1998 HONDA INTEGRA steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 586 of 1681

Transmission
Installation (cont'd)
to.
'14. Install new set rings on the end ol the intermediate
shaft and the driveshaft.
'15. lnstall the intermediate shaft.
SET RINGBeplace.
10 x 139 N.m14.0 kgf.m, 29 lbf.ft)
Install exhaust pipe A, and connect the primary
heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) connector.
g
ISELF-LOCKING NUT10 x 1.25 mm54 N.m (5.5 kgf.m,40 tbf.frlReplace.
GASKETReplace.
SELF,LOCKING NUTS8 x 1.25 mm22 N.m {2.2 kgf.m,16 tbt.tt)Replace.
SELF-LOCKING NUTS8 x 1.25 mm16 N'm 11.6 kgf.m,12 tbf.ft)Replace.
SHAFT
14-170
6 x 10 mm BOLT
cllPs,5
1 7. Install the right and lelt drivershafts (see section '16).
NOTE: Turn the right and le{t steering knuckle fully
outward, and slide the right driveshaft into the
differential until you leel its spring clip engage the
side gear. Slide the left driveshaft into the intermedi
ate shaft until you feel the spring clip of the inter
mediate shaft engage the driveshaft.
'18. Install right damper fork, then insrall the right and
lett ball joints to each lower arm with the castle nuts
and new cotter prns.
\
COTTERReplace.CASTLE NUT12 x 1.25 mm49-59 N.m15.0- 6.0 kgf.m,36-43 lbl.tt)
19. lnstall the splash shield.
DAMPEB PINCH EOLT10 x 1.25 mm43 N.m {4.4 kgf .m, l.32 lb{.tr} - '- i
:'g
SELF-LOCKING NUT12 x 1.25 mm64 N.m {6.5 kgf.m,47 lbt.ftlReplace.
PIN
SHIELD
Page 650 of 1681

Steering
Componsnt Location
lndox
*Stooring Wheel
Removal ....
Disassombly/Ro8$.mbly
Disassombly ......
F08$€mbly
Powcr Stosring Gosrbox
R6moval
............................ 17-3
............. 17 -1
................ 17-16
............................. 17_25
17-30
17.31
.......17-21
Sy3tom DGcription
Fluid Flow Disgram
Steering Pump .............. 17-5
Stocring Goarbox ...17.8
Troublorhooting
Gonoral Troubleshooting .............................. 17.10
Noiso lnd Vibration ...... 17-1i[
Fluid Losk3
lnspoction
Installation
Powor Steering Hos6, Lino3
Roplacom€nt .................. 17.34
Powor Steoring Pump
RGplac6montlolpeqtion lnd Adiu3tm6nl
Stoo.ing Operation
Powor A$bi Chock
with v.hiclo Parked
Stcering Linkage 6nd Goarbox
Pump Bolt
17.18
17.18
17.19
17-20
17.35
t7-36
17 -37
r7-39
Inspoction
................... 17.41
Rack Guide Adiustmont ..........................-.-.-. 17 -21
Ffuid Rcplacemont ........17-21
Pump Prc&suro Chock ...,........................,..,..., 17 -22
Fluid Leakage Inrpection ............................... 17-23
Dissssembly
R€aEs€mbly
In3tallation........... 17_58
Ball Joint Boot Replacem.ni ........................ 17-61
17-U
17.49
J ,urrar*TNTAL REsrRArNr sysrEM (sRsr
The Integra SRS includes a driver's airbag located in the steering wheel hub and a passenger's airbag located inthe dashboard above the glove box,
Information necessary to safely service the SRS is included in this Service Manual. ltems marked with an asterisk(*) on the contents page include, or are located near, SRS components. Servicing, dissssembling or replacing
these items will require special pr6cautions and tools, and should therefore be done by an authorized Acura dealer.
