1998 OPEL FRONTERA brake
[x] Cancel search: brakePage 1369 of 6000
6E–252
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
passage and on the IAC pintle, and excessive deposits
in the throttle bore and on the throttle plate.
Large vacuum leak – Check for a condition that causes
a large vacuum leak, such as an incorrectly installed or
faulty PCV valve or a disconnected brake booster
hose.Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P1508 – IAC System Low RPM
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Start the engine.
2. Turn all accessories “OFF”(A/C, rear defroster,
etc).
3. Using a Tech 2, command RPM up to 1500, down to
500, and the up to 1500 while monitoring the
“Engine Speed” on the Tech 2.
NOTE: This Tech 2 command may cause the engine to
“cut out” when RPM goes above 1500. If this occurs,
the “cutting out” will stop when the Tech 2 command for
the test is discontinued, or if the Tech 2 command is
changed to less than 1500 RPM.
Does the “Engine Speed” remain within the specified
value of the “Desired Idle” for each RPM command?
50 RPM
No trouble
found. Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 3
31. Disconnect the IAC.
2. Install IAC Node Light 5-8840-2312-0 or equivalent.
3. With the engine running, command RPM up to
1500, down to 500, and then up to 1500 while
observing the node light.
NOTE: This Tech 2 command may cause the engine to
“cut out” when RPM goes above 1500. If this occurs,
the “cutting out” will stop when the Tech 2 command for
the test is discontinued, or if the Tech 2 command is
changed to less than 1500 RPM.
Does each node light cycle red and green (never
“OFF”)?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 4
41. Check the following circuits for an open, short to
voltage, short ground, or poor connections at the
PCM:
IAC “A” Low.
IAC “A” High.
IAC “B” Low.
IAC “B” High.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
Page 1390 of 6000
6E–273 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
101. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
Restricted air intake system. Check for a
possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted
air filter element, or foreign objects blocking
the air intake system.
Throttle body. Check for objects blocking the
IAC passage or throttle bore, excessive
deposits in the IAC passage and on the IAC
pintle, and excessive deposits in the throttle
bore and on the throttle plate.
Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that
causes a large vacuum leak, such as an
incorrectly installed or faulty crankcase
ventilation valve or a disconnected brake
booster hose.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
11Check the injector connections. If any of the injectors
are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Perform the “Injector Coil/Balance Test” in Fuel
Metering System
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check for fuel in the pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
2. If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator
assembly. Refer to
Fuel Metering System.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
141. Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester J 26792 (ST-125). Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
for the procedure.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 15
151. Remove spark plugs. Check for wet plugs, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
deposits. Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 16
161. Check for a loose ignition coil ground.
Refer to
Electrical Ignition System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
Page 1400 of 6000
6E–283 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Cuts Out, Misses Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
101. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
Restricted air intake system. Check for a
possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted
air filter element, or foreign objects blocking
the air intake system.
Throttle body. Check for objects blocking the
IAC passage or throttle bore, excessive
deposits in the IAC passage and on the IAC
pintle, and excessive deposits in the throttle
bore and on the throttle plate.
Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that
causes a large vacuum leak, such as an
incorrectly installed or faulty PCV valve or
brake booster hose disconnected .
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
11Check the injector connections. If any of the injectors
are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Perform the “Injector Coil/Balance Test” in Fuel
Metering System
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check for fuel in the pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
2. If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator
assembly. Refer to
Fuel Metering System.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
141. Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester J 26792 (ST-125). Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
for the procedure.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 15
151. Remove spark plugs. Check for wet plugs, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
deposits. Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 16
161. Check for a loose ignition coil ground.
Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
Page 1762 of 6000

ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 29
13 Vacuum Hose
1) Disconnect vacuum hose from vacuum pump.
14. Starter Harness
1) Disconnect B terminal and put cable harness
close to chassis side.
2) Disconnect S terminal connector.
15. Engine Harness
1) Disconnect engine harness close to engine side.
16. Fuel Pipe
1) Remove fuel pipe from fuel pump and take care
not to spill fuel and let dust enter.
17. Engine Ground Cable
1) Disconnect ground cable from left rear side of
timing gear case.
