1998 HONDA CR-V clutch system
[x] Cancel search: clutch systemPage 637 of 1395
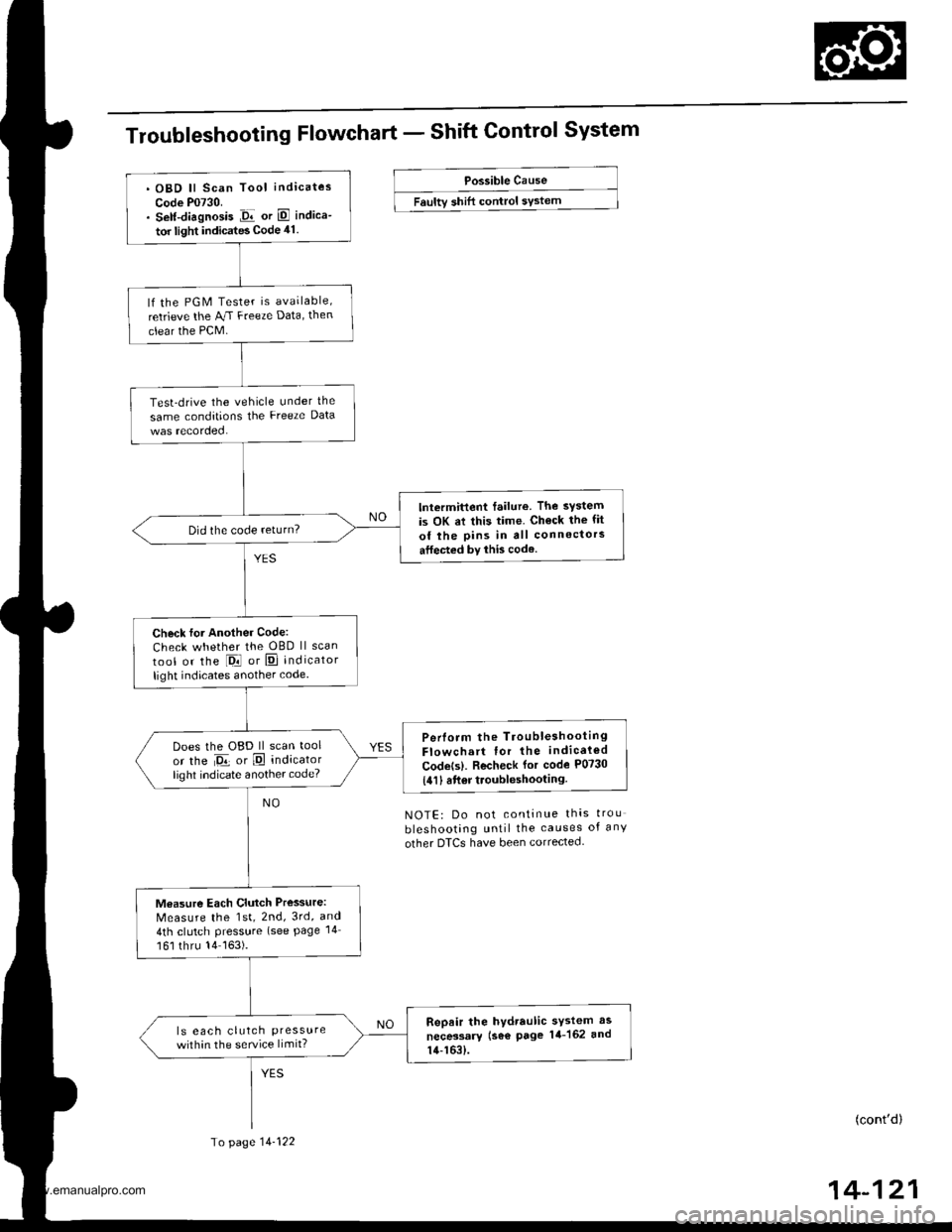
Troubleshooting Flowchart - Shift Control System
Possible Cause
Faultv shift control sYstem
NOTE: Do not continue thas trou
bleshooting until the causes of any
other DTCS have been corrected.
(cont'd)
14-121
. OBD ll Scan Tool indicates
Code P0730.. Self-diagnosis Jir or E indica-
tor light indicates Code 41.
lf the PGM Tester is available,
retrieve the AJ.I Freeze Data, then
clear the PCM.
Test-drive the vehicle under the
same conditions the Freeze Data
lntermittent failure. The system
is OK at this time. Ch€ck the fit
of the pins in all connectors
atfected by this code.
Did the code return?
Check for Another Code:
Check whether the OBD ll scan
tool or the l-Drl or E] indicator
light indicates another code.
Perlorm the TroubleshootingFlowchart for the indicaled
Codets). Recheck for code P0730
{411 6ft6r troubleshooting.
