1998 MITSUBISHI MONTERO head
[x] Cancel search: headPage 558 of 1501

cylinder head design and type of metal used.
Remove valve guide from cylinder head by pressing or tapping
on a stepped drift. See Fig. 8. Once valve guide is installed,
distance from cylinder head to top of valve guide must be checked.
This distance must be within specification.
Aluminum heads are often heated before installing valve
guide. Guide is sometimes chilled in dry ice before installation.
Combination of a heated head and chilled guide insures a tight guide
fit upon assembly. The new guide must be reamed to specification.
Fig. 8: Typical Valve Guide Remover & Installer
This Graphic For General Information Only
VALVES & VALVE SEATS
Valve Grinding
Valve stem O.D. should be measured in several areas to
indicate amount of wear. Replace valve if not within specification.
Valve margin area should be measured to ensure that valve can be
grounded. See Fig. 9.
Fig. 9: Measuring Valve Head Margin - Typical
This Graphic For General Information Only
If valve margin is less than specification, this will burn
the valves. Valve must be replaced. Due to minimum margin dimensions
Page 560 of 1501
the old insert and machining an oversize insert bore. Replacement
oversize insert is usually chilled and the cylinder head is sometimes
warmed. Valve seat is pressed into the head. This operation requires
specialized machine shop equipment.
Valve Seat Concentricity
Using dial gauge, install gauge pilot in valve guide.
Position gauge arm on the valve seat. Adjust dial indicator to zero.
Rotate arm 360 degrees and note reading. Runout should not exceed
specification.
To check valve-to-valve seat concentricity, coat valve face
lightly with Prussian Blue dye. Install valve and rotate it on valve
seat. If pattern is even and entire seat is coated at valve contact
point, valve is concentric with the seat.
REASSEMBLY
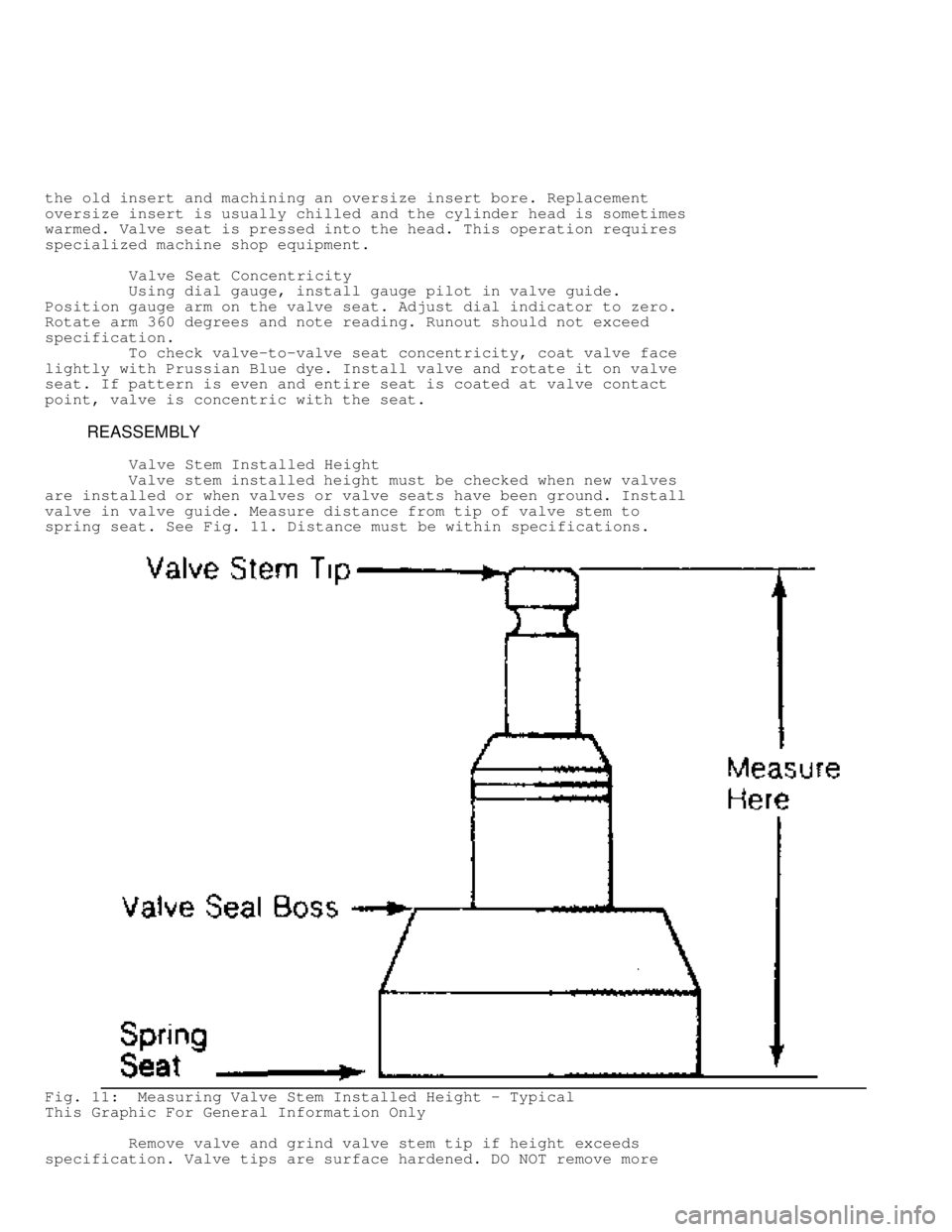
Valve Stem Installed Height
Valve stem installed height must be checked when new valves
are installed or when valves or valve seats have been ground. Install
valve in valve guide. Measure distance from tip of valve stem to
spring seat. See Fig. 11. Distance must be within specifications.
Fig. 11: Measuring Valve Stem Installed Height - Typical
This Graphic For General Information Only
Remove valve and grind valve stem tip if height exceeds
specification. Valve tips are surface hardened. DO NOT remove more
Page 561 of 1501

