1998 SSANGYONG MUSSO transmission
[x] Cancel search: transmissionPage 1044 of 1463

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-67
Table 6.1.3 - Diagnostic Trouble Messages
Description / Cause
There have been no faults recorded since the TCU was last cleared. If
the fault history has never been cleared, then there have been no
faults recorded since the TCU was originally powered up.
There is an internal fault within the TCU.
The voltage measured by the TCU corresponding to the battery sup-
ply voltage has been outside the range of the maximum operating
voltage of 16.5 volts.
The minimum operating voltage depends on the transmission tem-
perature but is typically between 8-9 V for a warm transmission.
The voltage measured by the TCU from the throttle potentiometer has
been outside acceptable levels.
This would typically indicate a loose connection in the wiring to, or
within, the throttle sensor which has caused the signal at the TCU to
read 0V or 5V.
The voltage measured by the TCU across the temperature Input ter-
minals has been outside acceptable levels.
This would typically be caused by a loose connection or short to ground
in the wiring to, or within, the temperature sensor which has caused
the signal at the TCU to read 0V or 5V.
The voltage measured by the TCU across the shift lever input termi-
nals has been outside acceptable levels for a significant length of
time. This would typically be caused by a loose connection or short to
ground in the wiring to, or within, the inhibitor switch which has caused
the signal at the TCU to read 0V or 5V.
The signal from the ignition, of ignition pulses, has either been non-
existent or has been unreliable.
There are two reasons this fault could occur. The first is due to a lack
of ignition pulses when other TCU inputs would indicate that the en-
gine is running, that is the gear lever is in a driving position, the throttle
is applied and vehicle speed increasing.
The second cause of this (aunt is the frequency of the pulses of the
ignition pulse input to the TCU indicate an unachievable engine speed.
The pulses from the shaft speed sensor have either been non-exis-
tent or have been unreliable.
There are three reasons this fault could occur. The first is due to a
sudden loss of speedometer pulses at a time when they were fre quent,
thus indicating an unachievable degree of deceleration of the drive
line. The second cause of this fault is that the frequency of the pulses
on the shaft speed sensor input to the TCU indicate an unachievable