Does the OBD ll scan tool
or the Da or E indicatorlighl indicate another code?
Measure Each Clutch Pressure:
Measure the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and
4th clutch Pressure (see Page 14
161 thru 14163).
Repair the hydraulic sYstem as
necessary (se€ page 14-162 and
14-163).
ls eac h clutch Pressurewithin the service limit?
To page 14-122
www.emanualpro.com
Page 670 of 1395

Symptom-to-Component Chart
Hydraulic System (cont'd)
SYMPTOMCheck these items on thePROBABLE CAUSE ListCheck these items onthe NOTES Lisr
Shift lever does not operate smoothly.o, JdPFails to shift; stuck in 4th gear.14, 41 , 48
Transmission will not shift into park in E position.6, 38, 61PStall rpm high; all clutch pressures are in specification.40D,K,OLock-up clutch does not disengage.18, 43, 44, 45, 46, 49,50,57
Lock-up clutch does not operate smoothly.14, 40, 43, 44, 45, 46, 49, 50. 57Lock-up clutch does not engage.'t8, 40, 43, 44, 45, 46, 49, 50, 56, 57Vibration in all positions.
No engine braking in I position.59
Shift position indicator does not indicate anv position,6. 38, 60
PROBABLE CAUSE
I 33 Thrust washer worn/damaged
ATF pump worn or binding34Clutch clearance incorrect
Regulator valve stuck or regulator valvespflng wornDrive plate delective or transmission mtsas-sembled
Servo valve stuck5ttTorque converter housing or transmissionhousing bearing worn/damagedMainshaft worn/damaged
Shift cable broken/out of adjustmentATF strainer clogged
7Final gears worn/damaged38Shift cable is worn where it attaches to thetransmission or at the body mountsIOne-way (sprag) clutch worn/damaged
1st gears worn/damaged {2 gears)39Modulator valve stuck10lst clutch defective40Torque converter check valve stuck112nd gears worn/damaged (2 gears)41Foreign material in separator plate't22nd clutch defectiveCPB valve stuck
t53rd clutch defective43Lock-up timing valve stuck144th clutch defective44Lock-up shift valve stucktcReverse gears worn/damaged (3 gears)Lock-up control valve stuck16Excessive ATF46Lock-up clutch Diston defective17Torque converter one-way clutch defective47Shift control solenoid valve A defecttve
18Linear solenoid assemblv defective (,98 - OOmodels)48Shift control solenoid valve B dsfectrve
49Lock-up control solenoid valve A defective'19CPC valve stuckLock-up control solenoid valve B deleqtve20l-2 shift valve stuck51Servo control valve stuck212-3 shift valve stuck52lst accumulator defective3-4 shift valve stuck53Foreign material in 2nd exhaust orifice2nd accumulator defective54Foreign material in 3rd exhaust orifice3rd accumulator defectiveForeign material in 4th exhaust orifice4th accumulator defective56Mainshaft speed sensor defective262nd orifice control valve stuckCountershaft speed sensor defective273-4 orifice control valve stuck583rd sub accumulator defective2aForeign material in main orifice59lst-hold clutch defective29Foreign material in lst orifice60A/T gear position switch defective or out ofadjustment30Foreign material in reverse orifice