. To avoid rondoring ths SRS inoparstivo. which could |rad to parsonal iniury or doath in the ov€nt of ! sev6.o
trontal collision, all SRS sarvice work must be perto.med by an authorizod Acura dsalor.. lmpropor 3orvic€ procadures, including inco[6ql rgmoval and inrtallation of the SRS, could l6ad to pgrsonal
iniury clus€d by unintentional doployment of the airbags,. Do nol bump tho SRS unh, (Xherwise, th6 3ystom may fail in cas€ ol a collision, or the airbags may d€ploy
when ths ignition switch is ON {ll).. All SRS electrical wiring harness€s aro covered with yallow insulation. Related component3 are located in ths
stcaring column. tront con3ol6, dashboard, d.shbolrd lower panel, and in the dashboard above ths glove box.
Do not u3o electrical test oquipm€nt on the3e circuii3.
NOTE: The original radio has a coded theft protection circuit. Be sure to get the customer's code number before- disconn€cting the battery.- removing the No. 47 (7.5 A) fuse from the under-hood fuse/relay box,- removing the radio.
After service, reconnect power to the radio and turn it on. When the word "CODE" is displayed. enter the cus-
tomer's 5-digit code to restore radio operation.
Page 652 of 1681
I
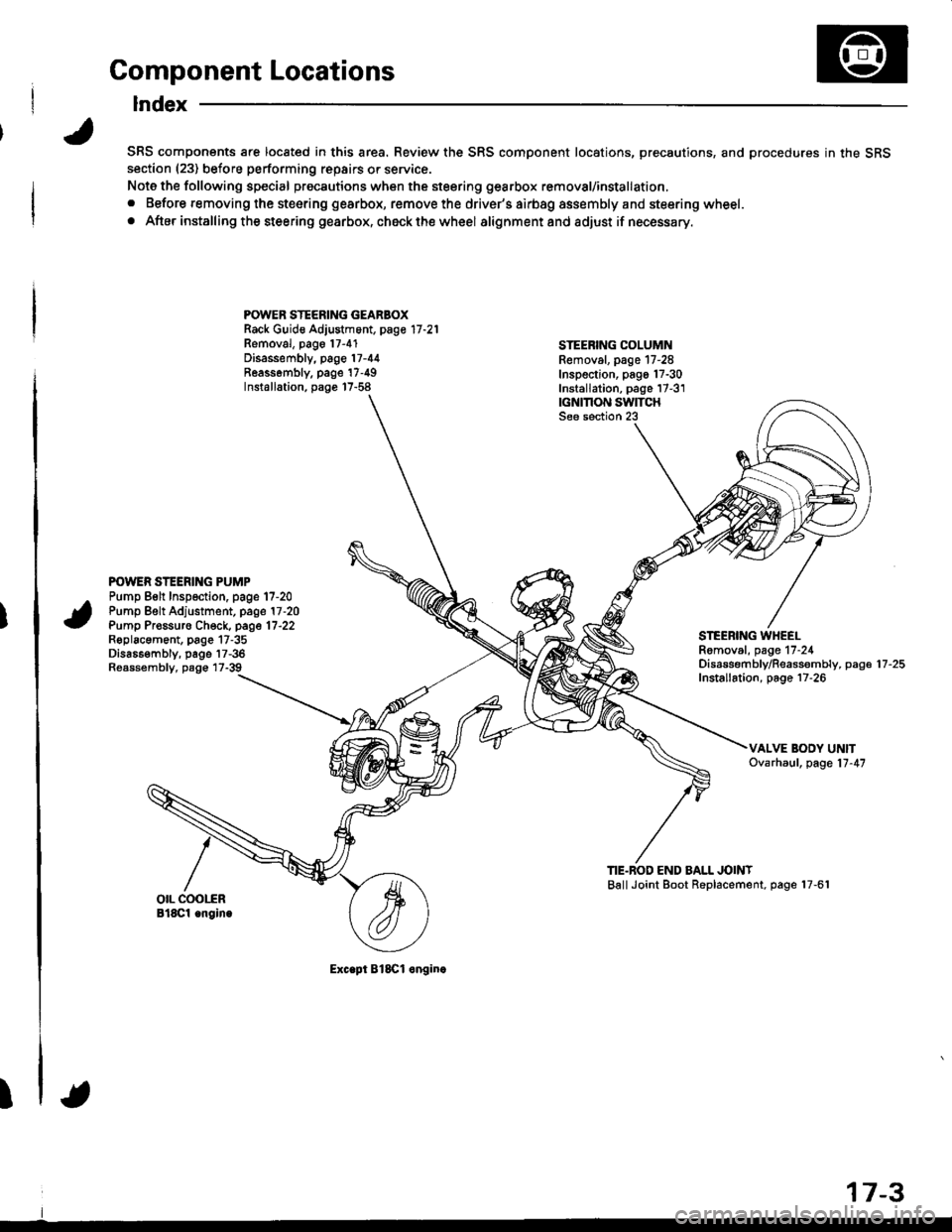
Component Locations
Index
SRS components are located in this area. Review the SRS component locations, precautions, and procedures in the SRSsection (23) before performing repairs or service.
