1998 OPEL FRONTERA relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 4732 of 6000
6E–75 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
17.This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes
an electrically erasable programmable read only
memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is replaced,
the new PCM must be programmed. Refer to
UBS
98 model year Immobilizer Workshop Manual.
No Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Attempt to start the engine.
Does the engine start?
—Go to Step 3Go to Step 6
3Check the meter fuse for the instrument cluster ignition
feed circuit.
Is the fuse OK?
—Go to Step 4Go to Step 16
4Ignition “ON,” probe the ignition feed circuit at the
cluster connector with a test light to ground.
Is the test light “ON?”
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 13
51. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the PCM.
3. Jumper the MIL driver circuit at the PCM connector
to ground.
4. Ignition “ON.”
Is the MIL “ON?”
—Go to Step 10Go to Step 11
6Check the PCM ignition feed and battery feed fuses (15
A engine fuse and 15 A PCM fuse).
Are both fuses OK?
—Go to Step 7Go to Step 15
71. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the PCM.
3. Ignition “ON.”
4. Probe the ignition feed circuit at the PCM harness
connector with a test light to ground.
Is the test light “ON?”
—Go to Step 8Go to Step 12
8Probe the battery feed circuit at the PCM harness
connector with a test light to ground.
Is the test light “ON?”
—Go to Step 9Go to Step 14
9Check for a faulty PCM ground connection.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
10Check for damaged terminals at the PCM.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
11Check for an open MIL driver circuit between the PCM
and the MIL.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 18
12Substitute a known “good” relay for the PCM main
relay.
Was the malfunction fixed?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
13Repair the open in the ignition feed circuit.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 4742 of 6000
6E–85 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
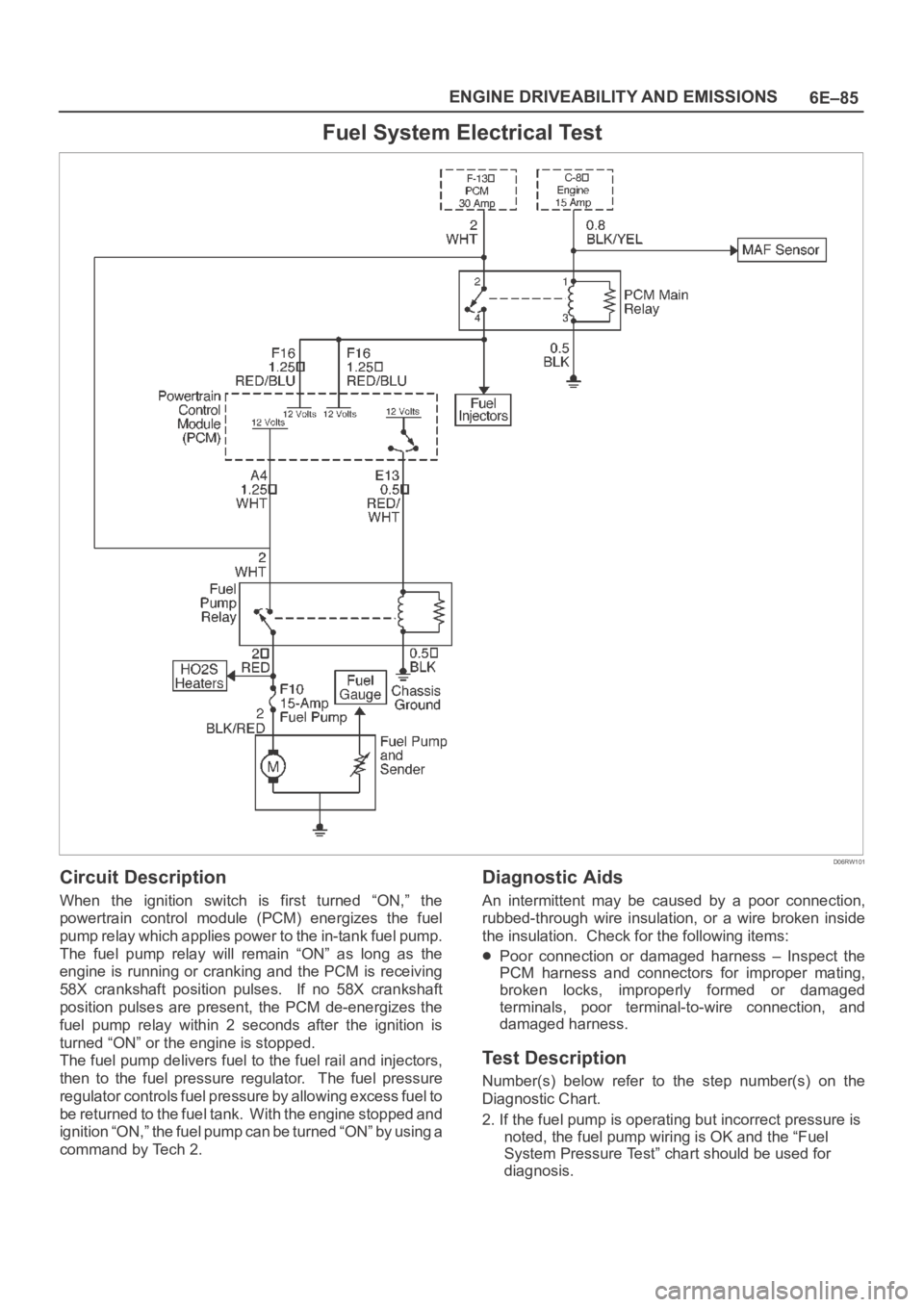
Fuel System Electrical Test
D06RW101
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is first turned “ON,” the
powertrain control module (PCM) energizes the fuel
pump relay which applies power to the in-tank fuel pump.
The fuel pump relay will remain “ON” as long as the
engine is running or cranking and the PCM is receiving
58X crankshaft position pulses. If no 58X crankshaft
position pulses are present, the PCM de-energizes the
fuel pump relay within 2 seconds after the ignition is
turned “ON” or the engine is stopped.
The fuel pump delivers fuel to the fuel rail and injectors,
then to the fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure
regulator controls fuel pressure by allowing excess fuel to
be returned to the fuel tank. With the engine stopped and
ignition “ON,” the fuel pump can be turned “ON” by using a
command by Tech 2.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for the following items:
Poor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