31Engine output low61Park gear mechanism defective32Needle bearing worn/damaged
14-154
www.emanualpro.com
Page 672 of 1395
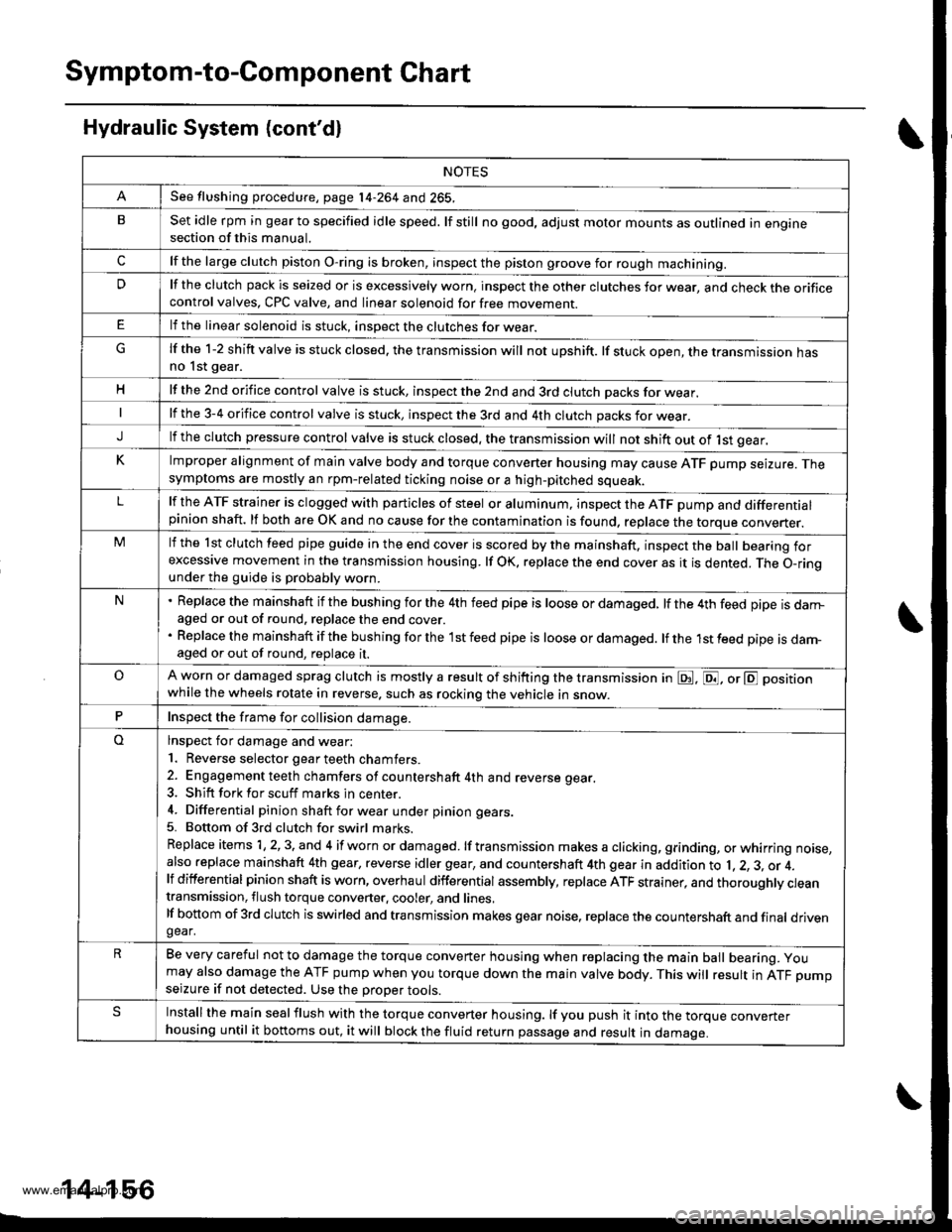
Symptom-to-Com ponent Chart
Hydraulic System (cont'd)
NOTES
See flushing procedure, page l4-264 and 265,
BSet idle rpm in gear to specified idle speed. lf still no good, adjust motor mounts as outlined in enginesection of this manual.
clf the large clutch piston O-ring is broken, inspect the piston groove for rough machining.
Dlf the clutch pack is seized or is excessively worn. inspect the other clutches fot wear, and check the orificecontrol valves, CPC valve, and linear solenoid for free movement.
lf the linear solenoid is stuck, inspect the clutches for wear.
lf the 1-2 shift valve is stuck closed. the transmission will not upshift. lf stuck open, the transmission hasno lst gear.
Hlf the 2nd orifice control valve is stuck, inspect the 2nd and 3rd clutch Dacks for wear.
lf the 3-4 orifice control valve is stuck, inspect the 3rd and 4th clutch packs for wear.
Jlf the clutch pressure control valve is stuck closed. the transmission will not shift out of lst gear.
Klmproper alignment of main valve body and torque converter housing may cause ATF pump seizure. Thesymptoms are mostly an rpm-related ticking noise or a high-pitched squeak.
Llf the ATF strainer is clogged with particles of steel or aluminum, inspect the ATF pump and differentialpinion shaft. lf both are OK and no cause for the contamination is found, replace the torque converter.
Mlf the lst clutch feed pipe guide in the end cover is scored by the mainshaft. inspect the ball bearing forexcessive movement in the transmission housing. lf oK, replace the end cover as it is dented. The o-rinounder the guide is probably worn.
N' Replace the mainshaft if the bushing for the 4th feed pipe is loose or damaged, lf the 4th feed pipe is darrFaged or out of round. replace the end cover.' Replace the mainshaft if the bushing for the l st feed pipe is loose or damaged. lf the 1st feed pipe is dam-aged or out of round, replace it.
oA worn or damaged sprag clutch is mostly a result of shifting the transmission in E!. E, or E positionwhile the wheels rotate in reverse. such as rocking the vehicle in snow.
PInspect the frame for collision damage.
lnspect for damage and wear:
l. Reverse selector gear teeth chamfers.