Note the following special precautions when the steering gearbox removal/installation,
. Before removing the steering gearbox, remove the driver's airbag assembly and steering wheel.
. After installing the steering gearbox, ch6ck the wheel alignmentand adjust if necessary.
POWER STEERING GEARBOXRack Guid€ Adjustment, page 17 -21
Removal, pago 17-4'1Disassembly, page 17-44Reassombly. page'17-49Installation, page 17-58
STEEBING COLUMNRemoval. page 17-28Inspection, pago 17-30Installation, page 17-3'1|GNMON SWITCHSee section 23
POWER STEERING PUMPPump Belt Inspection. page 17-20Pump Belt Adjustment, page 17 -20
Pump Pr€ssuro Check, page 17'22Roplacament, page 17-35Dis686embly, page 17-36Reassembly, page 17-39
STEEBING WHEELRomoval, page 17-24Disassembf y/Reassembly, paga 17 -25
Installation, page 17-26
TIE.BOD END BALL JOINTBallJoint Boot Replacement, page 17-61
Exc.pt BlSCl onginc
17-3
Page 653 of 1681

System Description
Fluid Flow Diagram
The system is a compact rotary-valve-type power steering, connected to the steering gearbox. The fluid pressure is pro-
vided by a vane-type pump which is driven by the engine crank pulley. The amount of fluid and pressure is regulated by
the flow control valve built into the pump. The fluid pressure from the pump is delivered to the valve body unit around the
pinion of the steering gearbox. The valve inside the valve body unit controls the hydraulic pressure and changes the direc-