PCM harness and connectors for improper mating,
broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection, and
damaged harness.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. If the fuel pump is operating but incorrect pressure is
noted, the fuel pump wiring is OK and the “Fuel
System Pressure Test” chart should be used for
diagnosis.
Page 4743 of 6000
6E–86
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
It is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure
before connecting a fuel pressure gauge. Refer to
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure, below.
A small amount of fuel may be released when
disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before disconnecting, to
catch any fuel that may leak out. Place the towel in
an approved container when the disconnect is
completed.
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
1. Remove the fuel cap.
2. Remove the fuel pump relay from the underhood
relay center.
3. Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4. Crank the engine for an additional 3 seconds.
Fuel Gauge Installation
1. Remove the shoulder fitting cap.
2. Install fuel gauge 5-8840-0378-0 to the fuel feed line
located in front of and above the right side valve train
cover .
3. Reinstall the fuel pump relay.
Fuel System Electrical Test
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Read the “Caution” above.
2. Relieve the fuel system pressure and install the fuel
pump pressure gauge to the test fitting.
3. Use Tech 2 to command the fuel pump “ON.”
Is there an immediate pressure build-up which
indicates the pump is running?
—Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Verify that the pump is not running by removing the
fuel filler cap and listening.
2. Command the pump “ON” with Tech 2.
Did the pump turn “OFF” after 2 seconds?
—
Te s t
completed
Go to Step 12
41. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Remove the fuel pump relay.
3. Using a test light connected to ground, probe the
battery feed to the relay.
Did the light illuminate?
—Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
5Repair short or open battery feed to fuel pump relay.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
61. Connect a test light between the two wires that
connect to the fuel pump relay pull-in coil.
2. Ignition “ON.”
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds and then turn
off?
—Go to Step 12Go to Step 7
71. With a test light connected to battery (–), probe the
fuel pump relay connector at the wire which runs
from the relay pull-in coil to the PCM.
2. Ignition “ON.”
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds and then turn
off?
—Go to Step 8Go to Step 9
8Locate and repair open in the fuel pump relay ground
circuit.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 4744 of 6000
6E–87 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Fuel System Electrical Test
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
9Check for short or open between the PCM and the fuel
pump relay.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
101. Check the fuel pump relay circuit for a poor terminal
connection at the PCM.