2. Engagement teeth chamfers of countershaft 4th and reverse gear.
3. Shift fork for scuff marks in center.
4. Differential pinion shaft for wear under pinion gears.
5. Bottom of 3rd clutch for swirl marks.
Replace items 1, 2, 3. and 4 if worn or damaged. lf transmission makes a clicking, grinding, or whirring noise,also replace mainshaft 4th gear, reverse idler gear, and countershaft 4th gear in addition to 1,2, 3, or 4.lf differential pinion shaft is worn, overhaul differential assembly, replace ATF strainer, and thoroughly cjeantransmission, flush torque converter. cooler, and lines,lf bottom of 3rd clutch is swirled and transmission makes gear noise. replace the countershaft and final drivenoear,
Be very careful not to damage the torque converter housing when replacing the main ball bearing. you
may also damage the ATF pump when you torque down the main valve body. This will result in ATF pumpseizure if not detected. Use the Drooer tools.
SInstall the main seal flush with the torque converter housing. lf you push it into the torque converterhousing until it bottoms out, it will block the fluid return passage and result in damage.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 794 of 1395

Description
Rear Differential
Outline
The Real-time 4WD-Dual Pump System model has a hydraulic clutch and a differential mechanism in the rear differential
assembly. Under normal conditions, the vehicle is driven by the front wheels. However, depending on to the driving force
of the front wheels and the road conditions. the system instantly transmits appropriate driving force to the rear wheels
without requiring the driver to switch between 2WD (tront wheel drive) and 4WD (four wheel drive). The switching mecha-
nism between 2WD and 4WD is integrated into the rear differential assembly to make the system light and compact.
ln addition, the dual-pump system switches off the rear-wheel-drive force when braking in a forward gear. This allows the
braking system to work properly on models equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS).
Construction
The rear differential assembly consists of the torque control differential case assembly and the rear differential carrier
assembly. The torque control differential case assembly consists of the differential clutch assembly, the companion
flange, and the oil pump body assembly. The rear differential carrier assembly consists of the differential mechanism. The
differential drive and driven gears are hypoid gears.
The oil pump body assembly consists of the front oil pump, the rear oil pump, the hydraulic control mechanism, and the
clutch piston. The clutch piston has a disc spring that constantly provides the differential clutch assembly with a preset
torque to Drevent abnormal sound.
The clutch guide in the differential clutch assembly is connected to the propeller shaft via the companion flange, and it
receives the driving force lrom the transfer assembly. The clutch guide rotates the clutch plate and the front oil pump in
the oil pump body.
The clutch hub in the differential clutch assembly has a clutch disc that is splined with the hypoid drive pinion gear. The
hypoid drive gear drives the rear oil pump.
The front and rear oil pumps are trochoidal pumps. The rear oil pump capacity is 2.5 percent larger that the front oil pump
to handle the rotation difference between the front and rear wheels caused by worn front tires and tight corner braking.
The oil pumps are designed so the fluid intake works as a fluid discharge when the oil pumps rotate in reverse. Genuine
Honda CVT fluid is used instead of differential fluid.
Operation
When there is a difference in rotation speed between the front wheels (clutch guide) and rear wheels (hypoid driven gear),
hydraulic pressure from the front and rear oil pumps engages the differential clutch, and drive force from the transler
assembly is applied to the rear wheels.
The hydraulic pressure control mechanism in the oil pump body selects 4WD mode when the vehicle is started abruptly,
or when accelerating in a forward or reverse gear (causing rotation difference between the front and rear wheels). or
when braking in reverse gear {when decelerating). lt switches to 2WD mode when the vehicle is driven at a constant speed
in forwar! or reverse gear (when there is no rotation difference between the front and rear wheels), or when braking in a
fo rwa rd gear (when decelerating).