tion of the tlow. The fluid then flows to the power cylinder, where rack thrust is generated. Fluid returning from the power
cylinder flows back to the reservoir, where the fluid is "filtered" and supplied to the pump again
li
I
VALVE BODY UNIT
GEARBOXFLOW CONTROL VALVEPOWER CYLINDER
17-4
Page 654 of 1681
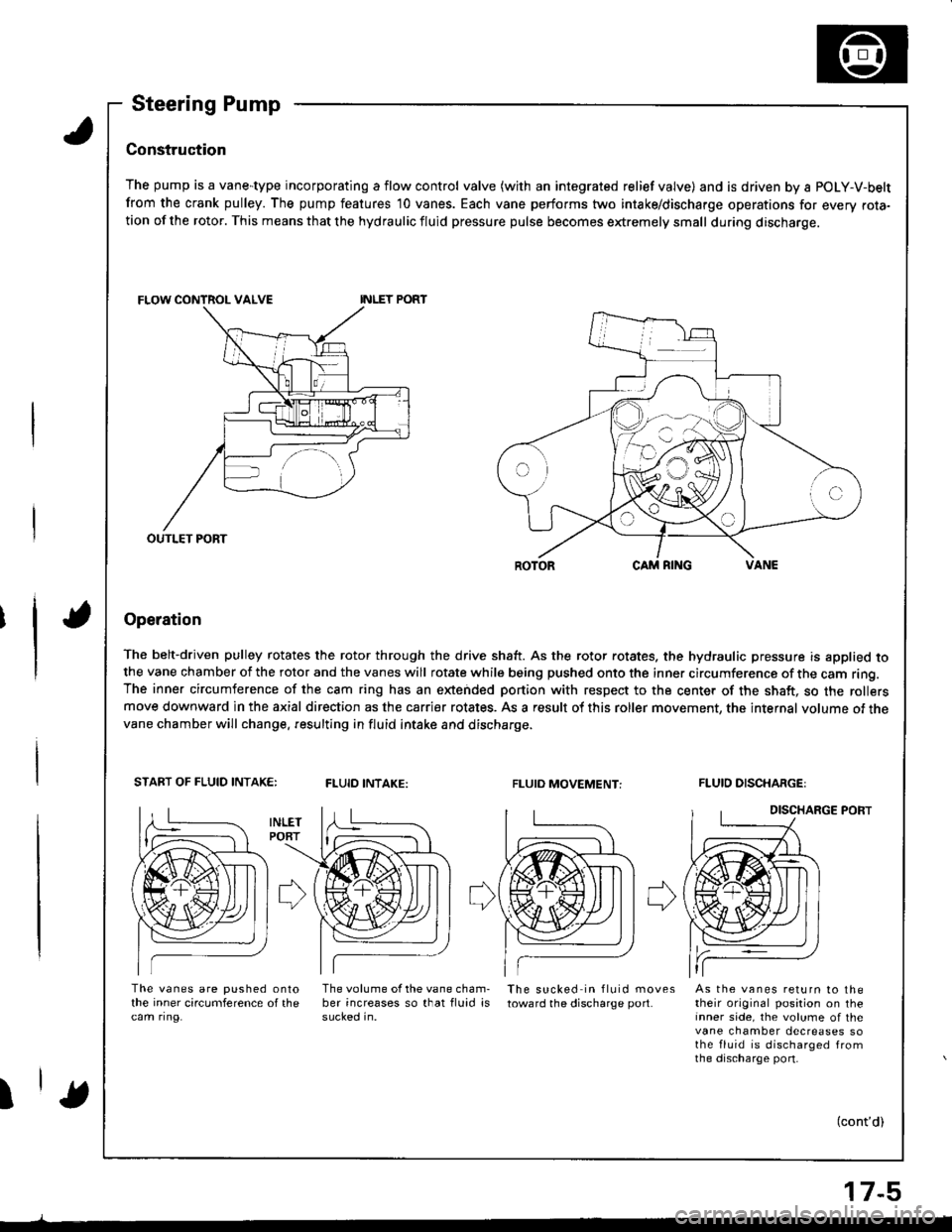
Steering Pump
Construc'tion
The pump is a vane-type incorporating a flow control valve (with an integrated relief valve) and is driven by a POLY-V-belt
from the crank pulley. The pump features 10 vanes. Each vane performs two intake/discharge operations for every rota-tion of the rotor. This means that the hydraulic fluid pressure pulse becomes extremely small during discharge.
Operation
The belt-driven pulley rotates the rotor through the drive shaft. As the rotor rotates. the hydraulic pressure is applied tothe vane chamber of the rotor and the vanes will rotate while being pushed onto the inner circumference of the cam ring.The inner circumference of the cam ring has an extended portion with respect to the center of the shaft, so the rollersmove downward in the axial direction as the carrier rotates. As a result of this roller movement, the internal volume of thevane chamber will change. resulting in fluid intake and discharge.
START OF FLUID INTAK€:FLUID INTAKE:FLUIO MOVEMENT:FLUID DISCHARGE:
DISCHARGE PORT
The vanes are pushed onlothe inner circumference of thecam ring.
The volume of the vane cham-ber increases so that fluid issucked in.