propeller shaft speed. The third is the presence of a high engine speed
in a driving gear with no speedometer pulses. Condition
Test Pass
Transmission Control
Module Fault
Battery Voltage Input
Fault
Throttle Input Fault
Temperature Input Fault
Shift Lever Position
Input Fault
(Inhibitor/PRNDL Switch)
Engine Speed Sensor
Fault
Shaft Speed Sensor
Fault
(Speedo Sensor)Solenoid
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Page 1045 of 1463
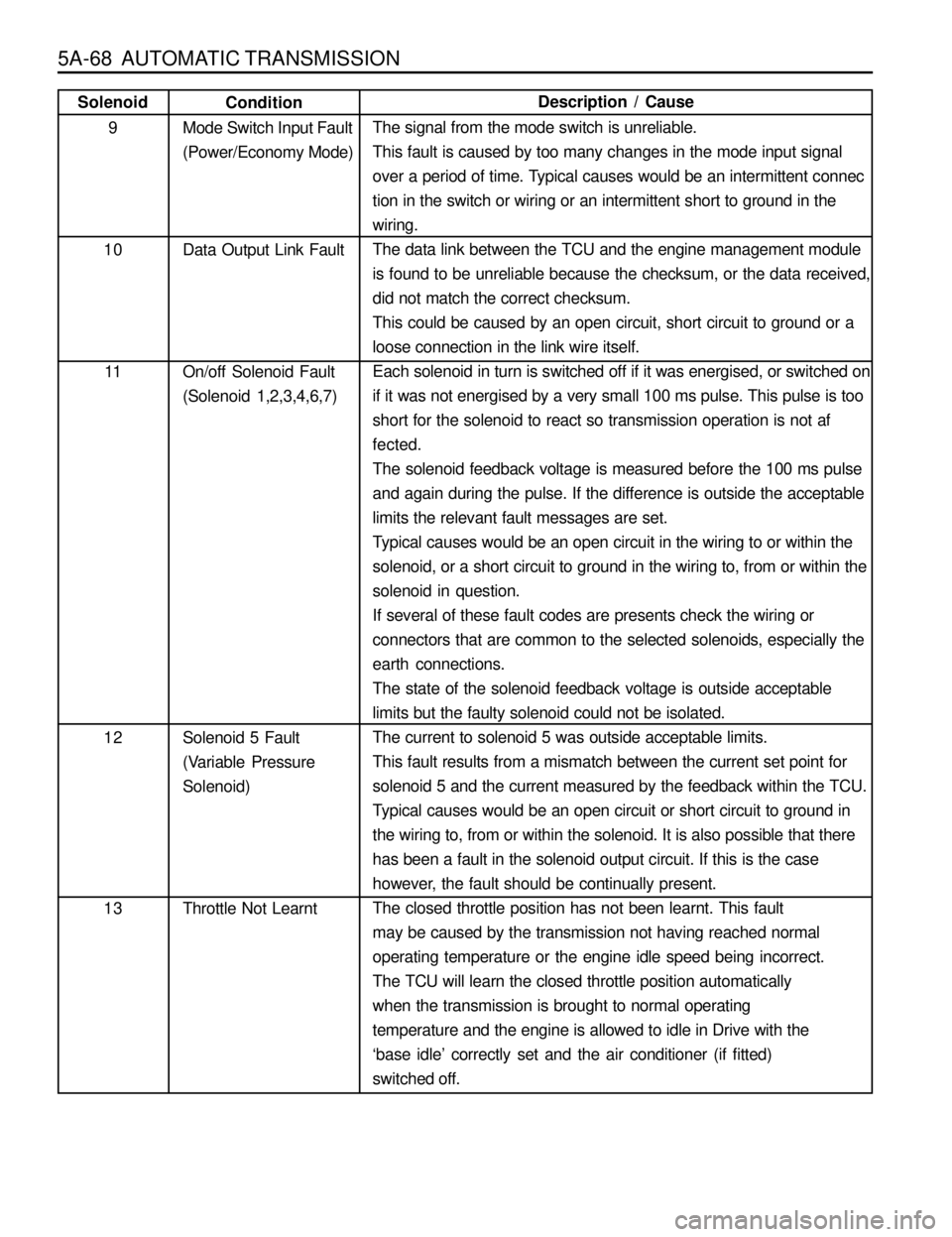
5A-68 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Description / Cause
The signal from the mode switch is unreliable.
This fault is caused by too many changes in the mode input signal
over a period of time. Typical causes would be an intermittent connec
tion in the switch or wiring or an intermittent short to ground in the
wiring.
The data link between the TCU and the engine management module
is found to be unreliable because the checksum, or the data received,
did not match the correct checksum.
This could be caused by an open circuit, short circuit to ground or a
loose connection in the link wire itself.
Each solenoid in turn is switched off if it was energised, or switched on
if it was not energised by a very small 100 ms pulse. This pulse is too
short for the solenoid to react so transmission operation is not af
fected.
The solenoid feedback voltage is measured before the 100 ms pulse
and again during the pulse. If the difference is outside the acceptable
limits the relevant fault messages are set.
Typical causes would be an open circuit in the wiring to or within the
solenoid, or a short circuit to ground in the wiring to, from or within the
solenoid in question.
If several of these fault codes are presents check the wiring or
connectors that are common to the selected solenoids, especially the
earth connections.
The state of the solenoid feedback voltage is outside acceptable
limits but the faulty solenoid could not be isolated.
The current to solenoid 5 was outside acceptable limits.
This fault results from a mismatch between the current set point for
solenoid 5 and the current measured by the feedback within the TCU.
Typical causes would be an open circuit or short circuit to ground in
the wiring to, from or within the solenoid. It is also possible that there
has been a fault in the solenoid output circuit. If this is the case
however, the fault should be continually present.
The closed throttle position has not been learnt. This fault
may be caused by the transmission not having reached normal
operating temperature or the engine idle speed being incorrect.