To protect the system, the differential clutch assembly is lubricated by hydraulic pressure generated by the oil pumps in
both 4WD and 2WD modes. Also, the thermal switch relieves the hydraulic pressure on the clutch piston and cancels 4WD
mode if the temDerature of the differential fluid rises above normal.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 795 of 1395
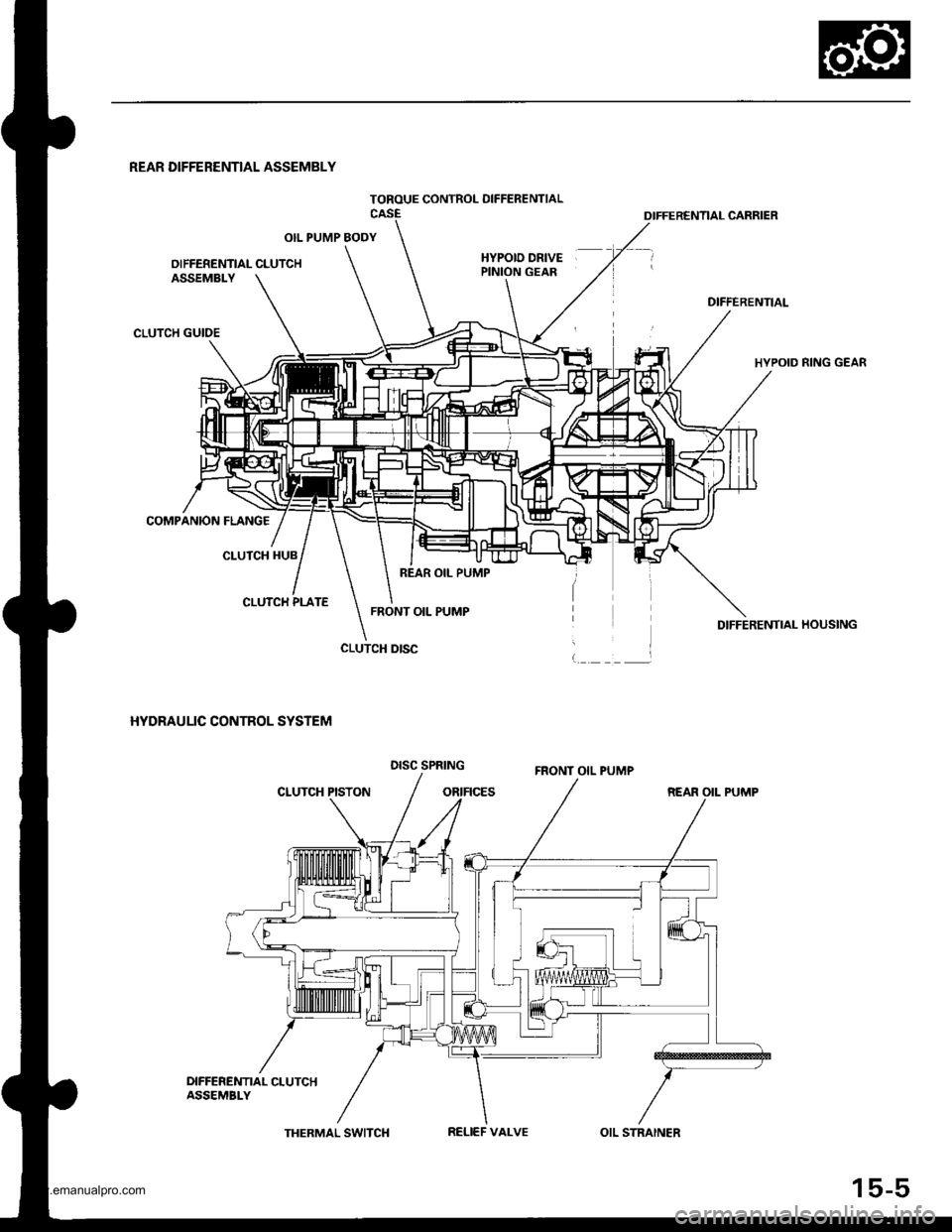
TOROUE CONTROL OIFFERENTIAL
REAR DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP BODY
OIFFERENTIAL CLUTCHHYPOID DRIVEPINION GEAR
OIFFERENTIAL CARRIER
DIFFERENTIAL
HYPOID RING GEAR
DIFFERENTIAI- HOUSING
REAR OII- PUMP
ASSEMBLY
CLUTCH GUIDE
COMPANION FLANG€
CLUTCH HUB
CLUTCH PLATE
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
CLUTCH PISTON
CLUTCH DISC
REAR OIL PUMP
FRONT OIL PUMP
DISC SPRINGFRONT OIL PUMP
DIFFEREMT|AL CLUTCHASSEMBI-Y
THERMAL SWITCHRELIEF VALVEOIL STRAINER
15-5
www.emanualpro.com
Page 796 of 1395
Description
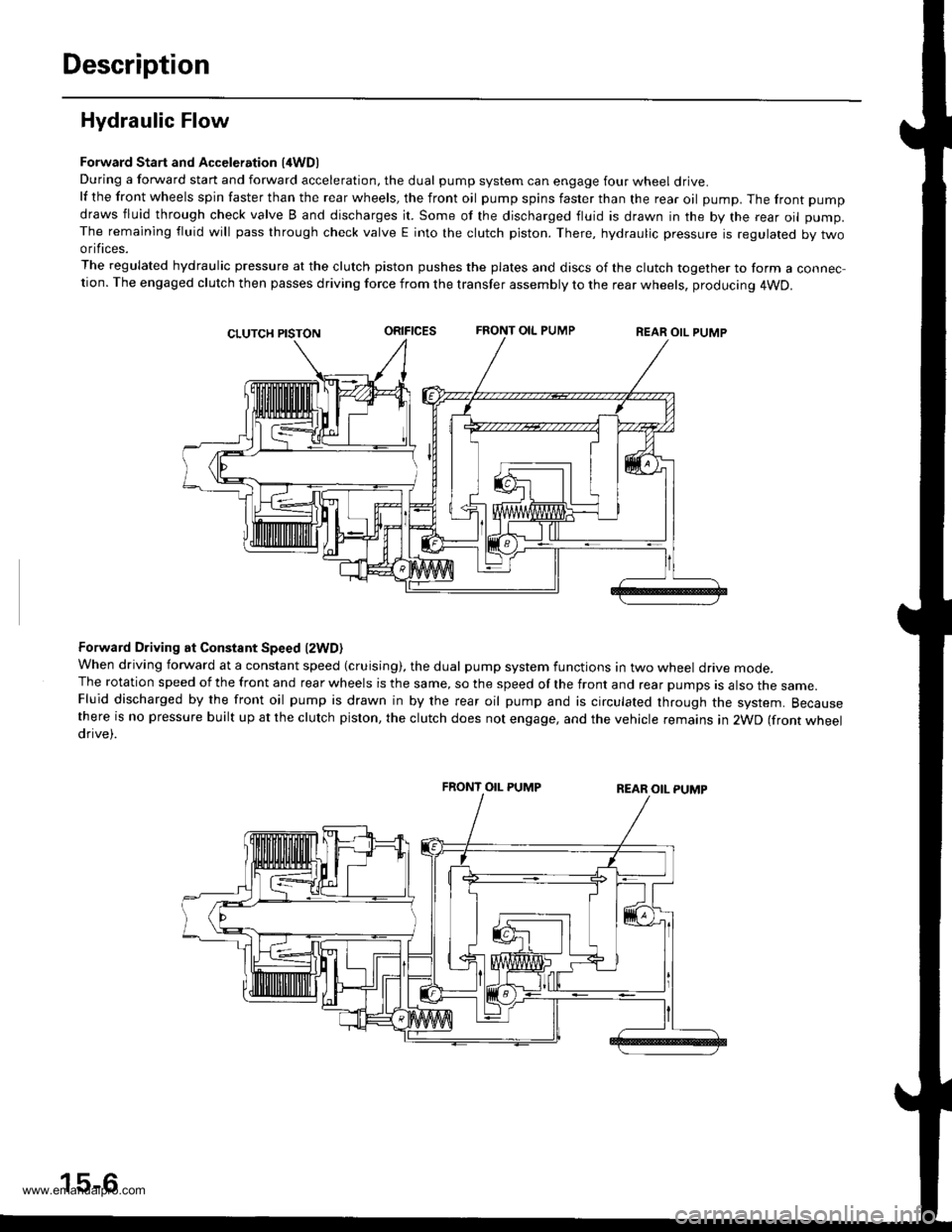
Hydraulic Flow
Forward Start and Acceleration l4WD)During a forward start and forward acceleration, the dual pump system can engage four wheel drive.lf the front wheels spin faster than the rear wheels, the front oil pump spins faster than the rear oil pump. The front pump
draws fluid through check valve B and discharges it. Some of the discharged fluid is drawn in the by the rear oil pump.The remaining fluid will pass through check valve E into the clutch piston. There, hydraulic pressure is regulated by twoorifices.
The regulated hydraulic pressure at the clutch piston pushes the plates and discs of the clutch together to form a connec-tion. The engaged clutch then passes driving force from the transfer assembly to the rear wheels, producing 4WD.
oRrFtcEsFRONT OIL PUMPREAR OIL PUMP
Forward Driving at Constant Speed lzWD)When driving forward at a constant speed (cruising), the dual pump system functions in two wheel drive mode.The rotation speed of the front and rear wheels is the same, so the speed of the front and rear pumps is also the same.Fluid discharged by the front oil pump is drawn in by the rear oil pump and is circulated through the system. Becausethere is no pressure built up at the clutch piston, the clutch does not engage, and the vehicle remains in 2WD (front wheeldrive).
