1998 HONDA CR-V shift lock
[x] Cancel search: shift lockPage 519 of 1395

Description
General Operation
The Automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and triple-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides 4
speeds forward and 1 reverse speed The unit is positioned in line with the engine'
There are two tvoes of automatic transmission on CR-V; the four-wheel drive (4WD) model ('97 - 00)' and the front-wheel
drive (2WD) model ('98 - 00).
Toroue Converter, G€ars, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump. turbine. and stator assembly in a single unit. The torque converter is connected to
the engine crankshatt. These parts turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is
a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is started. The torque converter assembly serves as a fly-
wheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has three parallel shafts: the mainshaft. the countershaft, and the sub-shaft. The mainshaft is in line with
the engine crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd. and 4th clutches, and gears lor 3rd,2nd,4th. reverse and 1st
(3rd gear is integral with the mainshaft, while reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd
clutch and gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse, 1st, and park. Reverse and 4th gears can be locked to the countershaft at its cen-
ter, providing 4th gear or reverse, depending on which way the selector is moved. The sub-shaft includes the lst-hold
clutch and gears for lst and 4th.
The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the countershaft and sub-shaft. When certain combinations
of gears are engaged by the ctutches, power is transmitted from the mainshaft to the countershaft to provide E, D!, tr, tr,
and E position ('97 - 98 models). and E. E, E, and E position ('99 - 00 models)'
Electlonic Control
The electronic controt system consists of the Powenrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid, and four
solenoid valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body, and
the lock up valve body. They are bolted to the torque converter housing. The main valve body contains the manual valve,
the 1-2 shift valve, the 2nd orifice control valve. the CPB {Clutch Pressure Back-up) valve, the modulator valve, the servo
control valve. the relief valve, and ATF pump gears. The secondary valve body contains the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4 shift
valve, the 3,4 orifice control valve. the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch Pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve
bodv contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve, the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up con-
trol valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the reverse shift tork, and the accumulators
The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing valve. The linear solenoid and the shift con-
trol solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted to the outside of the transmission housing, and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is
bolted to the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid trom the regulator passes through the manual valve to the
various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective feed pipes or internal hydraulic circuit
ShiftControl Mechanism
input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will acti-
vate. Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes
a line to one of the clutches. engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear. The shift control solenoid valves A and B are
controlled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
tn E! position (,97 - 98 modets) and in E position ('99 - O0 models), in 3rd and 4th, and in Del position in 3rd ('97 - 98
models) and in El position with Over,Drive (O/D) is OFF (by pressing rhe O/D switchl in 3rd ('99 - 00 models), pressurized
fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held
against the torque converter cover, As this takes place, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft.
Together with hydraulic control, the PcM optimizes the timing of the lock-up mechanism The lock-up valves control the
range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and the linear solenoid. When lock-up control
solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes. The lock-up control solenoid valves A and B and the
linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
{cont'd)
14-3
www.emanualpro.com
Page 520 of 1395

Description
General Operation (cont'dl
Gsar Selection'97 - 98 Models
The shift lever has seven positions; El PARK, ts REVERSE, N NEUTRAL, Ell 1st through 4th ranges, lpq 1st th.ough 3rdranges, P 2nd gear, and [ 1st gear
'99 - 00 Models
The shitt lever has six positions; El PARK, E REVERSE, E NEUTRAL. E ,lst through 4th ranges, and 1st through 3rd(when Over-Drive (O/D) is OFF) ranges. @ 2nd gear, and E 1st gear.
Starting is possible only in @ and @ positions. using a slide-type. neutral-safety switch.
Automatic Transaxle (A/T) Gear Position IndicatorThis indicator in the instrument panel shows which gear has been selected.