18. Vacuum Hose: Vacuum Tank
Disconnect vacuum hose from vacuum pump side.
19. Glow Plug Harness
20. Transmission Assembly
1) Set transmission support tool under the
transmission.
2) Remove transmission rear mount.
3) Remove transmission fixing bolt from rear of
engine assembly except two bolts.
4) Carefully hang up engine assembly with a hoist.
5) Remove remaining two transmission fixing bolts.
6) Remove transmission assembly.
7) Remove heater hose.
8) Disconnect wire harness connector for shift on
the fly.
9) Remove vacuum hose.
21. Prepare Engine Stand
22. Engine Assembly
1) Remove engine mount fixing bolts.
2) Carefully hang up the engine assembly.
3) Take out the engine assembly making sure not
to damage the brake oil pipe and other pipe etc.
INSTALLATION
1. Engine assembly
1) Install engine in mounting position by using
hoist.
2. Transmission Assembly
1) Refer to transmission installation steps in
section 7.
3. Engine Mounting
1) After all fixing bolts (left: two bolts, rights: two
bolts) were inserted in every hole, tighten fixing
bolts to the specified torque.
Torque: 40 Nꞏm (4 kgꞏm/29 lbꞏft)
4. Glow Plug Harness
5. Vacuum Hose
1) Connect Vacuum Hose to Vacuum Pump
6. Engine Ground Cable
7. Fuel Pipe
1) Install fuel pipe to fuel pump.
8. Engine Harness
9. Starter Harness
10. A/C Compressor Assembly
1) Tighten temporarily the fixing bolts (upper and
front lower sides of compressor.)2) Tighten fixing bolt (rear under side of
compressor) to the specified torque.
3) Tighten fixing bolts (front upper and lower sides
of compressor) to the specified torque.
To r q u e : 4 0 N ꞏm ( 4 k g ꞏm / 2 9 l b ꞏf t )
Legend
(1) Tensioner
(2) Bolt
(3) Bracket
(4) A/C compressor
(5) Bolt
11. A.C Generator Harness
12. Engine Ground Cable
1) Tighten ground cable to A/C compressor
bracket.
13. Air Cleaner cover & Duct
14. Intercooler Assembly
1) Refer to “Intercooler” in this manual.
15. Radiator Assembly
1) Install rubber cushion in under left and right part
of radiator and position radiator.
2) Fix radiator with bracket.
16. Cooling Fan Assembly
1) Install cooling fan assembly and tighten fixing
bolts to the specified torque.
Torque: 8 Nꞏm (0.8 kgꞏm/5.8 lb ft)
17. Fan Shroud
18. Radiator Hose
1) Connect upper and lower hose to engine side.
2) Pour coolant into radiator.
19. Install battery.
20. Connect window washer hose and install engine
hood.
1
2
3
4
5
For E urope
F06R200005
Page 1870 of 6000

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6D – 3
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BATTERY CHARGING
Observe the following safety precautions when
charging the battery:
1. Never attempt to charge the battery when the fluid
level is below the lower level line on the side of the
battery. In this case, the battery must be replaced.
2. Pay close attention to the battery during the
charging procedure.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate
of charge reduced if the battery feels hot to the
touch.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate
of charge reduced if the battery begins to gas or
spew electrolyte from the vent holes.
3. In order to more easily view the hydrometer blue
dot or ring, it may be necessary to jiggle or tilt the
battery.
4. Battery temperature can have a great effect on
battery charging capacity.
5. The sealed battery used on this vehicle may be
either quick-charged or slow-charged in the same
manner as other batteries.
Whichever method you decide to use, be sure that
you completely charge the battery. Never partially
charge the battery.
JUMP STARTING
JUMP STARTING WITH AN AUXILIARY
(BOOSTER) BATTERY
CAUTION: Never push or tow the vehicle in an
attempt to start it. Serious damage to the emission
system as well as other vehicle parts will result.
Treat both the discharged battery and the booster
battery with great care when using jumper cables.
Carefully follow the jump starting procedure, being
careful at all times to avoid sparking.