FRONT OIL PUMP
15-6
www.emanualpro.com
Page 797 of 1395
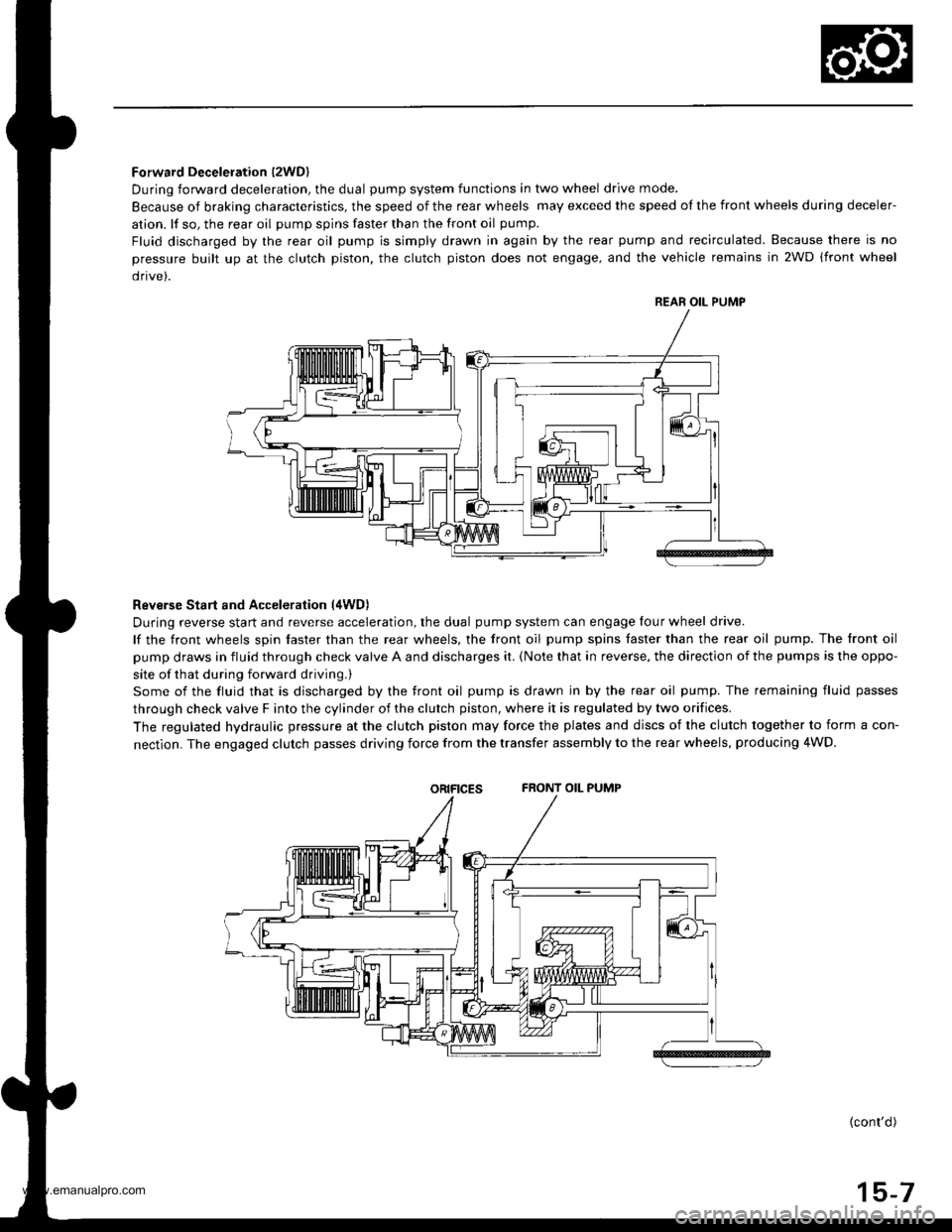
Forward Deceleration l2WDl
During forward deceleration, the dual pump system functions in two wheel drive mode.
Because of braking characteristics, the speed of the rear wheels may exceed the speed ol the front wheels during deceler-
ation. lf so, the rear oil pump spins faster than the front oil pump.
Fluid discharged by the rear oil pump is simply drawn in again by the rear pump and recirculated. Because there is no
pressure built up at the clutch piston. the clutch piston does not engage, and the vehicle remains in 2WD (front wheel
drive).
Reverse Start and Acceleration (4WD)
During reverse start and reverse acceleration, the dual pump system can engage four wheel drive.
lf the front wheels spin faster than the rear wheels, the front oil pump spins faster than the rear oil pump. The front oil
pump draws in fluid through check valve A and discharges it. {Note that in reverse, the direction of the pumps is the oppo-
site of that during forward driving.)
Some of the fluid that is discharged by the front oil pump is drawn in by the rear oil pump. The remaining fluid passes
through check valve F into the cylinder of the clutch piston, where it is regulated by two orifices.