Transler Mochanism {4WD}
The transfer mechanism consists of the transfer shaft drive gear. the transfer shaft. the transfer drive gear, the transfer driv-en gear shaft, and the companion flange, The transfer mechanism assembly is on the rear side ot the transmission. besidethe differential. The transfer shaft drive gear on the final driven gear drives the transfer shaft driven qear. power is transmit-ted to the rear differential via the transfer shaft and the Drooeller shaft.
Clutches
The four-speed automatic transmission uses hydraulically-actuated clutches to engage or disengage the transmission gears.When the hydraulic pressure is introduced into the clutch drum, the clutch piston moves. This presses the friction discs andsteel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is then transmifted through the engaged clutch pack to its hu$mounted gear. When hydraulic pressure is bled from the clutch pack, the piston releases the friction discs and steel plates, andthey are free to slide past each other. This allows the gearto spin independently on its shaft, transmitting no power.
lst Clutch
The 1st clutch engages/disengages lst gear, and is located at the end ofthe mainshaft, just behind the end cover.The 1st clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the mainshaft.
lst-hold Clutch
The 1st-hold clutch engages/disengages 1st-hold or E position, and is located at the middle of the sub-shaft. The 1st-holdclutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the sub-shaft.
2nd Clutch
The znd ciutch engages/disengages 2nd gear, and is located at the middle of the mainshaft. The 2nd clutch is joined back-to-back to the 4th clutch. The 2nd clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure through the mainshaft by a circuit connected to theinternal hydraulic circuit.
PositionDescription