2. If a problem is found, replace terminal as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
11Replace the PCM.
IMPORTANT:The replacement PCM must be
programmed. Refer to
UBS 98model year Immobilizer
Workshop Manual.
Is the action complete?—Verify repair—
121. Reconnect the fuel pump relay.
2. Disconnect the fuel pump electrical connector at the
fuel tank.
3. Using a test light connected to ground, probe the
fuel pump feed wire (harness side).
4. Command the fuel pump “ON” with Tech 2.
Did the light illuminate for 2 seconds?
—Go to Step 15Go to Step 13
131. Honk the horn to verify that the horn relay is
functioning.
2. Substitute the horn relay for the fuel pump relay.
3. Leave the test light connected as in step 12.
4. Command the fuel pump “ON” with Tech 2.
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds when the fuel
pump was commanded “ON?”
—Go to Step 17Go to Step 14
141. Re-connect the horn relay in its proper location.
2. Check for a short circuit, blown fuse or open circuit
between the relay and the fuel tank.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
151. With the fuel pump electrical connector at the fuel
tank disconnected, connect a test light between the
feed wire and the ground wire (harness side).
2. Command the fuel pump “ON” with Tech 2.
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds?
—Go to Step 18Go to Step 16
16Repair the open circuit in the fuel pump ground wire.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
171. Re-connect the horn relay in its proper location.
2. Replace the fuel pump relay.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
18Replace the fuel pump.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 4746 of 6000

6E–89 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
The valve or valve seat within the fuel pressure
regulator.
The fuel injector(s).
4. Fuel pressure that drops off during acceleration,
cruise, or hard cornering may case a lean condition.
A lean condition can cause a loss of power, surging,
or misfire. A lean condition can be diagnosed using
a Tech II Tech 2. If an extremely lean condition
occurs, the oxygen sensor(s) will stop toggling. The
oxygen sensor output voltage(s) will drop below 500
mV. Also, the fuel injector pulse width will increase.
IMPORTANT:Make sure the fuel system is not
operating in the “Fuel Cut-Off Mode.”
When the engine is at idle, the manifold pressure is
low (high vacuum). This low pressure (high vacuum)
is applied to the fuel pressure regulator diaphragm.
The low pressure (high vacuum) will offset the
pressure being applied to the fuel pressure regulator
diaphragm by the spring inside the fuel pressure
regulator. When this happens, the result is lower fuel
pressure. The fuel pressure at idle will vary slightly as
the barometric pressure changes, but the fuel
pressure at idle should always be less than the fuel
pressure noted in step 2 with the engine “OFF.”
16.Check the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation in order to
determine if that particular fuel injector is leaking. If
checking the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation does not
determine that a particular fuel injector is leaking,
use the following procedure:
Remove the fuel rail, but leave the fuel lines and
injectors connected to the fuel rail. Refer to
Fuel Rail
Assembly
in On-Vehicle Service.
Lift the fuel rail just enough to leave the fuel injector
nozzles in the fuel injector ports.
CAUTION: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury that may result from fuel spraying on
the engine, verify that the fuel rail is positioned over
the fuel injector ports and verify that the fuel injector
retaining clips are intact.
Pressurize the fuel system by connecting a 10 amp
fused jumper between B+ and the fuel pump relay
connector.
Visually and physically inspect the fuel injector
nozzles for leaks.
17.A rich condition may result from the fuel pressure
being above 376 kPa (55 psi). A rich condition may
cause a DTC P0132 or a DTC P0172 to set.
Driveability conditions associated with rich
conditions can include hard starting (followed by
black smoke) and a strong sulfur smell in the
exhaust.20.This test determines if the high fuel pressure is due
to a restricted fuel return line or if the high fuel
pressure is due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
21.A lean condition may result from fuel pressure
below 333 kPa (48 psi). A lean condition may
cause a DTC P0131 or a DTC P0171 to set.
Driveability conditions associated with lean
conditions can include hard starting (when the
engine is cold ), hesitation, poor driveability, lack of
power, surging , and misfiring.
22.Restricting the fuel return line causes the fuel
pressure to rise above the regulated fuel pressure.