The TCU will learn the closed throttle position automatically
when the transmission is brought to normal operating
temperature and the engine is allowed to idle in Drive with the
‘base idle’ correctly set and the air conditioner (if fitted)
switched off. Condition
Mode Switch Input Fault
(Power/Economy Mode)
Data Output Link Fault
On/off Solenoid Fault
(Solenoid 1,2,3,4,6,7)
Solenoid 5 Fault
(Variable Pressure
Solenoid)
Throttle Not LearntSolenoid
9
10
11
12
13
Page 1046 of 1463
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-69
MECHANICAL TESTS
In Vehicle Transmission Checks
Carry out the following tests before removing the transmission.
lSee Checking Transmission Fluid Level, Section 7.2.1.
lCheck that the transmission oil is not burnt (colour and smell are correct).
lEnsure that the transmission is not in limp home mode (LHM).
lCheck that the battery terminals and the earth connections are not corroded or loose.
lCheck the engine stall speed is within the handbook value.
lCheck that the cooler flow is not restricted.
lCheck that all electrical plug connections are tight.
lCarry out a road test to confirm the symptoms, if necessary.
lInspect the oil, ensure that there are no metal or other contaminants in the oil pan.
Diagnosing Oil Leaks
Determine the source of oil leaks by firstly cleaning down the affected area, then driving the vehicle.
Inspect the seals to confirm the source of the leak.
lTo determine the source of a rear servo oil leak, raise the vehicle on a hoist, then carry out a reverse stall.
lTo determine the source of a front servo leak, raise the vehicle on a hoist, then run the vehicle in second gear.
Troubleshooting Charts
The troubleshooting charts are set out as follows:
lTable 6.2.1 Drive Faults,
lTable 6.2.2 Faulty Shift Patterns.
lTable 6.2.3 Shift Quality Faults.
lTable 6.2.4 After Teardown Faults.
Table 6.2.1 - Drive Faults
Action
Check the fluid level. Top up as necessary.
Inspect and clean C1/C2 feed.
Reinstall/renew the ‘z’ link.
Remove, clean and re-install the PRV.
Inspect and replace as necessary.
Inspect and replace as necessary.
Inspect and replace as necessary.
Check servo adjustment or replace rear band
as necessary.
Check for failure in C3, C3 hub or C1/C2 cylin-
der. Repair as necessary.
Inspect and clean PRV.
Inspect and replace pump gears as necessary.
Inspect and repair as necessary. Possible Cause
Insufficient auto transmission fluid.
Blocked feed in C1/C2 cylinder.
‘Z’ link displaced.
Primal regulator valve (PRV) jammed open.
Overdrive shaft or input shaft seal rings
failed.
3-4 or 1-2 one way clutch (OWC) installed
backwards or failed.
C2 piston broken or cracked.
Rear band or servo faulty.
Failure in C3, C3 hub or C1/C2 cylinder.
Jammed primary regulator valve (PRV).
Damaged/broken pump gears.
Dislodged output shaft snap ring.Symptom
No Drive in D
No Drive in
Reverse
No engine braking
in Manual 1
Engine braking in
Manual 1 is OK
No drive in Drive
and Reverse
Page 1047 of 1463

5A-70 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Action
Inspect S1. Repair or replace as necessary.
Check for 12 Volts applied to S1 at all times or
for wiring fault.
Inspect S1. Repair or replace as necessary.
Check for 12 Volts applied to S1 at all times or
for wiring fault.
Inspect S2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Check for open circuit or wiring fault.
Inspect S2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Check for open circuit or wiring fault.
Inspect and adjust as necessary.
Inspect and repair as necessary.
Inspect and replace or refit as necessary.
Inspect ‘O’ ring. Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect the 2-3 shift valve. Repair or replace
as necessary.
Inspect C1 clutch. Repair or replace as neces-
sary.
Inspect ball. Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect C4. Repair C4 or replace C4 wave plate
as necessary.
Inspect rear band adjustment. Adjust as nec-
essary.
Inspect ball- Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect’0’ring. Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect C4 and C4 wave plate. Repair or re-
place as necessary.
Inspect inhibitor switch.
Repair or replace as necessary.
Inspect the 1-2 shift valve.
Repair or replace as necessary
Inspect inhibitor switch.
Repair or replace as necessary.
Inspect the 2-3 shift valve.
Repair or replace as necessary. Possible Cause
S1 always OFF.
S1 always ON.
S2 always OFF.
S2 always ON.
B1 failed.
Loose band adjustment.
Front servo piston or seal failed.
S1/S2 ball misplaced,
Smaller’0’ring on front servo piston failed
or missing.