Reverse; reverse selector engaged with countershaft reverse gear and 4th clutch locked.
Allclutches released.
General driving; starts off in 1st, shifts automatically to 2nd, 3rd, then 4th, depending on vehicle speedand throftle position. Downshifts through 3rd,2nd, and lst on deceleration to stop.The lock-up mechanism operates;n 3rd and 4th gear.
used for rapid €cceleration at highway speeds and general driving; stans off in 1st, shifts automatically to2nd_then 3rd, dejending on vehicle speed and throttle position. Downshifts through lower gears on decel-eration to stop. The lock-up mechanism comes into operation in 3rd gear.
Driving in 2nd_gear; stays in 2nd gear, does not shift up and down. For engine braking or better trac_tion starting off on loose or slippery surfaces.
Driving in 1st gear; stays in 1st gear, does not shift up. For engine braking.
tll PARK
t!!l l|EvEn>E
E NEUTRAL
Ell DRrvE ('97 - sB)E DRrvE ('ss - oo)(1st through 4th )
E DRrvE {'97 - s8)O DRTVE with over-Drive (O/D) is OFF('99 - 00)(1st through 3rd)
E SECOND
E FIRST
14-4
www.emanualpro.com
Page 523 of 1395
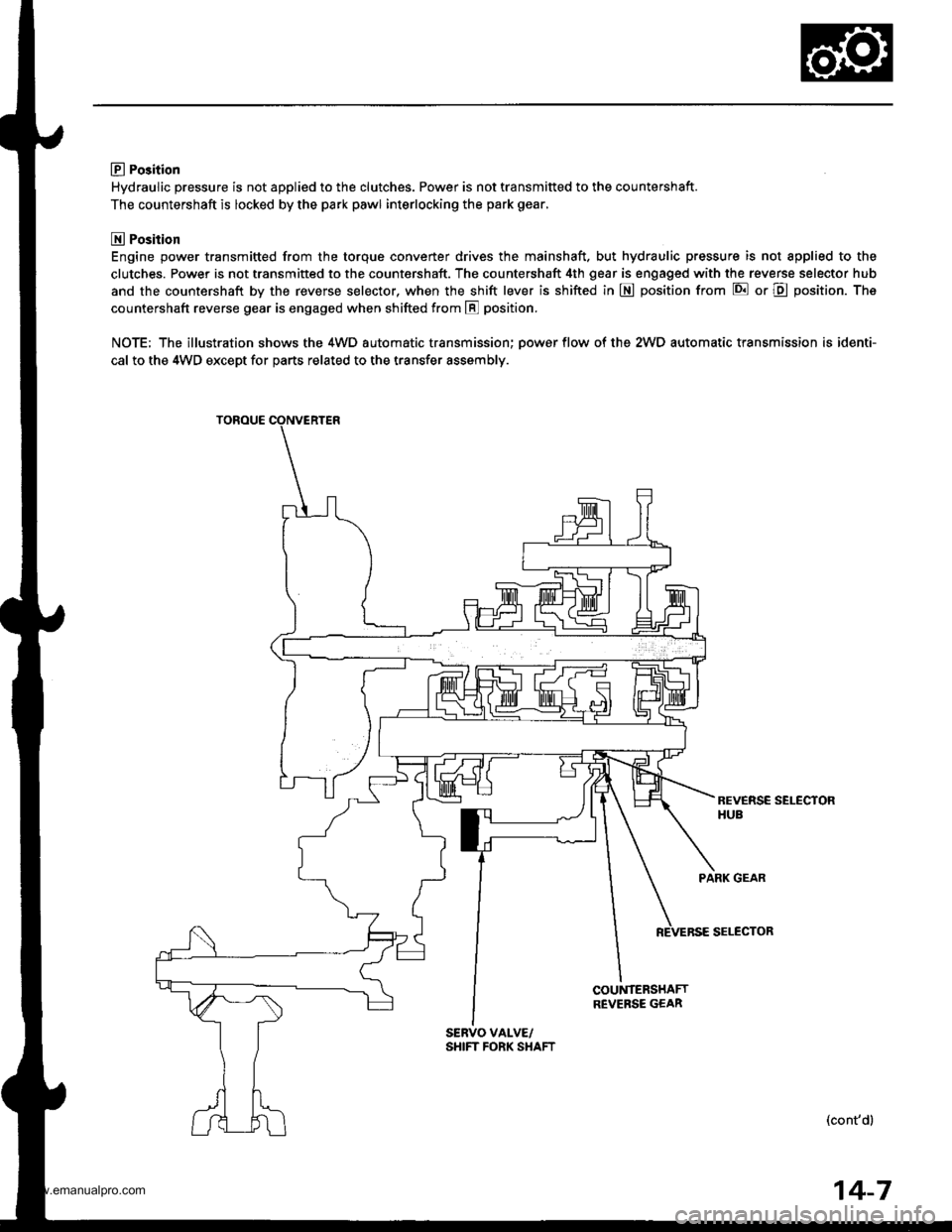
E Po3ition
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft.
The countershaft is locked by the park pawl interlocking the park gear,
E Position
Engine power transmitted from the torque converter drives the mainshaft. but hydraulic pressure is not applied to the
clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft. The countershaft 4th gear is engaged with the reverse selector hub
and the countershaft by the reverse selector, when the shift lever is shifted in E position from E or E position. The
countershaft reverse gear is engaged when shifted from E position.
NOTE; The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmission; oower flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identi-
cal to the 4WD exceDt for oarts related to the transfer assemblv.
