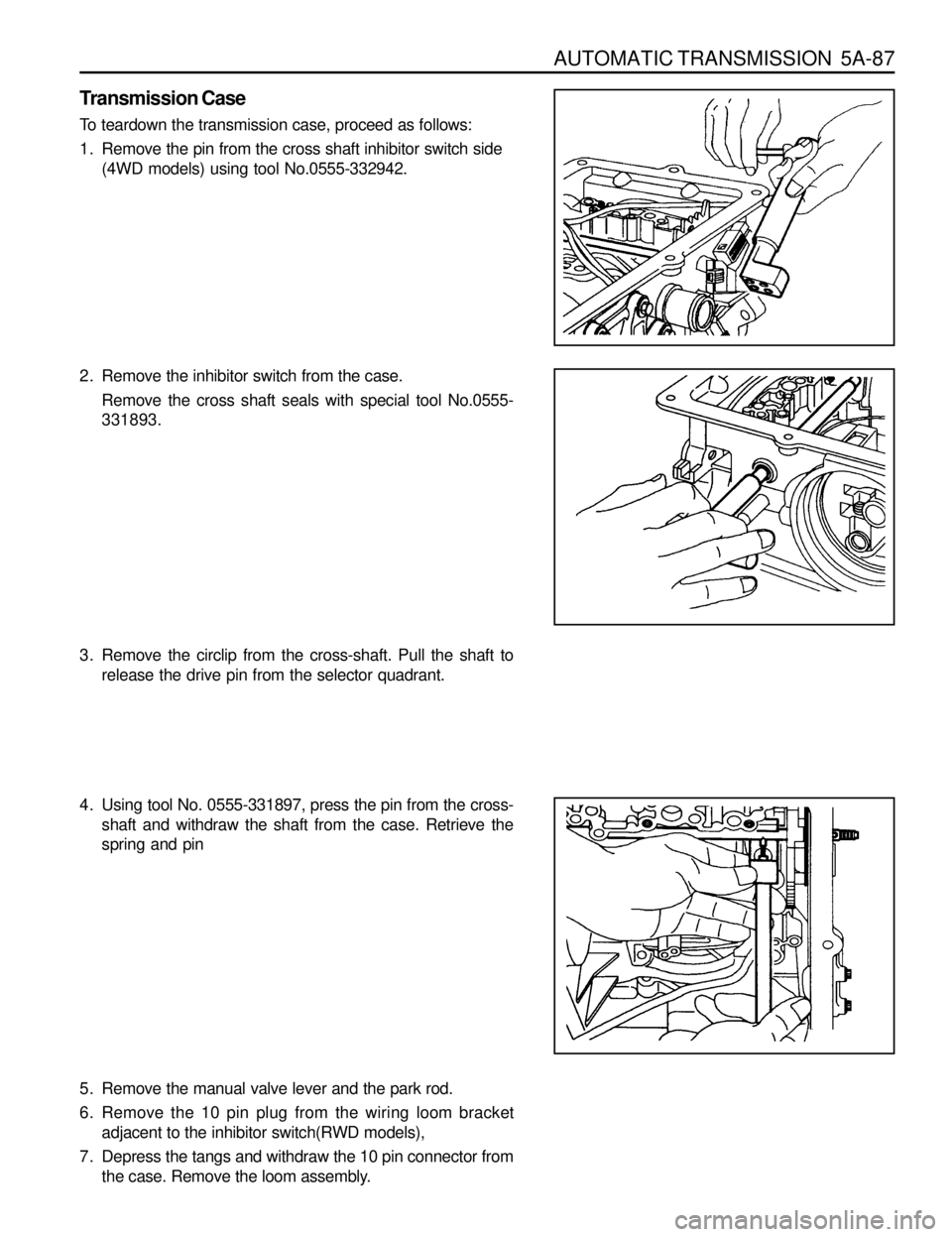
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-87
Transmission Case
To teardown the transmission case, proceed as follows:
1. Remove the pin from the cross shaft inhibitor switch side
(4WD models) using tool No.0555-332942.
2. Remove the inhibitor switch from the case.
Remove the cross shaft seals with special tool No.0555-
331893.
3. Remove the circlip from the cross-shaft. Pull the shaft to
release the drive pin from the selector quadrant.
4. Using tool No. 0555-331897, press the pin from the cross-
shaft and withdraw the shaft from the case. Retrieve the
spring and pin
5. Remove the manual valve lever and the park rod.
6. Remove the 10 pin plug from the wiring loom bracket
adjacent to the inhibitor switch(RWD models),
7. Depress the tangs and withdraw the 10 pin connector from
the case. Remove the loom assembly.