2-3 shift valve jammed.
C1 clutch failed or slipping in 3rd and 4th.
(Gives 1st in 3rd and 2nd in 4th.)
Over-run clutch (OC)/low ball misplaced.
C4 failed or C4 wave plate broken.
Rear band slipping when hot.
Reverse/Low-1st ball misplaced.
Rear servo inner ‘O’ ring missing.
C4 failed or C4 wave plate broken.
Inhibitor switch faulty.
1-2 shift valve jammed.
Inhibitor switch fault, 1-2 only.
2-3 shift valve jammed.Symptom
2-3 shift only
(no 4th or 1st)
1-4 shift only
1-3-4 (Delayed
1-2shift)
4-3 shift only
1-2-Neutral
(1st over run)
1-3 shift only
1-3-4 only
1-2-1 only
No manual 4-3,3-2
or 2-1
No manual 1st
1st gear only or
2nd,3rd, and 4th
only
1st and 2nd only
or 1st, 3rd and 4th
only
Page 1048 of 1463
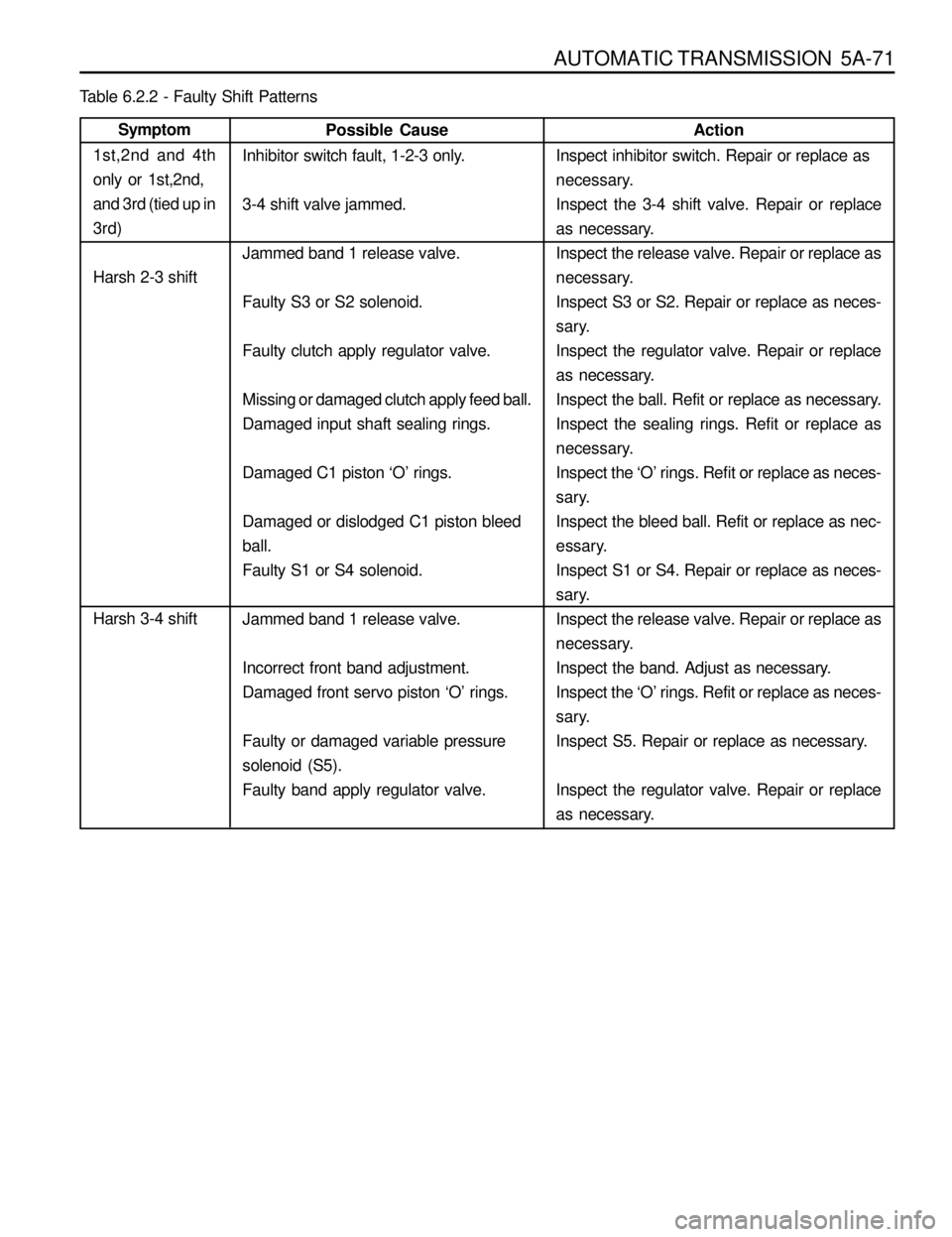
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-71
Table 6.2.2 - Faulty Shift Patterns
Action
Inspect inhibitor switch. Repair or replace as
necessary.