PARK GEAR
SELECTOR
(cont'd)
COUNTERSHAFTREVEBSE GEAR
14-7
www.emanualpro.com
Page 531 of 1395

Electronic Control System
The electronic control svstem consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid, and four solenoid
valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions. The PCM is located
below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
'97 - 98 Mod€ls
PGM.FIControl Sy3t6m
Throttl€ Poshion SensorSignalVehicle Sp.ed SensorSignal
Engino Coolant TamperetureService Check connectorSonsor Signrl
A/T Control Sy3tem
INTERLOCK
Shift Cont.ol
Shift ControlSolenoid valve ACONTROL UNITr
RShift ControlSolenoid Valve B
N
Linear SolenoidDr
Lock-up Control
Ds
Lock-up ControlSolenoid Valve A2
Lock-up ConirolSol6noid valvo B1
M.inshaft Spoed SensorSignel-D! Indicator Light
Count€rahaft Speedsensor SignelSelt-Oiagnosb signel
I
Sell-DiagnosisFunction
l-
{cont'd)
14-15
www.emanualpro.com
Page 532 of 1395

Description
PCM
PGM.FIControl System
Throttle Position SensorSignelVehicle Speed SensorSignal
Engin€ Coolsnt TomperatureSen30r SignalService Ch€ck Connectol
A/T Control Svstem
INTERLOCK
Shift Control
Shift ConlrolSolenoid Valve ACONTROL UNITr
RShift ControlSolenoid Valve B
N
Linear SolenoidD
Lock-up Control
2
Lock-up ControlSolenoid valve A1
Lock-up ControlSolenoid Valve BOver-DriveSwitch Signal
Mainshaft Speed SensorSignalE Indicator Light