The sucked in fluid movestoward the discharge port.As the vanes return to thetheir original position on theinner side, the volume of thevane chamber decreases sothe fluid is discharged fromthe discharge port-
I(cont'd)
OUTLET PORT
17-5
Page 655 of 1681
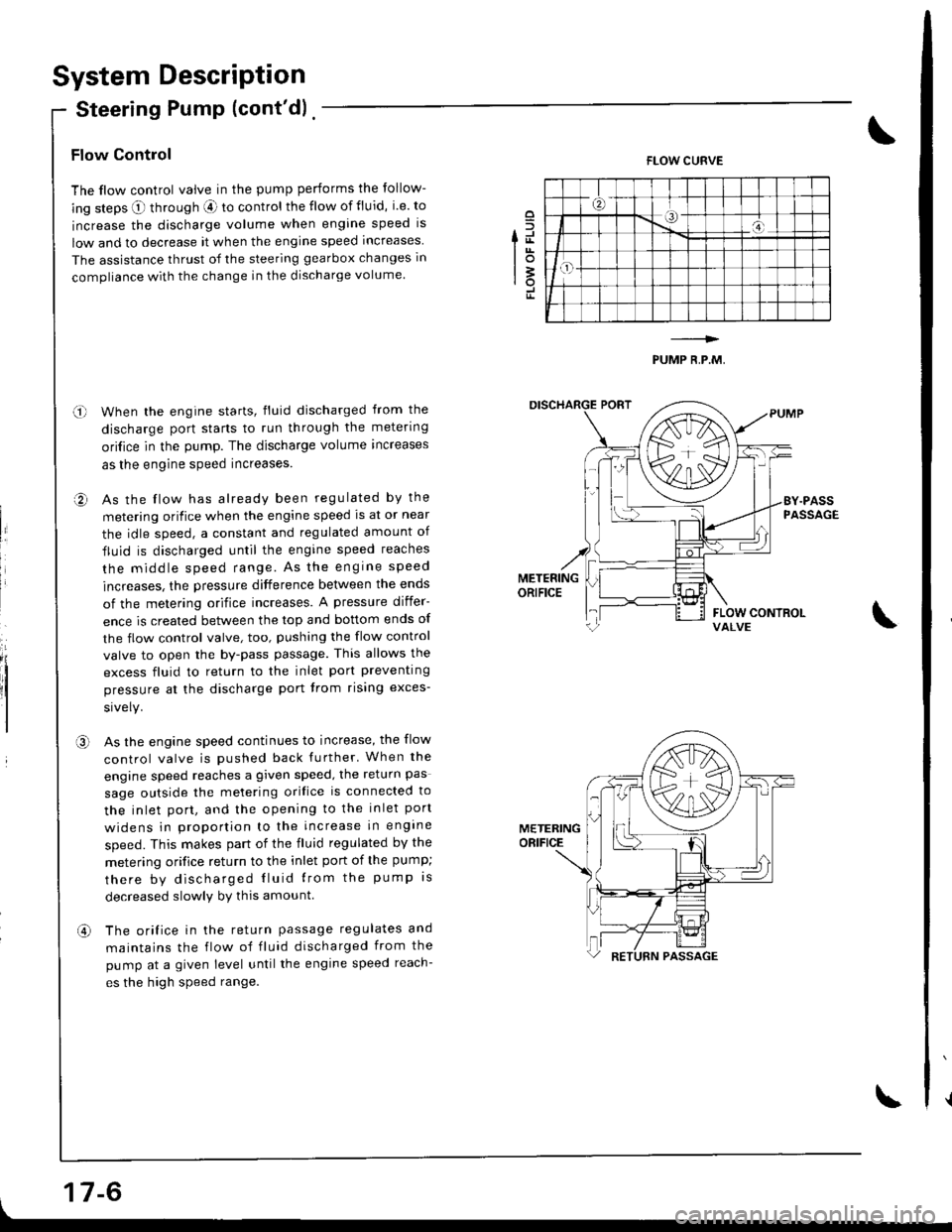
System Description
Steering Pump (cont'd) .
17-6
Flow Control
The flow control valve in the pump performs the follow-
ing steps O through aE ro control the flow of fluid, i.e. to
increase the discharge volume when engine speed is
low and to decrease it when the engine speed increases
The assistance thrust of the steering gearbox changes in
compliance with the change in the discharge volume.
When the engine starts, fluid discharged from the
discharge port starts to run through the metering
ori{ice in the pump. The discharge volume increases
as the engine speed increases.