Inspect the 3-4 shift valve. Repair or replace
as necessary.
Inspect the release valve. Repair or replace as
necessary.
Inspect S3 or S2. Repair or replace as neces-
sary.
Inspect the regulator valve. Repair or replace
as necessary.
Inspect the ball. Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect the sealing rings. Refit or replace as
necessary.
Inspect the ‘O’ rings. Refit or replace as neces-
sary.
Inspect the bleed ball. Refit or replace as nec-
essary.
Inspect S1 or S4. Repair or replace as neces-
sary.
Inspect the release valve. Repair or replace as
necessary.
Inspect the band. Adjust as necessary.
Inspect the ‘O’ rings. Refit or replace as neces-
sary.
Inspect S5. Repair or replace as necessary.
Inspect the regulator valve. Repair or replace
as necessary. Possible Cause
Inhibitor switch fault, 1-2-3 only.
3-4 shift valve jammed.
Jammed band 1 release valve.
Faulty S3 or S2 solenoid.
Faulty clutch apply regulator valve.
Missing or damaged clutch apply feed ball.
Damaged input shaft sealing rings.
Damaged C1 piston ‘O’ rings.
Damaged or dislodged C1 piston bleed
ball.
Faulty S1 or S4 solenoid.
Jammed band 1 release valve.
Incorrect front band adjustment.
Damaged front servo piston ‘O’ rings.
Faulty or damaged variable pressure
solenoid (S5).
Faulty band apply regulator valve.Symptom
1st,2nd and 4th
only or 1st,2nd,
and 3rd (tied up in
3rd)
Harsh 2-3 shift
Harsh 3-4 shift
Page 1049 of 1463
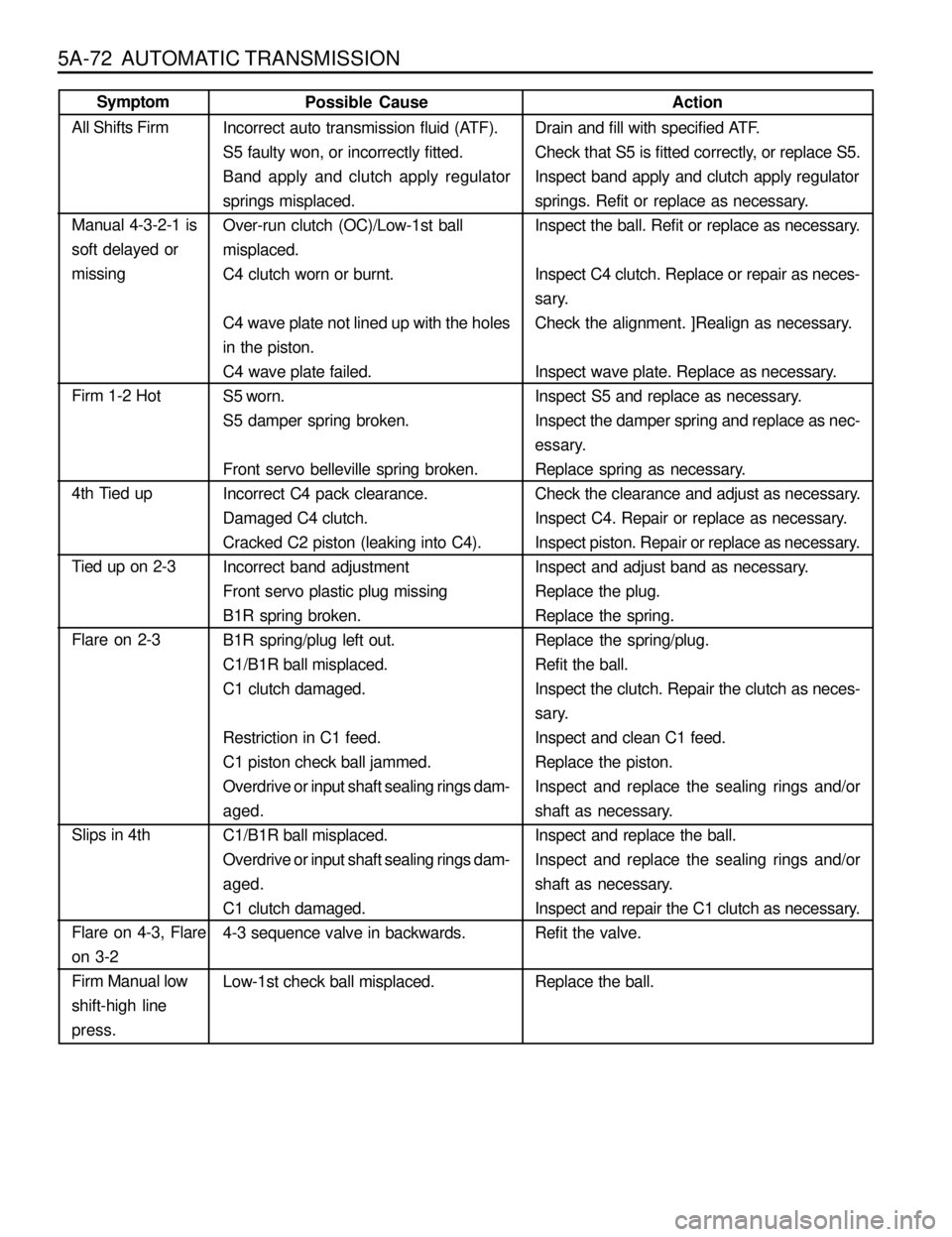
5A-72 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Action
Drain and fill with specified ATF.
Check that S5 is fitted correctly, or replace S5.
Inspect band apply and clutch apply regulator
springs. Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect the ball. Refit or replace as necessary.