Command the fuel pump “ON” with Tech 2. The fuel
pressure should rise above 376 kPa (55 psi) as the
fuel return line becomes partially closed.
NOTE: Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed 414 kPa
( 6 0 p s i ) . F u e l p r e s s u r e i n e x c e s s o f 4 1 4 k P a ( 6 0 p s i ) m a y
damage the fuel pressure regulator.
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
It is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure
before connecting a fuel pressure gauge. Refer to
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure, below.
A small amount of fuel may be released when
disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before disconnecting, to
catch any fuel that may leak out. Place the towel in
an approved container when the disconnect is
completed.
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
1. Remove the fuel cap.
2. Remove the fuel pump relay from the underhood
relay center.
3. Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4. Crank the engine for an additional 3 seconds.
Fuel Gauge Installation
1. Remove the shoulder fitting cap.
2. Install fuel gauge 5-8840-0378-0 to the fuel feed line
located in front of and above the right side valve train
cover.
3. Reinstall the fuel pump relay.
Page 4768 of 6000
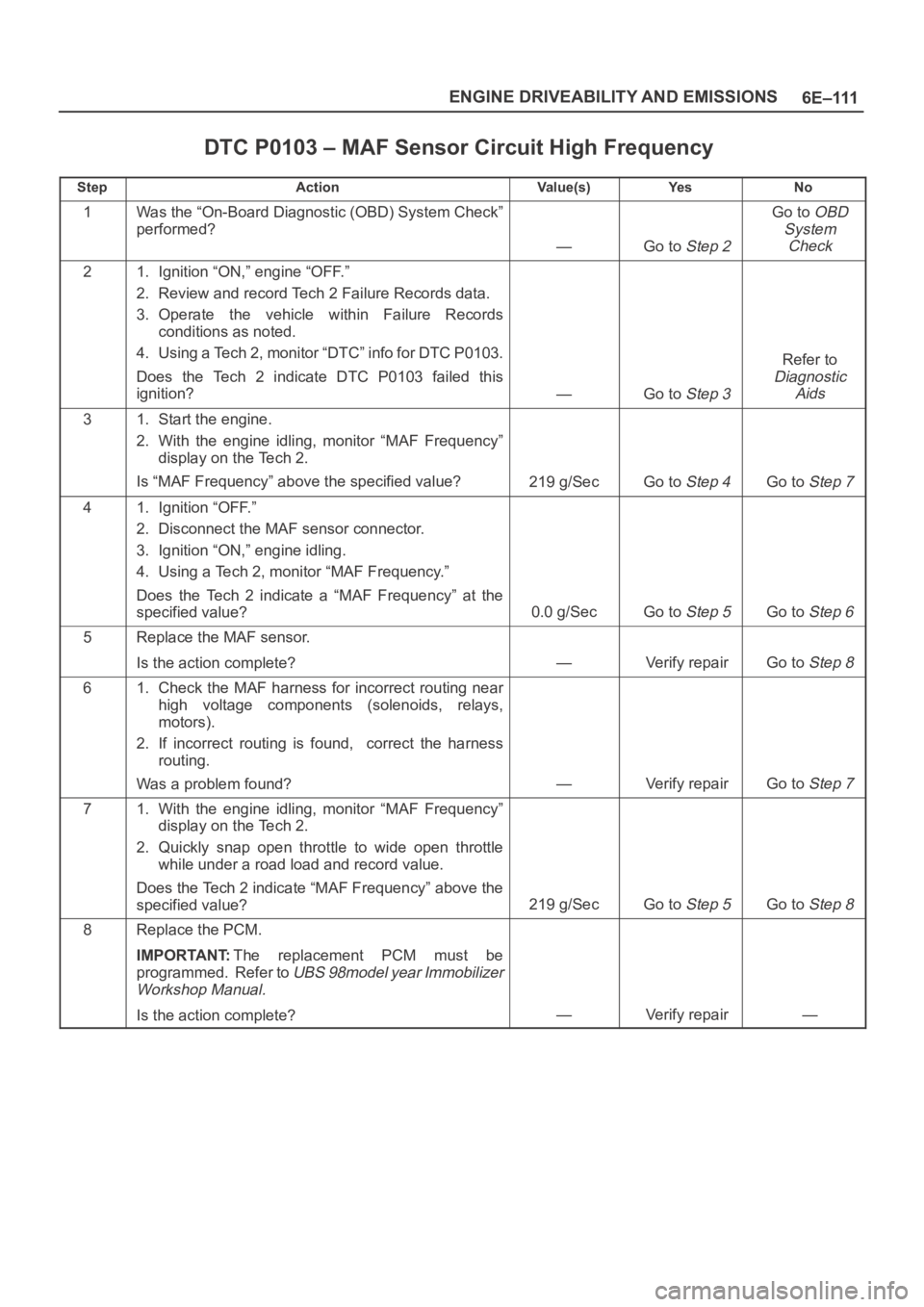
6E–111 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DTC P0103 – MAF Sensor Circuit High Frequency
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor “DTC” info for DTC P0103.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0103 failed this
ignition?