The regulated hydraulic pressure at the clutch piston may force the plates and discs of the clutch together to form a con-
nectlon. The engaged clutch passes driving force from the transfer assembly to the rear wheels, producing 4WD.
oRtFtcEsFRONT OIL PUMP
{cont'd)
15-7
REAR OIL PUMP
www.emanualpro.com
Page 798 of 1395
Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'dl
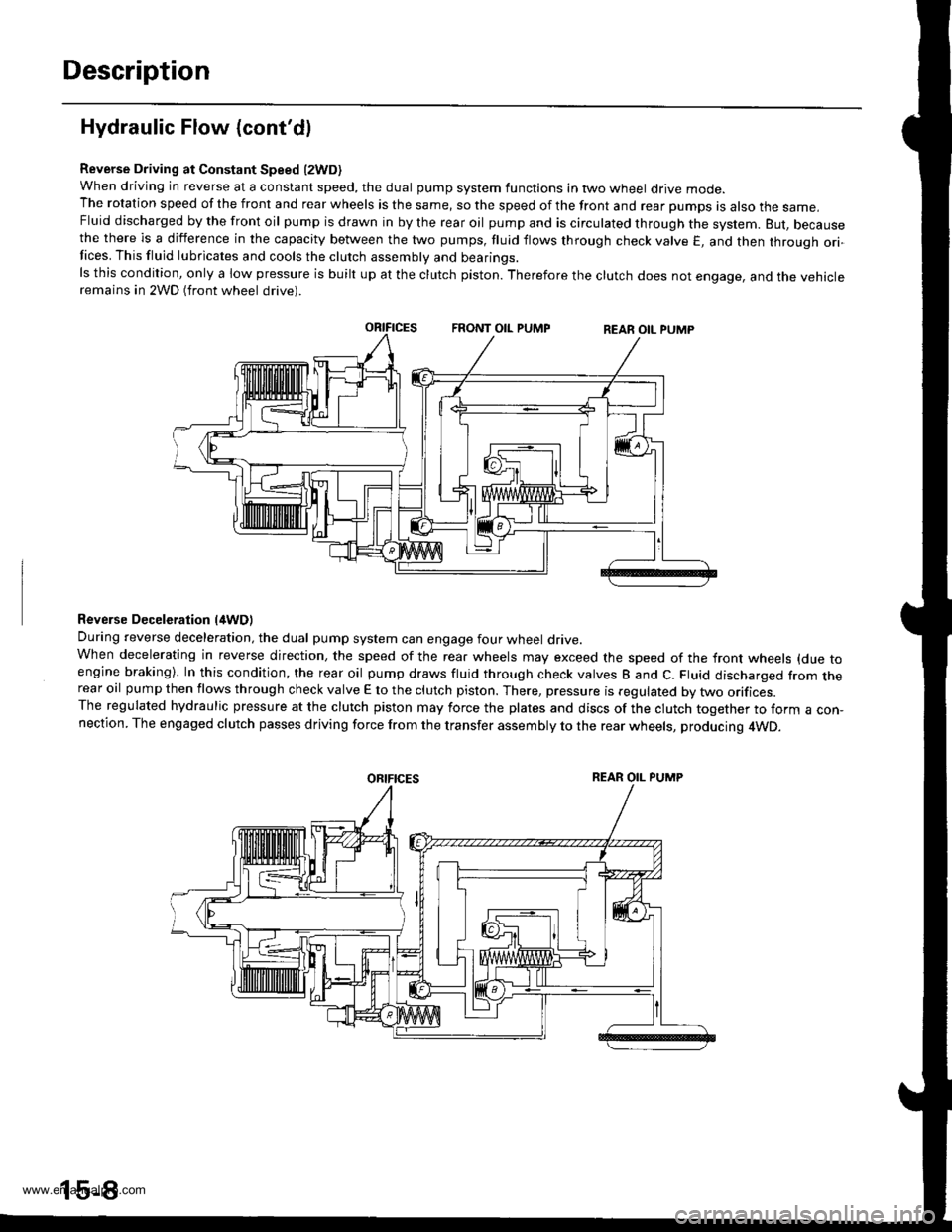
Reverse Driving at Constant Speed l2WD)when driving in reverse at a constant speed, the dual pump system functions in two wheel drive mode.The rotation speed of the front and rear wheels is the same, so the speed of the front and rear pumps is also the same,Fluid discharged by the front oil pump is drawn in by the rear oil pump and is circulated through the system. But, becausethe there is a difference in the capacity between the two pumps, fluid flows through check valve E, and then through ori-Iices. This fluid lubricates and cools the clutch assembly and bearings.ls this condition, only a low pressure is built up at the clutch piston. Therefore the clutch does not engage, and the vehicleremains in 2WD (front wheel drive).
Reverse Deceleration l/tWDl
During reverse deceleration, the dual pump system can engage four wheel drive.When decelerating in reverse direction, the speed of the rear wheels may exceed the speed of the front wheels (due toengine braking). In this condition, the rear oil pump draws fluid through check valves B and C. Fluid discharged from therear oil pump then flows through check valve E to the clutch piston. There, pressure is regulated by two orifices.The regulated hydraulic pressure at the clutch piston may force the plates and discs of the clutch together to form a con,nection. The engaged clutch passes driving force from the transfer assembly to the rear wheels, producing 4WD.
oRtFtcEsREAR OIL PUMP
www.emanualpro.com