Inspect C4 clutch. Replace or repair as neces-
sary.
Check the alignment. ]Realign as necessary.
Inspect wave plate. Replace as necessary.
Inspect S5 and replace as necessary.
Inspect the damper spring and replace as nec-
essary.
Replace spring as necessary.
Check the clearance and adjust as necessary.
Inspect C4. Repair or replace as necessary.
Inspect piston. Repair or replace as necessary.
Inspect and adjust band as necessary.
Replace the plug.
Replace the spring.
Replace the spring/plug.
Refit the ball.
Inspect the clutch. Repair the clutch as neces-
sary.
Inspect and clean C1 feed.
Replace the piston.
Inspect and replace the sealing rings and/or
shaft as necessary.
Inspect and replace the ball.
Inspect and replace the sealing rings and/or
shaft as necessary.
Inspect and repair the C1 clutch as necessary.
Refit the valve.
Replace the ball. Possible Cause
Incorrect auto transmission fluid (ATF).
S5 faulty won, or incorrectly fitted.
Band apply and clutch apply regulator
springs misplaced.
Over-run clutch (OC)/Low-1st ball
misplaced.
C4 clutch worn or burnt.
C4 wave plate not lined up with the holes
in the piston.
C4 wave plate failed.
S5 worn.
S5 damper spring broken.
Front servo belleville spring broken.
Incorrect C4 pack clearance.
Damaged C4 clutch.
Cracked C2 piston (leaking into C4).
Incorrect band adjustment
Front servo plastic plug missing
B1R spring broken.
B1R spring/plug left out.
C1/B1R ball misplaced.
C1 clutch damaged.
Restriction in C1 feed.
C1 piston check ball jammed.
Overdrive or input shaft sealing rings dam-
aged.
C1/B1R ball misplaced.
Overdrive or input shaft sealing rings dam-
aged.
C1 clutch damaged.
4-3 sequence valve in backwards.