WARNING: Failure to carefully follow the jump
starting procedure could result in the following:
1. Serious personal injury, particularly to your
eyes.
2. Property damage from a battery explosion,
battery acid, or an electrical fire.
3. Damage to the electronic components of one or
both vehicles.
Never expose the battery to an open flame or electrical
spark. Gas generated by the battery may catch fire or
explode. Remove any rings, watches, or other jewelry
before working around the battery. Protect your eyes by
wearing an approved set of goggles.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with your
eyes or skin.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with fabrics
or painted surfaces.
Battery fluid is a highly corrosive acid.Should battery fluid come in contact with your eyes,
skin, fabric, or a painted surface, immediately and
thoroughly rinse the affected area with clean tap water.
Never allow metal tools or jumper cables to come in
contact with the positive battery terminal, or any other
metal surface of the vehicle. This will protect against a
short circuit.
Always keep batteries out of the reach of young
children.
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE
1. Set the vehicle parking brake.
If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the selector lever in the “PARK”
position.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual
transmission place the shift lever in the “NEUTRAL”
position.
Turn “OFF” the ignition.
Turn “OFF” all lights and any other accessory
requiring electrical power.
2. Look at the built-in hydrometer.
If the indication area of the built-in hydrometer is
completely clear, do not try to jump start.
3. Attach the end of one jumper cable to the positive
terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to the
positive terminal of the discharged battery.
Do not allow the vehicles to touch each other.
This will cause a ground connection, effectively
neutralizing the charging procedure.
Be sure that the booster battery has a 12 volt rating.
4. Attach one end of the remaining cable to the
negative terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to a solid
engine ground (such as the A/C compressor
bracket or the generator mounting bracket) of the
vehicle with the discharged battery.
This ground connection must be at least 450 mm
(18 in) from the battery of the vehicle whose battery
is being charged.
WARNING: Never attach the end of the jumper
cable directly to the negative terminal of the dead
battery.
5. Start the engine of the vehicle with the good battery.
Make sure that all unnecessary electrical
accessories have been turned “OFF”.
6. Start the engine of the vehicle with the dead battery.
7. To remove the jumper cables, follow the above
directions in the reverse order.
Be sure to first disconnect the negative cable from
the vehicle with the discharged battery.
Page 1898 of 6000
6E–5 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–159. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–159. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1562
(Flash DTC 35) System Voltage Too Low
at Cranking 6E–160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–160. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–160. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1587
(Flash DTC 25) Brake SW Malfunction 6E–161. . . .
Circuit Description 6E–161. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–161. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–161. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–161. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1588
(Flash DTC 25) Brake SW Malfunction 6E–163. . . .
Circuit Description 6E–163. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–163. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–163. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–163. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0601
(Flash DTC 55) ECM Checksum Error 6E–165. . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–165. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–165. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–165. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0650
(Flash DTC 77) Check Engine Lam Circuit
Open/Short 6E–166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–166. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–166. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0654
(Flash DTC 27) Tachometer Circuit
Open/Short 6E–168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–168. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–168. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1655
(Flash DTC 17) Thermo Relay Circuit
Open/Short 6E–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–170. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–170. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1657
(Flash DTC 76) ECM Main Relay Circuit
Open/Short 6E–172. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–172. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–172. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–172. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–172. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1589
(Flash DTC 47) Transmission SW Circuit
Open/Short 6E–174. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–174. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–174. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–174. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–174. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Symptom Diagnosis 6E–176. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Default Matrix Table 6E–199. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
On–Vehicle Service Camshaft Position
(CMP) Sensor 6E–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection Procedure 6E–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–202. . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–202. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–202. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E–203.
Removal Procedure 6E–203. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–203. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor 6E–203. . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–203. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–204. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor 6E–204.
Removal Procedure 6E–204. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–205. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Temperature (OT) Sensor 6E–205. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–205. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–206. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 6E–206. . . . . . . . . .
Removal and Installation Procedure 6E–206. . . . . .
Engine Control Module (ECM) 6E–206. . . . . . . . . . . .
Service Precaution 6E–206. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Damage 6E–206. . .