Countershaft SpeedSensor SigntlSelt-Oiagnosis SigndSelf-DiagnosisFunc{ion
O/D OFFIndicetor Light
Electronic Gontrol System (cont'd)
'99 - 00 Models
14-16
www.emanualpro.com
Page 533 of 1395
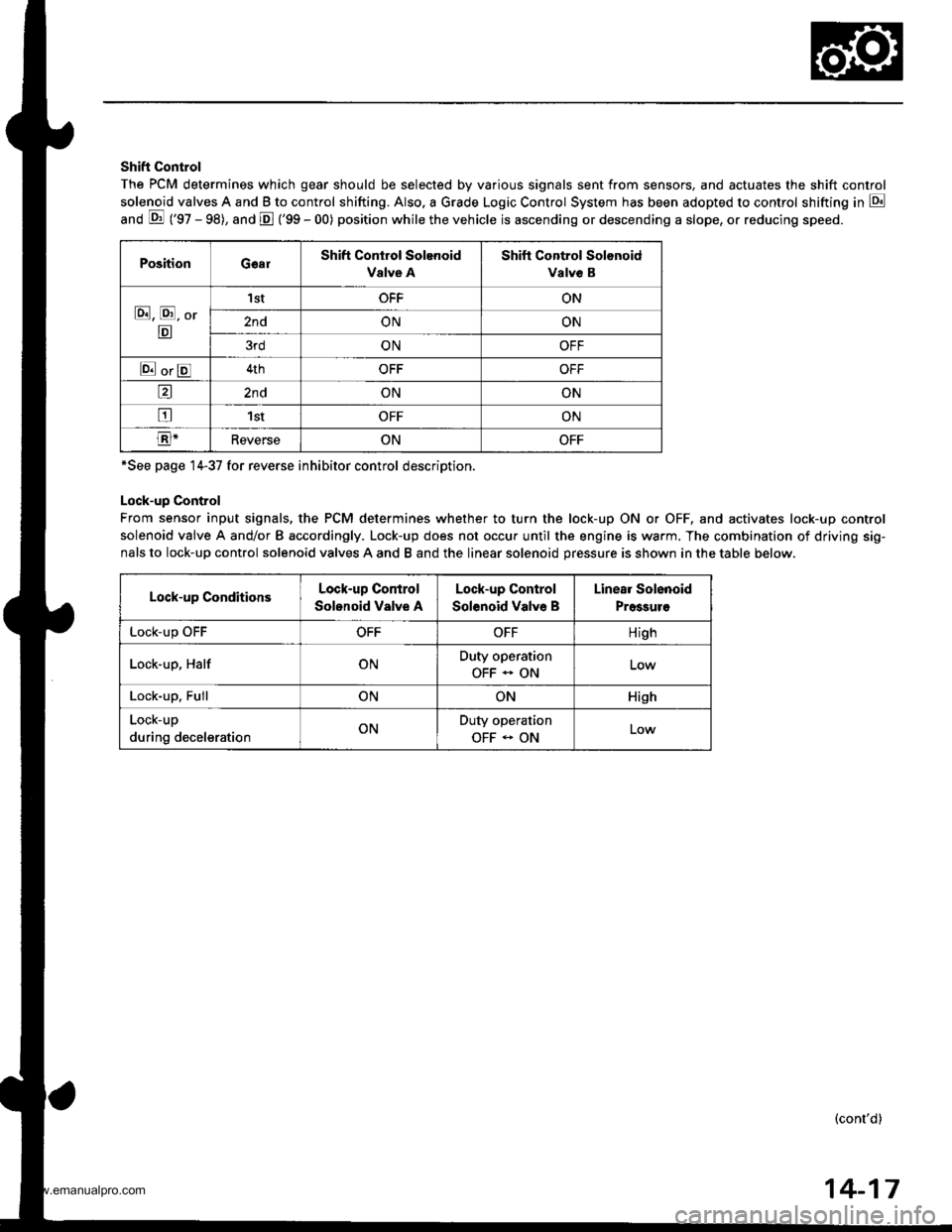
Shift Control
The PCM determines which gear should be selected by various signals sent from sensors, and actuates the shift control
solenoid valves A and B to control shifting. Also. a Grade Logic Control System has been adopted to control shifting in E
anO E ('gZ - gg), and E ('99 - 00) position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or reducing speeo.
PositionGearShift Control Solenoid
Valve A
Shift Control Solonoid
Valve B
E, E, Or
E
'I stOFFON
2ndONON
3rdONOFF
E orE4thOFFOFF
a2ndONON
tr1stOFFON
E-ReverseONOFF
*See page 14-37 for reverse inhibitor control description.
Lock-up Control
From sensor input signals, the PCM determines whether to turn the lock-up ON or OFF, and activates lock-up control
solenoid valve A and/or B accordingly. Lock-up does not occur until the engine is warm. The combination of driving sig-
nals to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid pressure is shown in the table below.
Lock-up ConditionsLock-up Control
Solonoid Valve A
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve B
Linear Solenoid
Pressuro
LOCK-Up \JrrOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF - ON