Low-1st check ball misplaced.Symptom
All Shifts Firm
Manual 4-3-2-1 is
soft delayed or
missing
Firm 1-2 Hot
4th Tied up
Tied up on 2-3
Flare on 2-3
Slips in 4th
Flare on 4-3, Flare
on 3-2
Firm Manual low
shift-high line
press.
Page 1050 of 1463
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-73
Table 6.2.3 - Shift Quality Faults
Action
Check the resistance. Replace the inhibitor
switch as necessary.
Inspect and replace the sensor as necessary.
Inspect and adjust the band as necessary.
Inspect and replace the’0’rings as necessary.
Inspect, repair or replace S5 as necessary.
Inspect, repair or replace S1 or S4 as neces-
sary.
Inspect, repair or replace the BAR as neces-
sary.
Inspect and repair as necessary.
Inspect and clean CCCV.
Inspect, repair or replace as necessary. Possible Cause
Faulty inhibitor switch.
Faulty throttle position sensor.
Incorrect front band adjustment.
Damaged front servo piston’0’rings.
Faulty or damaged variable pressure so-
lenoid (S5).
Faulty S1 or S4 solenoid.
Faulty band apply regulator valve (BAR).
Misassembled front servo return spring.
Jammed converter clutch control valve
(CCCV).
Faulty solenoid 7.Symptom
Harsh 1-2 shift
stalls when Drive
or Reverse
selected Shudder
on Rolldown
Page 1051 of 1463
5A-74 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Action
Inspect, repair C2 and adjust the linkage as neces-
sary.
Repair C2. Inspect, repair or replace S6 as neces-
sary.
Repair C2. Inspect, replace the sealing rings and/
or shaft as necessary.
Repair C2. Inspect, repair or replace the C2 piston
as necessary.
Inspect C4 and repair as necessary.
Inspect and adjust the C4 pack clearance as nec-
essary.
Repair C4. Inspect and replace the wave plate as
necessary.
Repair C4. Inspect and realign the wave plate as
necessary.
Repair C4. Inspect and realign the sealing rings
and/or shaft as necessary.
Repair C4. Inspect and refit the OWC as neces-
sary.
Repair C4. Inspect and replace the C2 piston as
necessary.
Repair C4. Inspect and refit the ball as necessary.
Inspect and repair B1 and replace the spring as
necessary.
Replace sealing ring.
Repair B1. Refit the ball as necessary.
Inspect and repair C1 and replace the spring.
Repair C1. Inspect and replace the sealing tongs
and/or shaft as necessary.
Repair C1. Inspect and replace the C1 piston as
necessary.
Repair C1. Inspect and refit the capsule as neces-
sary.
Repair C1. Inspect and refit the valve as neces-
sary.
Repair C1. Inspect and replace the ball as neces-
sary.
Inspect and adjust the band as necessary.
Inspect and refit the ball as necessary.
Inspect and replace the ‘O’ ring as necessary.
Inspect and refit the valve as necessary.
Inspect and replace the ‘O’ ring as necessary.
Inspect and refit the valve as necessary.
Possible Cause
T-bar linkage out of adjustment.
56 foiled - stuck low.
Overdrive/output shaft sealing rings damaged.
C2 piston cracked.
Incorrect C4 pack clearance.
C4 wave plate broken.
C4 wave plate not lined up properly.
Overdrive or output shaft sealing rings dam-
aged.
3-4 one way clutch (OWC) in backwards.
C2 piston cracked.
Over-run clutch (OC)/low-1st ball misplaced.
B1R spring broken.
Input shaft sealing ring cut.
C1/B1R ball misplaced.
B1R spring left out.
Overdrive or input shaft sealing rings damaged.
C1 piston cracked.
Ball capsule jammed.
4-3 sequence valve in backwards.
Clutch apply feed (CAF)/B1R ball left out.
Rear band incorrectly adjusted or damaged.
Reverse-low/first ball misplaced.
Input shaft ‘O’ ring missing or damaged.
Converter clutch regulator valve in backwards.
Input shaft ‘O’ ring missing or damaged.
C1 bias valve in backwards.
Symptom
C2 burnt
C4 burnt
B1 burnt
C1 burnt
Slips in reverse -
no manual 1st
Firm converter
lock or unlock
No lock up at light
throttle
Table 6.2.4 - After Teardown Faults