Removal Procedure 6E–207. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EEPROM 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Check 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Throttle Position (ITP) Sensor 6E–208. . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Function Check 6E–209. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–209. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) 6E–210. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–210. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection Procedure 6E–210. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–210. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Air Cleaner/Air Filter 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accel Position (AP) Sensor 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–212. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Pedal Replacement 6E–212. . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1908 of 6000
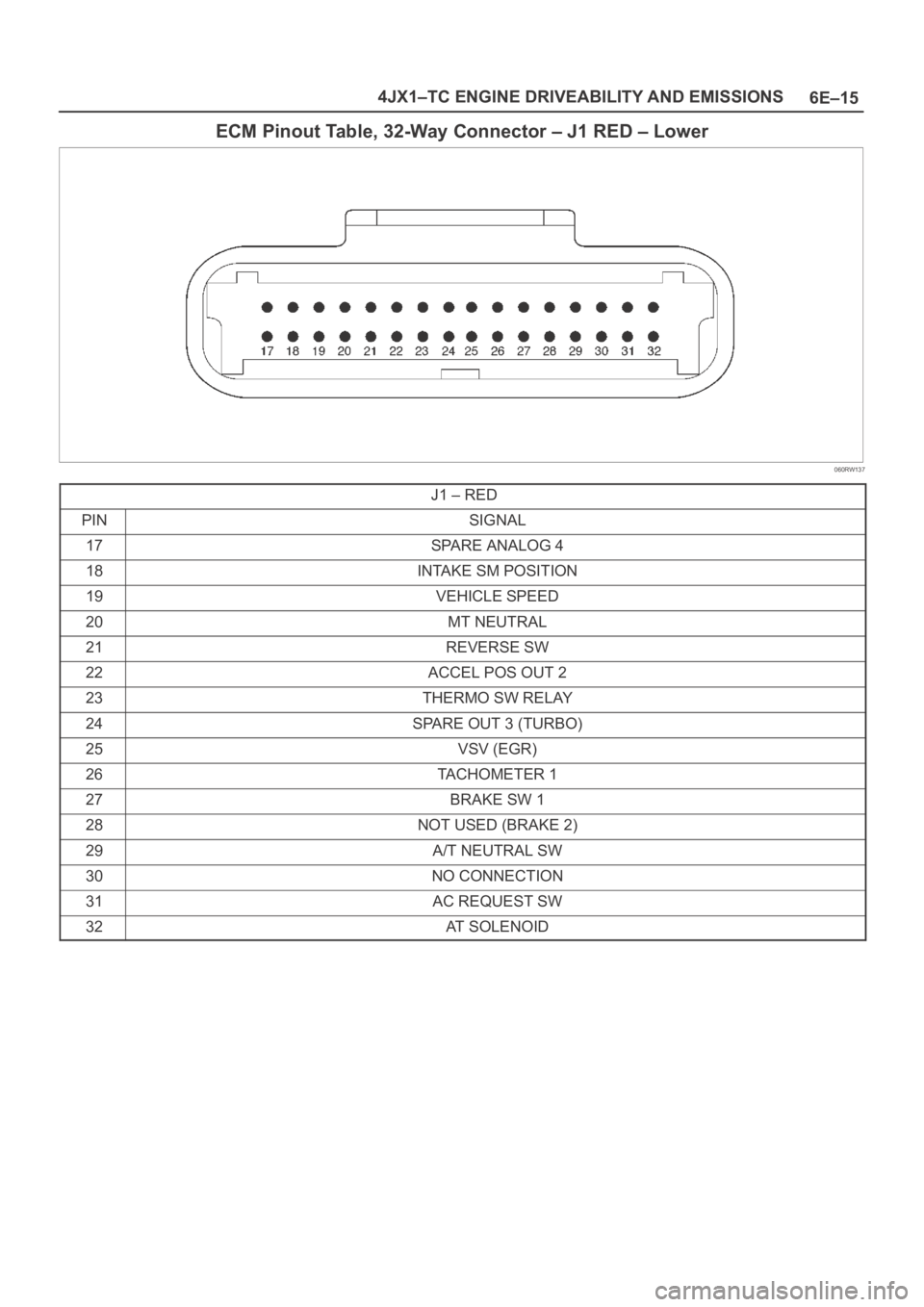
6E–15 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ECM Pinout Table, 32-Way Connector – J1 RED – Lower
060RW137
J1 – RED
PINSIGNAL
17SPARE ANALOG 4
18INTAKE SM POSITION
19VEHICLE SPEED
20MT NEUTRAL
21REVERSE SW
22ACCEL POS OUT 2
23THERMO SW RELAY
24SPARE OUT 3 (TURBO)
25VSV (EGR)
26TACHOMETER 1
27BRAKE SW 1
28NOT USED (BRAKE 2)
29A/T NEUTRAL SW
30NO CONNECTION
31AC REQUEST SW
32AT SOLENOID
Page 1919 of 6000

6E–26
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Output Components:
Output components are diagnosed for proper response to
control module commands. Components where
functional monitoring is not feasible will be monitored for
circuit continuity and out-of-range values if applicable.