Page 1069 of 1463
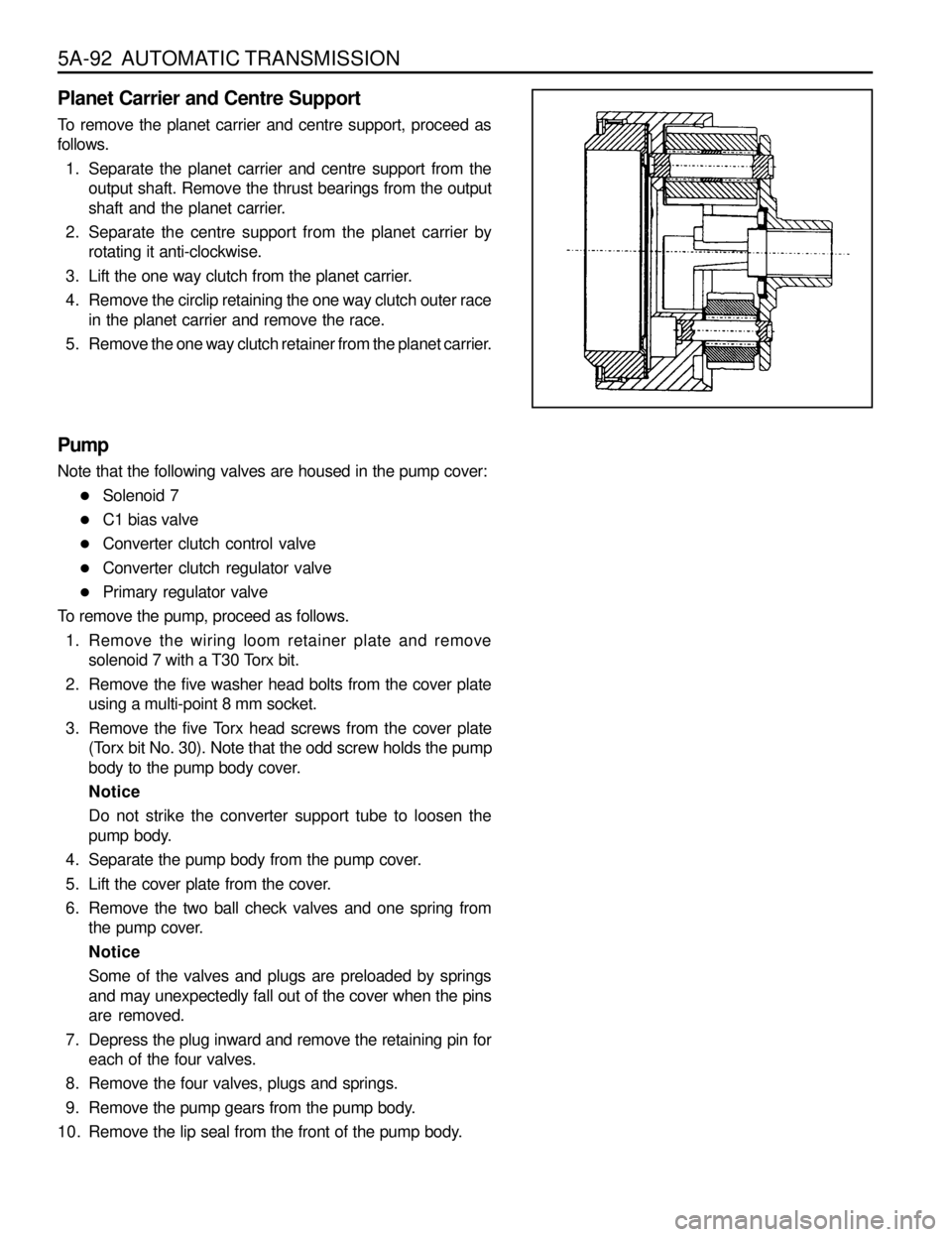
5A-92 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Planet Carrier and Centre Support
To remove the planet carrier and centre support, proceed as
follows.
1. Separate the planet carrier and centre support from the
output shaft. Remove the thrust bearings from the output
shaft and the planet carrier.
2. Separate the centre support from the planet carrier by
rotating it anti-clockwise.
3. Lift the one way clutch from the planet carrier.
4. Remove the circlip retaining the one way clutch outer race
in the planet carrier and remove the race.
5. Remove the one way clutch retainer from the planet carrier.
Pump
Note that the following valves are housed in the pump cover:
lSolenoid 7
lC1 bias valve
lConverter clutch control valve
lConverter clutch regulator valve
lPrimary regulator valve
To remove the pump, proceed as follows.
1. Remove the wiring loom retainer plate and remove
solenoid 7 with a T30 Torx bit.
2. Remove the five washer head bolts from the cover plate
using a multi-point 8 mm socket.
3. Remove the five Torx head screws from the cover plate
(Torx bit No. 30). Note that the odd screw holds the pump
body to the pump body cover.
Notice
Do not strike the converter support tube to loosen the
pump body.
4. Separate the pump body from the pump cover.
5. Lift the cover plate from the cover.
6. Remove the two ball check valves and one spring from
the pump cover.
Notice
Some of the valves and plugs are preloaded by springs
and may unexpectedly fall out of the cover when the pins
are removed.
7. Depress the plug inward and remove the retaining pin for
each of the four valves.
8. Remove the four valves, plugs and springs.
9. Remove the pump gears from the pump body.
10. Remove the lip seal from the front of the pump body.