Lock-up, FullONONHish
Lock-up
during decelerationONDuty operation
OFF - ONLow
(cont'd)
14-17
www.emanualpro.com
Page 536 of 1395
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'd)
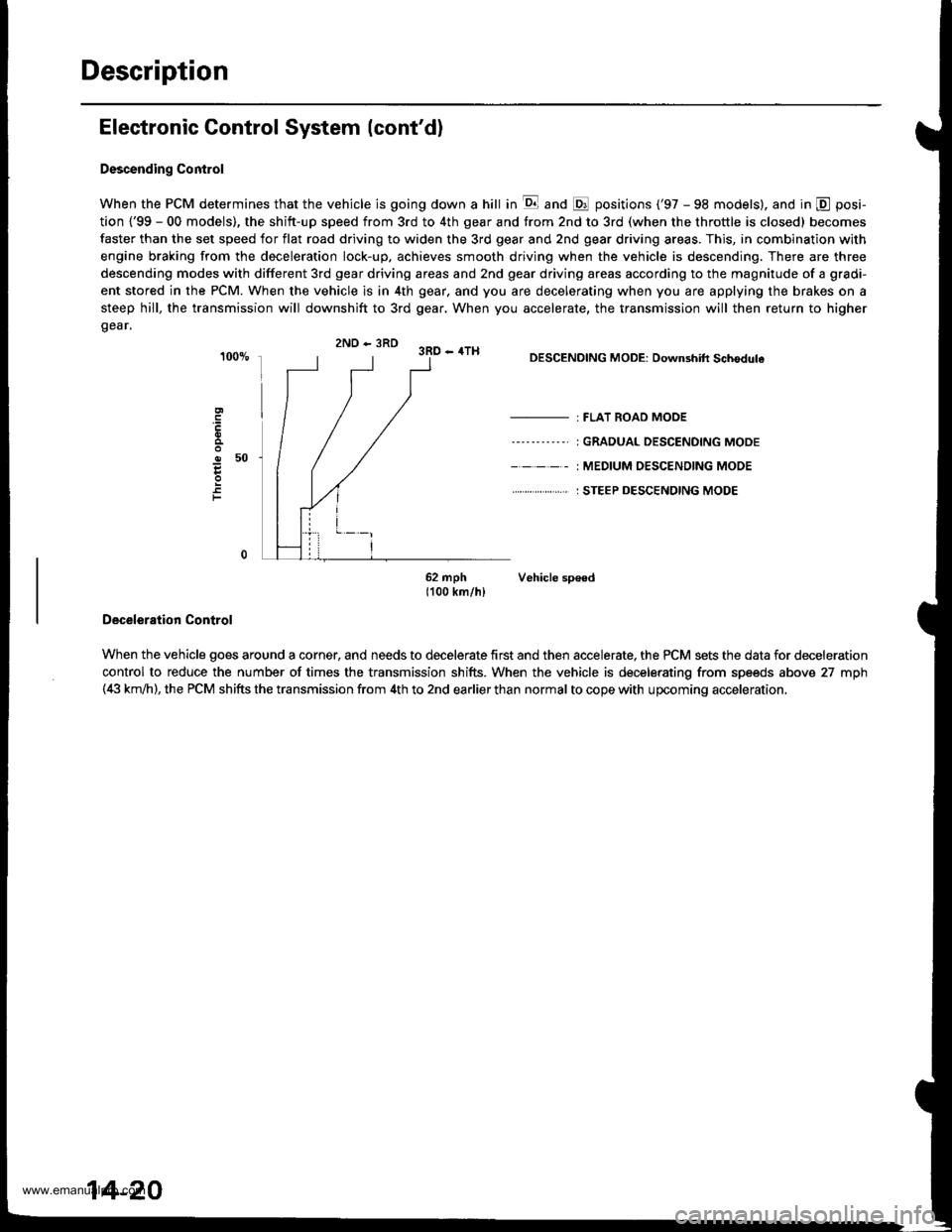
Descending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hill in E and @ positions ('97 - 98 models). and in @ posi-
tion {'99 - 00 models), the shitt-up speed from 3rd to 4th gear and from 2nd to 3rd (when the throttle is closed) becomes
faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear and 2nd gear driving areas. This, in combination with
engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle is descending. There are three
descending modes with different 3rd gear driving areas and 2nd gear driving areas according to the magnitude of a gradi-
ent stored in the PCM. When the vehicle is in 4th gear, and you are decelerating when you are applying the brakes on a
steep hill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear, When you accelerate, the transmission will then return to higher
gear.
2ND - 3RD 3RD - 4TH
o50
F
DESCENDING MODE: Downshift Schodule
- : FLAT ROAD MODE
----'-----' I GRADUAL DESCENDING MODE
- - - - - : MEDIUM OESC€NOING MODE
. . ... : STEEP DESCENDING MODE
62 mph Vehicle sp€ed1100 km/hl
Deceleration Control