than .010" (.25 mm) from tip. Chamfer sharp edge of reground valve
tip. Recheck valve stem installed height.
VALVE STEM OIL SEALS
Valve stem oil seals must be installed on valve stem. See
Fig. 2 . Seals are needed due to pressure differential at the ends of
valve guides. Atmospheric pressure above intake guide, combined with
manifold vacuum below guide, causes oil to be drawn into the cylinder.
Exhaust guides also have pressure differential created by
exhaust gas flowing past the guide, creating a low pressure area. This
low pressure area draws oil into the exhaust system.
Replacement (On Vehicle)
Mark rocker arm or overhead cam components for location.
Remove rocker arm components or overhead cam components. Components
must be installed in original location. Remove spark plugs. Valve stem
oil seals may be replaced by holding valves against seats using air
pressure.
Air pressure must be installed in cylinder using an adapter
for spark plug hole. An adapter can be constructed by welding air hose
connection to spark plug body with porcelain removed.
Install adapter in spark plug hole. Apply a minimum of 140
psi (9.8 kg/cm
�) to adapter. Air pressure should hold valve closed. If
air pressure does not hold valve closed, check for damaged or bent
valve. Cylinder head must be removed for service.
Using valve spring compressor, compress valve springs. Remove
valve locks. Carefully release spring compressor. Remove retainer or
rotator and valve spring. Remove valve stem oil seal.
If oversized valves have been installed, oversized oil seals
must be used. Coat valve stem with engine oil. Install protective
sleeve over end of valve stem. Install new oil seal over valve stem
and seat on valve guide. Remove protective sleeve. Install spring
seat, valve spring and retainer or rotator. Compress spring and
install valve locks. Remove spring compressor. Ensure valve locks
are fully seated.
Install rocker arms or overhead cam components. Tighten all
bolts to specification. Adjust valves if required. Remove adapter.
Install spark plugs, valve cover and gasket.
VALVE SPRING INSTALLED HEIGHT
Valve spring installed height should be checked during
reassembly. Measure height from lower edge of valve spring to the
upper edge. DO NOT include valve spring seat or retainer. Distance
must be within specifications. If valves and/or seats have been
ground, a valve spring shim may be required to correct spring height.
See Fig. 12 .
Fig. 12: Measuring Valve Spring Installed Height - Typical
This Graphic For General Information Only
Page 575 of 1501