Output components to be monitored include, but are not
limited to, the following circuit:
EGR VSV
EGR EVRV
Electronic Transmission controls
Injector
Intake throttle
Glow plug
MIL control
Refer to ECM and Sensors in General Descriptions.
Passive and Active Diagnostic Tests
A passive test is a diagnostic test which simply monitors a
vehicle system or component. Conversely, an active test,
actually takes some sort of action when performing
diagnostic functions, often in response to a failed passive
test.
Intrusive Diagnostic Tests
This is any on-board test run by the Diagnostic
Management System which may have an effect on
vehicle performance or emission levels.
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means that engine at temperature must
reach a minimum of 70
C (160F) and rise at least 22C
(40
F) over the course of a trip.
Freeze Frame
Freeze Frame is an element of the Diagnostic
Management System which stores various vehicle
information at the moment an emissions-related fault is
stored in memory and when the MIL is commanded on.
These data can help to identify the cause of a fault. Refer
to
Storing And Erasing Freeze Fame Data for more
detailed information.
Failure Records
Failure Records data is an enhancement of the OBD
Freeze Frame feature. Failure Records store the same
vehicle information as does Freeze Frame, but it will store
that information for any fault which is stored in on-board
memory, while Freeze Frame stores information only for
emission-related faults that command the MIL on.
Common OBD Terms
Diagnostic
When used as a noun, the word diagnostic refers to any
on-board test run by the vehicle’s Diagnostic
Management System. A diagnostic is simply a test run on
a system or component to determine if the system or
component is operating according to specification. There
are many diagnostics, shown in the following list:
EGR
engine speed
vehicle speed
ECT
MAP
VSV
IAT
ITP
AP
FT (Fuel Temp)
RP (Rail Pressure)
OT (Oil Temp)
EGR EVRV
Idle SW
Brake SW
The Diagnostic Executive
The Diagnostic Executive is a unique segment of
software which is designed to coordinate and prioritize
the diagnostic procedures as well as define the protocol
for recording and displaying their results. The main
responsibilities of the Diagnostic Executive are listed as
follows:
Commanding the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) on and
off
DTC logging and clearing
Freeze Frame data for the first emission related DTC
recorded
Current status information on each diagnostic
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are designed
to locate a faulty circuit or component through a process
of logical decisions. The charts are prepared with the
requirement that the vehicle functioned correctly at the
time of assembly and that there are not multiple faults
present.
There is a continuous self-diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complemented by
the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual. The
language of communicating the source of the malfunction
is a system of diagnostic trouble codes. When a
malfunction is detected by the control module, a
diagnostic trouble code is set and the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) (“Check Engine” lamp) is
illuminated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) looks the same as
the MIL you are already familiar with “Check Engine”
lamp.
Basically, the MIL is turned on when the ECM detects a
DTC that will impact the vehicle emissions.
When the MIL remains “ON” while the engine is
running, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a
driveability or emissions problem, a Powertrain
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check must be
performed. The procedures for these checks are
given in On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check.
These checks will expose faults which may not be
detected if other diagnostics are performed first.
DTC Types
Characteristic of Code