—Go to Step 3
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
31. Start the engine.
2. With the engine idling, monitor “MAF Frequency”
display on the Tech 2.
Is “MAF Frequency” above the specified value?
219 g/SecGo to Step 4Go to Step 7
41. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the MAF sensor connector.
3. Ignition “ON,” engine idling.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor “MAF Frequency.”
Does the Tech 2 indicate a “MAF Frequency” at the
specified value?
0.0 g/SecGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Replace the MAF sensor.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
61. Check the MAF harness for incorrect routing near
high voltage components (solenoids, relays,
motors).
2. If incorrect routing is found, correct the harness
routing.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. With the engine idling, monitor “MAF Frequency”
display on the Tech 2.
2. Quickly snap open throttle to wide open throttle
while under a road load and record value.
Does the Tech 2 indicate “MAF Frequency” above the
specified value?
219 g/SecGo to Step 5Go to Step 8
8Replace the PCM.
IMPORTANT:The replacement PCM must be
programmed. Refer to
UBS 98model year Immobilizer
Workshop Manual.
Is the action complete?—Verify repair—
Page 4903 of 6000
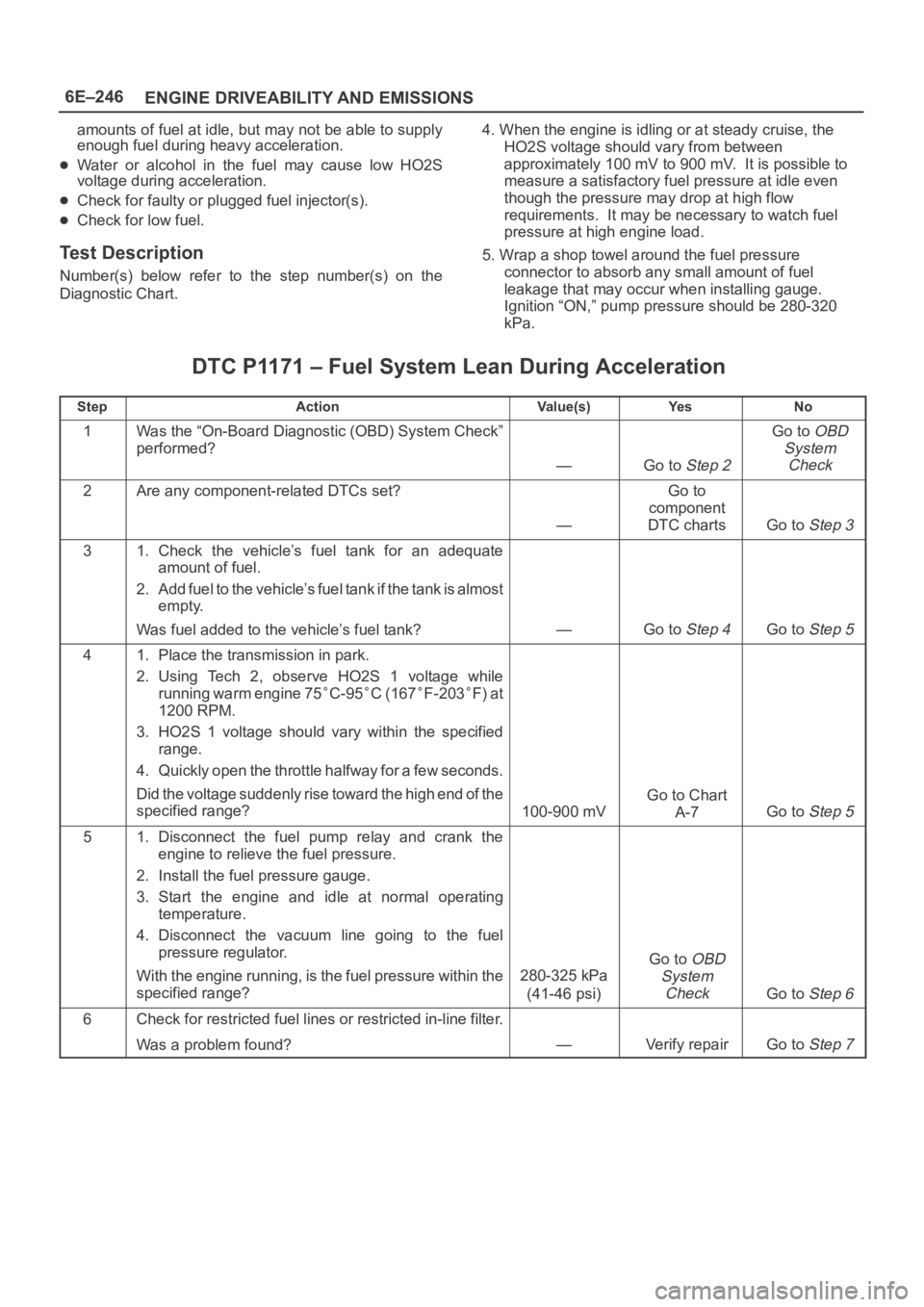
6E–246
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
amounts of fuel at idle, but may not be able to supply
enough fuel during heavy acceleration.
Water or alcohol in the fuel may cause low HO2S
voltage during acceleration.
Check for faulty or plugged fuel injector(s).
Check for low fuel.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.4. When the engine is idling or at steady cruise, the
HO2S voltage should vary from between
approximately 100 mV to 900 mV. It is possible to
measure a satisfactory fuel pressure at idle even
though the pressure may drop at high flow
requirements. It may be necessary to watch fuel
pressure at high engine load.
5. Wrap a shop towel around the fuel pressure
connector to absorb any small amount of fuel
leakage that may occur when installing gauge.
Ignition “ON,” pump pressure should be 280-320