CYLINDER BLOCK
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
NOTE: Always refer to appropriate engine overhaul article in the
ENGINES section for complete overhaul procedures and
specifications for the vehicle being repaired.
BLOCK CLEANING
Only cast cylinder blocks should be hot tank cleaned.
Aluminum cylinder blocks should be cleaned using cold tank method.
Cylinder block is cleaned in order to remove carbon deposits, gasket
residue and water jacket scale. Remove oil galley plugs, freeze plugs
and cam bearings prior to block cleaning.
BLOCK INSPECTION
Visually inspect the block. Check suspected areas for cracks
using the Dye Penetrant inspection method. Block may be checked for
cracks using the Magnaflux method.
Cracks are most commonly found at the bottom of the
cylinders, the main bearing saddles, near expansion plugs and between
the cylinders and water jackets. Inspect lifter bores for damage.
Inspect all head bolt holes for damaged threads. Threads should be
cleaned using tap to ensure proper head bolt torque. Consult machine
shop concerning possible welding and machining (if required).
CYLINDER BORE INSPECTION
Inspect the bore for scuffing or roughness. Cylinder bore
is dimensionally checked for out-of-round and taper using dial bore
gauge. For determining out-of-round, measure cylinder parallel and
perpendicular to the block centerline. Difference in the 2 readings
is the bore out-of-round. Cylinder bore must be checked at top, middle
and bottom of piston travel area.
Bore taper is obtained by measuring bore at the top and
bottom. If wear has exceeded allowable limits, block must be honed
or bored to next available oversize piston dimension.
CYLINDER HONING
Cylinder must be properly honed to allow new piston rings to
properly seat. Cross-hatching at correct angle and depth is critical
to lubrication of cylinder walls and pistons.
A flexible drive hone and power drill are commonly used.
Drive hone must be lubricated during operation. Mix equal parts of
kerosene and SAE 20w engine oil for lubrication.
Apply lubrication to cylinder wall. Operate cylinder hone
from top to bottom of cylinder using even strokes to produce 45 degree
cross-hatch pattern on the cylinder wall. DO NOT allow cylinder hone
to extend below cylinder during operation.
Recheck bore dimension after final honing. Wash cylinder
wall with hot soapy water to remove abrasive particles. Blow dry with
compressed air. Coat cleaned cylinder walls with lubricating oil.
DECK WARPAGE
Check deck for damage or warped head sealing surface. Place
a straightedge across gasket surface of the deck. Using feeler gauge,
measure clearance at center of straightedge. Measure across width and
Page 577 of 1501

NOTE: Always refer to appropriate engine overhaul article in the
ENGINES section for complete overhaul procedures and
specifications for the vehicle being repaired.
CLEANING & INSPECTION
Clean camshaft with solvent. Ensure all oil passages are
clear. Inspect cam lobes and bearing journals for pitting, flaking or
scoring. Using micrometer, measure bearing journal O.D.
Support camshaft at each end with "V" blocks. Position dial
indicator with tip resting on center bearing journal. Rotate camshaft
and note reading. If reading exceeds specification, replace camshaft.
Check cam lobe lift by measuring base circle of camshaft
using micrometer. Measure again at 90 degrees to tip of cam lobe. Cam
lift can be determined by subtracting base circle diameter from tip of
cam lobe measurement.
Different lift dimensions are given for intake and exhaust
cam lobes. Reading must be within specifications. Replace camshaft if
cam lobes or bearing journals are not within specifications.
Inspect camshaft gear for chipped, eroded or damaged teeth.
Replace gear if damaged. On camshafts using thrust plate, measure
distance between thrust plate and camshaft shoulder. Replace thrust
plate if not within specification.
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS
Removal & Installation
Remove the camshaft rear plug. The camshaft bearing remover
is assembled with its shoulder resting on the bearing to be removed
according to manufacturer's instructions. Tighten puller nut until
bearing is removed. Remove remaining bearings, leaving front and rear
bearings until last. These bearings act as guide for camshaft bearing
remover.
To install new bearings, puller is rearranged to pull
bearings toward the center of block. Ensure all lubrication passages
of bearing are aligned with cylinder block. Coat new camshaft rear
plug with sealant. Install camshaft rear plug. Ensure plug is even
in cylinder block.
CAMSHAFT INSTALLATION
Lubricate bearing surfaces and cam lobes with ample amount of
Molykote or camshaft lubricant. Carefully install camshaft. Use care
not to damage bearing journals during installation. Install thrust
plate retaining bolts (if equipped). Tighten bolts to specification.
On overhead camshafts, install bearing caps in original location.
Tighten bolts to specification. Check end play.
CAMSHAFT END PLAY
Using dial indicator, check end play. Position dial indicator
on front of engine block. Position indicator tip against camshaft.
Push camshaft toward rear of engine and adjust indicator to zero.
Move camshaft forward and note reading. Camshaft end play
must be within specification. End play may be adjusted by relocating
gear, shimming thrust plate or replacing thrust plate depending on
manufacturer.
TIMING CHAINS & BELTS
Page 579 of 1501

manufacturer. See Fig. 24.
Fig. 24: Timing Gear Mark Alignment - Typical
This Graphic For General Information Only
TIMING BELTS
Cogged tooth belts are commonly used on overhead cam
engines. Inspect belt teeth for rounded corners or cracking. Replace
belt if cracked, damaged, missing teeth or oil soaked.
Used timing belt must be installed in original direction of
rotation. Inspect all sprocket teeth for wear. Replace all worn
sprockets. Sprockets are marked for timing purposes. Engine is
positioned so that crankshaft sprocket mark will be upward. Camshaft
sprocket is aligned with reference mark on cylinder head and timing
belt is installed. See Fig. 25.
Page 587 of 1501