As the flow has already been regulated by the
metering orifice when the engine speed ls at or near
the idle speed, a constant and regulated amount of
fluid is discharged until the engine speed reaches
the middle speed range. As the engrne speed
increases, the pressure difference between the ends
of the metering orifice increases. A pressure differ-
ence is created between the top and bottom ends of
the flow control valve, too, pushing the flow control
valve to open the by-pass passage. This allows the
excess fluid to return to the inlet port preventing
pressure at the discharge port trom rising exces-
As the engine speed continues to increase, the flow
control valve is pushed back further' When the
engine speed reaches a given speed, the return pas
sage outside the melering orifice is connected to
the inlet port, and the opening to the inlet port
widens in prooortion to the increase in engine
speed. This makes part of the fluid regulated by the
metering orifice return to the inlet port of the pump;
there by discharged Iluid lrom the pump rs
decreased slowlv by this amount
The orifice in the return passage regulates and
maintains the flow of fluid discharged from the
pump at a given level untilthe engine speed reach-
es the high speed range.
o
fd
lot3rotr
FLOW CURVE
PUMP R,P.M,
o-l
a,
II
,a\
METERINGORIFICE
an
Page 657 of 1681

System DescriPtion
Steering Gearbox
it
The rack,and-pinion type steering gearbox has a Valve body unit incorporated with the pinion to control the steering fluid
pressure. steering fluid from the pump is regulated by a rotary valve in the valve body unit and is sent through the cylin-
derpipetothepowercy|inder,wherehydrauIicpressureisapp|ied.Thesteeringf|Uidintheothersideofthepowercy|in-
der returns through the cylinder pipe and valve body unit to the reservoir'
Valve Body Unit
Inside the valve body unit is the valve, which is coaxial with the pinion shaft, and controls the steering fluid pressure The
valve housing ls connected wirh the fluid pipe from the pump. return pipe to the reservoir, and the two cylinder pipes
from the respective power cylinder.
The pinion shaft is double - structured with the input shaft connected to the pinion gear, both of which are interconnected
with the torsion bar.
The pin inserted in the valve and the pinion shaft groove engage; this allows the pinion shaft to rotate together with the
Because of this construction. the difference in angle in the circumferential direction between the input shaft and the valve
becomes larger according ro the torsional strength ol the pinion or steering resistance. However. maximum torsion
between the shafts is regulated by the engaged splines of the shafts at the pin engagement section to hold the torsion bar
within the set value.
This allows the steering system to function as an ordinary rack-and-pinion type steering if the steering iluid is not pressur-
ized because of a faulty PumP.
VALVE
INPUT SHAFT
INPUT SHAFT
VALVE XOUSING
of
'I
lEng.ge with th€ Pinionshaft groove)
TORSION BARDift6rance in angle b6twe€n theinput ih.ft.nd pinion shalt
la-l
B
VALVE BODY UN]T
SECNON B.B
17-8
Page 658 of 1681

INPUT SHAFT
High assist at lower speedsl
When steering resistance is high, such as when driving at low speed, or when turning the wheel with the car stopped, the
diiference in angle created between the input shaft and the valve opens the tluid passage on one side, and closes the fluidpassage on the other side, at each pair of orifices. The fluid pressure lncreases in the side of the power cylinder fed by thelarger fluid passage. This increased pressure pushes on the rack piston, allowing the steering wheel to be turned with light
effon. On the other side of the power cylinder, the return passage opens allowing the steering fluid to return through theinput shaft to the reservoir. The fluid passages to the power cylinder automatically change in size, increasing as the steer-ing resistance increases. In other words, the passages become larger and power assist increases when the steering effort
would normally be high, (for example, when parking or making low speed turns), and the passages become smaller andpower assist decreases when the steering effort would normally be low, (for example, when driving at high speeds or
straight ahead).
FLUIO PASSAGE TOPOWER CYLINDER
Ce) r.r;
VK
Pressure Control
Low assist at higher speedsl
When steering resistance is low, such as when driving at high speeds, or when driving straight ahead. the lnput shaft is
near or in the neutral position, so there is liftle or no flow to any of the power cylinder orifices. Most of the feed pressure
from the pump is bypassed to the reservoir. Because of this, the pressure stays the same in both sides of the power cvlin-
der, resulting in low or no assist.
RETURN PASSAGE{To RESERVOIR)
POWER CYLINDERlHigh fluid pressurelI
ALVE FTom PUMP
RESERVOIR
SECTION A-A
17-9