kPa.
DTC P1171 – Fuel System Lean During Acceleration
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Are any component-related DTCs set?
—
Go to
component
DTC charts
Go to Step 3
31. Check the vehicle’s fuel tank for an adequate
amount of fuel.
2. Add fuel to the vehicle’s fuel tank if the tank is almost
empty.
Was fuel added to the vehicle’s fuel tank?
—Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
41. Place the transmission in park.
2. Using Tech 2, observe HO2S 1 voltage while
running warm engine 75
C-95C (167F-203F) at
1200 RPM.
3. HO2S 1 voltage should vary within the specified
range.
4. Quickly open the throttle halfway for a few seconds.
Did the voltage suddenly rise toward the high end of the
specified range?
100-900 mV
Go to Chart
A-7
Go to Step 5
51. Disconnect the fuel pump relay and crank the
engine to relieve the fuel pressure.
2. Install the fuel pressure gauge.
3. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
4. Disconnect the vacuum line going to the fuel
pressure regulator.
With the engine running, is the fuel pressure within the
specified range?
280-325 kPa
(41-46 psi)
Go to OBD
System
Check
Go to Step 6
6Check for restricted fuel lines or restricted in-line filter.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
Page 4904 of 6000

6E–247 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DTC P1171 – Fuel System Lean During Acceleration
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
71. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Remove the fuel pump relay and replace it with a
fused jumper which will connect the relay’s battery
terminal to the terminal leading to the fuel pump
fuse.
3. While the fuel pump is operating, use pliers to slowly
close the return line (do not exceed the first
specified value).
Using the pliers to restrict the return line, can the fuel
pressure be manipulated to exceed the second
specified value?
414 kPa
(60 psi)
325 kPa
(46 psi)
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 8
8Check for:
Faulty fuel pump
Restricted fuel pump strainer (sock)
Incorrect fuel pump
Incorrect fuel being used
Hot fuel
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—