When the vehicle goes around a corner, and needs to decelerate first and then accelerate, the PCM sets the data for deceleration
control to reduce the number of times the transmission shifts. When the vehicle is decelerating from speeds above 27 mph(4i| km,ih), the PCM shifts the transmission from 4th to 2nd earlier than normal to cope with upcoming acceleration,
14-20
www.emanualpro.com
Page 540 of 1395
Description
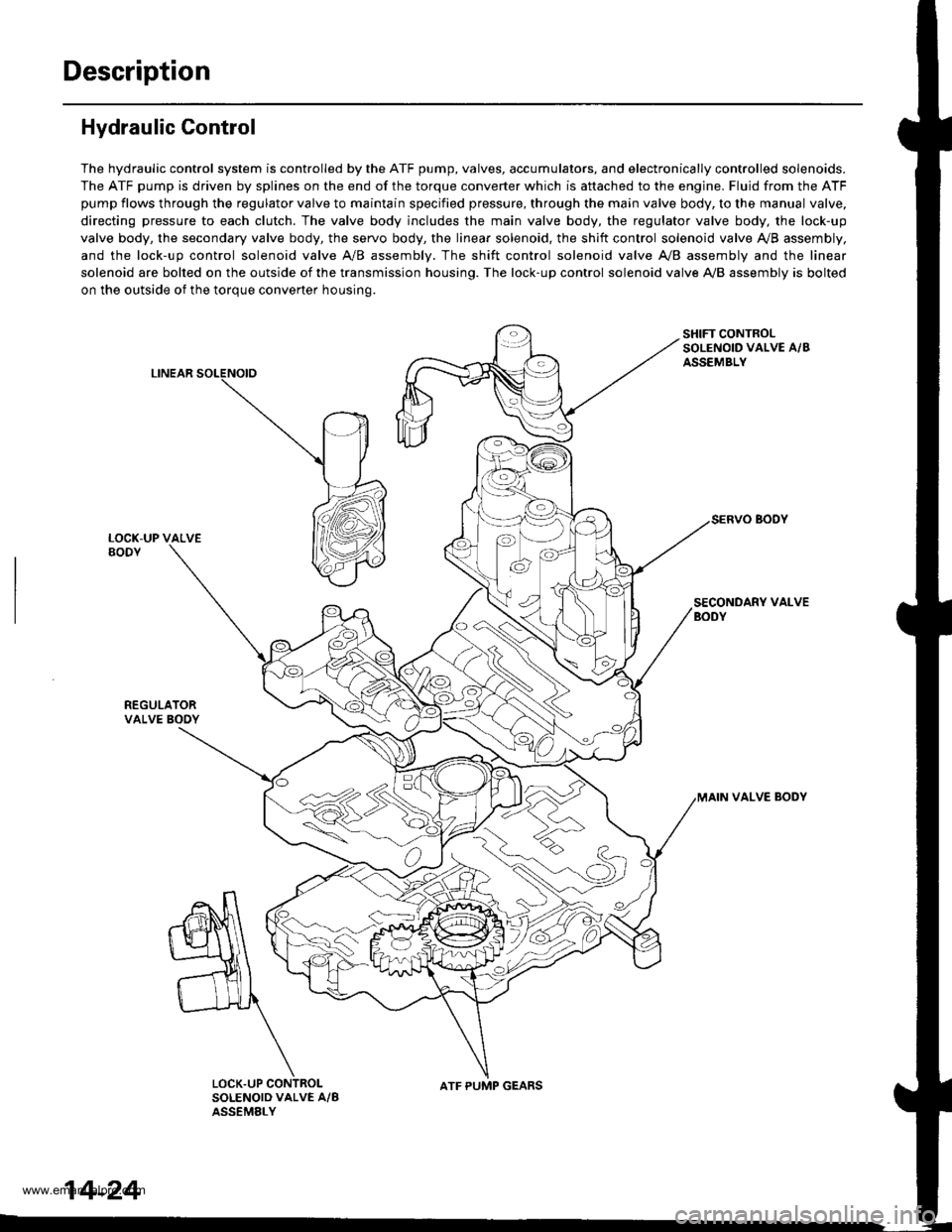
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids.
The ATF pump is driven by splines on the end of the torque converter which is aftached to the engine. Fluid from the ATF
pump flows through the regulator valve to maintain specified pressure, through the main valve body, to the manual valve,
directing pressure to each clutch. The valve body includes the main valve body, the regulator valve body, the lock-up
valve body, the secondary valve body, the servo body, the linear solenoid, the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve A,/B assembly and the linear
solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is bolted
on the outside of the torque converter housing.
LINEAR
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
SECONDARY VALVEBODY
REGULATORVALVE BOOY
VALVE BODY
SOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMELY
N
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-24
www.emanualpro.com