Engine pre-oiling can be done using pressure oiler (if
available). Connect pressure oiler to cylinder block oil passage
such as oil pressure sending unit. Operate pressure oiler long enough
to ensure correct amount of oil has filled crankcase. Check oil level
while pre-oiling.
If pressure oiler is not available, disconnect ignition
system. Remove oil pressure sending unit and replace with oil pressure
test gauge. Using starter motor, rotate engine starter until gauge
shows normal oil pressure for several seconds. DO NOT crank engine
for more than 30 seconds to avoid starter motor damage.
Ensure oil pressure has reached the most distant point from
the oil pump. Reinstall oil pressure sending unit. Reconnect ignition
system.
INITIAL START-UP
Start the engine and operate engine at low speed while
checking for coolant, fuel and oil leaks. Stop engine. Recheck coolant
and oil level. Adjust if necessary.
CAMSHAFT
Break-in procedure is required when a new or reground
camshaft has been installed. Operate and maintain engine speed between
1500-2500 RPM for approximately 30 minutes. Procedure may vary due to
manufacturers recommendations.
PISTON RINGS
Piston rings require a break-in procedure to ensure seating
of rings to cylinder walls. Serious damage may occur to rings if
correct procedures are not followed.
Extremely high piston ring temperatures are produced obtained
during break-in process. If rings are exposed to excessively high RPM
or high cylinder pressures, ring damage can occur. Follow piston ring
manufacturer's recommended break-in procedure.
FINAL ADJUSTMENTS
Check or adjust ignition timing and dwell (if applicable).
Adjust valves (if necessary). Adjust carburetion or injection idle
speed and mixture. Retighten cylinder heads (if required). If
cylinder head or block is aluminum, retighten bolts when engine is
cold. Follow the engine manufacturer's recommended break-in procedure
and maintenance schedule for new engines.
NOTE: Some manufacturer's require that head bolts be retightened
after specified amount of operation. This must be done to
prevent head gasket failure.
Page 588 of 1501

* ENGINE SYSTEMS UNIFORM INSPECTION GUIDELINES *
1998 Mitsubishi Montero
GENERAL INFORMATION
Engine Performance and Maintenance Motorist Assurance Program
Standards For Automotive Repair
All Makes and Models
INTRODUCTION TO MOTORIST ASSURANCE PROGRAM (MAP)
CONTENTS
Motorist Assurance Program (MAP)
OVERVIEW OF MOTORIST ASSURANCE PROGRAM
OVERVIEW OF SERVICE REQUIREMENTS AND SUGGESTIONS
Engine Assemblies
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLIES
LONG BLOCK ASSEMBLIES
SHORT BLOCK ASSEMBLIES
Engine Components
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSORS
ACCESSORY BELTS
ACCESSORY PULLEYS
ACTUATORS
AIR CONDITIONING CYCLING SWITCHES
AIR CONDITIONING PRESSURE SENSORS
AIR DUCTS AND TUBES
AIR FILTER ELEMENTS
AIR FILTER GASKETS
AIR FILTER HOUSINGS AND GASKETS
AIR FUEL RATIO SENSORS
AIR INJECTION CONTROL SOLENOIDS
AIR PLENUMS
AIR PUMP BELTS
AIR PUMPS (ELECTRIC-DRIVEN)
AIR TUBES
ASPIRATOR, CHECK AND DECEL VALVES
BAFFLES
BALLAST PRIMARY SUPPLY RESISTOR WIRES
BALLAST RESISTORS AND PRIMARY SUPPLY RESISTOR WIRES
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSORS
BATTERIES
BATTERY CABLES, WIRES AND CONNECTORS
BATTERY CONNECTORS
BATTERY TRAYS AND HOLD DOWN HARDWARE
BATTERY WIRES
BELT-DRIVEN AIR PUMPS
BELT IDLER ASSEMBLIES (ACCESSORY AND CAM BELTS)
BELT TENSIONERS (ACCESSORY AND CAM BELTS)
BOOST CONTROL MECHANISMS
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORS
CARBURETORS AND CHOKES
CASTING CORE PLUGS AND EXPANSION PLUGS
CHARGE AIR COOLERS "INTERCOOLERS" (CAC)
CHECK VALVES
CHOKES